I know you can send a header that tells the browser this page is forbidden like:
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden');
But how can I also display the custom error page that has been created on the server for this type of error?
By default, just sending the header displays a white page, but I remember a while back reading that you can use the customer error page. Does anybody know?
alex
477k200 gold badges877 silver badges980 bronze badges
asked Feb 21, 2011 at 2:16
0
Just echo your content after sending the header.
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden');
echo 'You are forbidden!';
answered Feb 21, 2011 at 2:21
alexalex
477k200 gold badges877 silver badges980 bronze badges
3
http_response_code was introduced in PHP 5.4 and made the things a lot easier!
http_response_code(403);
die('Forbidden');
answered Apr 25, 2017 at 14:44
Marcio MazzucatoMarcio Mazzucato
8,7618 gold badges64 silver badges78 bronze badges
Include the custom error page after changing the header.
showdev
28.3k37 gold badges53 silver badges72 bronze badges
answered Feb 21, 2011 at 2:30
3
For this you must first say for the browser that the user receive an error 403. For this you can use this code:
header("HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden" );
Then, the script send «error, error, error, error, error…….», so you must stop it. You can use
exit;
With this two lines the server send an error and stop the script.
Don’t forget : that emulate the error, but you must set it in a .htaccess file, with
ErrorDocument 403 /error403.php
answered Apr 18, 2013 at 17:26
PyrrhaPyrrha
2112 silver badges2 bronze badges
0
Seen a lot of the answers, but the correct one is to provide the full options for the header function call as per the php manual
void header ( string $string [, bool $replace = true [, int $http_response_code ]] )
If you invoke with
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden', true, 403);
the normal behavior of HTTP 403 as configured with Apache or any other server would follow.
answered Dec 11, 2016 at 4:24
I have read all the answers here and none of them was complete answer for my situation (which is exactly the same in this question) so here is how I gathered some parts of the suggested answers and come up with the exact solution:
- Land on your server’s real 403 page. (Go to a forbidden URL on your server, or go to any 403 page you like)
- Right-click and select ‘view source’. Select all the source and save it to file on your domain like: http://domain.com/403.html
- now go to your real forbidden page (or a forbidden situation in some part of your php) example: http://domain.com/members/this_is_forbidden.php
-
echo this code below before any HTML output or header! (even a whitespace will cause PHP to send HTML/TEXT HTTP Header and it won’t work)
The code below should be your first line!<?php header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden'); $contents = file_get_contents('/home/your_account/public_html/domain.com/403.html', TRUE); exit($contents);
Now you have the exact solution. I checked and verified with CPANEL Latest Visitors and it is registered as exact 403 event.
answered Oct 6, 2015 at 18:00
TarikTarik
4,23037 silver badges35 bronze badges
4
.htaccess
ErrorDocument 403 /403.html
answered Feb 21, 2011 at 2:31
6
To minimize the duty of the server make it simple:
.htaccess
ErrorDocument 403 "Forbidden"
PHP
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden');
die(); // or your message: die('Forbidden');
answered Feb 5, 2014 at 21:34
Use ModRewrite:
RewriteRule ^403.html$ - [F]
Just make sure you create a blank document called «403.html» in your www root or you’ll get a 404 error instead of 403.
answered Feb 1, 2015 at 22:46
Jay SudoJay Sudo
991 silver badge2 bronze badges
2
I understand you have a scenario with ErrorDocument already defined within your apache conf or .htaccess and want to make those pages appear when manually sending a 4xx status code via php.
Unfortunately this is not possible with common methods because php sends header directly to user’s browser (not to Apache web server) whereas ErrorDocument is a display handler for http status generated from Apache.
answered Nov 27, 2014 at 15:22
Refresh the page after sending the 403:
<?php
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden');
?>
<html><head>
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0;URL=http://my.error.page">
</head><body></body></html>
answered Oct 12, 2014 at 6:08
1
(PHP 5 >= 5.4.0, PHP 7, PHP 
http_response_code — Получает или устанавливает код ответа HTTP
Описание
http_response_code(int $response_code = 0): int|bool
Список параметров
-
response_code -
Код ответа устанавливается с помощью опционального параметра
response_code.
Возвращаемые значения
Если response_code задан, то будет возвращён предыдущий код
статуса. Если response_code не задан, то будет возвращён
текущий код статуса. Оба этих значения будут по умолчанию иметь код состояния 200,
если они используются в окружении веб-сервера.
Если response_code не задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера (например, в CLI), то будет возвращено false. Если
response_code задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера, то будет возвращено true (но только если не был установлен предыдущий
код статуса).
Примеры
Пример #1 Использование http_response_code() в окружении веб-сервера
<?php// Берём текущий код и устанавливаем новый
var_dump(http_response_code(404));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
Пример #2 Использование http_response_code() в CLI
<?php// Берём текущий код по умолчанию
var_dump(http_response_code());// Устанавливаем код
var_dump(http_response_code(201));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
bool(false) bool(true) int(201)
Смотрите также
- header() — Отправка HTTP-заголовка
- headers_list() — Возвращает список переданных заголовков (или готовых к отправке)
craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk ¶
11 years ago
If your version of PHP does not include this function:
<?phpif (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
if (
$code !== NULL) {
switch (
$code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
break;
}$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
} else {
$code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
}
return
$code;
}
}
?>
In this example I am using $GLOBALS, but you can use whatever storage mechanism you like... I don't think there is a way to return the current status code:
https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=52555
For reference the error codes I got from PHP's source code:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/sapi/cgi/cgi_main.c#354
And how the current http header is sent, with the variables it uses:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/main/SAPI.c#856
Stefan W ¶
9 years ago
Note that you can NOT set arbitrary response codes with this function, only those that are known to PHP (or the SAPI PHP is running on).
The following codes currently work as expected (with PHP running as Apache module):
200 – 208, 226
300 – 305, 307, 308
400 – 417, 422 – 424, 426, 428 – 429, 431
500 – 508, 510 – 511
Codes 0, 100, 101, and 102 will be sent as "200 OK".
Everything else will result in "500 Internal Server Error".
If you want to send responses with a freestyle status line, you need to use the `header()` function:
<?php header("HTTP/1.0 418 I'm A Teapot"); ?>
Thomas A. P. ¶
7 years ago
When setting the response code to non-standard ones like 420, Apache outputs 500 Internal Server Error.
This happens when using header(0,0,420) and http_response_code(420).
Use header('HTTP/1.1 420 Enhance Your Calm') instead.
Note that the response code in the string IS interpreted and used in the access log and output via http_response_code().
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
Status codes as an array:
<?php
$http_status_codes = array(100 => "Continue", 101 => "Switching Protocols", 102 => "Processing", 200 => "OK", 201 => "Created", 202 => "Accepted", 203 => "Non-Authoritative Information", 204 => "No Content", 205 => "Reset Content", 206 => "Partial Content", 207 => "Multi-Status", 300 => "Multiple Choices", 301 => "Moved Permanently", 302 => "Found", 303 => "See Other", 304 => "Not Modified", 305 => "Use Proxy", 306 => "(Unused)", 307 => "Temporary Redirect", 308 => "Permanent Redirect", 400 => "Bad Request", 401 => "Unauthorized", 402 => "Payment Required", 403 => "Forbidden", 404 => "Not Found", 405 => "Method Not Allowed", 406 => "Not Acceptable", 407 => "Proxy Authentication Required", 408 => "Request Timeout", 409 => "Conflict", 410 => "Gone", 411 => "Length Required", 412 => "Precondition Failed", 413 => "Request Entity Too Large", 414 => "Request-URI Too Long", 415 => "Unsupported Media Type", 416 => "Requested Range Not Satisfiable", 417 => "Expectation Failed", 418 => "I'm a teapot", 419 => "Authentication Timeout", 420 => "Enhance Your Calm", 422 => "Unprocessable Entity", 423 => "Locked", 424 => "Failed Dependency", 424 => "Method Failure", 425 => "Unordered Collection", 426 => "Upgrade Required", 428 => "Precondition Required", 429 => "Too Many Requests", 431 => "Request Header Fields Too Large", 444 => "No Response", 449 => "Retry With", 450 => "Blocked by Windows Parental Controls", 451 => "Unavailable For Legal Reasons", 494 => "Request Header Too Large", 495 => "Cert Error", 496 => "No Cert", 497 => "HTTP to HTTPS", 499 => "Client Closed Request", 500 => "Internal Server Error", 501 => "Not Implemented", 502 => "Bad Gateway", 503 => "Service Unavailable", 504 => "Gateway Timeout", 505 => "HTTP Version Not Supported", 506 => "Variant Also Negotiates", 507 => "Insufficient Storage", 508 => "Loop Detected", 509 => "Bandwidth Limit Exceeded", 510 => "Not Extended", 511 => "Network Authentication Required", 598 => "Network read timeout error", 599 => "Network connect timeout error");
?>
Source: Wikipedia "List_of_HTTP_status_codes"
viaujoc at videotron dot ca ¶
2 years ago
Do not mix the use of http_response_code() and manually setting the response code header because the actual HTTP status code being returned by the web server may not end up as expected. http_response_code() does not work if the response code has previously been set using the header() function. Example:
<?php
header('HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized');
http_response_code(403);
print(http_response_code());
?>
The raw HTTP response will be (notice the actual status code on the first line does not match the printed http_response_code in the body):
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Date: Tue, 24 Nov 2020 13:49:08 GMT
Server: Apache
Connection: Upgrade, Keep-Alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
403
I only tested it on Apache. I am not sure if this behavior is specific to Apache or common to all PHP distributions.
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
You can also create a enum by extending the SplEnum class.
<?php/** HTTP status codes */
class HttpStatusCode extends SplEnum {
const __default = self::OK;
const
SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
const OK = 200;
const CREATED = 201;
const ACCEPTED = 202;
const NONAUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
const NO_CONTENT = 204;
const RESET_CONTENT = 205;
const PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
const MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
const MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
const MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
const SEE_OTHER = 303;
const NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
const USE_PROXY = 305;
const BAD_REQUEST = 400;
const UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
const PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
const FORBIDDEN = 403;
const NOT_FOUND = 404;
const METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
const NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
const PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
const REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
const CONFLICT = 408;
const GONE = 410;
const LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
const PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
const REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
const REQUESTURI_TOO_LARGE = 414;
const UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
const REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
const EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
const IM_A_TEAPOT = 418;
const INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
const NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
const BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
const SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
const GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
const HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
}
Rob Zazueta ¶
10 years ago
The note above from "Anonymous" is wrong. I'm running this behind the AWS Elastic Loadbalancer and trying the header(':'.$error_code...) method mentioned above is treated as invalid HTTP.
The documentation for the header() function has the right way to implement this if you're still on < php 5.4:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
?>
Anonymous ¶
10 years ago
If you don't have PHP 5.4 and want to change the returned status code, you can simply write:
<?php
header(':', true, $statusCode);
?>
The ':' are mandatory, or it won't work
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
3 years ago
if you need a response code not supported by http_response_code(), such as WebDAV / RFC4918's "HTTP 507 Insufficient Storage", try:
<?php
header($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] . ' 507 Insufficient Storage');
?>
result: something like
HTTP/1.1 507 Insufficient Storage
Steven ¶
8 years ago
http_response_code is basically a shorthand way of writing a http status header, with the added bonus that PHP will work out a suitable Reason Phrase to provide by matching your response code to one of the values in an enumeration it maintains within php-src/main/http_status_codes.h. Note that this means your response code must match a response code that PHP knows about. You can't create your own response codes using this method, however you can using the header method.
In summary - The differences between "http_response_code" and "header" for setting response codes:
1. Using http_response_code will cause PHP to match and apply a Reason Phrase from a list of Reason Phrases that are hard-coded into the PHP source code.
2. Because of point 1 above, if you use http_response_code you must set a code that PHP knows about. You can't set your own custom code, however you can set a custom code (and Reason Phrase) if you use the header method.
Richard F. ¶
9 years ago
At least on my side with php-fpm and nginx this method does not change the text in the response, only the code.
<?php// HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
http_response_code(404);?>
The resulting response is HTTP/1.1 404 OK
stephen at bobs-bits dot com ¶
9 years ago
It's not mentioned explicitly, but the return value when SETTING, is the OLD status code.
e.g.
<?php
$a
= http_response_code();
$b = http_response_code(202);
$c = http_response_code();var_dump($a, $b, $c);// Result:
// int(200)
// int(200)
// int(202)
?>
Chandra Nakka ¶
5 years ago
On PHP 5.3 version, If you want to set HTTP response code. You can try this type of below trick :)
<?php
header
('Temporary-Header: True', true, 404);
header_remove('Temporary-Header');?>
yefremov {dot} sasha () gmail {dot} com ¶
8 years ago
@craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk@ wrote the function that replaces the original. It is very usefull, but has a bug. The original http_response_code always returns the previous or current code, not the code you are setting now. Here is my fixed version. I also use $GLOBALS to store the current code, but trigger_error() instead of exit. So now, how the function will behave in the case of error lies on the error handler. Or you can change it back to exit().
if (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
$prev_code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
if ($code === NULL) {
return $prev_code;
}
switch ($code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
trigger_error('Unknown http status code ' . $code, E_USER_ERROR); // exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
return $prev_code;
}
$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');
header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);
$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
// original function always returns the previous or current code
return $prev_code;
}
}
Anonymous ¶
5 years ago
http_response_code() does not actually send HTTP headers, it only prepares the header list to be sent later on.
So you can call http_reponse_code() to set, get and reset the HTTP response code before it gets sent.
Test code:
<php
http_response_code(500); // set the code
var_dump(headers_sent()); // check if headers are sent
http_response_code(200); // avoid a default browser page
Kubo2 ¶
7 years ago
If you want to set a HTTP response code without the need of specifying a protocol version, you can actually do it without http_response_code():
<?php
header
('Status: 404', TRUE, 404);?>
zweibieren at yahoo dot com ¶
8 years ago
The limited list given by Stefan W is out of date. I have just tested 301 and 302 and both work.
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
warning, it does not check if headers are already sent (if it is, it won't *actually* change the code, but a subsequent call will imply that it did!!),
you might wanna do something like
function ehttp_response_code(int $response_code = NULL): int {
if ($response_code === NULL) {
return http_response_code();
}
if (headers_sent()) {
throw new Exception('tried to change http response code after sending headers!');
}
return http_response_code($response_code);
}
На сервере используется nginx, я отправляю ответ user’у так:
file index.php
<?
header('HTTP/1.1 403 incorrect user');Но когда открываю эту страницу, то не вижу ответа.
Делал так:
since PHP 5.4.0 there is a spezialized function for that http_response_code() i.e.:
<?php
http_response_code(404);
?>То же, просто белая страница, пустая внутри. Или я не должен видеть этой ошибки в браузере?
-
Вопрос заданболее трёх лет назад
-
3895 просмотров
Не должны. Сообщение об ошибке, которое отображается в окне браузера, надо выдавать самому, отдельно от заголовков.
header('HTTP/1.1 403 incorrect user');
echo 'Incorrect user';Пригласить эксперта
Так она и должна бьіть белой.
Вам же на сайтах не маячит на всех страницах 200 ОК
Смотрите заголовки:
i.imgur.com/UoEsncT.png
Как реализовать?
Так, как ты реализуешь. Главное чтобы заголовки отправлялись до начала вывода и не был подавлен вывод ошибок.
Или я не должен видеть этой ошибки в браузере?
Должен.
То же, просто белая страница, пустая внутри.
Как уже сказали — смотри код ответа пришедший от сервера.
Если там 200 — смотри конфиг нжинкса
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
08 июн. 2023, в 12:24
1500 руб./в час
12 июн. 2023, в 12:01
40000 руб./за проект
12 июн. 2023, в 11:16
5000 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
(PHP 5 >= 5.4.0, PHP 7, PHP
http_response_code — Получает или устанавливает код ответа HTTP
Описание
http_response_code(int $response_code = 0): int|bool
Список параметров
-
response_code -
Код ответа устанавливается с помощью опционального параметра
response_code.
Возвращаемые значения
Если response_code задан, то будет возвращён предыдущий код
статуса. Если response_code не задан, то будет возвращён
текущий код статуса. Оба этих значения будут по умолчанию иметь код состояния 200,
если они используются в окружении веб-сервера.
Если response_code не задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера (например, в CLI), то будет возвращено false. Если
response_code задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера, то будет возвращено true (но только если не был установлен предыдущий
код статуса).
Примеры
Пример #1 Использование http_response_code() в окружении веб-сервера
<?php// Берём текущий код и устанавливаем новый
var_dump(http_response_code(404));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
Пример #2 Использование http_response_code() в CLI
<?php// Берём текущий код по умолчанию
var_dump(http_response_code());// Устанавливаем код
var_dump(http_response_code(201));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
bool(false) bool(true) int(201)
Смотрите также
- header() — Отправка HTTP-заголовка
- headers_list() — Возвращает список переданных заголовков (или готовых к отправке)
craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk ¶
11 years ago
If your version of PHP does not include this function:
<?phpif (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
if (
$code !== NULL) {
switch (
$code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
break;
}$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
} else {
$code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
}
return
$code;
}
}
?>
In this example I am using $GLOBALS, but you can use whatever storage mechanism you like... I don't think there is a way to return the current status code:
https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=52555
For reference the error codes I got from PHP's source code:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/sapi/cgi/cgi_main.c#354
And how the current http header is sent, with the variables it uses:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/main/SAPI.c#856
Stefan W ¶
9 years ago
Note that you can NOT set arbitrary response codes with this function, only those that are known to PHP (or the SAPI PHP is running on).
The following codes currently work as expected (with PHP running as Apache module):
200 – 208, 226
300 – 305, 307, 308
400 – 417, 422 – 424, 426, 428 – 429, 431
500 – 508, 510 – 511
Codes 0, 100, 101, and 102 will be sent as "200 OK".
Everything else will result in "500 Internal Server Error".
If you want to send responses with a freestyle status line, you need to use the `header()` function:
<?php header("HTTP/1.0 418 I'm A Teapot"); ?>
Thomas A. P. ¶
7 years ago
When setting the response code to non-standard ones like 420, Apache outputs 500 Internal Server Error.
This happens when using header(0,0,420) and http_response_code(420).
Use header('HTTP/1.1 420 Enhance Your Calm') instead.
Note that the response code in the string IS interpreted and used in the access log and output via http_response_code().
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
Status codes as an array:
<?php
$http_status_codes = array(100 => "Continue", 101 => "Switching Protocols", 102 => "Processing", 200 => "OK", 201 => "Created", 202 => "Accepted", 203 => "Non-Authoritative Information", 204 => "No Content", 205 => "Reset Content", 206 => "Partial Content", 207 => "Multi-Status", 300 => "Multiple Choices", 301 => "Moved Permanently", 302 => "Found", 303 => "See Other", 304 => "Not Modified", 305 => "Use Proxy", 306 => "(Unused)", 307 => "Temporary Redirect", 308 => "Permanent Redirect", 400 => "Bad Request", 401 => "Unauthorized", 402 => "Payment Required", 403 => "Forbidden", 404 => "Not Found", 405 => "Method Not Allowed", 406 => "Not Acceptable", 407 => "Proxy Authentication Required", 408 => "Request Timeout", 409 => "Conflict", 410 => "Gone", 411 => "Length Required", 412 => "Precondition Failed", 413 => "Request Entity Too Large", 414 => "Request-URI Too Long", 415 => "Unsupported Media Type", 416 => "Requested Range Not Satisfiable", 417 => "Expectation Failed", 418 => "I'm a teapot", 419 => "Authentication Timeout", 420 => "Enhance Your Calm", 422 => "Unprocessable Entity", 423 => "Locked", 424 => "Failed Dependency", 424 => "Method Failure", 425 => "Unordered Collection", 426 => "Upgrade Required", 428 => "Precondition Required", 429 => "Too Many Requests", 431 => "Request Header Fields Too Large", 444 => "No Response", 449 => "Retry With", 450 => "Blocked by Windows Parental Controls", 451 => "Unavailable For Legal Reasons", 494 => "Request Header Too Large", 495 => "Cert Error", 496 => "No Cert", 497 => "HTTP to HTTPS", 499 => "Client Closed Request", 500 => "Internal Server Error", 501 => "Not Implemented", 502 => "Bad Gateway", 503 => "Service Unavailable", 504 => "Gateway Timeout", 505 => "HTTP Version Not Supported", 506 => "Variant Also Negotiates", 507 => "Insufficient Storage", 508 => "Loop Detected", 509 => "Bandwidth Limit Exceeded", 510 => "Not Extended", 511 => "Network Authentication Required", 598 => "Network read timeout error", 599 => "Network connect timeout error");
?>
Source: Wikipedia "List_of_HTTP_status_codes"
viaujoc at videotron dot ca ¶
2 years ago
Do not mix the use of http_response_code() and manually setting the response code header because the actual HTTP status code being returned by the web server may not end up as expected. http_response_code() does not work if the response code has previously been set using the header() function. Example:
<?php
header('HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized');
http_response_code(403);
print(http_response_code());
?>
The raw HTTP response will be (notice the actual status code on the first line does not match the printed http_response_code in the body):
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Date: Tue, 24 Nov 2020 13:49:08 GMT
Server: Apache
Connection: Upgrade, Keep-Alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
403
I only tested it on Apache. I am not sure if this behavior is specific to Apache or common to all PHP distributions.
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
You can also create a enum by extending the SplEnum class.
<?php/** HTTP status codes */
class HttpStatusCode extends SplEnum {
const __default = self::OK;
const
SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
const OK = 200;
const CREATED = 201;
const ACCEPTED = 202;
const NONAUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
const NO_CONTENT = 204;
const RESET_CONTENT = 205;
const PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
const MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
const MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
const MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
const SEE_OTHER = 303;
const NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
const USE_PROXY = 305;
const BAD_REQUEST = 400;
const UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
const PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
const FORBIDDEN = 403;
const NOT_FOUND = 404;
const METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
const NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
const PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
const REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
const CONFLICT = 408;
const GONE = 410;
const LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
const PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
const REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
const REQUESTURI_TOO_LARGE = 414;
const UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
const REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
const EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
const IM_A_TEAPOT = 418;
const INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
const NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
const BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
const SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
const GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
const HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
}
Rob Zazueta ¶
10 years ago
The note above from "Anonymous" is wrong. I'm running this behind the AWS Elastic Loadbalancer and trying the header(':'.$error_code...) method mentioned above is treated as invalid HTTP.
The documentation for the header() function has the right way to implement this if you're still on < php 5.4:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
?>
Anonymous ¶
10 years ago
If you don't have PHP 5.4 and want to change the returned status code, you can simply write:
<?php
header(':', true, $statusCode);
?>
The ':' are mandatory, or it won't work
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
3 years ago
if you need a response code not supported by http_response_code(), such as WebDAV / RFC4918's "HTTP 507 Insufficient Storage", try:
<?php
header($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] . ' 507 Insufficient Storage');
?>
result: something like
HTTP/1.1 507 Insufficient Storage
Steven ¶
8 years ago
http_response_code is basically a shorthand way of writing a http status header, with the added bonus that PHP will work out a suitable Reason Phrase to provide by matching your response code to one of the values in an enumeration it maintains within php-src/main/http_status_codes.h. Note that this means your response code must match a response code that PHP knows about. You can't create your own response codes using this method, however you can using the header method.
In summary - The differences between "http_response_code" and "header" for setting response codes:
1. Using http_response_code will cause PHP to match and apply a Reason Phrase from a list of Reason Phrases that are hard-coded into the PHP source code.
2. Because of point 1 above, if you use http_response_code you must set a code that PHP knows about. You can't set your own custom code, however you can set a custom code (and Reason Phrase) if you use the header method.
Richard F. ¶
9 years ago
At least on my side with php-fpm and nginx this method does not change the text in the response, only the code.
<?php// HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
http_response_code(404);?>
The resulting response is HTTP/1.1 404 OK
stephen at bobs-bits dot com ¶
9 years ago
It's not mentioned explicitly, but the return value when SETTING, is the OLD status code.
e.g.
<?php
$a
= http_response_code();
$b = http_response_code(202);
$c = http_response_code();var_dump($a, $b, $c);// Result:
// int(200)
// int(200)
// int(202)
?>
Chandra Nakka ¶
5 years ago
On PHP 5.3 version, If you want to set HTTP response code. You can try this type of below trick :)
<?php
header
('Temporary-Header: True', true, 404);
header_remove('Temporary-Header');?>
yefremov {dot} sasha () gmail {dot} com ¶
8 years ago
@craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk@ wrote the function that replaces the original. It is very usefull, but has a bug. The original http_response_code always returns the previous or current code, not the code you are setting now. Here is my fixed version. I also use $GLOBALS to store the current code, but trigger_error() instead of exit. So now, how the function will behave in the case of error lies on the error handler. Or you can change it back to exit().
if (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
$prev_code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
if ($code === NULL) {
return $prev_code;
}
switch ($code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
trigger_error('Unknown http status code ' . $code, E_USER_ERROR); // exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
return $prev_code;
}
$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');
header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);
$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
// original function always returns the previous or current code
return $prev_code;
}
}
Anonymous ¶
4 years ago
http_response_code() does not actually send HTTP headers, it only prepares the header list to be sent later on.
So you can call http_reponse_code() to set, get and reset the HTTP response code before it gets sent.
Test code:
<php
http_response_code(500); // set the code
var_dump(headers_sent()); // check if headers are sent
http_response_code(200); // avoid a default browser page
Kubo2 ¶
7 years ago
If you want to set a HTTP response code without the need of specifying a protocol version, you can actually do it without http_response_code():
<?php
header
('Status: 404', TRUE, 404);?>
zweibieren at yahoo dot com ¶
8 years ago
The limited list given by Stefan W is out of date. I have just tested 301 and 302 and both work.
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
warning, it does not check if headers are already sent (if it is, it won't *actually* change the code, but a subsequent call will imply that it did!!),
you might wanna do something like
function ehttp_response_code(int $response_code = NULL): int {
if ($response_code === NULL) {
return http_response_code();
}
if (headers_sent()) {
throw new Exception('tried to change http response code after sending headers!');
}
return http_response_code($response_code);
}
Я знаю, что вы можете отправить заголовок, который сообщает браузеру, что эта страница запрещена:
Но как я могу также отобразить страницу пользовательской ошибки, которая была создана на сервере для такого типа ошибок?
По умолчанию просто отправка заголовка отображает белую страницу, но я помню некоторое время назад, чтобы прочитать страницу ошибки клиента. Кто-нибудь знает?
Включите страницу пользовательской ошибки после изменения заголовка.
Просто эхом ваш контент после отправки заголовка.
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden'); echo 'You are forbidden!';
Для этого вы должны сначала сказать браузеру, что пользователь получил ошибку 403. Для этого вы можете использовать этот код:
header("HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden" );
Затем сценарий отправляет «ошибку, ошибку, ошибку, ошибку, ошибку …….», поэтому вы должны ее остановить. Вы можете использовать
exit;
С помощью этих двух строк сервер отправляет ошибку и останавливает скрипт.
Не забывайте: эмулируйте ошибку, но вы должны установить ее в файле .htaccess, с
ErrorDocument 403 /error403.php
http_response_code был представлен в PHP 5.4 и сделал все намного проще!
http_response_code(403); die('Forbidden');
.htaccess
ErrorDocument 403 /403.html
Посмотрите много ответов, но правильный – предоставить полные опции для вызова функции заголовка в соответствии с руководством по php
void header ( string $string [, bool $replace = true [, int $http_response_code ]] )
Если вы вызываете
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden', true, 403);
нормальное поведение HTTP 403, настроенное с помощью Apache или любого другого сервера.
Чтобы свести к минимуму обязанности сервера, сделайте его простым:
.htaccess
ErrorDocument 403 "Forbidden"
PHP
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden'); die(); // or your message: die('Forbidden');
Используйте ModRewrite:
RewriteRule ^403.html$ - [F]
Просто убедитесь, что вы создали пустой документ под названием «403.html» в своем корневом каталоге www или получите ошибку 404 вместо 403.
Я прочитал все ответы здесь, и ни один из них не был полным ответом для моей ситуации (что точно так же в этом вопросе), вот как я собрал некоторые части предлагаемых ответов и придумал точное решение:
- Приземлитесь на настоящую 403 страницу вашего сервера. (Перейдите на запрещенный URL-адрес на своем сервере или перейдите на любую 403 страницу, которая вам нравится)
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «источник просмотра». Выберите весь источник и сохраните его в файле в вашем домене, например: http://domain.com/403.html.
- теперь перейдите на свою настоящую запретную страницу (или запретную ситуацию в какой-то части вашего php): http://domain.com/members/this_is_forbidden.php
-
echo этот код ниже перед любым выходом или заголовком HTML! (даже пробелы заставят PHP отправлять HTML / TEXT HTTP Header, и это не сработает) Код ниже должен быть вашей первой строкой !
<?php header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden'); $contents = file_get_contents('/home/your_account/public_html/domain.com/403.html', TRUE); exit($contents);
Теперь у вас есть точное решение. Я проверил и проверил с последними посетителями CPANEL и зарегистрировался как точное событие 403.
Я понимаю, что у вас есть сценарий с ErrorDocument, уже определенный в вашем apache conf или .htaccess, и вы хотите, чтобы эти страницы отображались при ручной отправке кода состояния 4xx через php.
К сожалению, это невозможно с распространенными методами, потому что php отправляет заголовок непосредственно в браузер пользователя (а не на веб-сервер Apache), тогда как ErrorDocument – это обработчик отображения для http-статуса, сгенерированного из Apache.
Обновите страницу после отправки 403:
<?php header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden'); ?> <html><head> <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0;URL=http://my.error.page"> </head><body></body></html>
Алекс, вы можете перенаправить на свою страницу с помощью заголовка, подобного этому:
header('Location: my403page.html');
И убедитесь, что на вашей странице 403 вы включаете исходный код заголовка:
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden');
Кроме того, вы можете просто создать заголовок и включить страницу 403 следующим образом:
header('HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden'); include('my403page.html');
ошибка 403 — как исправить, что за ошибка forbidden. Сегодня разбираемся с ошибкой 403 и да не забыть о «ErrorDocument 403«.
Что такое ошибка 403.
С самого начала — просто давайте посмотрим на такую ошибку — которую ранее мы создавали для других страниц, а уже потом прейдем к теории.
Собственная страница для вывода ошибки 403:
Вместо стандартной ошибки типа «forbidden» — у нас выводится собственная страница 403.
Вывод ошибки forbidden 403:
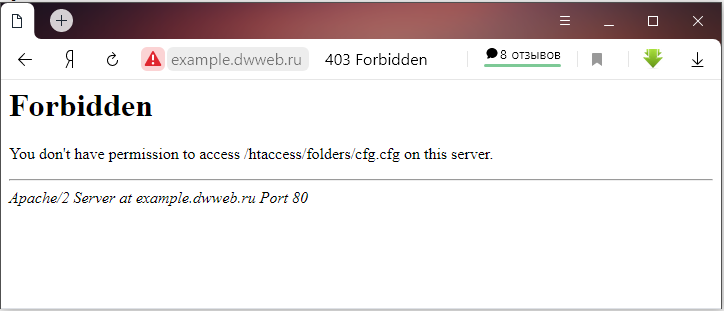
Такая же ошибка(самодельная) 403, которая выдает «Forbidden You don’t have permission to access /htaccess/folders/cfg.cfg on this server» — , что означает «Запрещено У вас нет разрешения на доступ к /htaccess/folders/cfg.cfg на этом сервере»
С примерами разобрались! Увидели, вживую созданные ошибки 403.
Но что же такое ошибка 403 forbidden
Если вы увидели «ошибка 403 forbidden» — значит, что данный файл, папка, закрыты для просмотра, т.е. запрещены.
Как исправить ошибку 403.
Данная ошибка возможно по нескольким причинам.
Где-то написано правило, которое запрещает вам увидеть информацию.
Ищем файл htaccess открываем его и ищем, где есть, например :
Файл htaccess может находиться в любом каталоге начиная с того, где лежит ваша папка/файл — подымаемся по каталогам вплоть до корневой и проверяем все файлы «htaccess».
Чтобы не встречаться с ошибкой 403.
Для того, чтобы никогда не встречаться с ошибкой 403 на своем сайте — изучайте теорию и воплощайте её на своем сайте!
ErrorDocument 403 htaccess — своя страница 403.html
Если вместо ответа сервера «forbidden» :
Вы хотите вывести свою ошибку 403, то вам нужно в файле htaccess прописать свойство :
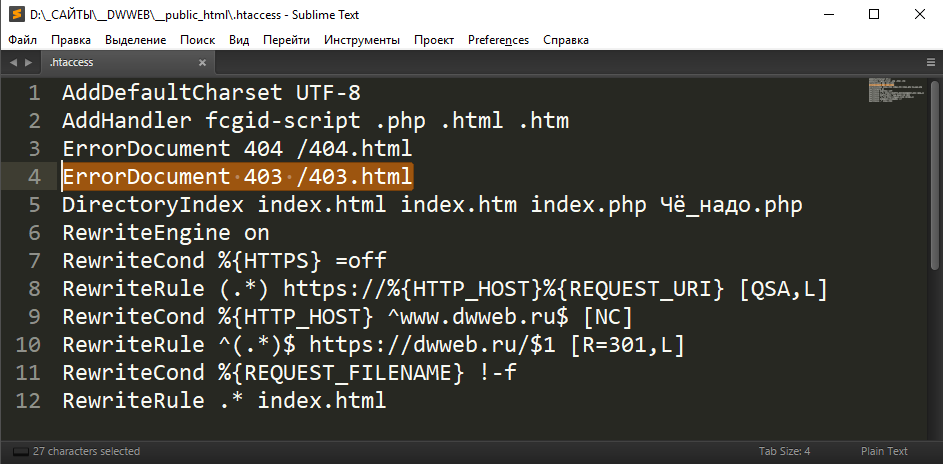
ErrorDocument 403 /403.html
Смотрим на наш файл htaccess — строка №4.
Именно в данном случае!
Файл htaccess располагается в корневой папке.
Для данного правила, которое показано выше будет выводиться страница 403, которая располагается:
Как собрать собственную страницу 403.html?
Для того, чтобы сделать у себя на сайте собственную страницу 403.html можно пойти несколькими путями:
Можно просто скачать ошибку, нажав по кнопке скачать:
Скачать страницу с ошибкой 403.html
Либо же вы можете самостоятельно собрать данную ошибку. Скопируйте код и сохраните его на компьютере.
Потом вам понадобится программа, которая умеет соединяться с сервером filezilla.
Либо через файл менеджер, который должен быть в админке сайта.
Далее нужны данные ftp… соединяемся и передаем на сервер.
Код страницы 403.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=»en»>
<head>
<meta charset=»UTF-8″>
<title>403</title>
</head>
<body>
<META HTTP-EQUIV=»REFRESH» CONTENT=»3; URL=https://dwweb.ru/»>
<TITLE>403</TITLE>
</HEAD><BODY>
<H1>Доступ запрещен</H1>
Чё вы здесь делаете!?
<HR>
</body>
</html>
Вопрос на засыпку об ошибке 403?
Если вы изучили выше приведенные примеры, то поняли, что у нас есть два варианта ошибки 403:
На главном сайте https://dwweb.ru/
И на поддомене «http://example.dwweb.ru»:
И выдают, по большому счету, они одно и тоже.
НО!
Если мы удалим из ссылки в этих двух случаях название файла и разрешение — т.е. попутаемся открыть папку, где лежат файлы, то получим совершенно разные результата!
Вопрос почему!?
Правила htaccess для данной папки идентичные в двух папках.
На главном сайте https://dwweb.ru/ — получим 404.
И на поддомене «http://example.dwweb.ru» — откроется папка, где лежит файл: