While using any WMIC command, if you get Access is denied error on Windows 11/10, this guide will help you get rid of the problem. No matter which WMIC parameter you use, you might come across the Access is denied message at times. In such situations, these solutions will help you troubleshoot the issue.
Although WMIC or Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line is deprecated from Windows 10 and is no longer in active development for Windows 11, you can use it on your computer. In case you don’t know, you can do various things with the help of WMIC commands. For example, you can check the battery level, find the hard disk health status, etc.
Here’s what you should do if the WMIC command gives Access is denied error when trying to connect remotely to a Windows 11/10 computer:
- Add LOCAL SERVICE in Group policy
- Enable Local Activation for Everyone user group
- Verify WMI permission
Before getting started with these steps, you log into an administrator account. Otherwise, you can make the necessary changes as described below.
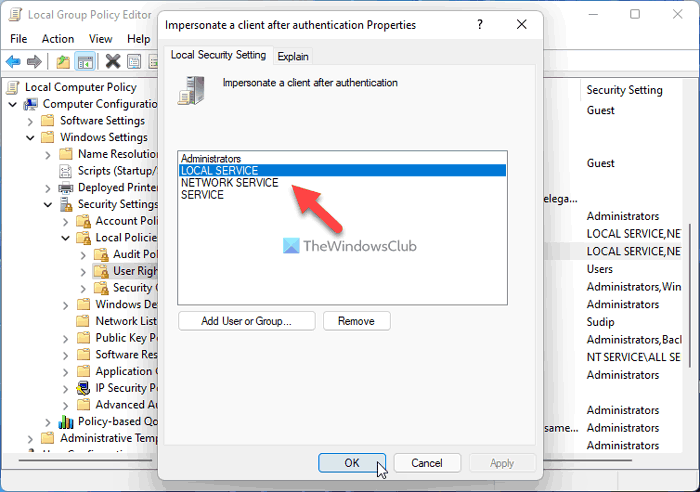
1] Add LOCAL SERVICE in Group policy
In simple words, you need to check or verify the WMI impersonation rights. For that, you can take the help of the Local Group Policy Editor. To do that, follow these steps:
- Press Win+R > type gpedit.msc > hit the Enter button.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment.
- Double-click on the Impersonate a client after authentication setting.
- Check if LOCAL SERVICE is included in the list.
However, if it is not included, you need to add it to the same group. For that, follow these steps:
- Click the Add User or Group button.
- Search for local service and click the Check Names button.
- Click the OK button.
Once done, you can close all the windows, restart your computer and check if you can run the WMIC commands or not.
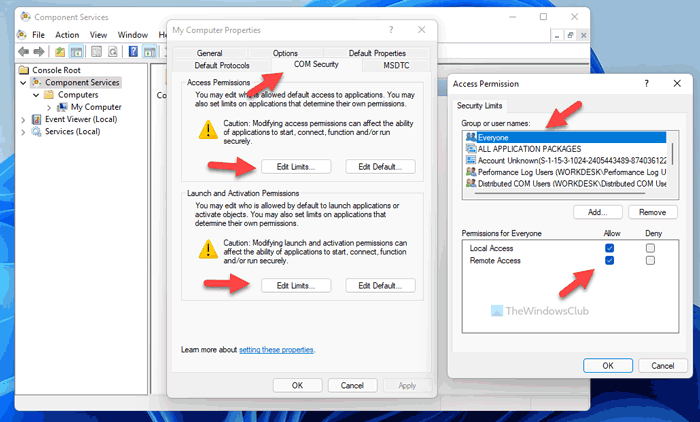
2] Enable Local Activation for Everyone user group
You need to set the correct DCOM permission on your computer. Otherwise, you will continue getting the Access is denied error while running a WMIC command. Follow the following steps to set the DCOM permission on Windows 11/10 PC:
- Press Win+R > type dcomcnfg > hit the Enter button.
- Navigate to Component Services > Computers > My Computer.
- Right-click on My Computer > Properties.
- Go to the COM Security tab.
- Click on the Edit Limits button.
- Select Everyone and tick both checkboxes under Allow.
- Click the OK button.
- Click on the other Edit Limits button.
- Select Everyone and tick the Local Launch and Local Activation checkboxes.
- Click the OK button.
However, if you cannot find the Everyone user group, you need to add it manually. For that, click the Add button, write everyone and click on the Check Names button. Then, click on the OK button.
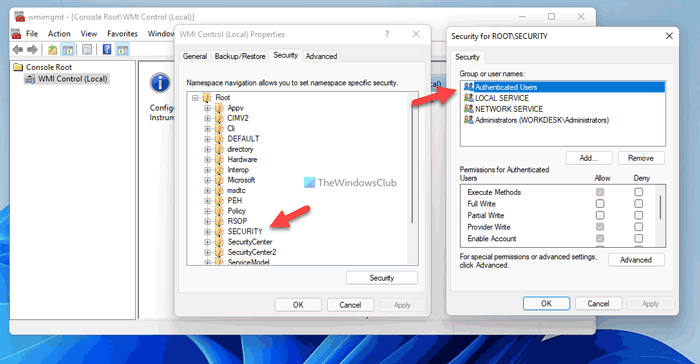
3] Verify WMI permission
It is yet another important step you need to follow if those two solutions don’t work for you. You need to make sure that a specific user has three permissions – Execute Methods, Provider Write, and Enable Account. If the Authenticated Users doesn’t have these three permissions, you may not be able to access WMIC on Windows 11 or Windows 10 computers.
Therefore, follow the following steps to verify the WMI permission:
- Press Win+R > type wmimgmt.msc > press the Enter button.
- Right-click on WMI Control and select Properties.
- Switch to the Security tab.
- Expand Root and go to SECURITY.
- Click on the Security button.
- Select Authenticated Users.
- Tick Execute Methods, Provider Write, and Enable Account checkboxes.
- Click the OK button to save the change.
However, if you cannot find the Authenticated Users in the Group or user names list, you need to add it manually. To do that, click the Add button, write authenticated users in the empty box, and click the Check Named button.
Then, you can change the permission as mentioned above. Once done, it is recommended to restart your computer. Following that, you will be able to use WMIC commands without any error.
How do I fix WMI Access is denied?
To fix WMI Access is denied or WMIC Access is denied, you need to follow the same set of solutions as mentioned above. You need to check the permission in various locations, including the Local Group Policy Editor, Component Services, and WmiMgmt. All the steps are mentioned above, and you can follow them one after one.
Read: How to locate or find Model Name or Serial Number of Windows computer using WMIC
How do I use WMIC on a remote computer?
To use WMIC commands on a remote computer, you need to enter this command: /node:target-computer-name, where the target-computer-name is the original name of the remote computer. However, your computer must be connected to the same local network to which your host computer is connected. Otherwise, it won’t work.
How do I fix WMI Access is denied 0x80070005 error?
Error 0x80070005 means that the Domain Controller/local Windows system could not verify the credentials for the target computer. So apart from trying the suggestions in this post, ensure that you are using the correct credentials.
Table of Contents
- WMI Service: Access Denied
- Symptoms:
- Troubleshooting:
- Security Descriptors by Operating System Version
WMI Service: Access Denied
There are times when the WMI Service within Microsoft Windows becomes corrupt, or the permissions are incorrect. This leads to access
denied errors when performing updates or other maintenance. This guide will show you how to check and repair the WMI Permissions on directories, as well as the WMI Service to ensure that it is configurable and workable.
Symptoms:
1. When installing software such as Microsoft Exchange Service Pack Upgrades, you may be greeted with an Access Denied
message
2. When attempting to stop, start or restart the Winmgmt service, the options are greyed out (GUI)
or you receive Access Denied (Command line)
Troubleshooting:
You will be making changes to permissions and registry entries, as well as some system permissions. Please make sure you have a good backup of the server or computer before continuing. If you are not comfortable making the
changes, there is a good chance you can corrupt your Windows Installation.
1. Log into Windows as an Administrative User
2. Check permissions on C::
Administrators: Full Control System: Full Control Users: Read Authenticated Users: Read Everyone: Read
3. Check permissions on C:WindowsSystem32
Administrators: Full Control System: Full Control Users: Read Authenticated Users: Read Everyone: Read
4. Check permissions on C:WindowsRegistration
Administrators: Full Control System: Full Control Users: Read Authenticated Users: Read Everyone: Read
5. Check permissions on C:WindowsRegistration*.clb (any file with the file extension .clb)
Administrators: Full Control System: Full Control Users: Read Authenticated Users: Read Everyone: Read
6. Open the Registry Editor, regedit
7. Navigate to HKEY_Classes_RootCLSID
8. Check permissions on CLSID
Administrators: Full Control System: Full Control Users: Read Authenticated Users: Read Everyone: Read Computer: Read
9. Open an elevated command prompt
10. Check the security descriptors for WinMGMT by using the command sc
sdshow winmgmt
The security descriptors are different based on Operating System version and service pack. Below are some suggested descriptors. They should match what you see in the command above, if not the command to change them is below.
Security Descriptors by Operating System Version
Windows Server 2012: D:(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;SU)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;SO)S:(AU;FA;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;WD) Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1: D:(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;SU)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;SO)S:(AU;FA;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;WD) Windows Server 2008 SP2 x64: D:(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;SU) Windows 8.1 x64: D:(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;SU) Windows 7 SP1 x86: D:(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;SU) Windows 7 SP1 x64: D:(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;SU)S:(AU;FA;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;WD) Windows XP SP3 x86: D:(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;SY)(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;BA)(A;;CCLCSWLOCRRC;;;AU)(A;;CCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRRC;;;PU)
11. If the security descriptors are not correct for you operating system version, then run the command sc sdset winmgmt *DESCRIPTORS* where
*DESCRIPTORS* is the appropriate set for your Operating System Version. (See above)
12. Restart the Server/Computer and check the WMI Service to see if the issue is resolved.
Почему не пускает?
Добрый день.
В локальной сети есть 2 компа. Хочу вывести инфу о ОС, используя:
get-wmiobject win32_operatingsystem -computername «compname».
В ответ слышу:
get-wmiobject : Отказано в доступе. (Исключение из HRESULT: 0x80070005 (E_ACCESSDENIED))
Также юзал :
get-wmiobject win32_operatingsystem -computername «compname» -Credential «username»
Ответ:
get-wmiobject : Сервер RPC недоступен. (Исключение из HRESULT: 0x800706BA)
Есть ли какие идеи, гугл не помог.
-
Вопрос заданболее трёх лет назад
-
3586 просмотров
Пригласить эксперта
Первопричина на нормально работающем компе без уже внесенных кривыми руками настроек — файрвол, как уже подсказал azarij
Не помогло — идем дальше:
1. не разрешается имя компьютера — пробуем ввести в формате IP адреса или полного доменного имени типа computername.domain.name вместо computername
2. Не подходит имя пользователя — пробуем ввести в формате remotecomputernameusername
3. Отключены службы удаленного доступа к RPC — решаем эту проблему. (вот тут статейка, какие сервисы проверять https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/window…
отключите фаервол на обоих машинах.
Также отказ в доступе часто происходит из за удаленного UAC
Нужно создать параметр DWORD
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciessystemLocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy
1
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
13 июн. 2023, в 18:02
5000 руб./за проект
13 июн. 2023, в 17:53
3000 руб./за проект
13 июн. 2023, в 17:47
10000 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
Версия 1.66.3
На Windows 7 x32 установлен IT-invent. Последние цифры ip 123.233
Сканируемый ПК Windows 7 x64 без IT-Invent. Последние цифры IP 124.93
Зашел в Сеть — Сканирование сети. Выбрал одиночный IP в поле IP и нажал добавить. В блоке Авторизация снял галочку «Использовать текущего пользователя»
Нажал «плюс» чтобы добавить логин и пароль, внёс. В поле домен указан адрес домена. При попытке оставить поле пустым выдает ошибку «Не указано имя домена»
При сканировании при ping проходит успешно. Выдает ошибку на WMI статус (отказано в доступе) и SNMP статус (No results received). В чем может быть причина?
Проверял другие программы инвентаризации TNI и 10СИК. Данные сканируются без ошибок
Брандмауэр и антивирус отключены
i’m trying to find processes on 3 terminal servers which have certain words in its $_.commandline property. Under my domain admin account, it worked OK. But I want this script to be usable for domain users, and doamin users get an error when runing this script.
What should i do, so that domain users can run this script just like domain admins? Thanks in advance!
Error:
Get-WmiObject : Access is denied. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070005 (E_ACCESS DENIED))
At N:FindWhoIsUsingFindWhoIsUsing.ps1:7 char:18
get-wmiobject <<<< win32_process -computername $server -EnableAllPrivileges|
CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Get-WmiObject], UnauthorizedAccessException
FullyQualifiedErrorId : System.UnauthorizedAccessException,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.GetWmiObjectCommand
Powershell Code:
Write-host "Who is using this profile?"
$profile = Read-host "specify profile name"
$servers = @("server-01","server-02","server-03")
Foreach($server in $servers)
{
Write-host $server
get-wmiobject win32_process -computername $server -EnableAllPrivileges|
where{$_.name -like "*Processname*" -and
$_.CommandLine -like "*$profile*"}|
select @{n="Server";e={$server}},@{n="User";e={$_.getowner().user}},@{n="ProcessID";e= {$_.ProcessID}},{$_.CommandLine}|fl
}
Write-host "DONE Searching!"