mjt at jpeto dot net ¶
13 years ago
I strongly recommend, that you use
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found");
instead of
header("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found");
I had big troubles with an Apache/2.0.59 (Unix) answering in HTTP/1.0 while I (accidentially) added a "HTTP/1.1 200 Ok" - Header.
Most of the pages were displayed correct, but on some of them apache added weird content to it:
A 4-digits HexCode on top of the page (before any output of my php script), seems to be some kind of checksum, because it changes from page to page and browser to browser. (same code for same page and browser)
"0" at the bottom of the page (after the complete output of my php script)
It took me quite a while to find out about the wrong protocol in the HTTP-header.
Marcel G ¶
13 years ago
Several times this one is asked on the net but an answer could not be found in the docs on php.net ...
If you want to redirect an user and tell him he will be redirected, e. g. "You will be redirected in about 5 secs. If not, click here." you cannot use header( 'Location: ...' ) as you can't sent any output before the headers are sent.
So, either you have to use the HTML meta refresh thingy or you use the following:
<?php
header( "refresh:5;url=wherever.php" );
echo 'You'll be redirected in about 5 secs. If not, click <a href="wherever.php">here</a>.';
?>
Hth someone
Dylan at WeDefy dot com ¶
15 years ago
A quick way to make redirects permanent or temporary is to make use of the $http_response_code parameter in header().
<?php
// 301 Moved Permanently
header("Location: /foo.php",TRUE,301);// 302 Found
header("Location: /foo.php",TRUE,302);
header("Location: /foo.php");// 303 See Other
header("Location: /foo.php",TRUE,303);// 307 Temporary Redirect
header("Location: /foo.php",TRUE,307);
?>
The HTTP status code changes the way browsers and robots handle redirects, so if you are using header(Location:) it's a good idea to set the status code at the same time. Browsers typically re-request a 307 page every time, cache a 302 page for the session, and cache a 301 page for longer, or even indefinitely. Search engines typically transfer "page rank" to the new location for 301 redirects, but not for 302, 303 or 307. If the status code is not specified, header('Location:') defaults to 302.
mandor at mandor dot net ¶
17 years ago
When using PHP to output an image, it won't be cached by the client so if you don't want them to download the image each time they reload the page, you will need to emulate part of the HTTP protocol.
Here's how:
<?php// Test image.
$fn = '/test/foo.png';// Getting headers sent by the client.
$headers = apache_request_headers(); // Checking if the client is validating his cache and if it is current.
if (isset($headers['If-Modified-Since']) && (strtotime($headers['If-Modified-Since']) == filemtime($fn))) {
// Client's cache IS current, so we just respond '304 Not Modified'.
header('Last-Modified: '.gmdate('D, d M Y H:i:s', filemtime($fn)).' GMT', true, 304);
} else {
// Image not cached or cache outdated, we respond '200 OK' and output the image.
header('Last-Modified: '.gmdate('D, d M Y H:i:s', filemtime($fn)).' GMT', true, 200);
header('Content-Length: '.filesize($fn));
header('Content-Type: image/png');
print file_get_contents($fn);
}?>
That way foo.png will be properly cached by the client and you'll save bandwith. :)
php at ober-mail dot de ¶
3 years ago
Since PHP 5.4, the function `http_response_code()` can be used to set the response code instead of using the `header()` function, which requires to also set the correct protocol version (which can lead to problems, as seen in other comments).
bebertjean at yahoo dot fr ¶
14 years ago
If using the 'header' function for the downloading of files, especially if you're passing the filename as a variable, remember to surround the filename with double quotes, otherwise you'll have problems in Firefox as soon as there's a space in the filename.
So instead of typing:
<?php
header("Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=" . basename($filename));
?>
you should type:
<?php
header("Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="" . basename($filename) . """);
?>
If you don't do this then when the user clicks on the link for a file named "Example file with spaces.txt", then Firefox's Save As dialog box will give it the name "Example", and it will have no extension.
See the page called "Filenames_with_spaces_are_truncated_upon_download" at
http://kb.mozillazine.org/ for more information. (Sorry, the site won't let me post such a long link...)
tim at sharpwebdevelopment dot com ¶
5 years ago
The header call can be misleading to novice php users.
when "header call" is stated, it refers the the top leftmost position of the file and not the "header()" function itself.
"<?php" opening tag must be placed before anything else, even whitespace.
yjf_victor ¶
7 years ago
According to the RFC 6226 (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6266), the only way to send Content-Disposition Header with encoding is:
Content-Disposition: attachment;
filename*= UTF-8''%e2%82%ac%20rates
for backward compatibility, what should be sent is:
Content-Disposition: attachment;
filename="EURO rates";
filename*=utf-8''%e2%82%ac%20rates
As a result, we should use
<?php
$filename = '中文文件名.exe'; // a filename in Chinese characters$contentDispositionField = 'Content-Disposition: attachment; '
. sprintf('filename="%s"; ', rawurlencode($filename))
. sprintf("filename*=utf-8''%s", rawurlencode($filename));header('Content-Type: application/octet-stream');header($contentDispositionField);readfile('file_to_download.exe');
?>
I have tested the code in IE6-10, firefox and Chrome.
David Spector ¶
1 year ago
Please note that there is no error checking for the header command, either in PHP, browsers, or Web Developer Tools.
If you use something like "header('text/javascript');" to set the MIME type for PHP response text (such as for echoed or Included data), you will get an undiagnosed failure.
The proper MIME-setting function is "header('Content-type: text/javascript');".
sk89q ¶
14 years ago
You can use HTTP's etags and last modified dates to ensure that you're not sending the browser data it already has cached.
<?php
$last_modified_time = filemtime($file);
$etag = md5_file($file);
header("Last-Modified: ".gmdate("D, d M Y H:i:s", $last_modified_time)." GMT");
header("Etag: $etag");
if (@
strtotime($_SERVER['HTTP_IF_MODIFIED_SINCE']) == $last_modified_time ||
trim($_SERVER['HTTP_IF_NONE_MATCH']) == $etag) {
header("HTTP/1.1 304 Not Modified");
exit;
}
?>
nospam at nospam dot com ¶
7 years ago
<?php// Response codes behaviors when using
header('Location: /target.php', true, $code) to forward user to another page:$code = 301;
// Use when the old page has been "permanently moved and any future requests should be sent to the target page instead. PageRank may be transferred."$code = 302; (default)
// "Temporary redirect so page is only cached if indicated by a Cache-Control or Expires header field."$code = 303;
// "This method exists primarily to allow the output of a POST-activated script to redirect the user agent to a selected resource. The new URI is not a substitute reference for the originally requested resource and is not cached."$code = 307;
// Beware that when used after a form is submitted using POST, it would carry over the posted values to the next page, such if target.php contains a form processing script, it will process the submitted info again!
// In other words, use 301 if permanent, 302 if temporary, and 303 if a results page from a submitted form.
// Maybe use 307 if a form processing script has moved.
?>
ben at indietorrent dot org ¶
11 years ago
Be aware that sending binary files to the user-agent (browser) over an encrypted connection (SSL/TLS) will fail in IE (Internet Explorer) versions 5, 6, 7, and 8 if any of the following headers is included:
Cache-control:no-store
Cache-control:no-cache
See: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/323308
Workaround: do not send those headers.
Also, be aware that IE versions 5, 6, 7, and 8 double-compress already-compressed files and do not reverse the process correctly, so ZIP files and similar are corrupted on download.
Workaround: disable compression (beyond text/html) for these particular versions of IE, e.g., using Apache's "BrowserMatch" directive. The following example disables compression in all versions of IE:
BrowserMatch ".*MSIE.*" gzip-only-text/html
David ¶
5 years ago
It seems the note saying the URI must be absolute is obsolete. Found on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_location
«An obsolete version of the HTTP 1.1 specifications (IETF RFC 2616) required a complete absolute URI for redirection.[2] The IETF HTTP working group found that the most popular web browsers tolerate the passing of a relative URL[3] and, consequently, the updated HTTP 1.1 specifications (IETF RFC 7231) relaxed the original constraint, allowing the use of relative URLs in Location headers.»
chris at ocproducts dot com ¶
6 years ago
Note that 'session_start' may overwrite your custom cache headers.
To remedy this you need to call:
session_cache_limiter('');
...after you set your custom cache headers. It will tell the PHP session code to not do any cache header changes of its own.
shutout2730 at yahoo dot com ¶
14 years ago
It is important to note that headers are actually sent when the first byte is output to the browser. If you are replacing headers in your scripts, this means that the placement of echo/print statements and output buffers may actually impact which headers are sent. In the case of redirects, if you forget to terminate your script after sending the header, adding a buffer or sending a character may change which page your users are sent to.
This redirects to 2.html since the second header replaces the first.
<?php
header("location: 1.html");
header("location: 2.html"); //replaces 1.html
?>
This redirects to 1.html since the header is sent as soon as the echo happens. You also won't see any "headers already sent" errors because the browser follows the redirect before it can display the error.
<?php
header("location: 1.html");
echo "send data";
header("location: 2.html"); //1.html already sent
?>
Wrapping the previous example in an output buffer actually changes the behavior of the script! This is because headers aren't sent until the output buffer is flushed.
<?php
ob_start();
header("location: 1.html");
echo "send data";
header("location: 2.html"); //replaces 1.html
ob_end_flush(); //now the headers are sent
?>
jp at webgraphe dot com ¶
19 years ago
A call to session_write_close() before the statement
<?php
header("Location: URL");
exit();
?>
is recommended if you want to be sure the session is updated before proceeding to the redirection.
We encountered a situation where the script accessed by the redirection wasn't loading the session correctly because the precedent script hadn't the time to update it (we used a database handler).
JP.
dev at omikrosys dot com ¶
13 years ago
Just to inform you all, do not get confused between Content-Transfer-Encoding and Content-Encoding
Content-Transfer-Encoding specifies the encoding used to transfer the data within the HTTP protocol, like raw binary or base64. (binary is more compact than base64. base64 having 33% overhead).
Eg Use:- header('Content-Transfer-Encoding: binary');
Content-Encoding is used to apply things like gzip compression to the content/data.
Eg Use:- header('Content-Encoding: gzip');
Angelica Perduta ¶
3 years ago
I made a script that generates an optimized image for use on web pages using a 404 script to resize and reduce original images, but on some servers it was generating the image but then not using it due to some kind of cache somewhere of the 404 status. I managed to get it to work with the following and although I don't quite understand it, I hope my posting here does help others with similar issues:
header_remove();
header("Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, max-age=0");
header("Cache-Control: post-check=0, pre-check=0", false);
header("Pragma: no-cache");
// ... and then try redirecting
// 201 = The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource however it's still not loading
// 302 "moved temporarily" does seems to load it!
header("location:$dst", FALSE, 302); // redirect to the file now we have it
mzheng[no-spam-thx] at ariba dot com ¶
14 years ago
For large files (100+ MBs), I found that it is essential to flush the file content ASAP, otherwise the download dialog doesn't show until a long time or never.
<?php
header("Content-Disposition: attachment; filename=" . urlencode($file));
header("Content-Type: application/force-download");
header("Content-Type: application/octet-stream");
header("Content-Type: application/download");
header("Content-Description: File Transfer");
header("Content-Length: " . filesize($file));
flush(); // this doesn't really matter.$fp = fopen($file, "r");
while (!feof($fp))
{
echo fread($fp, 65536);
flush(); // this is essential for large downloads
}
fclose($fp);
?>
razvan_bc at yahoo dot com ¶
5 years ago
<?php
/* This will give an error. Note the output
* above, which is before the header() call */
header('Location: http://www.example.com/');
exit;
?>
this example is pretty good BUT in time you use "exit" the parser will still work to decide what's happening next the "exit" 's action should do ('cause if you check the manual exit works in others situations too).
SO MY POINT IS : you should use :
<?php
header
('Location: http://www.example.com/');
die();?>
'CAUSE all die function does is to stop the script ,there is no other place for interpretation and the scope you choose to break the action of your script is quickly DONE!!!
there are many situations with others examples and the right choose for small parts of your scrips that make differences when you write your php framework at well!
Thanks Rasmus Lerdorf and his team to wrap off parts of unusual php functionality ,php 7 roolez!!!!!
scott at lucentminds dot com ¶
13 years ago
If you want to remove a header and keep it from being sent as part of the header response, just provide nothing as the header value after the header name. For example...
PHP, by default, always returns the following header:
"Content-Type: text/html"
Which your entire header response will look like
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: Apache/2.2.11 (Unix)
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.2.8
Date: Fri, 16 Oct 2009 23:05:07 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Connection: close
If you call the header name with no value like so...
<?php
header
( 'Content-Type:' );?>
Your headers now look like this:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: Apache/2.2.11 (Unix)
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.2.8
Date: Fri, 16 Oct 2009 23:05:07 GMT
Connection: close
Vinay Kotekar ¶
8 years ago
Saving php file in ANSI no isuess but when saving the file in UTF-8 format for various reasons remember to save the file without any BOM ( byte-order mark) support.
Otherwise you will face problem of headers not being properly sent
eg.
<?php header("Set-Cookie: name=user");?>
Would give something like this :-
Warning: Cannot modify header information - headers already sent by (output started at C:wwwinfo.php:1) in C:wwwinfo.php on line 1
Cody G. ¶
12 years ago
After lots of research and testing, I'd like to share my findings about my problems with Internet Explorer and file downloads.
Take a look at this code, which replicates the normal download of a Javascript:
<?php
if(strstr($_SERVER["HTTP_USER_AGENT"],"MSIE")==false) {
header("Content-type: text/javascript");
header("Content-Disposition: inline; filename="download.js"");
header("Content-Length: ".filesize("my-file.js"));
} else {
header("Content-type: application/force-download");
header("Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="download.js"");
header("Content-Length: ".filesize("my-file.js"));
}
header("Expires: Fri, 01 Jan 2010 05:00:00 GMT");
if(strstr($_SERVER["HTTP_USER_AGENT"],"MSIE")==false) {
header("Cache-Control: no-cache");
header("Pragma: no-cache");
}
include("my-file.js");
?>
Now let me explain:
I start out by checking for IE, then if not IE, I set Content-type (case-sensitive) to JS and set Content-Disposition (every header is case-sensitive from now on) to inline, because most browsers outside of IE like to display JS inline. (User may change settings). The Content-Length header is required by some browsers to activate download box. Then, if it is IE, the "application/force-download" Content-type is sometimes required to show the download box. Use this if you don't want your PDF to display in the browser (in IE). I use it here to make sure the box opens. Anyway, I set the Content-Disposition to attachment because I already know that the box will appear. Then I have the Content-Length again.
Now, here's my big point. I have the Cache-Control and Pragma headers sent only if not IE. THESE HEADERS WILL PREVENT DOWNLOAD ON IE!!! Only use the Expires header, after all, it will require the file to be downloaded again the next time. This is not a bug! IE stores downloads in the Temporary Internet Files folder until the download is complete. I know this because once I downloaded a huge file to My Documents, but the Download Dialog box put it in the Temp folder and moved it at the end. Just think about it. If IE requires the file to be downloaded to the Temp folder, setting the Cache-Control and Pragma headers will cause an error!
I hope this saves someone some time!
~Cody G.
Refugnic ¶
13 years ago
My files are in a compressed state (bz2). When the user clicks the link, I want them to get the uncompressed version of the file.
After decompressing the file, I ran into the problem, that the download dialog would always pop up, even when I told the dialog to 'Always perform this operation with this file type'.
As I found out, the problem was in the header directive 'Content-Disposition', namely the 'attachment' directive.
If you want your browser to simulate a plain link to a file, either change 'attachment' to 'inline' or omit it alltogether and you'll be fine.
This took me a while to figure out and I hope it will help someone else out there, who runs into the same problem.
Anonymous ¶
13 years ago
I just want to add, becuase I see here lots of wrong formated headers.
1. All used headers have first letters uppercase, so you MUST follow this. For example:
Location, not location
Content-Type, not content-type, nor CONTENT-TYPE
2. Then there MUST be colon and space, like
good: header("Content-Type: text/plain");
wrong: header("Content-Type:text/plain");
3. Location header MUST be absolute uri with scheme, domain, port, path, etc.
good: header("Location: http://www.example.com/something.php?a=1");
4. Relative URIs are NOT allowed
wrong: Location: /something.php?a=1
wrong: Location: ?a=1
It will make proxy server and http clients happier.
bMindful at fleetingiamge dot org ¶
20 years ago
If you haven't used, HTTP Response 204 can be very convenient. 204 tells the server to immediately termiante this request. This is helpful if you want a javascript (or similar) client-side function to execute a server-side function without refreshing or changing the current webpage. Great for updating database, setting global variables, etc.
header("status: 204"); (or the other call)
header("HTTP/1.0 204 No Response");
nobileelpirata at hotmail dot com ¶
16 years ago
This is the Headers to force a browser to use fresh content (no caching) in HTTP/1.0 and HTTP/1.1:
<?PHP
header( 'Expires: Sat, 26 Jul 1997 05:00:00 GMT' );
header( 'Last-Modified: ' . gmdate( 'D, d M Y H:i:s' ) . ' GMT' );
header( 'Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate' );
header( 'Cache-Control: post-check=0, pre-check=0', false );
header( 'Pragma: no-cache' );
?>
jamie ¶
14 years ago
The encoding of a file is discovered by the Content-Type, either in the HTML meta tag or as part of the HTTP header. Thus, the server and browser does not need - nor expect - a Unicode file to begin with a BOM mark. BOMs can confuse *nix systems too. More info at http://unicode.org/faq/utf_bom.html#bom1
On another note: Safari can display CMYK images (at least the OS X version, because it uses the services of QuickTime)
er dot ellison dot nyc at gmail dot com ¶
7 years ago
DO NOT PUT space between location and the colon that comes after that ,
// DO NOT USE THIS :
header("Location : #whatever"); // -> will not work !
// INSTEAD USE THIS ->
header("Location: #wahtever"); // -> will work forever !
ASchmidt at Anamera dot net ¶
5 years ago
Setting the "Location: " header has another undocumented side-effect!
It will also disregard any expressly set "Content-Type: " and forces:
"Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8"
The HTTP RFCs don't call for such a drastic action. They simply state that a redirect content SHOULD include a link to the destination page (in which case ANY HTML compatible content type would do). But PHP even overrides a perfectly standards-compliant
"Content-Type: application/xhtml+xml"!
hamza dot eljaouhari dot etudes at gmail dot com ¶
5 years ago
// Beware that adding a space between the keyword "Location" and the colon causes an Internal Sever Error
//This line causes the error
7
header('Location : index.php&controller=produit&action=index');
// While It must be written without the space
header('Location: index.php&controller=produit&action=index');
cedric at gn dot apc dot org ¶
12 years ago
Setting a Location header "returns a REDIRECT (302) status code to the browser unless the 201 or a 3xx status code has already been set". If you are sending a response to a POST request, you might want to look at RFC 2616 sections 10.3.3 and 10.3.4. It is suggested that if you want the browser to immediately GET the resource in the Location header in this circumstance, you should use a 303 status code not the 302 (with the same link as hypertext in the body for very old browsers). This may have (rare) consequences as mentioned in bug 42969.
My file .htaccess handles all requests from /word_here to my internal endpoint /page.php?name=word_here. The PHP script then checks if the requested page is in its array of pages.
If not, how can I simulate an error 404?
I tried this, but it didn’t result in my 404 page configured via ErrorDocument in the .htaccess showing up.
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found");
Am I right in thinking that it’s wrong to redirect to my error 404 page?
asked Sep 4, 2009 at 19:29
2
The up-to-date answer (as of PHP 5.4 or newer) for generating 404 pages is to use http_response_code:
<?php
http_response_code(404);
include('my_404.php'); // provide your own HTML for the error page
die();
die() is not strictly necessary, but it makes sure that you don’t continue the normal execution.
answered Jan 11, 2017 at 14:28
bladeblade
11.8k7 gold badges36 silver badges38 bronze badges
2
What you’re doing will work, and the browser will receive a 404 code. What it won’t do is display the «not found» page that you might be expecting, e.g.:
Not Found
The requested URL /test.php was not found on this server.
That’s because the web server doesn’t send that page when PHP returns a 404 code (at least Apache doesn’t). PHP is responsible for sending all its own output. So if you want a similar page, you’ll have to send the HTML yourself, e.g.:
<?php
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found", true, 404);
include("notFound.php");
?>
You could configure Apache to use the same page for its own 404 messages, by putting this in httpd.conf:
ErrorDocument 404 /notFound.php
Kzqai
22.5k25 gold badges105 silver badges135 bronze badges
answered Sep 4, 2009 at 19:50
JW.JW.
50.5k36 gold badges114 silver badges142 bronze badges
3
Try this:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
?>
answered Sep 4, 2009 at 19:36
Ates GoralAtes Goral
137k26 gold badges137 silver badges190 bronze badges
2
Create custom error pages through .htaccess file
1. 404 — page not found
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 404 /404.html
2. 500 — Internal Server Error
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 500 /500.html
3. 403 — Forbidden
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 403 /403.html
4. 400 — Bad request
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 400 /400.html
5. 401 — Authorization Required
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 401 /401.html
You can also redirect all error to single page. like
RewriteEngine On
ErrorDocument 404 /404.html
ErrorDocument 500 /404.html
ErrorDocument 403 /404.html
ErrorDocument 400 /404.html
ErrorDocument 401 /401.html
answered Mar 30, 2016 at 10:34
Irshad KhanIrshad Khan
5,6302 gold badges43 silver badges39 bronze badges
1
Did you remember to die() after sending the header? The 404 header doesn’t automatically stop processing, so it may appear not to have done anything if there is further processing happening.
It’s not good to REDIRECT to your 404 page, but you can INCLUDE the content from it with no problem. That way, you have a page that properly sends a 404 status from the correct URL, but it also has your «what are you looking for?» page for the human reader.
answered Sep 4, 2009 at 19:50
EliEli
97.1k20 gold badges76 silver badges81 bronze badges
Standard Apache 404 error looks like this:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>404 Not Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Not Found</h1>
<p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p>
</body></html> Thus, you can use the following PHP code to generate 404 page that looks exactly as standard apache 404 page:
function httpNotFound()
{
http_response_code(404);
header('Content-type: text/html');
// Generate standard apache 404 error page
echo <<<HTML
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>404 Not Found</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Not Found</h1>
<p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p>
</body></html>
HTML;
exit;
}
answered Mar 20 at 16:14
Dima L.Dima L.
3,39332 silver badges30 bronze badges
try putting
ErrorDocument 404 /(root directory)/(error file)
in .htaccess file.
Do this for any error but substitute 404 for your error.
StackedQ
3,9791 gold badge27 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered May 20, 2018 at 19:41
In the Drupal or WordPress CMS (and likely others), if you are trying to make some custom php code appear not to exist (unless some condition is met), the following works well by making the CMS’s 404 handler take over:
<?php
if(condition){
do stuff;
} else {
include('index.php');
}
?>
answered Jan 28, 2019 at 19:38
Mike GodinMike Godin
3,6563 gold badges27 silver badges29 bronze badges
Immediately after that line try closing the response using exit or die()
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found");
exit;
or
header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found");
die();
answered May 25, 2018 at 4:22
4
try this once.
$wp_query->set_404();
status_header(404);
get_template_part('404');
answered Mar 31, 2020 at 4:24
1
(PHP 5 >= 5.4.0, PHP 7, PHP
http_response_code — Получает или устанавливает код ответа HTTP
Описание
http_response_code(int $response_code = 0): int|bool
Список параметров
-
response_code -
Код ответа устанавливается с помощью опционального параметра
response_code.
Возвращаемые значения
Если response_code задан, то будет возвращён предыдущий код
статуса. Если response_code не задан, то будет возвращён
текущий код статуса. Оба этих значения будут по умолчанию иметь код состояния 200,
если они используются в окружении веб-сервера.
Если response_code не задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера (например, в CLI), то будет возвращено false. Если
response_code задан и используется не в окружении
веб-сервера, то будет возвращено true (но только если не был установлен предыдущий
код статуса).
Примеры
Пример #1 Использование http_response_code() в окружении веб-сервера
<?php// Берём текущий код и устанавливаем новый
var_dump(http_response_code(404));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
Пример #2 Использование http_response_code() в CLI
<?php// Берём текущий код по умолчанию
var_dump(http_response_code());// Устанавливаем код
var_dump(http_response_code(201));// Берём новый код
var_dump(http_response_code());
?>
Результат выполнения данного примера:
bool(false) bool(true) int(201)
Смотрите также
- header() — Отправка HTTP-заголовка
- headers_list() — Возвращает список переданных заголовков (или готовых к отправке)
craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk ¶
11 years ago
If your version of PHP does not include this function:
<?phpif (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
if (
$code !== NULL) {
switch (
$code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
break;
}$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
} else {
$code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
}
return
$code;
}
}
?>
In this example I am using $GLOBALS, but you can use whatever storage mechanism you like... I don't think there is a way to return the current status code:
https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=52555
For reference the error codes I got from PHP's source code:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/sapi/cgi/cgi_main.c#354
And how the current http header is sent, with the variables it uses:
http://lxr.php.net/opengrok/xref/PHP_5_4/main/SAPI.c#856
Stefan W ¶
8 years ago
Note that you can NOT set arbitrary response codes with this function, only those that are known to PHP (or the SAPI PHP is running on).
The following codes currently work as expected (with PHP running as Apache module):
200 – 208, 226
300 – 305, 307, 308
400 – 417, 422 – 424, 426, 428 – 429, 431
500 – 508, 510 – 511
Codes 0, 100, 101, and 102 will be sent as "200 OK".
Everything else will result in "500 Internal Server Error".
If you want to send responses with a freestyle status line, you need to use the `header()` function:
<?php header("HTTP/1.0 418 I'm A Teapot"); ?>
Thomas A. P. ¶
7 years ago
When setting the response code to non-standard ones like 420, Apache outputs 500 Internal Server Error.
This happens when using header(0,0,420) and http_response_code(420).
Use header('HTTP/1.1 420 Enhance Your Calm') instead.
Note that the response code in the string IS interpreted and used in the access log and output via http_response_code().
Anonymous ¶
9 years ago
Status codes as an array:
<?php
$http_status_codes = array(100 => "Continue", 101 => "Switching Protocols", 102 => "Processing", 200 => "OK", 201 => "Created", 202 => "Accepted", 203 => "Non-Authoritative Information", 204 => "No Content", 205 => "Reset Content", 206 => "Partial Content", 207 => "Multi-Status", 300 => "Multiple Choices", 301 => "Moved Permanently", 302 => "Found", 303 => "See Other", 304 => "Not Modified", 305 => "Use Proxy", 306 => "(Unused)", 307 => "Temporary Redirect", 308 => "Permanent Redirect", 400 => "Bad Request", 401 => "Unauthorized", 402 => "Payment Required", 403 => "Forbidden", 404 => "Not Found", 405 => "Method Not Allowed", 406 => "Not Acceptable", 407 => "Proxy Authentication Required", 408 => "Request Timeout", 409 => "Conflict", 410 => "Gone", 411 => "Length Required", 412 => "Precondition Failed", 413 => "Request Entity Too Large", 414 => "Request-URI Too Long", 415 => "Unsupported Media Type", 416 => "Requested Range Not Satisfiable", 417 => "Expectation Failed", 418 => "I'm a teapot", 419 => "Authentication Timeout", 420 => "Enhance Your Calm", 422 => "Unprocessable Entity", 423 => "Locked", 424 => "Failed Dependency", 424 => "Method Failure", 425 => "Unordered Collection", 426 => "Upgrade Required", 428 => "Precondition Required", 429 => "Too Many Requests", 431 => "Request Header Fields Too Large", 444 => "No Response", 449 => "Retry With", 450 => "Blocked by Windows Parental Controls", 451 => "Unavailable For Legal Reasons", 494 => "Request Header Too Large", 495 => "Cert Error", 496 => "No Cert", 497 => "HTTP to HTTPS", 499 => "Client Closed Request", 500 => "Internal Server Error", 501 => "Not Implemented", 502 => "Bad Gateway", 503 => "Service Unavailable", 504 => "Gateway Timeout", 505 => "HTTP Version Not Supported", 506 => "Variant Also Negotiates", 507 => "Insufficient Storage", 508 => "Loop Detected", 509 => "Bandwidth Limit Exceeded", 510 => "Not Extended", 511 => "Network Authentication Required", 598 => "Network read timeout error", 599 => "Network connect timeout error");
?>
Source: Wikipedia "List_of_HTTP_status_codes"
viaujoc at videotron dot ca ¶
2 years ago
Do not mix the use of http_response_code() and manually setting the response code header because the actual HTTP status code being returned by the web server may not end up as expected. http_response_code() does not work if the response code has previously been set using the header() function. Example:
<?php
header('HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized');
http_response_code(403);
print(http_response_code());
?>
The raw HTTP response will be (notice the actual status code on the first line does not match the printed http_response_code in the body):
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Date: Tue, 24 Nov 2020 13:49:08 GMT
Server: Apache
Connection: Upgrade, Keep-Alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
403
I only tested it on Apache. I am not sure if this behavior is specific to Apache or common to all PHP distributions.
Anonymous ¶
8 years ago
You can also create a enum by extending the SplEnum class.
<?php/** HTTP status codes */
class HttpStatusCode extends SplEnum {
const __default = self::OK;
const
SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS = 101;
const OK = 200;
const CREATED = 201;
const ACCEPTED = 202;
const NONAUTHORITATIVE_INFORMATION = 203;
const NO_CONTENT = 204;
const RESET_CONTENT = 205;
const PARTIAL_CONTENT = 206;
const MULTIPLE_CHOICES = 300;
const MOVED_PERMANENTLY = 301;
const MOVED_TEMPORARILY = 302;
const SEE_OTHER = 303;
const NOT_MODIFIED = 304;
const USE_PROXY = 305;
const BAD_REQUEST = 400;
const UNAUTHORIZED = 401;
const PAYMENT_REQUIRED = 402;
const FORBIDDEN = 403;
const NOT_FOUND = 404;
const METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED = 405;
const NOT_ACCEPTABLE = 406;
const PROXY_AUTHENTICATION_REQUIRED = 407;
const REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 408;
const CONFLICT = 408;
const GONE = 410;
const LENGTH_REQUIRED = 411;
const PRECONDITION_FAILED = 412;
const REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE = 413;
const REQUESTURI_TOO_LARGE = 414;
const UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE = 415;
const REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE = 416;
const EXPECTATION_FAILED = 417;
const IM_A_TEAPOT = 418;
const INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR = 500;
const NOT_IMPLEMENTED = 501;
const BAD_GATEWAY = 502;
const SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE = 503;
const GATEWAY_TIMEOUT = 504;
const HTTP_VERSION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 505;
}
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
2 years ago
if you need a response code not supported by http_response_code(), such as WebDAV / RFC4918's "HTTP 507 Insufficient Storage", try:
<?php
header($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] . ' 507 Insufficient Storage');
?>
result: something like
HTTP/1.1 507 Insufficient Storage
Rob Zazueta ¶
9 years ago
The note above from "Anonymous" is wrong. I'm running this behind the AWS Elastic Loadbalancer and trying the header(':'.$error_code...) method mentioned above is treated as invalid HTTP.
The documentation for the header() function has the right way to implement this if you're still on < php 5.4:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.0 404 Not Found");
?>
Anonymous ¶
10 years ago
If you don't have PHP 5.4 and want to change the returned status code, you can simply write:
<?php
header(':', true, $statusCode);
?>
The ':' are mandatory, or it won't work
Steven ¶
7 years ago
http_response_code is basically a shorthand way of writing a http status header, with the added bonus that PHP will work out a suitable Reason Phrase to provide by matching your response code to one of the values in an enumeration it maintains within php-src/main/http_status_codes.h. Note that this means your response code must match a response code that PHP knows about. You can't create your own response codes using this method, however you can using the header method.
In summary - The differences between "http_response_code" and "header" for setting response codes:
1. Using http_response_code will cause PHP to match and apply a Reason Phrase from a list of Reason Phrases that are hard-coded into the PHP source code.
2. Because of point 1 above, if you use http_response_code you must set a code that PHP knows about. You can't set your own custom code, however you can set a custom code (and Reason Phrase) if you use the header method.
Richard F. ¶
9 years ago
At least on my side with php-fpm and nginx this method does not change the text in the response, only the code.
<?php// HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
http_response_code(404);?>
The resulting response is HTTP/1.1 404 OK
stephen at bobs-bits dot com ¶
8 years ago
It's not mentioned explicitly, but the return value when SETTING, is the OLD status code.
e.g.
<?php
$a
= http_response_code();
$b = http_response_code(202);
$c = http_response_code();var_dump($a, $b, $c);// Result:
// int(200)
// int(200)
// int(202)
?>
Chandra Nakka ¶
5 years ago
On PHP 5.3 version, If you want to set HTTP response code. You can try this type of below trick :)
<?php
header
('Temporary-Header: True', true, 404);
header_remove('Temporary-Header');?>
yefremov {dot} sasha () gmail {dot} com ¶
8 years ago
@craig at craigfrancis dot co dot uk@ wrote the function that replaces the original. It is very usefull, but has a bug. The original http_response_code always returns the previous or current code, not the code you are setting now. Here is my fixed version. I also use $GLOBALS to store the current code, but trigger_error() instead of exit. So now, how the function will behave in the case of error lies on the error handler. Or you can change it back to exit().
if (!function_exists('http_response_code')) {
function http_response_code($code = NULL) {
$prev_code = (isset($GLOBALS['http_response_code']) ? $GLOBALS['http_response_code'] : 200);
if ($code === NULL) {
return $prev_code;
}
switch ($code) {
case 100: $text = 'Continue'; break;
case 101: $text = 'Switching Protocols'; break;
case 200: $text = 'OK'; break;
case 201: $text = 'Created'; break;
case 202: $text = 'Accepted'; break;
case 203: $text = 'Non-Authoritative Information'; break;
case 204: $text = 'No Content'; break;
case 205: $text = 'Reset Content'; break;
case 206: $text = 'Partial Content'; break;
case 300: $text = 'Multiple Choices'; break;
case 301: $text = 'Moved Permanently'; break;
case 302: $text = 'Moved Temporarily'; break;
case 303: $text = 'See Other'; break;
case 304: $text = 'Not Modified'; break;
case 305: $text = 'Use Proxy'; break;
case 400: $text = 'Bad Request'; break;
case 401: $text = 'Unauthorized'; break;
case 402: $text = 'Payment Required'; break;
case 403: $text = 'Forbidden'; break;
case 404: $text = 'Not Found'; break;
case 405: $text = 'Method Not Allowed'; break;
case 406: $text = 'Not Acceptable'; break;
case 407: $text = 'Proxy Authentication Required'; break;
case 408: $text = 'Request Time-out'; break;
case 409: $text = 'Conflict'; break;
case 410: $text = 'Gone'; break;
case 411: $text = 'Length Required'; break;
case 412: $text = 'Precondition Failed'; break;
case 413: $text = 'Request Entity Too Large'; break;
case 414: $text = 'Request-URI Too Large'; break;
case 415: $text = 'Unsupported Media Type'; break;
case 500: $text = 'Internal Server Error'; break;
case 501: $text = 'Not Implemented'; break;
case 502: $text = 'Bad Gateway'; break;
case 503: $text = 'Service Unavailable'; break;
case 504: $text = 'Gateway Time-out'; break;
case 505: $text = 'HTTP Version not supported'; break;
default:
trigger_error('Unknown http status code ' . $code, E_USER_ERROR); // exit('Unknown http status code "' . htmlentities($code) . '"');
return $prev_code;
}
$protocol = (isset($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL']) ? $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] : 'HTTP/1.0');
header($protocol . ' ' . $code . ' ' . $text);
$GLOBALS['http_response_code'] = $code;
// original function always returns the previous or current code
return $prev_code;
}
}
Anonymous ¶
4 years ago
http_response_code() does not actually send HTTP headers, it only prepares the header list to be sent later on.
So you can call http_reponse_code() to set, get and reset the HTTP response code before it gets sent.
Test code:
<php
http_response_code(500); // set the code
var_dump(headers_sent()); // check if headers are sent
http_response_code(200); // avoid a default browser page
Kubo2 ¶
6 years ago
If you want to set a HTTP response code without the need of specifying a protocol version, you can actually do it without http_response_code():
<?php
header
('Status: 404', TRUE, 404);?>
zweibieren at yahoo dot com ¶
7 years ago
The limited list given by Stefan W is out of date. I have just tested 301 and 302 and both work.
divinity76 at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
warning, it does not check if headers are already sent (if it is, it won't *actually* change the code, but a subsequent call will imply that it did!!),
you might wanna do something like
function ehttp_response_code(int $response_code = NULL): int {
if ($response_code === NULL) {
return http_response_code();
}
if (headers_sent()) {
throw new Exception('tried to change http response code after sending headers!');
}
return http_response_code($response_code);
}
In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to send a “404 Not Found” header using PHP.
This can be especially useful in cases when you need to display a 404 message if a particular database record does not exist.
By sending a 404 HTTP status code to the client, we can tell search engines and other crawlers that the resource does not exist.
To send a 404 to the client, we can use PHP’s http_response_code function like so.
//Send 404 response to client. http_response_code(404) //Include custom 404.php message include 'error/404.php'; //Kill the script. exit;
Note that this function is only available in PHP version 5.4 and after.
If you are using a PHP version that is older than 5.4, then you will need to use the header function instead.
//Use header function to send a 404 header($_SERVER["SERVER_PROTOCOL"]." 404 Not Found", true, 404); //Include custom message. include 'errors/404.php'; //End the script exit;
In the code above, we.
- Send the response code to the client.
- We include a PHP file that contains our custom “404 Not Found” error. This file is not mandatory, so feel free to remove it if you want to.
- We then terminated the PHP script by calling the exit statement.
If you run one of the code samples above and check the response in your browser’s developer tools, then you will see something like this.
Request URL:http://localhost/test.php Request Method:GET Status Code:404 Not Found Remote Address:[::1]:80 Referrer Policy:no-referrer-when-downgrade
Note the Status Code segment of the server’s HTTP response. This is the 404 header.
When should I use this?
In most cases, your web server will automatically handle 404 errors if a resource does not exist.
However, what happens if your script is dynamic and it selects data from your database? What if you have a dynamic page such as users.php?id=234 and user 234 does not exist?
The file users.php will exist, so your web server will send back a status of “200 OK”, regardless of whether a user with the ID 234 exists or not.
In cases like this, we may need to manually send a 404 Not Found header.
Why isn’t PHP showing the same 404 message as my web server?
You might notice that your web server does not serve its default “404 Not Found” error message when you manually send the header with PHP.
The default message that Apache displays whenever a resource could not be found.
This is because, as far as the web server is concerned, the file does exist and it has already done its job.
One solution to this problem is to make sure that PHP and your web server display the exact same 404 message.
For example, with Apache, you can specify the path of a custom error message by using the ErrorDocument directive.
ErrorDocument 404 /errors/404.php
The Nginx web server also allows you to configure custom error messages.
20.01.2021
Марат
83
0
php | header | 404 |
header 404. Как отправить на сервер заголовок header 404.
Ошибка отправки заголовка header 404. Все темы с примерами!
Всё о header(«HTTP/1.0 404 «)
- Код php заголовка 404
- Ошибка отправки header 404
- Для чего отправлять header 404, видео
- Пример отправки header 404
- Проверить попал ли в header 404
- Скачать можно здесь
Код php заголовка 404
Для того, чтобы отправить заголовок на сервер header 404 надо написать вот такую строчку:
header(«HTTP/1.0 404 «);
Естественно, что отправка 404 на сервер с помощью header должна осуществляться в самом верху страницы.
ВНИМАНИЕ! ЭТО ВАЖНО!
В самом верху страницы — это значит, что никакого, символа, ни точки, ни пробела ни переноса — вообще ничего, если у вас есть впереди php код, то код должен быть таким:
<?
здесь может быть сколько угодно кода php //
НО! — никакого echo, print_r, var_dump и других выводящих функций!
header(«HTTP/1.0 404 «);
exit ;//
используется в том случае, если требуется остановить выполнение ниже идущего кода.
?>
Ошибка отправки header 404
Если вы отправите заголовок header 404, как показано ниже, то вы получите ошибку отправки header 404:
<?
здесь код
?>
<br> Привет мир
<?
header(«HTTP/1.0 404 «);
?>
Пример ошибки отправки header 404:
Если перед отправкой заголовка header 404 будет выводящий код, то получите ошибку.
Давайте сделаем ошибку отправки header 404 специально!!
Поместим какой-то текст произвольного содержания, перед отправкой header 404 :
echo ‘Здесь текст, который выводится ранее, чем header 404’;
header(«HTTP/1.0 404 «);
Посмотрим это на скрине:
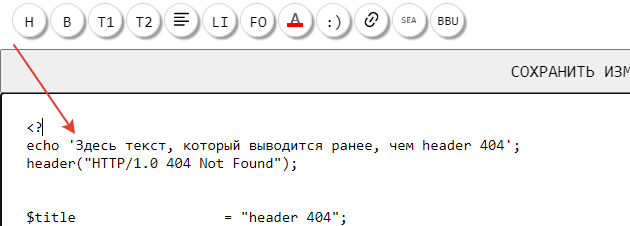
Вывод ошибки отправки header 404
Здесь текст, который выводится ранее, чем header 404
Warning: Cannot modify header information — headers already sent by (output started at
путь/page/php/header/001_header_404.html:3) in
путь/page/php/header/001_header_404.html on line 4
Вывод ошибки отправки header 404 на странице
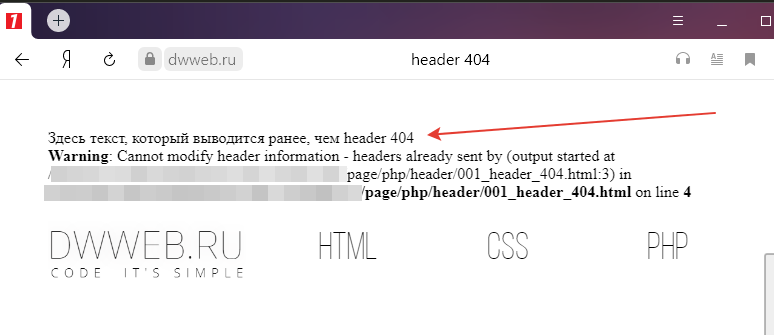
Для чего отправлять header 404
Чтобы не гадать — по какой из причин вам может понадобится использовать отправку заголовка header 404 -приведу собственную причину использования header 404.
На нашем сайте используется единая точка входа, — по всем запросам в адресной строке… будут перенаправляться на ту страницу, на которую настроена переадресация!
И даже те, страницы, которые не существуют… все равно будут перенаправляться… на главную.
Вот как раз для такого случая…
Естественно, что ничего не понятно!
Я делал специальное видео, где использовал приведенный код!
Видео — использование header 404
Друзья!
Мне очень нужны подписчики!
Пожалуйста подпишись на Дзене!
Заранее спасибо!
Пример отправки header 404
Для того, чтобы разобраться в том, как работает отправка заголовка header 404 нам потребуется какая-то страница, которая не существует!
Вообще любая!
Например такая :
У вас должна открыться такая страница 404 (несколько тем посвятили теме 404)
Но где здесь отправленный header 404 через php!? Этот скрин я вам привел специально — если вы захотите, то сделал отдельный архив -> сложил 404 через php + задний фон второй вариант 404 через php
И теперь, чтобы увидеть, где заголовок надо -> нажимаем ctrl + U
Нажмите, чтобы открыть в новом окне.
Проверить попал ли в header 404
Как проверить правильно ли был отправлен заголовок с помощью header 404!?
Если у вас возникли проблемы с пониманием того, что происходит заголовками, то существует огромное количество сайтов, которые могут показать всё, что вы отправляете!
Выбрал первый попавший… https://bertal.ru/ — заходим на сайт в вставляем в адресную строку свой адрес страницы.
Нажмите, чтобы открыть в новом окне.
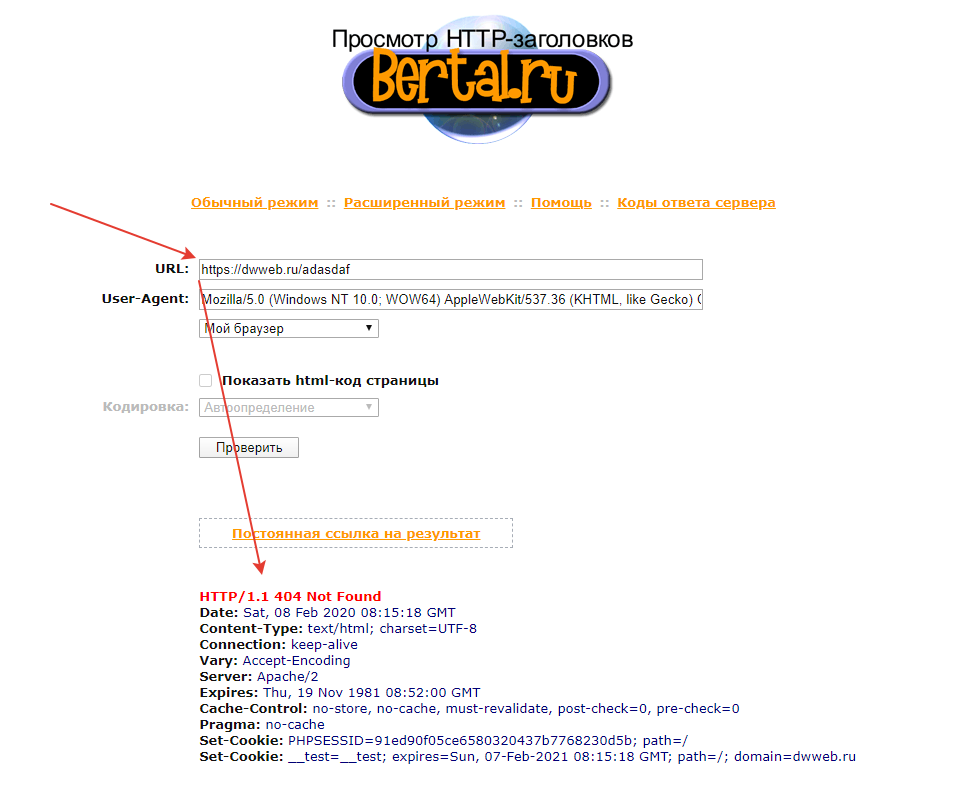
P.S.
Вообще… после случая с санкциями… пошел посмотреть, а что вообще творится со страницами на моем другом сайте и обнаружил, что робот проиндексировал папки(директории) – как отдельные страницы – и описанная тема… как раз востребована была там.
Не благодарите, но ссылкой можете поделиться!
Название скрипта :php header 404
COMMENTS+
BBcode
Добрый день всем, сегодня на очереди 404 страница. 404 страница – это страница, которая открывается тогда, когда пользователь переходит по не существующему адресу (URL). Я уверен, Вы ее часто встречали. Приведу Вам пример 404 страницы моего блога:
Если Вы “в живую” хотите увидеть как же выглядит эта “волшебная страница” на WPnew.ru, просто наберите в строке браузера несуществующий адрес в блоге. Например, я ввел случайный набор чисел и букв:
404 страница нужно обязательно! Она позволит удержать посетителя Вашего блога. Обычно те, кто видят стандартную 404 страницу ошибки, просто уходят с блога (а что еще делать, если перед их глазами какая-то непонятная надпись “Error 404. Page not found”).
Давайте приступим.
- В шаблоне демонстрируемого блога (напомню, он имеет адрес FanBar.ru) не оказалась той самой заветной страницы. Если у Вас также ее нет, просто создаем страницу под названием 404.php в теме блога, а у кого она есть, откройте данный файл:
- После открытия файла добавьте на первую строчку следующее (если у Вас эта строчка уже есть, то не нужно):
<!--?php get_header(); ?-->
А в конце (последняя строчка) добавьте следующий код:
<!--?php get_footer(); ?-->
- Откройте файл page.php и исходя из него поставьте примерно в то же место код:
<!--?php get_sidebar(); ?-->
Так как у каждого пользователя свой шаблон WordPress, я не могу рассказать Вам как точно сделать дизайн 404 страницы для Вашего блога. Ориентируйтесь на файл page.php, используйте FireBug, ознакомьтесь с языком CSS, экспериментируйте.
Готовая 404 страница.
Приведу пример 404.php блога FanBar.ru. Я в нее добавил все необходимые комментарии, чтобы объяснить Вам какой код что делает, чтобы облегчить Вам процесс создания 404 страницы ошибки. Эту страницу Вы можете скачать тут (просто разархивируйте архив), а кому лень скачивать, смотрите код ниже:
<!--Вывод шапки-->
<!--?php get_header(); ?-->
<!--Это вывод сайдбара, у Вас наверняка по-другому, и он стоит в конце, наверное,смотрите page.php.
Должно быть наподобие <?php get_sidebar(); ?>, поставьте ее туда же, где она стоит в page.php-->
<!--?php include_once("side1.php"); ?-->
<!--?php include_once("side2.php"); ?-->
<!--Конец вывода сайдбара-->
<!--Индивидуальный стиль шаблона, у Вас, наверняка что-то другое. Используйте FireBug, чтобы узнать название своего стиля-->
<div class="wrap">
<!--Конец стиля-->
<!--Название страницы-->
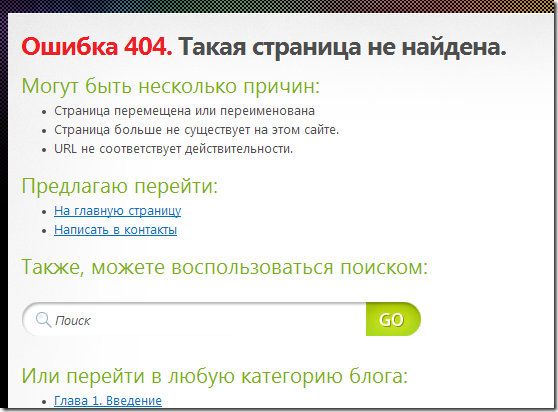
<h1 class="posttitle">Ошибка 404. Такая страница не найдена.</h1>
<!--Конец названия-->
<!--Начиная отсюда можно скопировать, просто заменив fanbar.ru на адрес своего блога и изменив страницу Контакты-->
<h3>Могут быть несколько причин:</h3>
<ul>
<li>Страница перемещена или переименована</li>
<li>Страница больше не существует на этом сайте.</li>
<li>URL не соответствует действительности.</li>
</ul>
<h3>Предлагаю перейти:</h3>
<ul>
<li><a href="https://fanbar.ru">На главную страницу</a></li>
<li><a href="https://fanbar.ru/kontakty">Написать в контакты</a></li>
</ul>
<!--Заканчивать процесс копирования тут-->
<h3>Также, можете воспользоваться поиском:</h3>
<!--Вывод поиска. Найдите на своем блоге поиск (обычно в sidebar.php и скопируйте оттуда. У меня он выглядит так-->
<form method="get" id="searchform" action="http://fanbar.ru/">
<div style="margin-left:70px;">
<input alt="search" type="text" value="<?php echo wp_specialchars($s, 1); ?>" name="s" id="s"></div>
</form><!--Конец вывода поиска-->
<!--Вывод категорий блога. Можете просто скопировать-->
<h3>Или перейти в любую категорию блога:</h3>
<ul>
<!--?php wp_list_cats('sort_column=name'); ?--></ul>
<!--Конец вывода категорий блога.-->
<!--Закрытие стиля wrap, который был в начале. Читайте урок про CSS, если не понятно. -->
</div>
<!--Вывод футера (подвала) темы-->
<!--?php get_footer(); ?-->
В принципе, все. Будут вопросы – пишите в комментариях. И не забывайте завтра — воскресенье, бесплатная видеоконференция со мной. Участвуйте все!
_____________________________
Следующий урок: Урок 56 Плагин Tweetmeme: выводим кнопку retweet на блоге.
<!—Вывод шапки—>
<?php get_header(); ?><!—Это вывод сайдбара, у Вас наверняка по-другому, и он стоит в конце, наверное,смотрите page.php.
Должно быть наподобие <?php get_sidebar(); ?>, поставьте ее туда же, где она стоит в page.php—>
<?php include_once(«side1.php»); ?>
<?php include_once(«side2.php»); ?>
<!—Конец вывода сайдбара—><!—Индивидуальный стиль шаблона, у Вас, наверняка что-то другое. Используйте FireBug, чтобы узнать название своего стиля—>
<div class=»wrap»>
<!—Конец стиля—><!—Название страницы—>
<h1 class=»posttitle»>Ошибка 404. Такая страница не найдена.</h1></br>
<!—Конец названия—>
<!—Начиная отсюда можно скопировать, просто заменив fanbar.ru на адрес своего блога и изменив страницу Контакты—>
<h3>Могут быть несколько причин:</h3>
<ul>
<li>Страница перемещена или переименована</li>
<li>Страница больше не существует на этом сайте.</li>
<li>URL не соответствует действительности.</li>
</ul>
<h3>Предлагаю перейти:</h3>
<ul>
<li><a href=»http://fanbar.ru»>На главную страницу</a></li>
<li><a href=»http://fanbar.ru/kontakty»>Написать в контакты</a></li>
</ul>
<!—Заканчивать процесс копирования тут—>
<h3>Также, можете воспользоваться поиском:</h3>
<!—Вывод поиска. Найдите на своем блоге поиск (обычно в sidebar.php и скопируйте оттуда. У меня он выглядит так—>
<form method=»get» id=»searchform» action=»http://fanbar.ru/»>
<div style=»margin-left:70px;»>
<input alt=»search» type=»text» value=»<?php echo wp_specialchars($s, 1); ?>» name=»s» id=»s» />
</div>
</form>
<!—Конец вывода поиска—>
<!—Вывод категорий блога. Можете просто скопировать—>
<h3>Или перейти в любую категорию блога:</h3>
<ul>
<?php wp_list_cats(‘sort_column=name’); ?>
</ul>
<!—Конец вывода категорий блога.—>
<!—Закрытие стиля wrap, который был в начале. Читайте урок про CSS, если не понятно. —>
</div>
<!—Вывод футера (подвала) темы—>
<?php get_footer(); ?>
Как вам урок?
Спасибо, очень приятно быть полезными!
Лучшая благодарность — это комментарий к уроку и «шеринг» в соц. сетях. Спасибо!
Помогите стать лучше, скажите что не так?
Непонятно
Урок устарел
Другое
Спасибо за помощь в развитии проекта!