Пересказ статьи Rajendra Gupta. How to manage SQL Server logs effectively
В статье дается обзор журналов SQL Server для управления и устранения неполадок на сервере.
Введение
Журналы являются лучшим средством администратора баз данных при решении любых проблем. Эти проблемы могут быть связаны с конфигурацией сервера, запуском, восстановлением, производительностью, флагами трассировки, тупиковыми ситуациями, вводом-выводом или задержками. Предположим, например, что ваш экземпляр SQL Server перезапускается по непонятным причинам, и после перезапуска службы SQL работают, однако ваше приложение не имеет доступа к базе данных. Таким образом, для исследования проблемы вам нужно заглянуть в последний журнал SQL Server, чтобы проконтролировать процесс восстановления базы данных и узнать оценку времени его завершения.
Администратор базы данных может также сконфигурировать SQL Server для выполнения дополнительных записей в журналы ошибок. Например, мы можем включить флаг трассировки для захвата информации о тупиковых ситуациях. DBA должен регулярно просматривать эти журналы в поисках потенциальных проблем. Вы можете обнаружить в журналах такую информацию, как сбой резервного копирования, ошибки входа, ошибки ввода-вывода. Эти журналы ошибок являются отличным средством для обнаружения существующих и потенциальных проблем в экземплярах SQL Server.
Журналы SQL Server известны как SQL Server Error logs. Журналы ошибок содержат информационные сообщения, предупреждения и сообщения о критичных ошибках. Вы можете просматривать некоторые из этих журналов также в просмотрщике событий Windows. Однако рекомендуется использовать журналы SQL Server для получения подробной информации.
Журналы SQL Server и их местонахождение
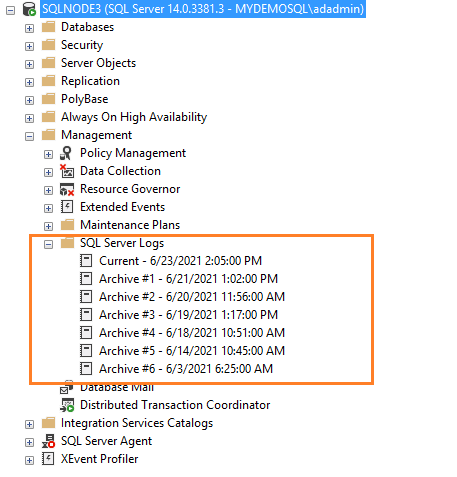
Если вы подключены к экземпляру SQL Server в SSMS, перейдите к Management -> SQL Server Logs. Как показано ниже, имеется текущий журнал и шесть архивных журналов (Archive#1 — Archive #6).
Метод 1: Использование расширенной процедуры xp_readerrorlog
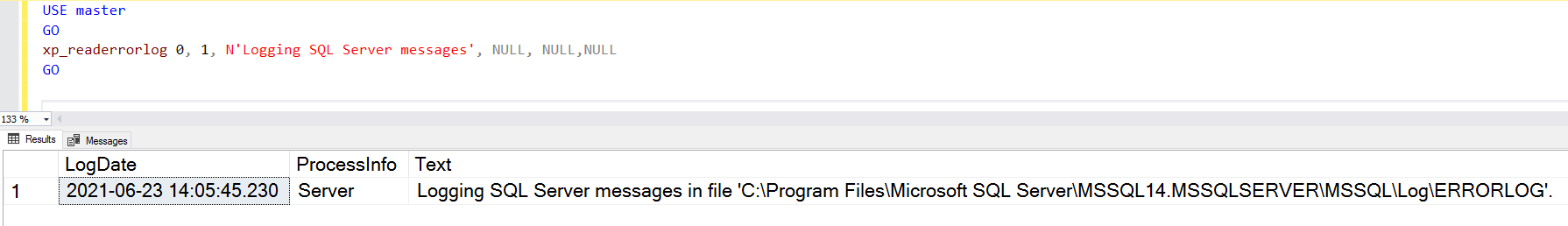
Текущие журналы являются самыми последними файлами журнала ошибок, и вы можете использовать их для просмотра недавней деятельности с момента запуска SQL Server или ручного перезапуска файла журнала. Журнал ошибок SQL Server является текстовым файлом, хранящимся в каталоге журналов экземпляра SQL Server. Вы можете использовать расширенную процедуру xp_readerrorlog для нахождения текущего местоположения журнала ошибок.
USE master
GO
xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N'Logging SQL Server messages', NULL, NULL,NULL
GO
Этот запрос имеет следующие параметры:
- Файл журнала ошибок: значение 0 для текущего, 1 для Archive#1, 2 для Archive #2.
- Тип файла журнала: значение 0 для журнала ошибок SQL Server, 1 для агента SQL Server.
- Строка поиска 1
- Строка поиска 2
- Время от
- Время до
- Сортировка результатов — по возрастанию (N’ASC) или по убыванию (N’Desc)
Для моего демонстрационного экземпляра файл журнала ошибок находится в папке C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL14.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogERRORLOG.
Метод 2: Использование функции SERVERPROPERTY()
Мы можем использовать в запросе функцию SERVERPROPERTY, и также определить местонахождение SQL Server ERRORLOG.
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('ErrorLogFileName') AS 'Error log location'
Метод 3: использование менеджера конфигурации SQL Server
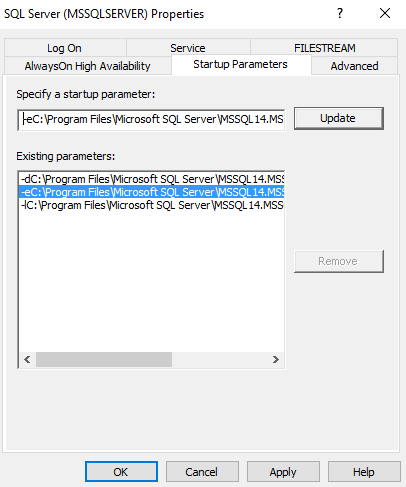
Откройте SQL Server Configuration Manager и посмотрите параметры запуска. Местоположение файлов журнала указывается с помощью переключателя -e.
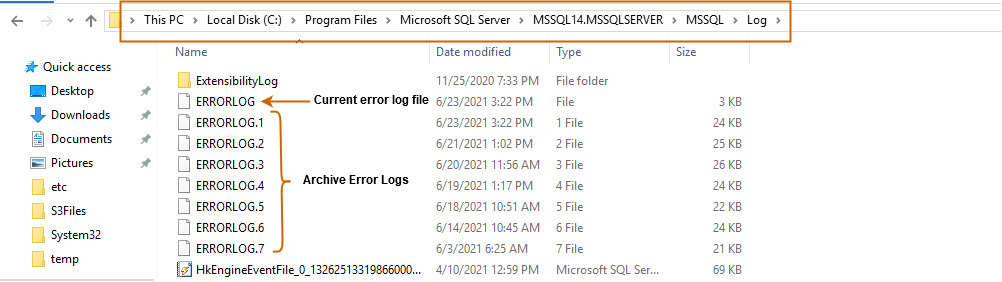
Вы можете развернуть каталог журналов и просмотреть текущий или архивные файлы журнала. Эти журналы ошибок можно открыть в текстовом редакторе, таком как Notepad или Visual Studio Code.
Конфигурирование числа файлов журнала SQL Server и их размеров
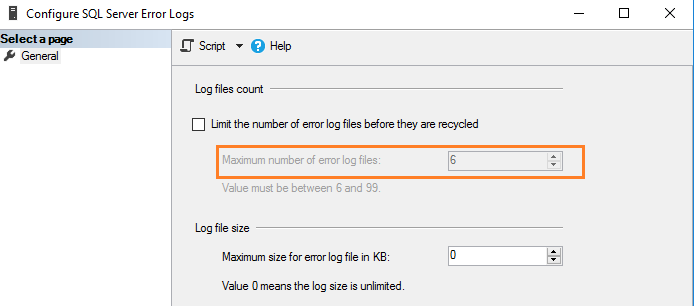
По умолчанию SQL Server поддерживает текущий и 6 архивных файлов журнала. Чтобы уточнить значение, выполните щелчок правой кнопкой на папке SQL Server Logs в SSMS и выберите Configure.
SQL Server записывает всю информацию в текущий файл журнала, независимо от размера файла журнала. В загруженной системе или в экземпляре с большим количеством ошибок вам может быть сложно просмотреть файл журнала в SSMS. SQL Server создает новый файл журнала и архивирует текущий файл в следующих случях.
- При перезапуске службы SQL.
- При перезагрузке журнала ошибок вручную.
Однако если вы часто перезапускаете серверы по неизвестным причинам, то можете потерять все исторические данные в архивных журналах, поскольку их поддерживается только шесть. Поскольку ошибки содержат ценную информацию, которая может помочь в решении проблем, вы можете не захотеть потерять эти важные данные. Тогда, возможно, вы захотите сохранять файлы журнала производственной системы в течение недели или даже месяца.
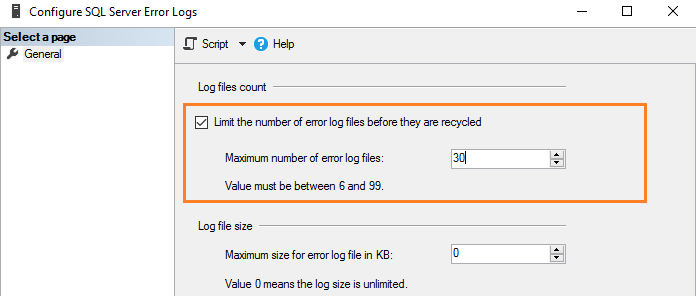
SQL Server позволяет сконфигурировать от 6 до 99 файлов журнала ошибок. Вы не можете указать значение меньше шести, поскольку в любом случае будет поддерживаться шесть архивных журналов ошибок.
Для изменения значения по умолчанию числа файлов журнала ошибок поставьте галочку в поле с названием “Limit the number of error log files before they are recycled”. Например, следующий скриншот показывает максимальное число файлов журнала ошибок, равное 30.
Это эквивалентно выполнению скрипта T-SQL, который использует расширенную хранимую процедуру и обновляет значение регистра.
USE [master]
GO
EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', N'SoftwareMicrosoftMSSQLServerMSSQLServer', N'NumErrorLogs', REG_DWORD, 30
GO
Замечание. Следует перезапустить службу SQL, чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
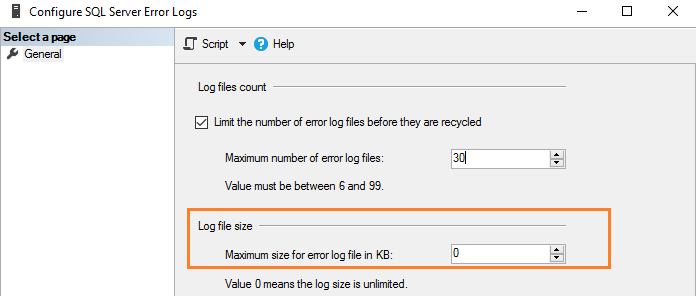
Как утверждалось ранее, по умолчанию размер журнала ошибок не ограничен. Например, если вы не запускаете SQL Server в течение длительного периода и вручную не перегружаете файлы журнала, этот файл вырастет до громадных размеров. Поэтому в конфигурации журнала ошибок показано значение 0, соответствующее неограниченному размеру журнала.
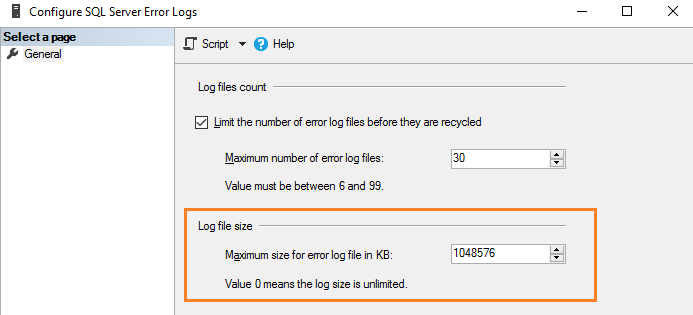
Вы можете задать размер в Кб для ограничения размера журнала ошибок в соответствии с вашими требованиями. Например, здесь мы ограничиваем размер файла журнала в 1Гб.
Эквивалентный скрипт T-SQL обновляет ErrorLogSizeInKb в регистре SQL Server.
USE [master]
GO
EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', N'SoftwareMicrosoftMSSQLServerMSSQLServer', N'ErrorLogSizeInKb', REG_DWORD, 1048576
GO
Перезагрузка журналов ошибок вручную
SQL Server позволяет вручную перегружать журналы ошибок для эффективного управления ими. Например, предположим, что вы увеличили число файлов журнала ошибок до 30. Тогда мы можем создать задание для агента SQL Server, который перегружает журналы ошибок в полночь. Тем самым мы имеем файл журнала ошибок на каждый день, если SQL Server не будет перезапущен в этом промежутке. Для перезагрузки вручную выполните системную хранимую процедуру sp_cycle_errorlog. Эту процедуру может выполнить пользователь с фиксированной серверной ролью sysadmin.
EXEC sp_cycle_errorlog
GO
Файл журнала SQL Server Agent
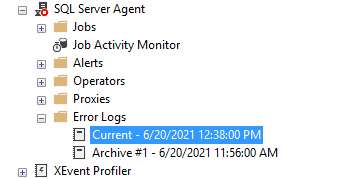
Агент SQL Server также имеет отдельный журнал ошибок, подобный журналам SQL Server. Вы можете обнаружить его в папке SQL Server Agent – > Error logs.
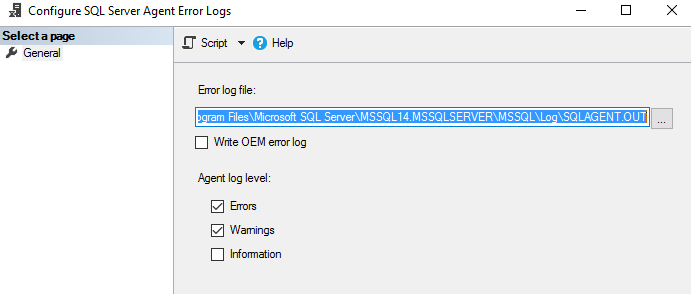
Щелкните правой кнопкой на папке Error log и выберите команду Configure. Это даст местоположение журнала ошибок агента и уровень журнала агента.
Файл журнала агента имеет расширение *.OUT и хранится в папке log при конфигурации по умолчанию. Например, в моей системе файл журнала находится здесь: C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL14.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogSQLAGENT.OUT.
По умолчанию в файл журнала записываются ошибки и предупреждения; однако мы можем включить информационные сообщения:
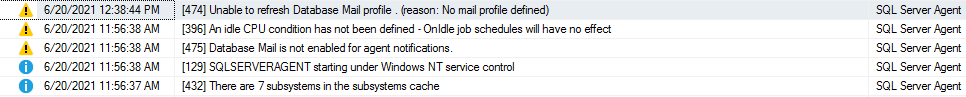
- Предупреждения: Эти сообщения предоставляют информацию о потенциальных проблемах. Например, “Job X was deleted while it was running” (задание Х было удалено во время выполнения).
- Сообщение об ошибках: оно дает информацию, которая требует немедленного вмешательства администратора баз данных, например, невозможность почтового сеанса.
Чтобы добавить информационное сообщение, поставьте галочку в поле Information.
SQL Server использует до 9 файлов журнала агента SQL Server. Имя текущего файла SQLAGENT.OUT. Файл с расширением .1 указывает на первый архивный журнал ошибок агента. Аналогично расширение .9 указывает на 9-й (самый старый) архив журнала ошибок.
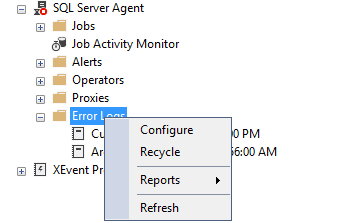
Файлы журнала агента SQL Server перегружаются всякий раз, когда перезапускается SQL Server Agent. Для того, чтобы сделать это вручную, выполните щелчок правой кнопкой на папке Error Logs folder и выберите Recycle.
Или используйте хранимую процедуру sp_cycle_agent_errorlog для перезагрузки файлов журнала агента SQL Server вручную.
USE msdb ;
GO
EXEC dbo.sp_cycle_agent_errorlog ;
GO
Хранимая процедура архивирует текущий журнал ошибок агента, используя следующий процесс:
- Создается новый текущий журнал ошибок агента.
- Текущий журнал ошибок SQLAgent.out преобразуется в SQLAgent.1.
- SQLAgent.1 преобразуется в SQLAgent.2
Заключение
Файл журнала ошибок SQL Server содержит информацию, предупреждения и критические сообщения экземпляра. Это полезно для решения проблем, аудита входа (успешно, отказ). Администратор базы данных может сконфигурировать требуемое число архивных журналов ошибок и каталогов для хранения этих файлов.
Вы должны регулярно просматривать записи в журнале в качестве подготовки ежедневных или еженедельных отчетов о состоянии сервера.
Ingenious Guide to View Log File of SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server application is one of the biggest waves in the relational database management system and handles huge databases in a well-structured manner. However, when it comes to viewing SQL Server log files, some users face trouble. We are sure that you must be aware of how good the MS SQL Server database is for both beginners as well as expert users.
But, Digital Crimes Can Takes Place In SQL Server Too!!!!
Nowadays, Ex-employees or hackers intentionally modifies the values of databases in order to damage the organization assets. And it becomes difficult to analyze or examine who is the culprit manually. As a result, the Organizations run into big trouble.
Hold On!! There Is A Good News
In SQL Server, there is a transaction Log file that keep records of all transactions & modifications in database executed on a database in a Microsoft SQL Server. By reading the Log file, one can easily check who deleted data from table in SQL Server database. Plus, it is used by forensic investigator to examine SQL Server Transaction Log and view & check every log detail in a detailed manner. In short, with SQL Log file, it becomes easy to find out which query performed on which table at what time.
Here, we are going to answer how to view log file of SQL Server by using various workarounds. Just go through this article once and understand how to open or read transaction log file in Microsoft SQL Server 2017 / 2016 / 2014 / 2012 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2005.
Moreover, if user want to restore the deleted query from a log file, then they can go through this blog – How to Recover Data from Log file in SQL Server – A Complete Guide .
Now, first of all, users need to find out the location of the log files. Then only they can proceed with a desired solution. So, to understand where your log files are, simply follow the below steps:
- Open SSMS & Connect to SQL Instance.
- Go to Management >> SQL Server Logs.
- Now, View the Log & Archive Logs simply.
Methods Use For How to View Transaction Log File of SQL Server
In the following section, you will understand how to open, check and read transaction file to retrieve information about the data which had been altered. Before we move on towards the solution, let’s look at the ways to find the location of SQL logs easily. So, let’s get started!!
As users saw the location of the log files, let’s move ahead. From the start of SQL Server or manual log file recycling, users can use these logs to view recent activities.
1st Method – xp_readerrorlog() function
Users can use the extended xp_readerrorlog process to find the current location of the log file.
USE master
GO
xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N'Logging SQL Server messages', NULL, NULL,NULL
GO
Now, we have some predefined guidelines for this procedure as mentioned below:
- End-time
- from time
- Search string1
- Search string 2
- Sort results – Ascending (N’ASC) or descending (N’Desc)
- Error log file: value 0 for the current, 1 for Archive#1, 2 for Archive #2
- Logfile type: Value 0 for SQL Server error log, 1 for SQL Server Agent log
Just as an example: The log file location is C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL14.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogERRORLOG. Now users can see these files easily.
2nd Method – SERVERPROPERTY() function
Search the SERVERPROPERTY query to find the location of your SQL Server Log files.
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('ErrorLogFileName') AS 'Error log location'
#Approach 1: Use Log File Viewer in SQL Server Management Studio
Basically, this method exclusively used to open and view the information about following logs in SSMS:
- Audit Collection
- Database Mail
- Job History
- Data Collection
- SQL Server
- SQL Server Agent
- Windows Events
Its prime function of Log File Viewer is to provide the report of activities taken place in SQL Server Management Studio. In fact, one can open the Log File Viewer wizard in different ways on the basis of information that you want to check. Now, go through the instructions to view log details in SQL Server.
How to View Log File of SQL Server Via. Log File Viewer
Step-1. Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio application. Here, we are using SQL Server 2014 environment for reading SQL Server Error Log.

Step-2. Connect to Server windows pops-up. Here, you need to select the Server Name and Type of Authentication. Afterward, click on Connect.

Step-3. In Object Explorer, go to Management as shown in the screenshot to examine or read log file of SQL Server 2014.

Step-4. Now, move to SQL Server Logs option.

Step-5. Now, Right-click on SQL Server Logs and select View >> SQL Server Log sequentially.

Step-6. All the Log summary displayed on Log File Viewer window. Here, you can select other logs such as SQL Server Agent , Database Mail from the left panel to check its information too.

#Approach 2: View Log File of SQL Server Via. Undocumented fn_dblog()
Originally, the function fn_dblog() is used to extract data from Transaction file of SQL Server for forensic purposes to analyze every log event performed on the table. So, let’s check out how to read transaction log file in Microsoft SQL Server 2017 / 2016 / 2014 / 2012 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2005 editions.
Steps to View Log File in SQL Server Using Fn_dblog()
Step 1: We have a table named as ‘Employee’. So, first view the values of the table using the following T-SQL.Select * from employee.

Step 2: Afterward, alter the table data using update command. For this, execute the query;Update employee set department ='IT' where emp_name = 'jeevan'

Step 3: Again, view the table values using the Select Query. Now, you can see a modified table.

Step 4: Run the fn_dblog function according to the need. Here, we execute the query to check out the time when update operation was executed.
Select [Begin Time], [Transaction Name] from fn_dblog(null , null) where [Transaction Name] = ‘Update’

Step 5: In a situation, when you want to analyze all the logs such as Delete etc. , then run the following T-SQL query.
Select [Begin Time], [Transaction Name] from fn_dblog(null, null)
However, there are some consequences attached with fn_dblog(). Actually, this function only provide the time of the query when it was committed instead of which data entry gets affected. Due to which, it becomes cumbersome to find out which table data get altered.
This problem is overcome with the third technique where user can view the log file of SQL Server without any hassle. Apart from this, both the described technique can run in SQL Server Management Studio only. You cannot read a Transaction Log File in offline environment with Log File Viewer and Fn_dblog().
#Approach 3: Use Smart Solution to Analyze Transaction File Easily
To get exact information from SQL Log File, take the help of SysTools SQL Log Reader Software. With the help of this software, user can scan and analyze T-log file in human readable format. However, the tool works in Online as well as Offline environment. User can get the information like Transaction , Login Name , Time , Table Name , Query . It is a best software solution that answers the question – how to read SQL Server Transaction Log file.
Download Free SQL Log Analyzer
Related : How to Fix Log File Corruption – Step-By-Step Guide
In fact, after viewing the log file of SQL Server, user can export the query in Live SQL Server database environment , SQL Compatible Scripts , and in CSV format. Moreover , the software can read Transaction log file of every SQL Server edition.
Conclusion
That’s all about how to View Log file of SQL Server. Now, go through the above-mentioned methods and opt for the best that is suitable for you and examine the SQL Server Transaction Log file without any hassles at all. Make sure that you are confident while executing the manual method or simply go for the automated solution.
Also Read: SQL Server Transaction Log Forensics
Frequently Asked Questions
How to open SQL Server database Transaction Log file (.ldf) in readable format?
Try SQL Log Analyzer tool to easily scan and read the Transaction .ldf file records.
How to view SQL Log file in SSMS?
Use Fn_dblog() function to read the details of transaction in SQL Server.
Can I read log file of SQL Server 2008?
With the help of SQL Log Viewer, one can read .ldf file and view Transaction, Transaction time, Table name and Query of Microsoft SQL Server 2017, 2016, 2014, 2012, 2008 and SQL Server 2005
Is it possible to examine SQL Transaction Log file?
Yes, with the help of mentioned workaround, one can easily examine SQL LDF file.
Просмотр журнала ошибок SQL Server в среде SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
В журнал ошибок SQL Server записываются пользовательские и определенные системные события, которые могут пригодиться при устранении неполадок.
Просмотр журналов
В среде SQL Server Management Studio выберите элемент Обозреватель объектов. Чтобы открыть обозреватель объектов, нажмите клавишу F8. Либо в главном меню щелкните Вид и выберите пункт Обозреватель объектов:
В обозревателе объектов подключитесь к экземпляру SQL Server и разверните его.
Найдите и разверните раздел Управление (при условии, что у вас есть разрешения на его просмотр).
Щелкните элемент Журналы SQL Server правой кнопкой мыши, выберите пункт Вид, а затем журнал SQL Server.
Появится средство просмотра журнала (возможно, придется немного подождать) со списком журналов для просмотра.
Открытие средства просмотра файла журнала
Средство просмотра журнала используется в среде SQL Server Management Studio для доступа к сведениям об ошибках и событиях, записываемых в следующие журналы.
Агент SQL Server
События Windows (К ним можно получить доступ с помощью программы просмотра событий Windows.)
Начиная с SQL Server 2012 (11.x), в списке «Зарегистрированные серверы» можно просматривать файлы журналов SQL Server на локальных и удаленных экземплярах SQL Server. В списке «Зарегистрированные серверы» можно просматривать файлы журнала как для экземпляров в сети, так и для экземпляров вне сети. Дополнительные сведения о доступе в сети см. далее в разделе «Просмотр файлов журнала в сети с зарегистрированных серверов». Дополнительные сведения о доступе к автономным файлам журнала SQL Server см. в разделе Просмотр автономных файлов журнала.
Открыть средство просмотра журнала можно несколькими способами (в зависимости от того, какие сведения нужно просмотреть).
Разрешения
Чтобы получить доступ к файлам журнала для экземпляров SQL Server , которые находятся в сети, требуется членство в предопределенной роли сервера securityadmin.
Чтобы получить доступ к файлам журнала для экземпляров SQL Server , которые находятся вне сети, необходим доступ на чтение к пространству WMI RootMicrosoftSqlServerComputerManagement10 , а также к папке, в которой хранятся файлы журнала. Дополнительные сведения см. в подразделе «Безопасность» раздела Просмотр автономных файлов журнала.
Безопасность
Требуется членство в предопределенной роли сервера securityadmin.
Просмотр файлов журнала
Просмотр журналов, связанных с общими операциями SQL Server
В обозревателе объектов разверните узел Управление.
Выполните одно из приведенных ниже действий.
Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Журналы SQL Server, выберите Просмотр, а затем Журнал SQL Server или Журнал SQL Server и Windows.
Разверните узел Журналы SQL Server, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши любой файл журнала и выберите Просмотреть журнал SQL Server. Можно также дважды щелкнуть любой файл журнала.
Доступны журналы Компонент Database Mail, SQL Server, Агент SQL Serverи Windows NT.
Просмотр журналов, связанных с заданиями
В обозревателе объектов откройте Агент SQL Server, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Заданияи выберите Просмотр журнала.
Доступны журналы Компонент Database Mail, Журнал заданийи Агент SQL Server.
Просмотр журналов, связанных с планами обслуживания
В обозревателе объектов раскройте узел Управление, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Планы обслуживанияи выберите Просмотр журнала.
Доступны журналы Компонент Database Mail, Журнал заданий, Планы обслуживания, План удаленного обслуживанияи Агент SQL Server.
Просмотр журналов, связанных с коллекциями данных
В обозревателе объектов раскройте узел Управление, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Сбор данныхи выберите команду Просмотреть журналы.
Доступны журналы Сбор данных, Журнал заданийи Агент SQL Server.
Просмотр журналов, связанных с компонентом Database Mail
В обозревателе объектов раскройте узел Управление, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Компонент Database Mailи выберите команду Просмотреть журнал компонента Database Mail.
Доступны журналы Компонент Database Mail, Журнал заданий, Планы обслуживания, Планы удаленного обслуживания, SQL Server, Агент SQL Serverи Windows NT.
Просмотр журналов, связанных с коллекциями аудитов
В обозревателе объектов разверните узел Безопасность, затем узел Аудиты, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши аудит и выберите команду Просмотреть журналы.
Доступны журналы Коллекция аудитов и Windows NT.
Анализ работы MS SQL Server, для тех кто видит его впервые
Недавно столкнулся с проблемой — занедужил SVN на ubuntu server. Сам я программирую под windows и с linux “на Вы”… Погуглил по ошибке — безрезультатно. Ошибка оказалась самая типовая (сервер неожиданно закрыл соединение) и ни о чем конкретном не говорящая. Следовательно, надо погружаться глубже и анализировать логи/настройки/права/и т.п., а с этим, как раз, я “на Вы”.
В результате, конечно, разобрался и нашел всё что нужно, но время потрачено много. В очередной раз думая, как глобально (да-да, во всём мире или хотя бы на ⅙ части суши) уменьшить бесполезно потраченные часы — решил написать статью, которая поможет людям быстро сориентироваться в незнакомом программном обеспечении.
Писать я буду не про линукс — проблему хоть и решил, но профессионалом вряд ли стал. Напишу про более знакомый мне MS SQL. Благо, уже приходилось много раз отвечать на вопросы и список типовых уже готов.
Для кого пишу
Если вы админ в Сбере (или в Яндексе или <другая топ-100 компания>), вы можете сохранить статью в избранное. Да, пригодится! Когда к вам, в очередной раз, с одними и теми же вопросами придут новички — Вы дадите им ссылку на нее. Это сэкономит Ваше время.
Если без шуток, эта СУБД часто используется в небольших компаниях. Часто совместно с 1С либо другим ПО. Отдельного БД-админа таким компаниям держать затратно — надо будет выкручиваться обычному ИТ-шнику. Для таких и пишу.
Какие проблемы рассмотрим
Если сервер вам сообщает “закончилось место на диске Е” — глубокий анализ не нужен. Не будем рассматривать ошибки, решение которых очевидно из текста сообщения. Также не будем рассматривать ошибки по которым гугл сразу выдает ссылку на msdn с решением.
Рассмотрим проблемы по которым не очевидно что гуглить. Такие как, например, внезапное падение производительности или, например, отсутствие соединения. Рассмотрим основные инструменты для настройки. Рассмотрим средства анализа. Поищем где лежат логи и другая полезная информация. И в целом, попробую в одной статье собрать нужную информацию для быстрого старта.
Самое первое
Начнем с лидера списка частых вопросов, настолько он опережает всех, что рассмотрим его отдельно. Вдобавок, об этом пишут во всех статьях про работу MS SQL — и я не буду нарушать традицию.
Если у вас вдруг, ни с того ни с сего, стало работать медленно, а вы ничего не меняли (как поставили, так всё и работало, никто ничего не трогал) — в первую очередь, обновите статистику и перестройте индексы. Только удостоверившись, что это выполнено — имеет смысл копать глубже. Еще раз подчеркну — делать это нужно обязательно, вопрос только как часто.
В интернете полно рецептов как это делать, приводятся примеры скриптов. Предположу, что все те методы для “профи” и новичкам непонятны. Что ж, опишу способ наипростейший: для его внедрения вам потребуется только владение мышью.
- SSMS — приложение “Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio”, находится в “Пуске”. Устанавливается отдельной галочкой (Client management tools) с дистрибутива сервера. Начиная с 2016 версии, доступно бесплатно на сайте MS в виде отдельного приложения. Старшие версии студии нормально работают с младшими версиями сервера. Наоборот — тоже иногда работают (основные функции).
docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/ssms/download-sql-server-management-studio-ssms “SSMS is free! It does not require a license to install and use.” - Profiler — приложение “SQL Server Profiler”, находится в “Пуске”, устанавливается вместе с SSMS.
- Performance Monitor (Системный монитор) — оснастка панели управления. Позволяет мониторить счетчики производительности, журналировать и просматривать историю замеров.
Обновление статистики с помощью “плана обслуживания”:
- запускаем SSMS;
- подключаемся к нужному серверу;
- разворачиваем в Object Inspector дерево: Management Maintenance Plans (Планы обслуживания)
- правой кнопкой на узле, выбираем “Maintenance Plan Wizard”
- в визарде мышкой отмечаем нужные нам задачи:
- rebuild index (перестроить индекс)
- update statistics (обновить статистику)
- Обновление статистики — неблокирующая операция. Можно выполнять в рабочем режиме. Дополнительную нагрузку конечно создаст, но ведь у вас и так всё тормозит, будет чуть больше — незаметно.
- Перестроение индекса — блокирующая операция. Запускать только в нерабочее время. Есть исключение — Enterprise редакция сервера допускает выполнение “онлайнового ребилда”. Эта опция включается галочкой в настройках задачи. Обратите внимание, галочка есть во всех редакциях, но работает только в Enterprise.
- Конечно, эти задачи необходимо выполнять регулярно. Предлагаю простой способ определения, как часто это делать:
- при первых проблемах выполняете план обслуживания;
- если помогло — ждете пока не начнутся проблемы снова (как правило, до очередного закрытия месяца/расчета зп/ и т.п. массовых операций);
- получившийся срок нормальной работы и будет вам ориентиром;
- например, настройте выполнение плана обслуживания в два раза чаще.
Сервер работает медленно — что делать?
Используемые сервером ресурсы
Как и любой другой программе, серверу нужны: время процессора, данные на диске, объемы оперативной памяти и пропускная способность сети.
Оценить нехватку того либо иного ресурса в первом приближении можно с помощью Task Manager (Диспетчер задач), как бы по кэпски это не звучало.
Загрузка ЦП
Посмотреть загрузку в диспетчере сможет даже школьник. Здесь нам надо просто убедиться, что если процессор загружен, то именно процессом sqlserver.exe.
Если это ваш случай, то надо переходить к анализу активности пользователей, чтобы понять, что именно стало причиной загрузки (листаем ниже).
Загрузка диска
Многие смотрят только загрузку процессора, но не надо забывать что СУБД — это хранилище данных. Объемы данных растут, производительность процессоров растет, а скорость HDD практически не меняется. С SSD ситуация получше, но терабайты на них хранить затратно.
Получается так, что я чаще сталкиваюсь с ситуациями, когда узким местом становится именно дисковая система, а не ЦПУ.
- Remove From My Forums
-
Вопрос
-
I have two questions and would greatly appreciate any help on this from the experts.
1. Sql server 2005 Logs the information at many places, we are trying to consolidate them. So I would like to know all the sources from where I can get the SQL server logs without missing any log information.
2. I would also like to know, when we have a trace file (.trc), how can we convert them into a flat file without using Profiler UI utility. To be more specific, I have a situation where I have enabled C2 Auditing and as a result it generates a .trc file and I want to access it programmatically without using the profiler UI. I would like to know what are the other log information which C2 audit generated trace doesn’t cover and where it could be find.
Ответы
-
1. Are you talking about the .ldf files? Are you having difficulty finding them? Do you have databases on many different servers with many different drives?
2. You can use the T-SQL function fn_trace_gettable (http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188425.aspx) to load the data into a table. You could use SSIS to transform the data from a table to a flat file. What is the purpose of changing the data from .trc to a flat file?
Paul A. Mestemaker II
Program Manager
Microsoft SQL Server
http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlrem/ -
If you are referring to SQL Server Error Logs they can be found in <install_folder>Microsoft SQL ServerMSSQL.1MSSQLLOG with filename ERRORLOG.n where n is a number
This article covers an overview of SQL Server logs for monitoring and troubleshooting issues in SQL Server.
Introduction
The logs are the best resources for a database administrator in troubleshooting any issues. These issues can be related to server configuration, startup, recovery, performance, trace flags, deadlocks, IO, or Checkpoint delay. For
example, suppose your SQL Server instance restarted due to unknown reasons, and after startup, SQL Services are up;
however, your application cannot access the database. Therefore, to investigate issues, you can look at the latest
SQL Server logs and monitor the database recovery process and estimated time in completion.
The database administrator can also configure SQL Server for additional logging into the error logs. For example, we can enable a trace flag to capture deadlocks information. The DBA should review these logs proactively to look for potential problems. You can identify information such as backup failure, login failure, IO errors by reviewing logs. These error logs are great to look for existing or potential problems in SQL Server instances.
SQL Server logs are known as SQL Server Error logs. This error log has informational, warning, and critical error messages. You can view a few of these logs in the Windows event viewer logs as well. However, it is recommended to use SQL Server logs to get detailed information.
SQL Server Logs and its location
Once you connect to a SQL Server instance in SSMS, navigate to Management -> SQL Server Logs. As shown below, it
has the current log and six archive logs ( Archive#1 to Archive #6).

Method 1: Using the xp_readerrorlog extended procedure
The current logs are the latest error log file, and you can use them to view recent activity since SQL Server starts
or manual log file recycling. SQL Server error log is a text file stored in the log directory of SQL Server
instance. You can use the extended procedure xp_readerrorlog to find out the current location of
the error log.
|
USE master GO xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N‘Logging SQL Server messages’, NULL, NULL,NULL GO |
This query has the following parameters:
- Error log file: value 0 for the current , 1 for Archive#1, 2 for Archive #2
- Logfile type: Value 0 for SQL Server error log, 1 for SQL Server Agent log
- Search string1
- Search string 2
- from time
- end-time
- Sort results – Ascending (N’ASC) or descending (N’Desc)
For my demo instance, the error log file location is C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL14.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogERRORLOG.

Method 2: Using the SERVERPROPERTY() function
We can query the SERVERPROPERTY function as well to identify the location of the SQL Server ERRORLOG.
|
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY(‘ErrorLogFileName’) AS ‘Error log location’ |

Method 3: Using the SQL Server Configuration Manager
Alternatively, open SQL Server Configuration Manager and view startup parameters. The log file location is specified
using the -e switch.

You can browse the log directory and view the current archive error log files. These error logs can be opened in a
text editor such as Notepad or Visual Studio Code.

Configure the number of SQL Server Log files and their size
By default, SQL Server maintains a current and six archived log files. To validate the value, right-click on the SQL
Server Logs folder in SSMS and Configure.

SQL Server logs all information in the current log file irrespective of log file size. On a busy system or instance
with many errors, you might find it challenging to view the log file in SSMS. SQL Server creates a new log file and
archives the current file in the following case.
- During SQL Service restart
- Manual error log recycle
However, if you restart servers frequently due to unknown reasons, you might lose all historical archive log data because it maintains only six archive logs. Since the error contains valuable information that can help you troubleshoot, we might not want to lose this crucial data. Instead, we might want to retain log files on a critical production system for a week or even a month.
SQL Server allows the configuration of up to 6 to 99 error log files. We cannot specify a value less than six because, in any case, it maintains six archive error logs.
To change the default number of error log files, put a check on the box labeled – “Limit the number of error
log files before they are recycled”. For example, the following screenshot shows a maximum of 30 error
log files.

Its equivalent T-SQL script uses xp_instance_regwrite extended stored procedure and updates the registry value.
|
USE [master] GO EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE’, N‘SoftwareMicrosoftMSSQLServerMSSQLServer’, N‘NumErrorLogs’, REG_DWORD, 30 GO |
- Note: SQL Services must be restarted so that these changes are in effect
As stated earlier, by default, the error log size is unlimited. For example, if you do not start SQL Server for a
longer period and do not manually recycle log files, this file will grow huge. Therefore, in the error log
configuration, value 0 shows log size is unlimited.

You can specify the size in KB to limit the error log size as per your requirement. For example, here, we limit log file size to 1 GB

Its equivalent T-SQL script updates the ErrorLogSizeInKb in the SQL Server registry.
|
USE [master] GO EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE’, N‘SoftwareMicrosoftMSSQLServerMSSQLServer’, N‘ErrorLogSizeInKb’, REG_DWORD, 1048576 GO |
Manual recycle error logs
SQL Server allows recycling error logs manually to manage them effectively. For example, suppose you increased the number of error log files to 30. Thus, we can create a SQL Server agent job that recycles error logs at midnight. This way, we have an error log file for each day unless SQL Service is restarted in between. To recycle manually, execute the system stored procedure sp_cycle_errorlog. The user with the sysadmin fix server role can execute this stored procedure.
SQL Server Agent log file
SQL Server agent also has a separate error log similar to the SQL Server logs. You can find it under the SQL Server Agent – > Error logs folder.

Right-click on the Error log folder and Configure. It gives the agent error log location and agent log level.
The agent log file extension is *.OUT and stored in the log folder as per default configuration. For example, in my
system, the log file directory is C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL14.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogSQLAGENT.OUT.
By default, agent log file logs errors and warnings; however, we can include information messages:
- Warning messages: These messages provide information about potential problems. For example, “Job X was deleted while it was running”
- Error message: It gives information that requires immediate intervention of a DBA, such as being unable to start a mail session

To add the information message, put a tick on the checkbox labeled Information.

SQL Server uses up to 9 SQL Server agent log files. The current file name is SQLAGENT.OUT. The file with extension .1 indicates the first archived agent error log. Similarly, an extension .9 indicates the 9th (oldest) archived error log.
SQL Server agent log files are recycled each time SQL Server Agent is restarted. To do it manually, right-click on
the Error Logs folder and Recycle.

Alternatively, use the stored procedure sp_cycle_agent_errorlog to recycle SQL Server agent log files manually.
|
USE msdb ; GO EXEC dbo.sp_cycle_agent_errorlog ; GO |
The stored procure archives the current agent error log using the following process:
- A new current agent error log is created
- Current Agent error log SQLAgent.out coverts to SQLAgent.1
- SQLAgent.1 converts to SQLAgent.2
Conclusion
The SQL Server error log file has information, warning, and critical messages of an instance. It is helpful for troubleshooting, audit logins (success, failure). The database administrator can configure the number of required archived error logs and directories to store these files.
You should proactively look for messages getting logged as part of your daily and weekly health check reports.
- Author
- Recent Posts
Hi! I am Rajendra Gupta, Database Specialist and Architect, helping organizations implement Microsoft SQL Server, Azure, Couchbase, AWS solutions fast and efficiently, fix related issues, and Performance Tuning with over 14 years of experience.
I am the author of the book «DP-300 Administering Relational Database on Microsoft Azure». I published more than 650 technical articles on MSSQLTips, SQLShack, Quest, CodingSight, and SeveralNines.
I am the creator of one of the biggest free online collections of articles on a single topic, with his 50-part series on SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
Based on my contribution to the SQL Server community, I have been recognized as the prestigious Best Author of the Year continuously in 2019, 2020, and 2021 (2nd Rank) at SQLShack and the MSSQLTIPS champions award in 2020.
Personal Blog: https://www.dbblogger.com
I am always interested in new challenges so if you need consulting help, reach me at rajendra.gupta16@gmail.com
View all posts by Rajendra Gupta