My file .htaccess handles all requests from /word_here to my internal endpoint /page.php?name=word_here. The PHP script then checks if the requested page is in its array of pages.
If not, how can I simulate an error 404?
I tried this, but it didn’t result in my 404 page configured via ErrorDocument in the .htaccess showing up.
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found");
Am I right in thinking that it’s wrong to redirect to my error 404 page?
asked Sep 4, 2009 at 19:29
2
The up-to-date answer (as of PHP 5.4 or newer) for generating 404 pages is to use http_response_code:
<?php
http_response_code(404);
include('my_404.php'); // provide your own HTML for the error page
die();
die() is not strictly necessary, but it makes sure that you don’t continue the normal execution.
answered Jan 11, 2017 at 14:28
bladeblade
11.8k7 gold badges36 silver badges38 bronze badges
2
What you’re doing will work, and the browser will receive a 404 code. What it won’t do is display the «not found» page that you might be expecting, e.g.:
Not Found
The requested URL /test.php was not found on this server.
That’s because the web server doesn’t send that page when PHP returns a 404 code (at least Apache doesn’t). PHP is responsible for sending all its own output. So if you want a similar page, you’ll have to send the HTML yourself, e.g.:
<?php
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found", true, 404);
include("notFound.php");
?>
You could configure Apache to use the same page for its own 404 messages, by putting this in httpd.conf:
ErrorDocument 404 /notFound.php
Kzqai
22.5k25 gold badges105 silver badges135 bronze badges
answered Sep 4, 2009 at 19:50
JW.JW.
50.5k36 gold badges114 silver badges142 bronze badges
3
Try this:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
?>
answered Sep 4, 2009 at 19:36
Ates GoralAtes Goral
137k26 gold badges137 silver badges190 bronze badges
2
Create custom error pages through .htaccess file
1. 404 — page not found
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 404 /404.html
2. 500 — Internal Server Error
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 500 /500.html
3. 403 — Forbidden
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 403 /403.html
4. 400 — Bad request
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 400 /400.html
5. 401 — Authorization Required
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 401 /401.html
You can also redirect all error to single page. like
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 404 /404.html
ErrorDocument 500 /404.html
ErrorDocument 403 /404.html
ErrorDocument 400 /404.html
ErrorDocument 401 /401.html
answered Mar 30, 2016 at 10:34
Irshad KhanIrshad Khan
5,6302 gold badges43 silver badges39 bronze badges
1
Did you remember to die() after sending the header? The 404 header doesn’t automatically stop processing, so it may appear not to have done anything if there is further processing happening.
It’s not good to REDIRECT to your 404 page, but you can INCLUDE the content from it with no problem. That way, you have a page that properly sends a 404 status from the correct URL, but it also has your «what are you looking for?» page for the human reader.
answered Sep 4, 2009 at 19:50
EliEli
97.1k20 gold badges76 silver badges81 bronze badges
Standard Apache 404 error looks like this:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>404 Not Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Not Found</h1>
<p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p>
</body></html> Thus, you can use the following PHP code to generate 404 page that looks exactly as standard apache 404 page:
function httpNotFound()
{
http_response_code(404);
header('Content-type: text/html');
// Generate standard apache 404 error page
echo <<<HTML
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>404 Not Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Not Found</h1>
<p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p>
</body></html>
HTML;
exit;
}
answered Mar 20 at 16:14
Dima L.Dima L.
3,39332 silver badges30 bronze badges
try putting
ErrorDocument 404 /(root directory)/(error file)
in .htaccess file.
Do this for any error but substitute 404 for your error.
StackedQ
3,9791 gold badge27 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered May 20, 2018 at 19:41
In the Drupal or WordPress CMS (and likely others), if you are trying to make some custom php code appear not to exist (unless some condition is met), the following works well by making the CMS’s 404 handler take over:
<?php
if(condition){
do stuff;
} else {
include('index.php');
}
?>
answered Jan 28, 2019 at 19:38
Mike GodinMike Godin
3,6563 gold badges27 silver badges29 bronze badges
Immediately after that line try closing the response using exit or die()
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found");
exit;
or
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found");
die();
answered May 25, 2018 at 4:22
4
try this once.
$wp_query->set_404();
status_header(404);
get_template_part('404');
answered Mar 31, 2020 at 4:24
1
Опубликовано:
10 апреля 2015
Обновлено:
11 апреля 2019
77 865
Сайты развиваются: создаются новые разделы, меняется структура, удаляются страницы или переделываются их адреса. Часто за всеми этими процессами уследить очень сложно даже опытному веб-мастеру. Чем старше сайт – тем больше вероятность того, что каждый день он получают процент пользователей, попадающих на страницы, которых больше не существует. Как это отследить? Как оповестить робота и клиента, что таких страниц больше нет? Что показывать пользователю на странице 404? Отвечаю!
404 NOT FOUND – что означает?
Определение: “404 ошибка сервера (not found) — самая распространенная ошибка при пользовании Интернетом, основная причина — ошибка в написании адреса Web-страницы. Сервер понял запрос, но не нашёл соответствующего ресурса по указанному URI.”
Для чего нужна 404 страница?
1. Поисковому роботу необходимо сообщить, что такой страницы не существует, для этого используется 404 код ответа сервера. Это очень важно, чтобы не плодились дубли и не размывать релевантность страниц в индексе поисковых систем.
Проверить ответ это очень просто, наберите несуществующий адрес страницы тут – http://bertal.ru/.
2. Пользователю необходимо сообщить, что запрашиваемой страницы больше (или вообще) не существует, и предоставить возможность работать с сайтом дальше.
Как настроить ответ сервера?
404 ошибка сервера через htaccess
Если Ваш сервер или CMS не настроены атоматически, то придётся это сделать Вам самим – добавьте в htaccess строчку:
1 |
ErrorDocument 404 http://www.site.ru/404.php |
Теперь, когда пользователь введёт неверный адрес, то он будет направлен на этот адрес. Страница может располагаться где угодно, но мы для примера поместили ее в корне сайта: /404.php.
404 ошибка сервера в PHP
Велосипеда изобретать не надо – существует специальная функция header, которая успешно поможет Вам это сделать.
1 |
header(«HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found»); |
Как должна выглядеть страница 404?
- В дизайне сайта (а не страница по умолчанию вашего хостинга)
- Содержать информацию о том, что произошла ошибка
- Иметь форму поиска по сайту
- Иметь небольшую карту сайта с основными разделами.
Креативные 404 страницы – вред или польза?
Смешное оформление 404 страницы – это красиво и оригинально, но не стоит слишком сильно увлекаться. Не стоит забывать, чтобы пользователю в первую очередь необходимо решить какие-то задачи на вашем сайте, а не зависать на 404 странице, Вы должны максимально упростить и помочь ему в достижении его целей.
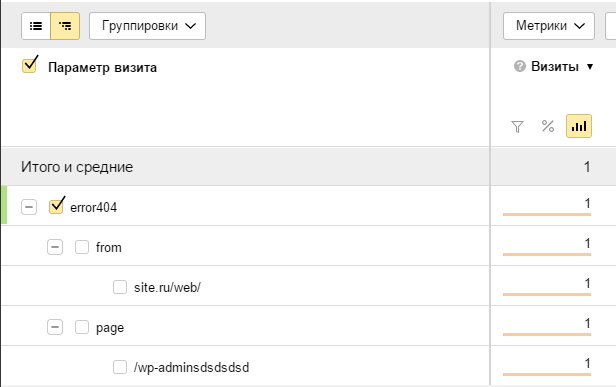
Как отследить, сколько таких пользователей попадают на страницу 404?
Яндекс.Метрика
Для этого удобно использовать “Параметры визитов”.
В код счётчика необходимо добавить строчку: params:window.yaParams||{ }});
Таким образом, должно получиться как-то так:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
w.yaCounterХХХХХХХХ = new Ya.Metrika({id:ХХХХХХХХ, webvisor:true, clickmap:true, trackLinks:true, accurateTrackBounce:true, trackHash:true, ut:"noindex", params:window.yaParams||{ }}); |
На самой же странице 404 в любом месте необходимо разместить следующий JS-код:
1 2 3 |
var url = document.location.pathname + document.location.search var url_referrer = document.referrer; var yaParams = {error404: {page: url, from: url_referrer}}; |
Где url – текущий адрес страницы 404, а url_referrer – адрес, с которого на него попали. Таким образом, мы в Яндекс.Метрике сможем отлеживать не только все 404 страницы, но и адреса, по которым на неё перешли.
Отчёт в Метрике необходимо смотреть тут: все отчеты -> содержание -> параметры визитов.
Подробнее о параметрах визита в Яндекс.Метрике: http://help.yandex.ru/metrika/content/visit-params.xml
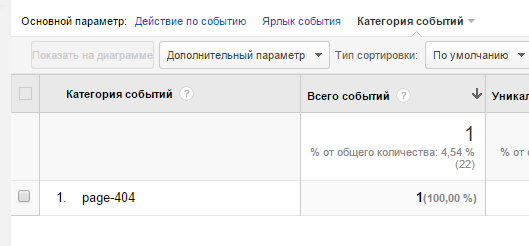
Google.Analytics
Для отслеживания ошибок используем “события”. Добавляем JS-код в тело страницы:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
jQuery(document).ready(function() { var url = document.location.pathname + document.location.search var url_referrer = document.referrer; ga('send', {'hitType': 'event', 'eventCategory': 'page-404', 'eventAction': url, 'eventLabel': url_referrer }); }); |
Где hitType – тип события, eventCategory – категория, eventAction – адрес ошибки, url_referrer – откуда на 404 страницу попали.
Отчёт в Гугл.Аналитикс: Поведение -> События -> Обзор.
Подробнее о настройке событий в Аналитикс: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/1033068?hl=ru
Как использовать полученные данные?
Если ошибки 404 внутри сайта – исправьте все ссылки на правильные или уберите вовсе. Если эти ссылки с внешних ресурсов? и Вам никак не повлиять на них, то поставьте 301 редирект на максимально релевантные страницы. Любите своих клиентов и не заставляйте их думать или что-то искать на Вашем сайте.

Я написал письмо в службу поддержки yandex, и мне пришло письмо, в котором сообщалось, что переживать не надо. Единственно, настоятельно желательно, чтобы я каким-то способом закрыл старые странички от индексирования (через robots.txt, вызов ошибки 404 или перенаправление) и удалил странички из базы по адресу http://webmaster.yandex.ru/delurl.xml. Удалять по указанному адресу желательно, чтобы быстрее прекратилась индексация страниц.
По некоторым причинам я предпочел способ вызова ошибки 404. Ошибка 404 вызывается в том случае, если ресурс на который идет ссылка не обнаружен. И тут я обнаружил, что у меня то и нет вызова этой ошибки, т.е. какие бы данные пользователь не ввел бы на старом сайте, что-то все равно выводится. Такая ситуация на мой взгляд не допустима, и я пошел с ней бороться.
Мой сайт написан был на php, поэтому я очень быстро нашел команду для вызова ошибки 404. Она имеет вид:
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
exit;
Казалось бы все просто, но нет же. Никак эти две команды не хотели работать. Тогда я почитал дополнительно материал и выяснил, что header() должна вызываться до отправки любого другого вывода. Т.е. она должна быть исключительно самой первой при выводе, поэтому ее нельзя использовать внутри require_once().
Но как оказалось существуют три замечательные функции, которые позволяют решить эту проблему:
-
ob_start() — задает начало области, которую надо поместить в буфер, я поместил ее самой первой при выводе.
- ob_end_flush() — окончание задания буфер и сразу вывод. Т.е. первые две функции задают область, которую сначала нужно вывести в буфер, а потом сразу вывести.
- ob_end_clean() — очищает буфер, и следующая команда как бы выводится самой первой.
С использованием этих команд организация вызова ошибки 404 выглядит следующим образом:
- Самая первая команда — ob_start()
- Далее идет основное содержание, которое пока копируется в буфер.
- Проверка на предмет вызова ошибки 404. Например, проверка наличия определенного значения. Если после проверки имеются причины вызвать ошибку, то задается код:
ob_end_clean() ; header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found"); exit;Тем самым будет выдано сообщение об ошибке и осуществлен выход.
- Выводим содержимое буфера командой ob_end_flush(). Идея в том, что если была вызвана ошибка, то сюда не попадем. Если ошибки не было, то выводим буфер.
Далее в файле .htaccess можно указать файл, который будет сопоставляться ошибке 404, но это уже совершенно другая история…
(PHP 5 >= 5.4.0, PHP 7, PHP
http_response_code — Получает или устанавливает код ответа HTTP
Описание
http_response_code(int $response_code = 0): int|bool
Список параметров
-
response_code -
Код ответа устанавливается с помощью опционального параметра
response_code.
Возвращаемые значения
Если response_code задан, то будет возвращён предыдущий код
статуса. Если response_code не задан, то будет возвращён
текущий код статуса. Оба этих значения будут по умолчанию иметь код состояния 200,
если они используются в окружении веб-сервера.
Если response_code не задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера (например, в CLI), то будет возвращено false. Если
response_code задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера, то будет возвращено true (но только если не был установлен предыдущий
код статуса).
Примеры
Пример #1 Использование http_response_code() в окружении веб-сервера
<?php// Берём текущий код и устанавливаем новый
var_dump(http_response_code(404));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
Пример #2 Использование http_response_code() в CLI
<?php// Берём текущий код по умолчанию
var_dump(http_response_code());// Устанавливаем код
var_dump(http_response_code(201));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
bool(false) bool(true) int(201)
Смотрите также
- header() — Отправка HTTP-заголовка
- headers_list() — Возвращает список переданных заголовков (или готовых к отправке)
craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk ¶
11 years ago
If your version of PHP does not include this function:
<?phpif (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
if (
$code !== NULL) {
switch (
$code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
break;
}$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
} else {
$code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
}
return
$code;
}
}
?>
In this example I am using $GLOBALS, but you can use whatever storage mechanism you like... I don't think there is a way to return the current status code:
https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=52555
For reference the error codes I got from PHP's source code:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/sapi/cgi/cgi_main.c#354
And how the current http header is sent, with the variables it uses:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/main/SAPI.c#856
Stefan W ¶
8 years ago
Note that you can NOT set arbitrary response codes with this function, only those that are known to PHP (or the SAPI PHP is running on).
The following codes currently work as expected (with PHP running as Apache module):
200 – 208, 226
300 – 305, 307, 308
400 – 417, 422 – 424, 426, 428 – 429, 431
500 – 508, 510 – 511
Codes 0, 100, 101, and 102 will be sent as "200 OK".
Everything else will result in "500 Internal Server Error".
If you want to send responses with a freestyle status line, you need to use the `header()` function:
<?php header("HTTP/1.0 418 I'm A Teapot"); ?>
Thomas A. P. ¶
7 years ago
When setting the response code to non-standard ones like 420, Apache outputs 500 Internal Server Error.
This happens when using header(0,0,420) and http_response_code(420).
Use header('HTTP/1.1 420 Enhance Your Calm') instead.
Note that the response code in the string IS interpreted and used in the access log and output via http_response_code().
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
Status codes as an array:
<?php
$http_status_codes = array(100 => "Continue", 101 => "Switching Protocols", 102 => "Processing", 200 => "OK", 201 => "Created", 202 => "Accepted", 203 => "Non-Authoritative Information", 204 => "No Content", 205 => "Reset Content", 206 => "Partial Content", 207 => "Multi-Status", 300 => "Multiple Choices", 301 => "Moved Permanently", 302 => "Found", 303 => "See Other", 304 => "Not Modified", 305 => "Use Proxy", 306 => "(Unused)", 307 => "Temporary Redirect", 308 => "Permanent Redirect", 400 => "Bad Request", 401 => "Unauthorized", 402 => "Payment Required", 403 => "Forbidden", 404 => "Not Found", 405 => "Method Not Allowed", 406 => "Not Acceptable", 407 => "Proxy Authentication Required", 408 => "Request Timeout", 409 => "Conflict", 410 => "Gone", 411 => "Length Required", 412 => "Precondition Failed", 413 => "Request Entity Too Large", 414 => "Request-URI Too Long", 415 => "Unsupported Media Type", 416 => "Requested Range Not Satisfiable", 417 => "Expectation Failed", 418 => "I'm a teapot", 419 => "Authentication Timeout", 420 => "Enhance Your Calm", 422 => "Unprocessable Entity", 423 => "Locked", 424 => "Failed Dependency", 424 => "Method Failure", 425 => "Unordered Collection", 426 => "Upgrade Required", 428 => "Precondition Required", 429 => "Too Many Requests", 431 => "Request Header Fields Too Large", 444 => "No Response", 449 => "Retry With", 450 => "Blocked by Windows Parental Controls", 451 => "Unavailable For Legal Reasons", 494 => "Request Header Too Large", 495 => "Cert Error", 496 => "No Cert", 497 => "HTTP to HTTPS", 499 => "Client Closed Request", 500 => "Internal Server Error", 501 => "Not Implemented", 502 => "Bad Gateway", 503 => "Service Unavailable", 504 => "Gateway Timeout", 505 => "HTTP Version Not Supported", 506 => "Variant Also Negotiates", 507 => "Insufficient Storage", 508 => "Loop Detected", 509 => "Bandwidth Limit Exceeded", 510 => "Not Extended", 511 => "Network Authentication Required", 598 => "Network read timeout error", 599 => "Network connect timeout error");
?>
Source: Wikipedia "List_of_HTTP_status_codes"
viaujoc at videotron dot ca ¶
2 years ago
Do not mix the use of http_response_code() and manually setting the response code header because the actual HTTP status code being returned by the web server may not end up as expected. http_response_code() does not work if the response code has previously been set using the header() function. Example:
<?php
header('HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized');
http_response_code(403);
print(http_response_code());
?>
The raw HTTP response will be (notice the actual status code on the first line does not match the printed http_response_code in the body):
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Date: Tue, 24 Nov 2020 13:49:08 GMT
Server: Apache
Connection: Upgrade, Keep-Alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
403
I only tested it on Apache. I am not sure if this behavior is specific to Apache or common to all PHP distributions.
Anonymous ¶
8 years ago
You can also create a enum by extending the SplEnum class.
<?php/** HTTP status codes */
class HttpStatusCode extends SplEnum {
const __default = self::OK;
const
SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
const OK = 200;
const CREATED = 201;
const ACCEPTED = 202;
const NONAUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
const NO_CONTENT = 204;
const RESET_CONTENT = 205;
const PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
const MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
const MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
const MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
const SEE_OTHER = 303;
const NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
const USE_PROXY = 305;
const BAD_REQUEST = 400;
const UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
const PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
const FORBIDDEN = 403;
const NOT_FOUND = 404;
const METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
const NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
const PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
const REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
const CONFLICT = 408;
const GONE = 410;
const LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
const PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
const REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
const REQUESTURI_TOO_LARGE = 414;
const UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
const REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
const EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
const IM_A_TEAPOT = 418;
const INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
const NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
const BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
const SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
const GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
const HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
}
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
2 years ago
if you need a response code not supported by http_response_code(), such as WebDAV / RFC4918's "HTTP 507 Insufficient Storage", try:
<?php
header($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] . ' 507 Insufficient Storage');
?>
result: something like
HTTP/1.1 507 Insufficient Storage
Rob Zazueta ¶
9 years ago
The note above from "Anonymous" is wrong. I'm running this behind the AWS Elastic Loadbalancer and trying the header(':'.$error_code...) method mentioned above is treated as invalid HTTP.
The documentation for the header() function has the right way to implement this if you're still on < php 5.4:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
?>
Anonymous ¶
10 years ago
If you don't have PHP 5.4 and want to change the returned status code, you can simply write:
<?php
header(':', true, $statusCode);
?>
The ':' are mandatory, or it won't work
Steven ¶
7 years ago
http_response_code is basically a shorthand way of writing a http status header, with the added bonus that PHP will work out a suitable Reason Phrase to provide by matching your response code to one of the values in an enumeration it maintains within php-src/main/http_status_codes.h. Note that this means your response code must match a response code that PHP knows about. You can't create your own response codes using this method, however you can using the header method.
In summary - The differences between "http_response_code" and "header" for setting response codes:
1. Using http_response_code will cause PHP to match and apply a Reason Phrase from a list of Reason Phrases that are hard-coded into the PHP source code.
2. Because of point 1 above, if you use http_response_code you must set a code that PHP knows about. You can't set your own custom code, however you can set a custom code (and Reason Phrase) if you use the header method.
Richard F. ¶
9 years ago
At least on my side with php-fpm and nginx this method does not change the text in the response, only the code.
<?php// HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
http_response_code(404);?>
The resulting response is HTTP/1.1 404 OK
stephen at bobs-bits dot com ¶
8 years ago
It's not mentioned explicitly, but the return value when SETTING, is the OLD status code.
e.g.
<?php
$a
= http_response_code();
$b = http_response_code(202);
$c = http_response_code();var_dump($a, $b, $c);// Result:
// int(200)
// int(200)
// int(202)
?>
Chandra Nakka ¶
5 years ago
On PHP 5.3 version, If you want to set HTTP response code. You can try this type of below trick :)
<?php
header
('Temporary-Header: True', true, 404);
header_remove('Temporary-Header');?>
yefremov {dot} sasha () gmail {dot} com ¶
8 years ago
@craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk@ wrote the function that replaces the original. It is very usefull, but has a bug. The original http_response_code always returns the previous or current code, not the code you are setting now. Here is my fixed version. I also use $GLOBALS to store the current code, but trigger_error() instead of exit. So now, how the function will behave in the case of error lies on the error handler. Or you can change it back to exit().
if (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
$prev_code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
if ($code === NULL) {
return $prev_code;
}
switch ($code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
trigger_error('Unknown http status code ' . $code, E_USER_ERROR); // exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
return $prev_code;
}
$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');
header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);
$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
// original function always returns the previous or current code
return $prev_code;
}
}
Anonymous ¶
4 years ago
http_response_code() does not actually send HTTP headers, it only prepares the header list to be sent later on.
So you can call http_reponse_code() to set, get and reset the HTTP response code before it gets sent.
Test code:
<php
http_response_code(500); // set the code
var_dump(headers_sent()); // check if headers are sent
http_response_code(200); // avoid a default browser page
Kubo2 ¶
6 years ago
If you want to set a HTTP response code without the need of specifying a protocol version, you can actually do it without http_response_code():
<?php
header
('Status: 404', TRUE, 404);?>
zweibieren at yahoo dot com ¶
7 years ago
The limited list given by Stefan W is out of date. I have just tested 301 and 302 and both work.
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
warning, it does not check if headers are already sent (if it is, it won't *actually* change the code, but a subsequent call will imply that it did!!),
you might wanna do something like
function ehttp_response_code(int $response_code = NULL): int {
if ($response_code === NULL) {
return http_response_code();
}
if (headers_sent()) {
throw new Exception('tried to change http response code after sending headers!');
}
return http_response_code($response_code);
}
In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to send a “404 Not Found” header using PHP.
This can be especially useful in cases when you need to display a 404 message if a particular database record does not exist.
By sending a 404 HTTP status code to the client, we can tell search engines and other crawlers that the resource does not exist.
To send a 404 to the client, we can use PHP’s http_response_code function like so.
//Send 404 response to client. http_response_code(404) //Include custom 404.php message include 'error/404.php'; //Kill the script. exit;
Note that this function is only available in PHP version 5.4 and after.
If you are using a PHP version that is older than 5.4, then you will need to use the header function instead.
//Use header function to send a 404 header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found", true, 404); //Include custom message. include 'errors/404.php'; //End the script exit;
In the code above, we.
- Send the response code to the client.
- We include a PHP file that contains our custom “404 Not Found” error. This file is not mandatory, so feel free to remove it if you want to.
- We then terminated the PHP script by calling the exit statement.
If you run one of the code samples above and check the response in your browser’s developer tools, then you will see something like this.
Request URL:http://localhost/test.php Request Method:GET Status Code:404 Not Found Remote Address:[::1]:80 Referrer Policy:no-referrer-when-downgrade
Note the Status Code segment of the server’s HTTP response. This is the 404 header.
When should I use this?
In most cases, your web server will automatically handle 404 errors if a resource does not exist.
However, what happens if your script is dynamic and it selects data from your database? What if you have a dynamic page such as users.php?id=234 and user 234 does not exist?
The file users.php will exist, so your web server will send back a status of “200 OK”, regardless of whether a user with the ID 234 exists or not.
In cases like this, we may need to manually send a 404 Not Found header.
Why isn’t PHP showing the same 404 message as my web server?
You might notice that your web server does not serve its default “404 Not Found” error message when you manually send the header with PHP.
The default message that Apache displays whenever a resource could not be found.
This is because, as far as the web server is concerned, the file does exist and it has already done its job.
One solution to this problem is to make sure that PHP and your web server display the exact same 404 message.
For example, with Apache, you can specify the path of a custom error message by using the ErrorDocument directive.
ErrorDocument 404 /errors/404.php
The Nginx web server also allows you to configure custom error messages.
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
header("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found");
header("Status: 404 Not Found");— не работает
-
Вопрос заданболее трёх лет назад
-
12885 просмотров
В помощь Вам http-response-code(404) клац
писать до любого вывода
Пригласить эксперта
Ставьте error_reporting(-1); в начале кода и смотрите что не так.
Скорее всего перед header() был вывод данных.
А может вы что-то не так поняли? Ваш код всего-лишь объявляет, что данная страница — страница ошибки. Чтобы именно вызвать 404 попробуйте exit(header('Location: /error404/'));
Попробуйте добавить exit(); сразу после вызова header();
Так-же перед вызовом header(); у Вас не должно быть вывода информации, если первый вариант не помог, попробуйте убрать закрывающий PHP тег ?> (если он есть)
На самом деле Вы всего лишь отправили заголовок, чтобы показать страницу нужно взять include или заголовок location.
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
09 июн. 2023, в 01:21
10000 руб./за проект
09 июн. 2023, в 01:06
50000 руб./за проект
09 июн. 2023, в 00:36
1000 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
(PHP 5 >= 5.4.0, PHP 7, PHP 
http_response_code — Получает или устанавливает код ответа HTTP
Описание
http_response_code(int $response_code = 0): int|bool
Список параметров
-
response_code -
Код ответа устанавливается с помощью опционального параметра
response_code.
Возвращаемые значения
Если response_code задан, то будет возвращён предыдущий код
статуса. Если response_code не задан, то будет возвращён
текущий код статуса. Оба этих значения будут по умолчанию иметь код состояния 200,
если они используются в окружении веб-сервера.
Если response_code не задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера (например, в CLI), то будет возвращено false. Если
response_code задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера, то будет возвращено true (но только если не был установлен предыдущий
код статуса).
Примеры
Пример #1 Использование http_response_code() в окружении веб-сервера
<?php// Берём текущий код и устанавливаем новый
var_dump(http_response_code(404));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
Пример #2 Использование http_response_code() в CLI
<?php// Берём текущий код по умолчанию
var_dump(http_response_code());// Устанавливаем код
var_dump(http_response_code(201));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
bool(false) bool(true) int(201)
Смотрите также
- header() — Отправка HTTP-заголовка
- headers_list() — Возвращает список переданных заголовков (или готовых к отправке)
craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk ¶
11 years ago
If your version of PHP does not include this function:
<?phpif (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
if (
$code !== NULL) {
switch (
$code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
break;
}$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
} else {
$code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
}
return
$code;
}
}
?>
In this example I am using $GLOBALS, but you can use whatever storage mechanism you like... I don't think there is a way to return the current status code:
https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=52555
For reference the error codes I got from PHP's source code:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/sapi/cgi/cgi_main.c#354
And how the current http header is sent, with the variables it uses:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/main/SAPI.c#856
Stefan W ¶
9 years ago
Note that you can NOT set arbitrary response codes with this function, only those that are known to PHP (or the SAPI PHP is running on).
The following codes currently work as expected (with PHP running as Apache module):
200 – 208, 226
300 – 305, 307, 308
400 – 417, 422 – 424, 426, 428 – 429, 431
500 – 508, 510 – 511
Codes 0, 100, 101, and 102 will be sent as "200 OK".
Everything else will result in "500 Internal Server Error".
If you want to send responses with a freestyle status line, you need to use the `header()` function:
<?php header("HTTP/1.0 418 I'm A Teapot"); ?>
Thomas A. P. ¶
7 years ago
When setting the response code to non-standard ones like 420, Apache outputs 500 Internal Server Error.
This happens when using header(0,0,420) and http_response_code(420).
Use header('HTTP/1.1 420 Enhance Your Calm') instead.
Note that the response code in the string IS interpreted and used in the access log and output via http_response_code().
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
Status codes as an array:
<?php
$http_status_codes = array(100 => "Continue", 101 => "Switching Protocols", 102 => "Processing", 200 => "OK", 201 => "Created", 202 => "Accepted", 203 => "Non-Authoritative Information", 204 => "No Content", 205 => "Reset Content", 206 => "Partial Content", 207 => "Multi-Status", 300 => "Multiple Choices", 301 => "Moved Permanently", 302 => "Found", 303 => "See Other", 304 => "Not Modified", 305 => "Use Proxy", 306 => "(Unused)", 307 => "Temporary Redirect", 308 => "Permanent Redirect", 400 => "Bad Request", 401 => "Unauthorized", 402 => "Payment Required", 403 => "Forbidden", 404 => "Not Found", 405 => "Method Not Allowed", 406 => "Not Acceptable", 407 => "Proxy Authentication Required", 408 => "Request Timeout", 409 => "Conflict", 410 => "Gone", 411 => "Length Required", 412 => "Precondition Failed", 413 => "Request Entity Too Large", 414 => "Request-URI Too Long", 415 => "Unsupported Media Type", 416 => "Requested Range Not Satisfiable", 417 => "Expectation Failed", 418 => "I'm a teapot", 419 => "Authentication Timeout", 420 => "Enhance Your Calm", 422 => "Unprocessable Entity", 423 => "Locked", 424 => "Failed Dependency", 424 => "Method Failure", 425 => "Unordered Collection", 426 => "Upgrade Required", 428 => "Precondition Required", 429 => "Too Many Requests", 431 => "Request Header Fields Too Large", 444 => "No Response", 449 => "Retry With", 450 => "Blocked by Windows Parental Controls", 451 => "Unavailable For Legal Reasons", 494 => "Request Header Too Large", 495 => "Cert Error", 496 => "No Cert", 497 => "HTTP to HTTPS", 499 => "Client Closed Request", 500 => "Internal Server Error", 501 => "Not Implemented", 502 => "Bad Gateway", 503 => "Service Unavailable", 504 => "Gateway Timeout", 505 => "HTTP Version Not Supported", 506 => "Variant Also Negotiates", 507 => "Insufficient Storage", 508 => "Loop Detected", 509 => "Bandwidth Limit Exceeded", 510 => "Not Extended", 511 => "Network Authentication Required", 598 => "Network read timeout error", 599 => "Network connect timeout error");
?>
Source: Wikipedia "List_of_HTTP_status_codes"
viaujoc at videotron dot ca ¶
2 years ago
Do not mix the use of http_response_code() and manually setting the response code header because the actual HTTP status code being returned by the web server may not end up as expected. http_response_code() does not work if the response code has previously been set using the header() function. Example:
<?php
header('HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized');
http_response_code(403);
print(http_response_code());
?>
The raw HTTP response will be (notice the actual status code on the first line does not match the printed http_response_code in the body):
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Date: Tue, 24 Nov 2020 13:49:08 GMT
Server: Apache
Connection: Upgrade, Keep-Alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
403
I only tested it on Apache. I am not sure if this behavior is specific to Apache or common to all PHP distributions.
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
You can also create a enum by extending the SplEnum class.
<?php/** HTTP status codes */
class HttpStatusCode extends SplEnum {
const __default = self::OK;
const
SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
const OK = 200;
const CREATED = 201;
const ACCEPTED = 202;
const NONAUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
const NO_CONTENT = 204;
const RESET_CONTENT = 205;
const PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
const MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
const MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
const MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
const SEE_OTHER = 303;
const NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
const USE_PROXY = 305;
const BAD_REQUEST = 400;
const UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
const PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
const FORBIDDEN = 403;
const NOT_FOUND = 404;
const METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
const NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
const PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
const REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
const CONFLICT = 408;
const GONE = 410;
const LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
const PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
const REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
const REQUESTURI_TOO_LARGE = 414;
const UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
const REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
const EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
const IM_A_TEAPOT = 418;
const INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
const NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
const BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
const SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
const GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
const HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
}
Rob Zazueta ¶
10 years ago
The note above from "Anonymous" is wrong. I'm running this behind the AWS Elastic Loadbalancer and trying the header(':'.$error_code...) method mentioned above is treated as invalid HTTP.
The documentation for the header() function has the right way to implement this if you're still on < php 5.4:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
?>
Anonymous ¶
10 years ago
If you don't have PHP 5.4 and want to change the returned status code, you can simply write:
<?php
header(':', true, $statusCode);
?>
The ':' are mandatory, or it won't work
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
3 years ago
if you need a response code not supported by http_response_code(), such as WebDAV / RFC4918's "HTTP 507 Insufficient Storage", try:
<?php
header($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] . ' 507 Insufficient Storage');
?>
result: something like
HTTP/1.1 507 Insufficient Storage
Steven ¶
8 years ago
http_response_code is basically a shorthand way of writing a http status header, with the added bonus that PHP will work out a suitable Reason Phrase to provide by matching your response code to one of the values in an enumeration it maintains within php-src/main/http_status_codes.h. Note that this means your response code must match a response code that PHP knows about. You can't create your own response codes using this method, however you can using the header method.
In summary - The differences between "http_response_code" and "header" for setting response codes:
1. Using http_response_code will cause PHP to match and apply a Reason Phrase from a list of Reason Phrases that are hard-coded into the PHP source code.
2. Because of point 1 above, if you use http_response_code you must set a code that PHP knows about. You can't set your own custom code, however you can set a custom code (and Reason Phrase) if you use the header method.
Richard F. ¶
9 years ago
At least on my side with php-fpm and nginx this method does not change the text in the response, only the code.
<?php// HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
http_response_code(404);?>
The resulting response is HTTP/1.1 404 OK
stephen at bobs-bits dot com ¶
9 years ago
It's not mentioned explicitly, but the return value when SETTING, is the OLD status code.
e.g.
<?php
$a
= http_response_code();
$b = http_response_code(202);
$c = http_response_code();var_dump($a, $b, $c);// Result:
// int(200)
// int(200)
// int(202)
?>
Chandra Nakka ¶
5 years ago
On PHP 5.3 version, If you want to set HTTP response code. You can try this type of below trick :)
<?php
header
('Temporary-Header: True', true, 404);
header_remove('Temporary-Header');?>
yefremov {dot} sasha () gmail {dot} com ¶
8 years ago
@craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk@ wrote the function that replaces the original. It is very usefull, but has a bug. The original http_response_code always returns the previous or current code, not the code you are setting now. Here is my fixed version. I also use $GLOBALS to store the current code, but trigger_error() instead of exit. So now, how the function will behave in the case of error lies on the error handler. Or you can change it back to exit().
if (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
$prev_code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
if ($code === NULL) {
return $prev_code;
}
switch ($code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
trigger_error('Unknown http status code ' . $code, E_USER_ERROR); // exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
return $prev_code;
}
$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');
header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);
$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
// original function always returns the previous or current code
return $prev_code;
}
}
Anonymous ¶
5 years ago
http_response_code() does not actually send HTTP headers, it only prepares the header list to be sent later on.
So you can call http_reponse_code() to set, get and reset the HTTP response code before it gets sent.
Test code:
<php
http_response_code(500); // set the code
var_dump(headers_sent()); // check if headers are sent
http_response_code(200); // avoid a default browser page
Kubo2 ¶
7 years ago
If you want to set a HTTP response code without the need of specifying a protocol version, you can actually do it without http_response_code():
<?php
header
('Status: 404', TRUE, 404);?>
zweibieren at yahoo dot com ¶
8 years ago
The limited list given by Stefan W is out of date. I have just tested 301 and 302 and both work.
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
warning, it does not check if headers are already sent (if it is, it won't *actually* change the code, but a subsequent call will imply that it did!!),
you might wanna do something like
function ehttp_response_code(int $response_code = NULL): int {
if ($response_code === NULL) {
return http_response_code();
}
if (headers_sent()) {
throw new Exception('tried to change http response code after sending headers!');
}
return http_response_code($response_code);
}
Если пользователь вобьет в адресную строку
некорректный URL мы должны показать страницу
с ошибкой. Пусть контент страницы с ошибкой
будет хранится в соответствующем файле:
<div>
page not found
</div>
Для того, чтобы определить некорректность
запроса, нам необходимо проверить существование
файла контента, соответствующего запрошенному URL:
<?php
$path = 'view' . $url . '.php';
if (file_exists($path)) {
// файл есть
} else {
// файла нет
}
?>
Давайте будем отдавать файл контента, если
он есть, и файл с ошибкой, если контента нет:
<?php
$path = 'view' . $url . '.php';
if (file_exists($path)) {
$content = file_get_contents($path);
} else {
$content = file_get_contents('view/404.php');
}
?>
В случае с ошибкой мы должны отправить в
браузер заголовок с 404 ошибкой, чтобы
явно сообщить о том, что страница не найдена.
Сделаем это:
<?php
$path = 'view' . $url . '.php';
if (file_exists($path)) {
$content = file_get_contents($path);
} else {
header('HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found');
$content = file_get_contents('view/404.php');
}
?>
Реализуйте в вашем движке отдачу страницы
с 404 ошибкой.
In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to send a “404 Not Found” header using PHP.
This can be especially useful in cases when you need to display a 404 message if a particular database record does not exist.
By sending a 404 HTTP status code to the client, we can tell search engines and other crawlers that the resource does not exist.
To send a 404 to the client, we can use PHP’s http_response_code function like so.
//Send 404 response to client. http_response_code(404) //Include custom 404.php message include 'error/404.php'; //Kill the script. exit;
Note that this function is only available in PHP version 5.4 and after.
If you are using a PHP version that is older than 5.4, then you will need to use the header function instead.
//Use header function to send a 404 header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found", true, 404); //Include custom message. include 'errors/404.php'; //End the script exit;
In the code above, we.
- Send the response code to the client.
- We include a PHP file that contains our custom “404 Not Found” error. This file is not mandatory, so feel free to remove it if you want to.
- We then terminated the PHP script by calling the exit statement.
If you run one of the code samples above and check the response in your browser’s developer tools, then you will see something like this.
Request URL:http://localhost/test.php Request Method:GET Status Code:404 Not Found Remote Address:[::1]:80 Referrer Policy:no-referrer-when-downgrade
Note the Status Code segment of the server’s HTTP response. This is the 404 header.
When should I use this?
In most cases, your web server will automatically handle 404 errors if a resource does not exist.
However, what happens if your script is dynamic and it selects data from your database? What if you have a dynamic page such as users.php?id=234 and user 234 does not exist?
The file users.php will exist, so your web server will send back a status of “200 OK”, regardless of whether a user with the ID 234 exists or not.
In cases like this, we may need to manually send a 404 Not Found header.
Why isn’t PHP showing the same 404 message as my web server?
You might notice that your web server does not serve its default “404 Not Found” error message when you manually send the header with PHP.
The default message that Apache displays whenever a resource could not be found.
This is because, as far as the web server is concerned, the file does exist and it has already done its job.
One solution to this problem is to make sure that PHP and your web server display the exact same 404 message.
For example, with Apache, you can specify the path of a custom error message by using the ErrorDocument directive.
ErrorDocument 404 /errors/404.php
The Nginx web server also allows you to configure custom error messages.