Just happened to me, and turned out to be different than all other cases listed here.
I happen to have two virtual servers hosted in the same cluster, each with it own IP address. The host configured one of the servers to be the SQL Server, and the other to be the Web server. However, SQL Server is installed and running on both. The host forgot to mention which of the servers is the SQL and which is the Web, so I just assumed the first is Web, second is SQL.
When I connected to the (what I thought is) SQL Server and tried to connect via SSMS, choosing Windows Authentication, I got the error mentioned in this question. After pulling lots of hairs, I went over all the setting, including SQL Server Network Configuration, Protocols for MSSQLSERVER:
Double clicking the TCP/IP gave me this:
The IP address was of the other virtual server! This finally made me realize I simply confused between the servers, and all worked well on the second server.
You may encounter the SQL Server Error 18456 if the server could not authenticate the connection and this can be caused by the non-availability of the administrator rights to the SQL server or if the TCP/IP protocol is disabled in the SQL server settings.
The issue arises when the user tries to connect to the SQL server (local or remote) but encounters the error 18456 (with different states).
You can fix the SQL server error 18456 by trying the solutions below but before that, check if restarting the server, client computer, and networking computers solves the issue. Moreover, make sure you are typing the correct username and password (not copy-pasting the address).
Also, check if you are entering the correct database name (no typo in it) and make sure you have updated the configuration file accordingly. Furthermore, check if unlocking the account (by using the query ALTER LOGIN WITH PASSWORD= UNLOCK) solves the issue. If you are seeing the errors in the SQL errors log, then make sure your SQL server is not under attack. Last but not least, make sure the server’s clock and client computer clock is correctly set.
Launch the SQL Server as Administrator and Disable UAC on the Server
You may encounter the error 18456 if the SQL server does not have the elevated permissions to execute its operation and launching it as administrator (or disabling the UAC controls on the server) may solve the problem.
Open the SQL Server as Administrator
- Click Windows and type SQL Server Management Studio.
- Now right-click on SMSS and select Run as Administrator.
Launch Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio as Administrator - Then click Yes (if UAC prompt received) and check if the SQL server is clear of the error 18456.
- If not, then check if disabling UAC on the server machine solves the issue.
Launch the SQL Server in a Single User Mode
- Click Windows, type, and open the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- Now right-click on the SQL Server service (in the SQL Server Services tab) and select Properties.
Open Properties of the SQL Server - Then head to the Startup Parameters tab and in the Specify a Startup Parameter box, type:
-m
- Now click on Add and apply the changes.
Add the “-m” Parameter to the Startup Parameters of the SQL Server - Then right-click on the SQL Server service and select Restart.
Restart the SQL Server Service - Now click Windows, type: SQL Server Management Studio, right-click on SMSS, and select Run as Administrator.
- Now check if you can connect to the SQL Server as administrator.
- If so, then add the domain account to the SQL server and assign it the SysAdmin role.
- Now go back to the SQL Server Configuration Manager window and remove the -m parameter in the Startup Parameters tab.
- Then restart the SQL Server service (step 3) and check if the SQL server is working fine.
If the issue persists, check if the startup parameters or path details are properly configured. If the issue is still there, make sure your user account does have the required permissions to the database/ reporting services, and then check if the issue is resolved.
Enable the TCP/IP Protocol in the Server Configuration Manager
The error code 18456 in the SQL server means that the server could not authenticate the connection and this can happen if the TCP/IP protocol required to access the database on a network is disabled in the Server Configuration Manager. In this context, enabling the TCP/IP in the SQL Server Configuration Manager may solve the problem.
- Click Windows and expand Microsoft SQL Server with a year name like 2008 (you may need to scroll a bit to find the option).
- Now open SQL Server Configuration Manager and click Yes (if UAC prompt received).
- Then, expand SQL Server Network Configuration and select Protocols for (the server/database name) in the left pane.
- Now, in the right pane, double-click on TCP/IP and select Yes in the dropdown of Enabled.
Open TCP/IP in Protocols of SQL Server Network Configuration - Then apply your changes and click Windows.
Enable TCP/IP in SQL - Now type Services, right-click on the result of Services, and select Run as Administrator.
Open Services as Administrator - Then right-click on the SQL Server (with the server’s name) and select Restart.
Restart the SQL Service in the Services Window - Now check if the SQL server is clear of the error 18456.
If that did not do the trick, then make sure you are connecting to the right port of the SQL server (especially if you are using the server in a multi-server environment).
Change the Authentication Mode of the SQL Server
The SQL server might show the error 18456 if the authentication method of the SQL server is not properly configured (e.g: you are trying to login using SQL server authentication whereas the server is configured to use the Windows authentication). In this case, changing the authentication method of the SQL server may solve the problem. Before moving on make sure the status login for the present user (for example SA) is enabled.
- In the Object Explorer of Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio, right-click on your server and select Properties.
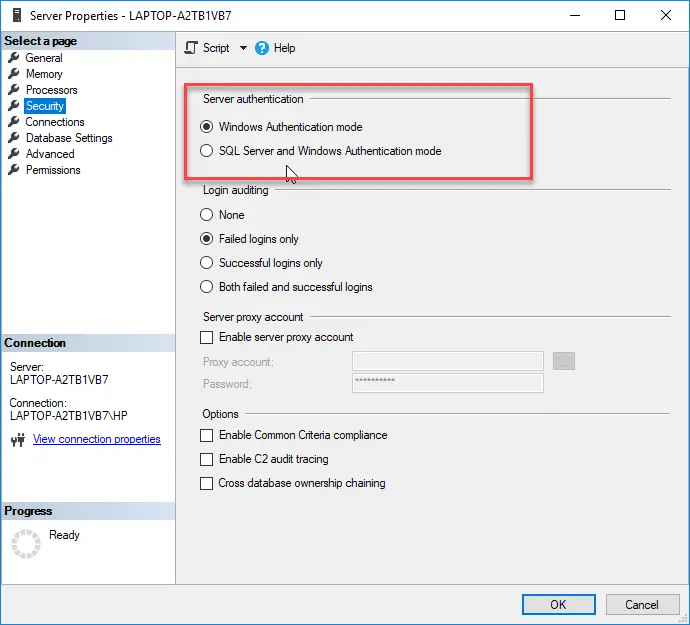
- Now, in the left pane, select Security, and in the right pane, select SQL Server and Windows Authentication (or vice versa).
Enable SQL Server and Windows Authentication - Then apply your changes and in the Object Explorer, right-click on the server.
- Now choose Restart and once restarted, check if you can connect to the database without error 18456.
If you cannot log into SQL, then you may install MS Power Tools and run the following in an elevated command:
psexec.exe -i -s ssms.exe
Afterward, you may use the installation account of SQL to make the changes and also make sure the SA account is not disabled:
Enable the SA Account and Reset the Account Password
If you cannot connect to the SQL Server, then enabling the SA account of the SQL server and resetting its password may solve the problem.
- Launch Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (you may have to use the domain admin account) and expand Security.
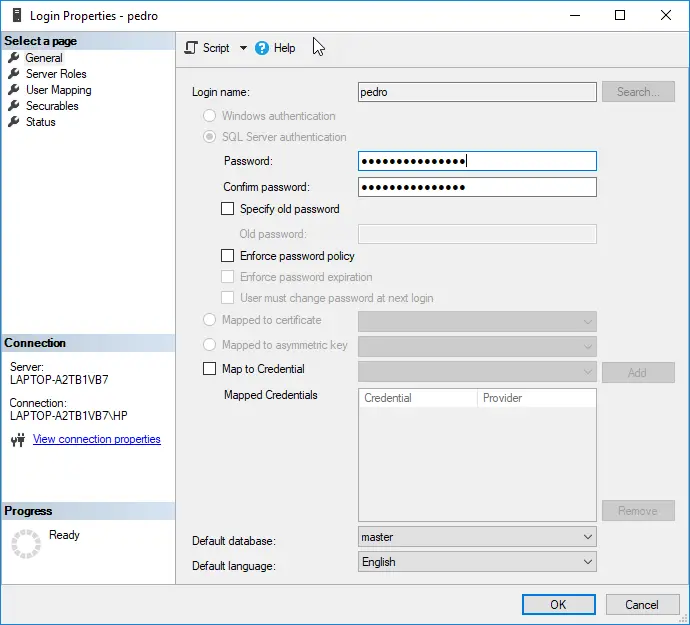
- Then double-click on Logins and open SA.
Open the SA Account in the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio - Now enter a new password and confirm the password (make sure you use a strong password).
- Then head to the Server Roles tab and make sure the following roles are selected:
Public Sysadmin
Enable the Public and Sysadmin Server Roles for the SA Account - Now head to the Status tab and in the right pane, select Enabled (under Login).
Enable the SA Account in SQL - Then apply your changes and click the Windows button.
- Now type Services and right-click on it.
- Then select Run as Administrator and steer to the SQL Server service.
- Now right-click on it and select Restart.
- Once the service is restarted, check if the error 18456 of the SQL server is cleared.
Create a New Login and Restart the Reporting Services
If you cannot use any account to connect to the database, then creating a new login and restarting the reporting services may solve the problem.
- Launch the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and expand its Security tab.
- Then expand Logins and right-click on it.
- Now select New Login and enter the credentials (in the login name select the computer account) if using the SQL Server Authentication.
Create a New Login in the SQL Server - Then make sure to uncheck “User Must Change Password at Next Login” and select the database.
- Now head to the Server Roles tab and select the Public role.
- Then, in the User Mapping tab, make sure to choose the database and select db_owner.
Select db_owner for the Database in SQL - Now apply your changes and click Windows.
- Then type Services and right-click on the result of Services. Then select Run as Administrator.
- Now right-click on the SQL Server Reporting Service and select Restart.
Restart the SQL Server Reporting Service - Then reconnect to the database and check if the SQL server is clear of the error 18456.
If so, make sure that you have created a user in BUILTINadministrators, and then you can use that user to manage the SQL Server. If you have restored the database from a backup, it will be better to remove and re-add the users to clear any old user entries. If you want to run the SQL server as a different user, then type Microsoft SQL Server in the Windows Search, Shift+Right-click on the SQL Server, and select Run as a Different User. Last but not least, check if using Azure Data Studio with the SQL server sorts out the issue.
Kevin Arrows
Kevin Arrows is a highly experienced and knowledgeable technology specialist with over a decade of industry experience. He holds a Microsoft Certified Technology Specialist (MCTS) certification and has a deep passion for staying up-to-date on the latest tech developments. Kevin has written extensively on a wide range of tech-related topics, showcasing his expertise and knowledge in areas such as software development, cybersecurity, and cloud computing. His contributions to the tech field have been widely recognized and respected by his peers, and he is highly regarded for his ability to explain complex technical concepts in a clear and concise manner.
Sql server error 18456 is common issue appear during login process on Microsoft SQL Server. This error can happen when you try to login with local administrator, as well as under the domain administrator and under the sa. Microsoft SQL Server login failed error can be encountered due to varied reasons. Most of the time, an error code comes up with a description that gives a hint about what has gone wrong. But I some cases the error come without any description. In this article, we’ll take a look at the typical reasons of the error 18456 appear on SQL Server during login process and show different ways to solve this error.
The view of error:
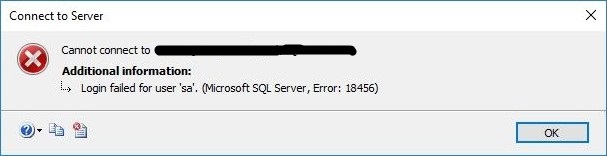
“Login failed for user ‘<user_name>’. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456)”.
Kevin Arrows
Kevin Arrows is a highly experienced and knowledgeable technology specialist with over a decade of industry experience. He holds a Microsoft Certified Technology Specialist (MCTS) certification and has a deep passion for staying up-to-date on the latest tech developments. Kevin has written extensively on a wide range of tech-related topics, showcasing his expertise and knowledge in areas such as software development, cybersecurity, and cloud computing. His contributions to the tech field have been widely recognized and respected by his peers, and he is highly regarded for his ability to explain complex technical concepts in a clear and concise manner.
Sql server error 18456 is common issue appear during login process on Microsoft SQL Server. This error can happen when you try to login with local administrator, as well as under the domain administrator and under the sa. Microsoft SQL Server login failed error can be encountered due to varied reasons. Most of the time, an error code comes up with a description that gives a hint about what has gone wrong. But I some cases the error come without any description. In this article, we’ll take a look at the typical reasons of the error 18456 appear on SQL Server during login process and show different ways to solve this error.
The view of error:
“Login failed for user ‘<user_name>’. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456)”.
How To FIX SQL Server Error 18456
Troubleshoot with Short Solutions
Here, you have some possible reasons:
- The login does not exist or was not typed correctly
- Make sure that the username or password are correct
- The password is incorrect
- The user forgot the password or login
- The Windows Authentication is not in Mixed mode
- A virus resets all the passwords
- A malicious hacker reset the password
- The logins were damaged or the master database is damaged
- The database was migrated, but the logins were not migrated
- The administrator modified the passwords by mistake
- Restart the SLQ Server service
Troubleshoot with State of the Microsoft SQL error 18456
Most of the time the SQL error 18456 come with the severity and state number. A state number might not mean much, yet it can offer more details as to what is wrong and where to look next.
To get a more detailed info about Microsoft SQL Server Error 18456 reason, you need to open the SQL Server error log file – ERROR.LOG. This is plain text file located under folder MSSQLLog. Below are some states of the error 18456 sql server. The descriptions and potential solutions offer a quick explanation and potential troubleshooting guide.
| State | Error Description |
| 1 | Error information is not available. This state usually means you do not have permission to receive the error details |
| 2 | Invalid user ID |
| 5 | User ID is not valid. |
| 6 | Attempt to use a Windows login name with SQL Authentication |
| 7 | Login disabled |
| 8 | Password is incorrect |
| 9 | Password is not valid |
| 11-12 | Valid login but server access failure |
| 13 | SQL Server service paused |
| 16 | Authorization is correct, but access to the selected database is not allowed |
| 18 | Change password required |
| 27 | Initial database not found |
| 38 | Could not find database requested by user |
|
102 – 111 |
AAD failure. |
| 122 – 124 | Failure due to empty user name or password. |
| 126 | Database requested by user does not exist. |
| 132 – 133 | AAD failure. |
Common Solution for Error 18456
If the issue cannot be resolved from with short solutions above, read below for additional information:
Read also other SQL Server Helping Posts:
- SQL Server Error 233
- Fix SQL server error 26 and error 40
- Restore Master Database
Checking the Server Authentication Mode
In this case you are trying to login on SQL Server using sql user. Once we login to SSMS using Windows Authentication, we need to check the security settings to confirm whether MSSQL is set up to allow both Windows and SQL Authentication.
Check and Change SQL Server Authentication Mode from GUI:
- In SSMS, right-click the Server Name at the top of the Object Explorer window and choose Properties.
- Next, click the Security page.
- If you find Windows Authentication is the only mode configured, this is the likely cause of sql server error 18456, Login failed for user ‘’.
- Setting the Server authentication mode to allow SQL Server and Windows Authentication, you will be able to login to MS-SQL with a SQL user and password or a Windows user and password. After making this change, you will need to restart the SQL Server service.
Server Authentication Mode
Change SQL Server Authentication Mode from regedit
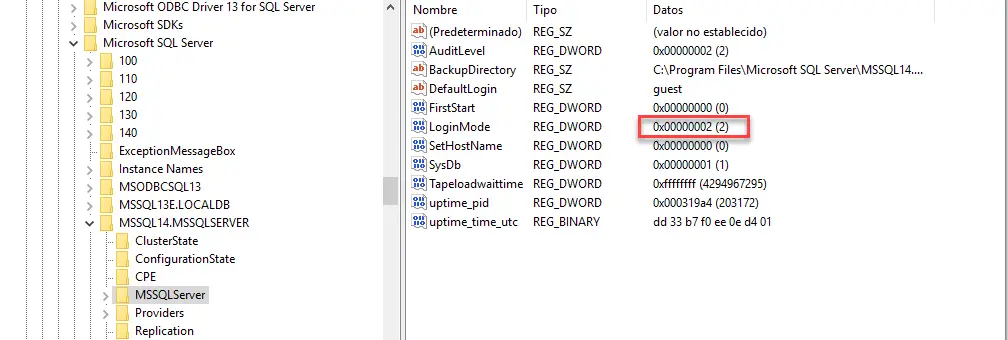
You can use the registry to modify the authentication mode. Use the regedit to change the registry:
Image (regedit)
- machineHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQLXX.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLServer
- Change the login mode value.
- 2 is mixed mode.
- 1 is Windows Authentication.
Change SQL Server Authentication Mode from regedit
Checking pass expired or login disabled
Check out that the password is not expired.
- Open SSMS, Instance – Security – Logins and find the user that have issue
- On general tab check if the Enforce password expiration and enforce password policy are checked
- Un-check them
Check out that the login is enabled.
- Open SSMS, Instance – Security – Logins and find the user that have issue
- On status tab and check if is selected the “Enabled” option
Reset the Password of the user
If you forget your password, you can ask your DBA to reset your account. The easiest way to reset the password is by using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
- Go to security and Logins:
- Select the login and you can change the password:
Checking pass expired or login disabled
- If you do not like to use SSMS, you can use T-SQL to create users and change the password:
USE [master] GOALTER LOGIN [Test] WITH ‘newpasswordtest’GOChange Windows Authentication
So we hope that you fixed the issue with the sql server error 18456.
Updated in July 2020 with a few new states.
I think we’ve all dealt with error 18456, whether it be an application unable to access SQL Server, credentials changing over time, or a user who can’t type a password correctly.
The trick to troubleshooting this error number is that the error message returned to the client or application trying to connect is intentionally vague – the error message is similar for most errors, and the state is always 1. In a few cases, some additional information is included, but for the most part several of these conditions appear the same to the end user. The reason for this is to be careful not to disclose too much information to a would-be attacker.
But this makes troubleshooting hard.
In order to figure out what is really going wrong, you need to have alternative access to the SQL Server and inspect the log for the true state in the error message. I helped our support team just today solve a client’s 18456 issues – once we tracked down the error log and saw that it was state 16, it was easy to determine that their login had been set up with a default database that had been detached long ago.
When I see folks struggling with this problem, I almost always see them pointed to this old MSDN blog post (or this other version from MSDN), which has a very brief partial list and a lot of unanswered questions. A newer list appears here, with some useful info, but it is still incomplete.
So here is what I consider a more complete listing of all the various states for login failures. I included an instance of 18470 under state 1 for completeness.
| State | Example / Description (note: the verbose message usually has [CLIENT: <IP>] suffix) |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Error: 18470, Severity: 14, State: 1. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: The account is disabled. |
| State 1 now occurs when a login is disabled – but actually, the error in the log is 18470, not 18456 – because the login is disabled, it doesn’t get that far. See state 7.Prior to SQL Server 2005, State 1 always appeared in the log for all login failures, making for fun troubleshooting. 🙂 | |
| 2 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 2. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. |
| The login (whether using SQL or Windows Authentication) does not exist. For Windows Auth, it likely means that the login hasn’t explicitly been given access to SQL Server – which may mean it is not a member of an appropriate domain group. It could also mean that you’ve created a server-level login, mapped a database user with a different name to that login, and are trying to connect using the user name, not the login name. This is the same as State 5, but State 2 indicates that the login attempt came from a remote machine. | |
| 5 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 5. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. |
| Like state 2, the login does not exist in SQL Server, but the login attempt came from the local machine. For both state 2 and 5, prior to SQL Server 2008, the reason was not included in the error log – just the login failed message. And starting in Denali, for both state 2 and 5, this error can happen if you specify the correct username and password for a contained database user, but the wrong (or no) database. Note that if you are trying to connect to a contained database using the connection dialog in SSMS, and you try to <Browse server…> for the database instead of typing the name explicitly, you will first receive a prompt «Browsing the available databases on the server requires connecting to the server. This may take a few moments. Would you like to continue?» If the SQL auth credentials do not also match a login at the server level, you will then receive an error message, because your contained user does not have access to master.sys.databases. The error message in the UI is, «Failed to connect to server <server>. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)Login failed for user ‘<x>’. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456).» The takeaway here: always specify the database name explicitly in the options tab of the connection dialog; do not use the browse feature. | |
| 6 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 6. Login failed for user ‘<xy>’. Reason: Attempting to use an NT account name with SQL Server Authentication. |
| This means you tried to specify SQL authentication but entered a Windows-style login in the form of DomainUsername. Make sure you choose Windows Authentication (and you shouldn’t have to enter your domain / username when using Win Auth unless you are using runas /netonly to launch Management Studio). In SQL Server 2012 at least, you will only get state 6 if the domainusername format matches an actual domain and username that SQL Server recognizes. If the domain is invalid or if the username isn’t an actual Windows account in that domain, it will revert to state 5 (for local attempts) or state 2 (for remote attempts), since the login doesn’t exist. | |
| 7 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 7. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: An error occurred while evaluating the password. |
| The login is disabled *and* the password is incorrect. This shows that password validation occurs first, since if the password is correct and the login is disabled, you get error 18470 (see state 1 above). It’s possible that your application is sending cached credentials and the password has been changed or reset in the meantime – you may try logging out and logging back in to refresh these credentials. | |
| 8 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 8. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Password did not match that for the login provided. |
|
Probably the simplest of all: the password is incorrect (cASe sEnsiTiVitY catches a lot of folks here). Note that it will say «the login provided» even if you attempted to connect as a contained database user but forgot to specify a database, specified the wrong database, or typed the password incorrectly – unless it finds a match, SQL Server doesn’t have any idea you were attempting to use a contained database user. An interesting case here is Docker containers – |
|
| 9 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 9. Login failed for user ‘<xy>’. |
| Like state 2, I have not seen this in the wild. It allegedly means that the password violated a password policy check, but I tried creating a login conforming to a weak password policy, strengthened the policy, and I could still log in fine. And obviously you can’t create a login with, or later set, a password that doesn’t meet the policy. Let me know if you’ve seen it. | |
| 10 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 10. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| This is a rather complicated variation on state 9; as KB #925744 states, this means that password checking could not be performed because the login is disabled or locked on the domain controller (note that if SQL Server does not start, it could be because the account that is locked or disabled is the SQL Server service account). No reason or additional information is provided in the «verbose» message in the error log. | |
| 11 12 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 11. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Login-based server access validation failed with an infrastructure error. Check for previous errors. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 12. |
| States 11 and 12 mean that SQL Server was able to authenticate you, but weren’t able to validate with the underlying Windows permissions. It could be that the Windows login has no profile or that permissions could not be checked due to UAC. Try running SSMS as administrator and/or disabling UAC. Another reason could be that the domain controller could not be reached. You may need to resort to re-creating the login (see this post from Simon Sabin). Finally, PSS has recently released more information about states 11 and 12; see this post for potential scenarios and solutions, and also see states 146-149 below for changes in SQL Server 2016. | |
| 13 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 13. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: SQL Server service is paused. No new connections can be accepted at this time. |
| This state occurs when the SQL Server service has been paused (which you can do easily and even accidentally from the context menu in Object Explorer). | |
| 16 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 16. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. You may also see: A connection was successfully established with the server, but then an error occurred during the pre-login handshake. |
| State 16, which only occurs prior to SQL Server 2008, means that the default database was inaccessible. This could be because the database has been removed, renamed, or is offline (it may be set to AutoClose). This state does not indicate a reason in the error log. In 2008 and beyond, this is reported as state 40 (see below), with a reason. In SQL Server 2005, this state may also be reported if the user’s default database is online but the database they explicitly requested is not available for the reasons stated above (also see state 27). If you get the pre-login handshake message, it may be because you’ve disabled SSL on the server. | |
| 18 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 18. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| Supposedly this indicates that the user needs to change their password. In SQL Server 2005, 2008 R2 and SQL Server 2012, I found this was raised as error 18488, not 18456; this is because for SQL logins the change password dialog just delays logging in, and is not actually a login failure. I suspect that, like state 16, this state will no longer appear in future versions of SQL Server. | |
| 23 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 23. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Access to server validation failed while revalidating the login on the connection. |
| There could be a few reasons for state 23. The most common one is that connections are being attempted while the service is being shut down. However if this error occurs and it is not surrounded in the log by messages about SQL Server shutting down, and there is no companion reason along with the message, I would look at KB #937745, which implies that this could be the result of an overloaded server that can’t service any additional logins because of connection pooling issues. Finally, if there *is* a companion reason, it may be the message indicated to the right, indicating that SQL Server was running as a valid domain account and, upon restarting, it can’t validate the account because the domain controller is offline or the account is locked or no longer valid. Try changing the service account to LocalSystem until you can sort out the domain issues. | |
| 27 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 27. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| State 27, like state 16, only occurs prior to SQL Server 2008. It means that the database specified in the connection string has been removed, renamed, or is offline (possibly due to AutoClose) – though in every case I tried, it was reported as state 16. This state does not indicate a reason in the error log. In 2008 and onward this is reported as state 38 (see below), with a reason. | |
| 28 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 28. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| I have not experienced this issue but I suspect it involves overloaded connection pooling and connection resets. I think you will only see state 28 prior to SQL Server 2008. | |
| 38 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 38. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to open the database specified in the login properties. or Reason: Cannot open database «<database>» requested by the login. The login failed. |
|
The database specified in the connection string, or selected in the Options > Connection Properties tab of the SSMS connection dialog, is no longer valid or online (it might be set to AutoClose or the user may simply not have permission). I came across this once when I typed <default> here instead of picking that option from the list. This is reported as state 27 or state 16 prior to SQL Server 2008.
Note that this could also be a symptom of an orphaned login. After establishing mirroring, Availability Groups, log shipping, etc. you may have created a new login or associated a user with a login on the primary database. The database-level user information gets replayed on the secondary servers, but the login information does not. Everything will work fine – until you have a failover. In this situation, you will need to synchronize the login and user information (for one example, see this script from the late Robert Davis). |
|
| 40 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 40. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to open the explicitly specified database. |
| Usually this means the login’s default database is offline (perhaps due to AutoClose) or no longer exists. Resolve by fixing the missing database, or changing the login’s default database using ALTER LOGIN (for older versions, use sp_defaultdb, which is now deprecated). This is reported as state 16 prior to SQL Server 2008. | |
| 46 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 46. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to open the database configured in the login object while revalidating the login on the connection. |
| State 46 may occur when the login (or login mapping to the service account) does not have a valid database selected as their default database. (I am guessing here but I think this may occur when the login in question is attempting to perform log shipping. Again, just a guess based on the few conversations I discovered online.) It can also occur if the classifier function (Resource Governor) or a logon trigger refers to a database that is offline, no longer exists, or is set to AutoClose. | |
| 50 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 50. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Current collation did not match the database’s collation during connection reset. |
| As the message implies, this can occur if the default collation for the login is incompatible with the collation of their default database (or the database explicitly specified in the connection string). It can also happen if they are using a client tool like Management Studio which may, when they have been disconnected, try to connect to master upon reconnection instead of their default database. | |
| 51 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 51. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to send an environment change notification to a log shipping partner node while revalidating the login. |
| Like states 11 & 12, this could have to do with UAC, or that the domain controller could not be reached, or that the domain account could not authenticate against the log shipping partner, or that the log shipping partner was down. Try changing the service account for SQL Server to a known domain or local account, rather than the built-in local service accounts, and validating that the partner instance is accessible, as well as the database that is being requested in the connection string and the default database of the login. Note that this could be trigged by the failover partner connection string attribute, and that the database may no longer exist or may be offline, single user, etc. | |
| 56 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 56. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed attempted retry of a process token validation. |
| State 56 is not very common – again, like states 11 & 12, this could have to do with UAC, or that the domain controller could not be reached. Try changing the service account for SQL Server to a known domain or local account, rather than the built-in local service accounts. | |
| 58 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 58. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: An attempt to login using SQL authentication failed. Server is configured for Windows authentication only. |
| State 58 occurs when SQL Server is set to use Windows Authentication only, and a client attempts to log in using SQL Authentication. It can also occur when SIDs do not match (in which case the error text might be slightly different). | |
| 62 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 62. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| State 62 occurs when a Windows Authentication account tries to access a contained database, and the contained database exists, but the SIDs do not match. | |
| 65 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 65. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Password did not match that for the user provided. [Database: ‘<x>’] |
| Contained user exists, the database is correct, but the password is invalid. This can also happen if you use a SQL login to connect to a contained database that has a contained user with the same name but a different password (one of several reasons this is not recommended). | |
| 102 103 … 110 111 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 102. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 103. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 104. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 105. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 106. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 107. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 108. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 109. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 110. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 111. |
| Documented by Microsoft as Azure Active Directory login failures. | |
| 122 123 124 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 122. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 123. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 124. |
| According to Microsoft, these indicate a blank or missing username and/or password. | |
| 126 | Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 126. |
| The docs say «Database requested by user does not exist.» But it’s not clear why you would get 126 instead of, say, 38 or 40. | |
| 132 133 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 132. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 133. |
| Documented by paschott and by Microsoft as Azure Active Directory login failures. | |
| 146 147 148 149 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 146. Login failed for user ‘<Windows auth login>’. Reason: Token-based server access validation failed with an infrastructure error. Login lacks Connect SQL permission. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 147. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 148. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 149. |
| These states replace states 11 and 12 above, but only in SQL Server 2016 or better. The goal was to make the actual underlying issue easier for the sysadmin to diagnose between SQL auth and Windows auth logins, and between connect and endpoint permissions (all without giving any further info to the user trying to log in). For more details, see the latter part of this post. |
I am sure I missed some, but I hope that is a helpful summary of most of the 18456 errors you are likely to come across. Please let me know if you spot any inaccuracies or if you know of any states (or reasons) that I missed.
If you are using contained databases, there will be a little extra complication in solving login failures, especially if you try to create contained users with the same name as server-level logins. This is a ball of wax you just probably don’t want to get into…
Thanks to Jonathan Kehayias (blog | twitter), Bob Ward (CSS blog | twitter), and Rick Byham for input and sanity checking.
If you are experiencing ‘Login failed Microsoft SQL Server error 18456’ while trying to connect to SQL Server (local or remote) in Windows 10/8/7 computer, then you are in right place for the solution. Here, you will be guided with easy steps/methods to resolve the issue. Let’s starts the discussion.
‘Microsoft SQL Server’: MS SQL Server or Microsoft SQL Server is RDMS (Relational Database Management System) designed & developed by Microsoft. As Database server, it is software with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications which may run either on same computer or on another computer across the network/internet. It is written in C & C++ programming language and available for Linux, Microsoft Windows Server and Microsoft Windows Operating System.
However, several users reported that they faced ‘Login failed Microsoft SQL Server error 18456’ problem while they tried to connect to Microsoft SQL Server on their Windows 10 computer or on Windows Server. This error prevents you from logging-in into MS SQL Server (local or remote) for some reasons. There could be several reasons behind this error including required administrator permissions not give SQL Server, disabled TCP/IP protocol in SQL Server settings and other reasons. Let’s take a look at error message.
“Login failed for user ‘<user_name>’. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456)”
Here, <user_name> is username of MS SQL Server received by the user. One possible way to resolve the issue is to restart the MS SQL Server, your computer (Client), and networking equipments/computers. Also, you should make sure you are entering correct username & password and not copy-pasting the address. Entering wrong SQL Server login credentials could be one possible reason behind Login failed error. So, make sure you are entering correct details.
You should also make sure you are entering correct database name in MS SQL Server and make sure you have updated the configuration file accordingly. You can try to resolve the issue by unlocking the account by using query ALTER LOGIN WITH PASSWORD = UNLOCK. Sometimes, this type of error can be occurred if SQL Server is under attack. Let’s go for the solution.
How to fix Login failed Microsoft SQL Server error 18456 on Windows 10 or Windows Server?
Method 1: Run MS SQL Server as Administrator and disable UAC on the server
This error can be occurred with SQL server is not running with administrator permission. You can run SQL Server with Admin permission and then disable UAC on the server in order to fix the issue.
Run SQL Server as Administrator:
Step 1: Type ‘SQL Server Management Studio’ in ‘Windows Search box’, right-click on SQL Server Management Studio from the results appeared, and select ‘Run as Administrator’
Step 2: Click on ‘Yes’ button on UAC dialog box and check if you login into SQL Server without any issue
Step 3: If not, then check if disabling UAC on the server machine resolve the issue
Run the SQL Server in Single User Mode:
Step 1: Type ‘SQL Server Configuration Manager’ in Windows Search box, right-click on SQL Server service, and select ‘Properties’
Step 2: In the ‘Properties’ window, click on ‘Startup Paramenters’ tab and type ‘-m’ inside ‘Specify a startup parameter’ box and then hit ‘Add’ and ‘Apply’ button
Step 3: Now, right-click on SQL Server service and select ‘Restart’ to restart the service
Step 4: Now, type ‘SQL Server Management Studio’ in Windows Search box and right-click on results appear and select ‘Run as Administrator’, and check if the error is resolved.
Step 5: If so, then Add the domain account to SQL Server and assign it the ‘SysAdmin’ role
Step 6: Now, back to the ‘SQL Server Configuration Manager’ window, and remove ‘-m’ parameter in ‘Startup Parameters’ tab
Step 7: Finally, restart SQL Server service again using ‘step 3’ and check if the issue is resolved.
Method 2: Enable TCP/IP protocol in SQL Server Conjuration Manager
Step 1: Type ‘SQL Server Configuration Manager’ in Windows Search box and open it from results appeared. Click ‘Yes’ if UAC prompt appeared
Step 2: In the eloped window, in left pane, find and expand ‘SQL Server Network Configuration’ and select ‘Protocols For’ option
Step 3: Now, in right pane, find and double-click on ‘TCP/IP’ and select ‘Yes’ in dropdown of ‘Enabled’ and then hit ‘Apply’ to save the changes
Step 4: Now, press ‘Windows + R’ keys on keyboard, type ‘services.msc’ in the opened ‘Run’ window and hit ‘OK’ to open ‘Services’ window
Step 5: In the opened window, find and right-click on SQL Server with server name, and select ‘Restart’ option to restart the service
Step 6: Once done, check if the error is resolved.
Method 3: Change Authentication Mode of SQL Server
Step 1: Open ‘SQL Server Management Studio’ via Windows Search and in ‘Objects Explorer’, find and right-click on your Sever and select ‘Properties’
Step 2: In the opened ‘Server Properties’ window, in left pane, select ‘Security’ and in right pane, select ‘SQL Server and Windows Authentication Mode’ radio option
Step 3: Finally, hit ‘Apply’ to save the changes and in ‘Object Explorer’ of SQL Server Management Studio, right-click on your server and select ‘Restart’ to restart the server and check if the error is resolved.
Step 4: If not, run the following command in ‘Windows PowerShell (Admin)’ or install MS Power tools and then run the command
psexec.exe -i -s ssms.exe
Step 5: Check if the issue is resolved after execution the above command
Method 4: Enable SA Account and reset account password
One possible way to resolve the issue is to enable SA account of SQL server and reset its password.
Step 1: Open ‘Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio’ and expound ‘Security’ in left pane
Step 2: Double-click on ‘Logins’ and open ‘SA’
Step 3: Now, enter new password and confirm the password, and then go to ‘Server Roles’ tab and select ‘Public’ and ‘SysAdmin’ role options
Step 4: Now, go to ‘Status’ tab and in right pane, select ‘Enabled’ under ‘Login’ and then hit ‘Apply’ to save the changes
Step 5: Now, open ‘Services’ Window via Windows Search, find and right-click on SQL Server Service and select ‘Restart’ to restart the service. Once done, check if the error is resolved.
Method 5: Create new login and restart the ‘Reporting Services’
If the issue is still persist, then you can create new login and restart the reporting services.
Step 1: Open ‘Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio’ and expand ‘Security’ tab in left pane
Step 2: Now, expand ‘Logins’, right-click on it and select ‘New login’, enter the credentials, in the login name, select your computer account
Step 3: Deselect ‘User Must Change Password at next Login’ checkbox and select the Database
Step 4: Now, go to ‘Server Roles’ and select ‘Public’ role, and go to ‘User Mapping’ tab, and select the database and select db_owner, and then save the changes
Step 5: Now, open ‘Services’ window via Windows Search, find and right-click on SQL Server Reporting Service and select ‘Restart’ to restart the service.
Step 6: After that, try reconnecting to the database and check if the error is resolved.
Fix Windows PC problems with ‘PC Repair Tool’ [Recommended Solution]
‘PC Repair Tool’ is easy & quick way to find and fix BSOD errors, DLL errors, EXE errors, problems with programs, malware or viruses issues, system files or registry issues and other system issues with just few clicks. You can get this tool through button/link below.
Conclusion
I am sure this post helped you on How to fix Login failed Microsoft SQL Server error 18456 on Windows 10/Windows Server with several easy steps/methods. You can read & follow our instructions to do so. That’s all. For any suggestions or queries, please write on comment box below.