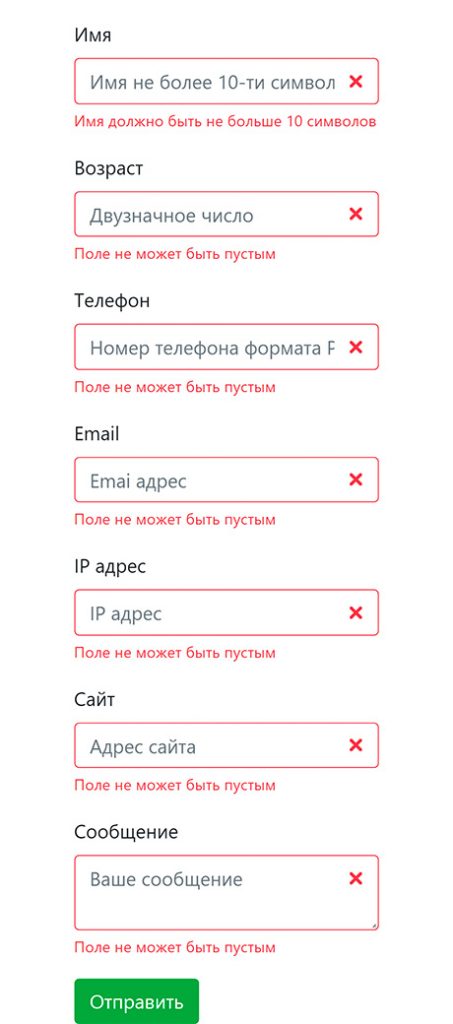
Такая задача: проверяя введённые данные на стороне сервера, прервать выполнение скрипта отправки и вывести соответствующее сообщение об ошибке (такое как «введённое имя слишком короткое», «неправильно введён номер телефона» и т. д.).
Чего я не понимаю — как вернуть какое-либо значение при завершении выполнения скрипта, чтобы его можно было перехварить в php-файле с формой ввода. Я себе это представляю как-то так:
<!-- action.php - файл проверки данных и отправки сообщения -->
<form id="FeedbackFrom" name="FeedbackFrom" method="post" action="request.php">
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
<?php
if ($_GET['mail'] == 0 && $errorCode == "TooShortName") {
echo "<p class="error"> Введённое имя слишком короткое </p>";
}
else if ($_GET['mail'] == 0 && $errorCode == "TooShortName") {
echo "<p class="error"> Введённое имя слишком длинное </p>";
}
?>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
<?php
if ($_GET['mail'] == 0 && $errorCode == "InvalidMail") {
echo "<p class="error"> Адрес электронной почты ведён неправильно </p>";
}
?>
<input type ="submit" id="Submitt"/>
</form>
- Есть
exit, но он ничего не возвращает. Код ошибки там ловится какими-то извращенскими способами; непонятно, как поймать его в блокеif. - Есть исключения и конструкция
try-catch. Но во-первых, нужно создавать отдельный класс для каждой ошибки, во-вторых как это «поймать» при аварийном завершенииrequest.php?
задан 27 сен 2016 в 8:31
Боков ГлебБоков Глеб
1,0382 золотых знака24 серебряных знака59 бронзовых знаков
<?php
$error = array();
$name = '';
$email = '';
// Если пришло значение
if(isset($_POST['name'])){
$name = $_POST['name'];
// Если там пусто
if(!$_POST['name']){
$error['name'] = 'Пустое имя';
}
}
// Если пришло значение
if(isset($_POST['email'])){
$email = $_POST['email'];
// Если там пусто
if(!$_POST['email']){
$error['email'] = 'Пустой email';
}
}
if(isset($_POST['name']) && isset($_POST['email']) && (!$error)){
mail($_POST['email'], 'Вы правильно заполнили форму', 'Ok' );
die(); // Тут должен быть редирект на другую страницу
}
?>
<form id="FeedbackFrom" name="FeedbackFrom" method="post" action="request.php">
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" value="<?php echo $name; ?>">
<?php
if(isset($error['name'])){
echo '<p class="error">' . $error['name'] . '</p>';
}
?>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" value="<?php echo $email; ?>">
<?php
if(isset($error['email'])){
echo '<p class="error">' . $error['email'] . '</p>';
}
?>
<input type ="submit" id="Submitt"/>
</form>
ответ дан 27 сен 2016 в 8:52
Если вкратце — как вариант в этих блоках ставить метку что есть ошибки заполнения
if ($_GET['mail'] == 0 && $errorCode == "TooShortName") {
$form_invalid = true;
echo "<p class="error"> Введённое имя слишком короткое </p>";
}
И в конце файла
if ( empty($form_invalid) ) {
// http://www.w3schools.com/php/filter_sanitize_email.asp
$email = filter_var($email, FILTER_SANITIZE_EMAIL);
mail($_POST['email'], 'Вы правильно заполнили форму', 'Ok' );
header('Location: action.php?mail_send=true');
die(); // Тут должен быть редирект на другую страницу, иначе при каждой перезагрузке станицы будет отправляться письмо
}
Но как по мне лучше использовать AJAX, это гораздо удобнее.
ответ дан 27 сен 2016 в 9:19
3
(PHP 4, PHP 5, PHP 7, PHP 
error_reporting — Sets which PHP errors are reported
Description
error_reporting(?int $error_level = null): int
Parameters
-
error_level -
The new error_reporting
level. It takes on either a bitmask, or named constants. Using named
constants is strongly encouraged to ensure compatibility for future
versions. As error levels are added, the range of integers increases,
so older integer-based error levels will not always behave as expected.The available error level constants and the actual
meanings of these error levels are described in the
predefined constants.
Return Values
Returns the old error_reporting
level or the current level if no error_level parameter is
given.
Changelog
| Version | Description |
|---|---|
| 8.0.0 |
error_level is nullable now.
|
Examples
Example #1 error_reporting() examples
<?php// Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);// Report simple running errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);// Reporting E_NOTICE can be good too (to report uninitialized
// variables or catch variable name misspellings ...)
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE | E_NOTICE);// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(-1);// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);?>
Notes
Tip
Passing in the value -1 will show every possible error,
even when new levels and constants are added in future PHP versions. The
behavior is equivalent to passing E_ALL constant.
See Also
- The display_errors directive
- The html_errors directive
- The xmlrpc_errors directive
- ini_set() — Sets the value of a configuration option
info at hephoz dot de ¶
14 years ago
If you just see a blank page instead of an error reporting and you have no server access so you can't edit php configuration files like php.ini try this:
- create a new file in which you include the faulty script:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("display_errors", 1);
include("file_with_errors.php");
?>
- execute this file instead of the faulty script file
now errors of your faulty script should be reported.
this works fine with me. hope it solves your problem as well!
jcastromail at yahoo dot es ¶
2 years ago
Under PHP 8.0, error_reporting() does not return 0 when then the code uses a @ character.
For example
<?php
$a
=$array[20]; // error_reporting() returns 0 in php <8 and 4437 in PHP>=8?>
dave at davidhbrown dot us ¶
17 years ago
The example of E_ALL ^ E_NOTICE is a 'bit' confusing for those of us not wholly conversant with bitwise operators.
If you wish to remove notices from the current level, whatever that unknown level might be, use & ~ instead:
<?php
//....
$errorlevel=error_reporting();
error_reporting($errorlevel & ~E_NOTICE);
//...code that generates notices
error_reporting($errorlevel);
//...
?>
^ is the xor (bit flipping) operator and would actually turn notices *on* if they were previously off (in the error level on its left). It works in the example because E_ALL is guaranteed to have the bit for E_NOTICE set, so when ^ flips that bit, it is in fact turned off. & ~ (and not) will always turn off the bits specified by the right-hand parameter, whether or not they were on or off.
Fernando Piancastelli ¶
18 years ago
The error_reporting() function won't be effective if your display_errors directive in php.ini is set to "Off", regardless of level reporting you set. I had to set
display_errors = On
error_reporting = ~E_ALL
to keep no error reporting as default, but be able to change error reporting level in my scripts.
I'm using PHP 4.3.9 and Apache 2.0.
ecervetti at orupaca dot fr ¶
14 years ago
It could save two minutes to someone:
E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE integer value is 6135
huhiko334 at yandex dot ru ¶
4 years ago
If you get a weird mysql warnings like "Warning: mysql_query() : Your query requires a full tablescan...", don't look for error_reporting settings - it's set in php.ini.
You can turn it off with
ini_set("mysql.trace_mode","Off");
in your script
http://tinymy.link/mctct
kevinson112 at yahoo dot com ¶
5 years ago
I had the problem that if there was an error, php would just give me a blank page. Any error at all forced a blank page instead of any output whatsoever, even though I made sure that I had error_reporting set to E_ALL, display_errors turned on, etc etc. But simply running the file in a different directory allowed it to show errors!
Turns out that the error_log file in the one directory was full (2.0 Gb). I erased the file and now errors are displayed normally. It might also help to turn error logging off.
https://techysupport.co/norton-tech-support/
luisdev ¶
5 years ago
This article refers to these two reporting levels:
// Report all PHP errors (see changelog)
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Report all PHP errors
error_reporting(-1);
What is the difference between those two levels?
Please update this article with a clear explanation of the difference and the possible use cases.
qeremy ! gmail ¶
8 years ago
If you want to see all errors in your local environment, you can set your project URL like "foo.com.local" locally and put that in bootstrap file.
<?php
if (substr($_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'], -6) == '.local') {
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
// or error_reporting(E_ALL);
}
?>
adam at adamhahn dot com ¶
6 years ago
To expand upon the note by chris at ocproducts dot com. If you prepend @ to error_reporting(), the function will always return 0.
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
var_dump(
error_reporting(), // value of E_ALL,
@error_reporting() // value is 0
);
?>
keithm at aoeex dot com ¶
12 years ago
Some E_STRICT errors seem to be thrown during the page's compilation process. This means they cannot be disabled by dynamically altering the error level at run time within that page.
The work-around for this was to rename the file and replace the original with a error_reporting() call and then a require() call.
Ex, rename index.php to index.inc.php, then re-create index.php as:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~(E_STRICT|E_NOTICE));
require('index.inc.php');
?>
That allows you to alter the error reporting prior to the file being compiled.
I discovered this recently when I was given code from another development firm that triggered several E_STRICT errors and I wanted to disable E_STRICT on a per-page basis.
chris at ocproducts dot com ¶
6 years ago
The error_reporting() function will return 0 if error suppression is currently active somewhere in the call tree (via the @ operator).
Rash ¶
8 years ago
If you are using the PHP development server, run from the command line via `php -S servername:port`, every single error/notice/warning will be reported in the command line itself, with file name, and line number, and stack trace.
So if you want to keep a log of all the errors even after page reloads (for help in debugging, maybe), running the PHP development server can be useful.
vdephily at bluemetrix dot com ¶
18 years ago
Note that E_NOTICE will warn you about uninitialized variables, but assigning a key/value pair counts as initialization, and will not trigger any error :
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);$foo = $bar; //notice : $bar uninitialized$bar['foo'] = 'hello'; // no notice, although $bar itself has never been initialized (with "$bar = array()" for example)$bar = array('foobar' => 'barfoo');
$foo = $bar['foobar'] // ok$foo = $bar['nope'] // notice : no such index
?>
&IT ¶
3 years ago
error_reporting(E_ALL);
if (!ini_get('display_errors')) {
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
}
lhenry at lhenry dot com ¶
3 years ago
In php7, what was generally a notice or a deprecated is now a warning : the same level of a mysql error … unacceptable for me.
I do have dozen of old projects and I surely d'ont want to define every variable which I eventually wrote 20y ago.
So two option: let php7 degrade my expensive SSDs writing Gb/hours or implement smthing like server level monitoring ( with auto_[pre-ap]pend_file in php.ini) and turn off E_WARNING
Custom overriding the level of php errors should be super handy and flexible …
rojaro at gmail dot com ¶
12 years ago
To enable error reporting for *ALL* error messages including every error level (including E_STRICT, E_NOTICE etc.), simply use:
<?php error_reporting(-1); ?>
j dot schriver at vindiou dot com ¶
22 years ago
error_reporting() has no effect if you have defined your own error handler with set_error_handler()
[Editor's Note: This is not quite accurate.
E_ERROR, E_PARSE, E_CORE_ERROR, E_CORE_WARNING, E_COMPILE_ERROR and E_COMPILE_WARNING error levels will be handled as per the error_reporting settings.
All other levels of errors will be passed to the custom error handler defined by set_error_handler().
Zeev Suraski suggests that a simple way to use the defined levels of error reporting with your custom error handlers is to add the following line to the top of your error handling function:
if (!($type & error_reporting())) return;
-zak@php.net]
kc8yds at gmail dot com ¶
14 years ago
this is to show all errors for code that may be run on different versions
for php 5 it shows E_ALL^E_STRICT and for other versions just E_ALL
if anyone sees any problems with it please correct this post
<?php
ini_set('error_reporting', version_compare(PHP_VERSION,5,'>=') && version_compare(PHP_VERSION,6,'<') ?E_ALL^E_STRICT:E_ALL);
?>
fredrik at demomusic dot nu ¶
17 years ago
Remember that the error_reporting value is an integer, not a string ie "E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE".
This is very useful to remember when setting error_reporting levels in httpd.conf:
Use the table above or:
<?php
ini_set("error_reporting", E_YOUR_ERROR_LEVEL);
echo ini_get("error_reporting");
?>
To get the appropriate integer for your error-level. Then use:
php_admin_value error_reporting YOUR_INT
in httpd.conf
I want to share this rather straightforward tip as it is rather annoying for new php users trying to understand why things are not working when the error-level is set to (int) "E_ALL" = 0...
Maybe the PHP-developers should make ie error_reporting("E_ALL"); output a E_NOTICE informative message about the mistake?
Alex ¶
16 years ago
error_reporting() may give unexpected results if the @ error suppression directive is used.
<?php
@include 'config.php';
include 'foo.bar'; // non-existent file
?>
config.php
<?php
error_reporting(0);
?>
will throw an error level E_WARNING in relation to the non-existent file (depending of course on your configuration settings). If the suppressor is removed, this works as expected.
Alternatively using ini_set('display_errors', 0) in config.php will achieve the same result. This is contrary to the note above which says that the two instructions are equivalent.
teynon1 at gmail dot com ¶
11 years ago
It might be a good idea to include E_COMPILE_ERROR in error_reporting.
If you have a customer error handler that does not output warnings, you may get a white screen of death if a "require" fails.
Example:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
function
myErrorHandler($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline) {
// Do something other than output message.
return true;
}$old_error_handler = set_error_handler("myErrorHandler");
require
"this file does not exist";
?>
To prevent this, simply include E_COMPILE_ERROR in the error_reporting.
<?php
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE | E_COMPILE_ERROR);
?>
Daz Williams (The Northeast) ¶
14 years ago
Only display php errors to the developer...
<?php
if($_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']=="00.00.00.00")
{
ini_set('display_errors','On');
}
else
{
ini_set('display_errors','Off');
}
?>
Just replace 00.00.00.00 with your ip address.
DarkGool ¶
17 years ago
In phpinfo() error reporting level display like a bit (such as 4095)
Maybe it is a simply method to understand what a level set on your host
if you are not have access to php.ini file
<?php
$bit = ini_get('error_reporting');
while ($bit > 0) {
for($i = 0, $n = 0; $i <= $bit; $i = 1 * pow(2, $n), $n++) {
$end = $i;
}
$res[] = $end;
$bit = $bit - $end;
}
?>
In $res you will have all constants of error reporting
$res[]=int(16) // E_CORE_ERROR
$res[]=int(8) // E_NOTICE
...
misplacedme at gmail dot com ¶
13 years ago
I always code with E_ALL set.
After a couple of pages of
<?php
$username = (isset($_POST['username']) && !empty($_POST['username']))....
?>
I made this function to make things a little bit quicker. Unset values passed by reference won't trigger a notice.
<?php
function test_ref(&$var,$test_function='',$negate=false) {
$stat = true;
if(!isset($var)) $stat = false;
if (!empty($test_function) && function_exists($test_function)){
$stat = $test_function($var);
$stat = ($negate) ? $stat^1 : $stat;
}
elseif($test_function == 'empty') {
$stat = empty($var);
$stat = ($negate) ? $stat^1 : $stat;
}
elseif (!function_exists($test_function)) {
$stat = false;
trigger_error("$test_function() is not a valid function");
}
$stat = ($stat) ? true : false;
return $stat;
}
$a = '';
$b = '15';test_ref($a,'empty',true); //False
test_ref($a,'is_int'); //False
test_ref($a,'is_numeric'); //False
test_ref($b,'empty',true); //true
test_ref($b,'is_int'); //False
test_ref($b,'is_numeric'); //false
test_ref($unset,'is_numeric'); //false
test_ref($b,'is_number'); //returns false, with an error.
?>
forcemdt ¶
9 years ago
Php >5.4
Creating a Custom Error Handler
set_error_handler("customError",E_ALL);
function customError($errno, $errstr)
{
echo "<b>Error:</b> [$errno] $errstr<br>";
echo "Ending Script";
die();
}
crautcher Проблема с обработкой ошибочного заполнения формы. На данный момент имеется форма добавления объявления. Ситуация такая , если пользователь ошибся или не заполнил одну графу , а остальные правильно , открывается страница с сообщением о неверно заполненной графе и предлагается вернуться обратно и заполнить ее.
ОДНАКО , вот и наступает проблема. Все те поля ,которые были правильно заполнены оказываются пустыми. И приходится по новой заполнять их.
Помогите пожалуйста , кто нибудь((( за спасибо или за пиво)). Нужно применить сессии и чтобы при ошибке в той же форме рядом с «ошибочной» графой выводилось предупреждение об ошибке. Сам пробовал , не получается. Самоучка(((
Добавлено через 2 минуты
crautcher, Спасибо Вам огромное , буду пробовать. Просто никогда не применял сам сессии. Если что-то не получится я еще обращусь к Вам)) Но Надеюсь , что справлюсь. Еще раз , благодарю . Радости не будет предела.
Добавлено через 9 минут
Сообщение от crautcher
Затем выводи, где нужно $_SESSION[‘LastError’]
Это в форме я так понимаю ? Рядом с «ошибочным» полем ? Можете на одном примере показать ? К примеру графа «имя»
PHP предлагает гибкие настройки вывода ошибок, среди которых функия error_reporting($level) – задает, какие ошибки PHP попадут в отчет, могут быть значения:
E_ALL– все ошибки,E_ERROR– критические ошибки,E_WARNING– предупреждения,E_PARSE– ошибки синтаксиса,E_NOTICE– замечания,E_CORE_ERROR– ошибки обработчика,E_CORE_WARNING– предупреждения обработчика,E_COMPILE_ERROR– ошибки компилятора,E_COMPILE_WARNING– предупреждения компилятора,E_USER_ERROR– ошибки пользователей,E_USER_WARNING– предупреждения пользователей,E_USER_NOTICE– уведомления пользователей.
1
Вывод ошибок в браузере
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On'); PHP
В htaccess
php_value error_reporting "E_ALL"
php_flag display_errors Onhtaccess
На рабочем проекте вывод ошибок лучше сделать только у авторизированного пользователя или в крайнем случаи по IP.
2
Запись ошибок в лог файл
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'Off');
ini_set('log_errors', 'On');
ini_set('error_log', $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'] . '/logs/php-errors.log');PHP
Файлы логов также не должны быть доступны из браузера, храните их в закрытой директории с файлом .htaccess:
Order Allow,Deny
Deny from allhtaccess
Или запретить доступ к файлам по расширению .log (заодно и другие системные файлы и исходники):
<FilesMatch ".(htaccess|htpasswd|bak|ini|log|sh|inc|config|psd|fla|ai)$">
Order Allow,Deny
Deny from all
</FilesMatch>htaccess
3
Отправка ошибок на e-mail
Ошибки можно отправлять на е-mail разработчика, но приведенные методы не работает при критических ошибках.
Первый – register_shutdown_function() регистрирует функцию, которая выполнится при завершении работы скрипта, error_get_last() получает последнюю ошибку.
register_shutdown_function('error_alert');
function error_alert()
{
$error = error_get_last();
if (!empty($error)) {
mail('mail@example.com', 'Ошибка на сайте example.com', print_r($error, true));
}
}PHP
Стоит учесть что оператор управления ошибками (знак @) работать в данном случаи не будет и письмо будет отправляться при каждой ошибке.
Второй метод использует «пользовательский обработчик ошибок», поэтому в браузер ошибки выводится не будут.
function error_alert($type, $message, $file, $line, $vars)
{
$error = array(
'type' => $type,
'message' => $message,
'file' => $file,
'line' => $line
);
error_log(print_r($error, true), 1, 'mail@example.com', 'From: mail@example.com');
}
set_error_handler('error_alert');PHP
4
Пользовательские ошибки
PHP позволяет разработчику самому объявлять ошибки, которые выведутся в браузере или в логе. Для создания ошибки используется функция trigger_error():
trigger_error('Пользовательская ошибка', E_USER_ERROR);PHP
Результат:
Fatal error: Пользовательская ошибка in /public_html/script.php on line 2E_USER_ERROR– критическая ошибка,E_USER_WARNING– не критическая,E_USER_NOTICE– сообщения которые не являются ошибками,E_USER_DEPRECATED– сообщения о устаревшем коде.
10.10.2019, обновлено 09.10.2021
Другие публикации

Список основных кодов состояния HTTP, без WebDAV.

Изображения нужно сжимать для ускорения скорости загрузки сайта, но как это сделать? На многих хостингах нет…

JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) – текстовый формат обмена данными, основанный на JavaScript, который представляет собой набор пар {ключ: значение}. Значение может быть массивом, числом, строкой и…

phpQuery – это удобный HTML парсер взявший за основу селекторы, фильтры и методы jQuery, которые позволяют…

AJAX позволяет отправить и получить данные без перезагрузки страницы. Например, делать проверку форм, подгружать контент и т.д. А функции JQuery значительно упрощают работу.

После регистрации в системе эквайринга Сбербанка и получив доступ к тестовой среде, можно приступить к интеграции с…

Список основных кодов состояния HTTP, без WebDAV.

Изображения нужно сжимать для ускорения скорости загрузки сайта, но как это сделать? На многих хостингах нет…

JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) – текстовый формат обмена данными, основанный на JavaScript, который представляет собой набор пар {ключ: значение}. Значение может быть массивом, числом, строкой и…

phpQuery – это удобный HTML парсер взявший за основу селекторы, фильтры и методы jQuery, которые позволяют…

AJAX позволяет отправить и получить данные без перезагрузки страницы. Например, делать проверку форм, подгружать контент и т.д. А функции JQuery значительно упрощают работу.

После регистрации в системе эквайринга Сбербанка и получив доступ к тестовой среде, можно приступить к интеграции с…