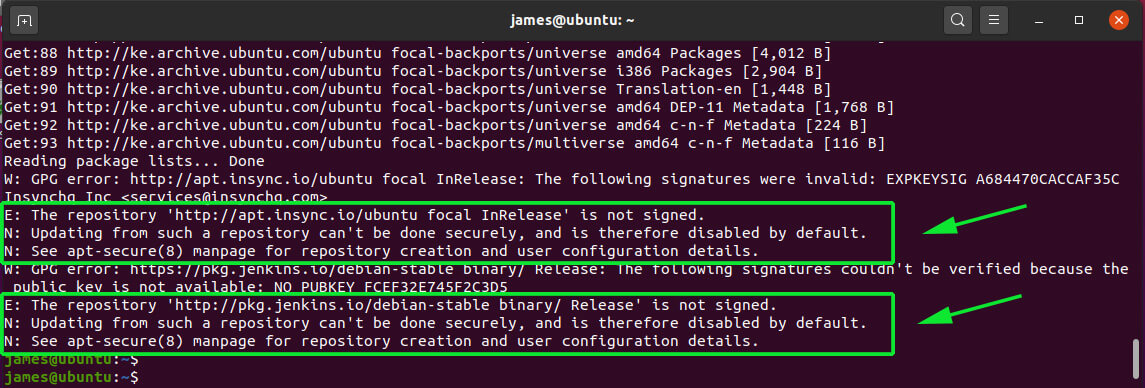
A few days back, I tried to update my Ubuntu 20.04 PC and I run into an error ‘the repository is not signed‘ and I could not go past that. Other times, you may happen upon the error ‘The repository does not have a release file‘ when trying to add a third-party repository. If you have encountered such errors before and got stuck, don’t lose your sleep. In this guide, we will focus on how to resolve such errors on Ubuntu 20.04. Without much further ado, let’s dive right in.
Before we delve into the root cause of this error. Let’s briefly mention about PPAs. What is it? PPA (Personal Package Archive) is a platform that allows developers to make available their own repositories and distribute their applications.
Why use PPAs instead of relying on Ubuntu’s main repositories?
This is a question that you might be asking given that each Ubuntu version comes with its own set of repositories which provide a wide selection of software packages. In fact, Ubuntu has over 47,000 software packages provided by the 4 main repositories. Each version of Ubuntu comes with 4 main repositories:
1) Main – Maintained by Canonical and provides free and opensource software.
2) Universe – Maintained by the Community and provides free and opensource software.
3) Restricted – Contains proprietary drivers for additional devices.
4) Multiverse – Contains copyright-restricted software.
Ubuntu’s APT package manager stores a list of repositories in the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
Essentially, Ubuntu has control over which software packages and versions that you will get on your system. The problem arises when a developer releases their own version of the software. Usually, Ubuntu will not make it available immediately in their repositories. They carry out multiple tests to check the compatibility and stability of the application. This may take several months for the application to be made available and certainly, not everyone is willing to wait that long to get the application.
Similarly, when a developer wishes their application to be included in Ubuntu’s official repositories, Ubuntu takes time before making the final decision on whether or not to include the application in its official repositories.
And this is where PPA comes in.
Installing software applications using PPAs.
Thankfully, Ubuntu provides Launchpad, which is a platform that allows developers to create their own repositories. As an end-user, you can add the PPA repo to your sources.list file and upon updating your Ubuntu system, your system will then know the availability of the software and allow you to install it using the APT package manager.
For example, to install FFmpeg4, you would add the ffmpeg4 launchpad PPA as follows:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jonathonf/ffmpeg-4
Thereafter, you will be prompted to hit the ‘ENTER’ button to continue with adding the PPA.
Press [ENTER] to continue or Ctrl-c to cancel adding it.Once the PPA is added, update your system and install the application as shown.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install ffmpeg4
The issue with third-party PPAs
Sometimes, some third-party PPAs can wreak havoc in your system and you may get warnings on the terminal such as the ones indicated below while updating Ubuntu.
Other times, you may encounter the ‘The repository does not have a release file‘ error such as the one shown below.
E: The repository 'http://ppa.launchpad.net/niko2040/e19/ubuntu focal Release' does not have a Release file. N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default. N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.
Resolving the ‘repository is not signed’ issue
To resolve this error, you need to delete the troublesome PPA from your the repository on your system. To achieve this, launch the ‘Software and Updates’ tool as shown.
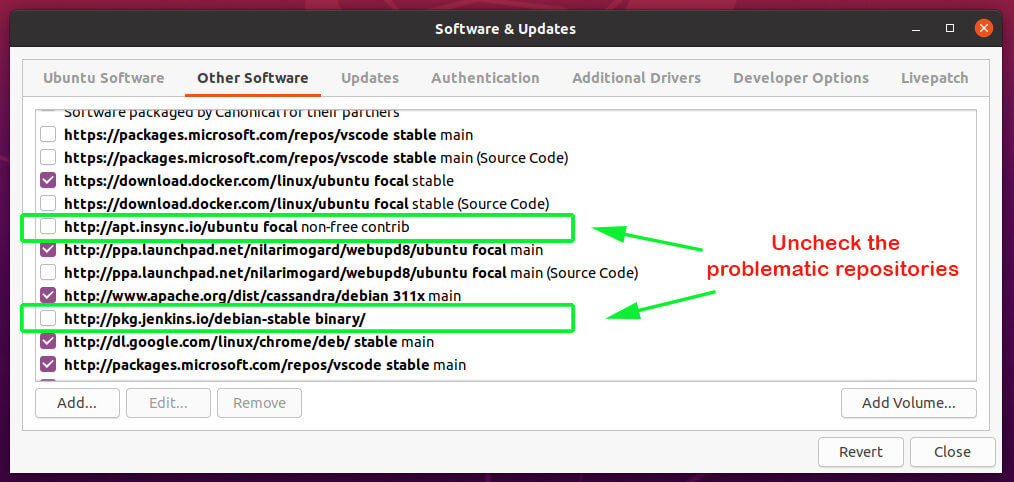
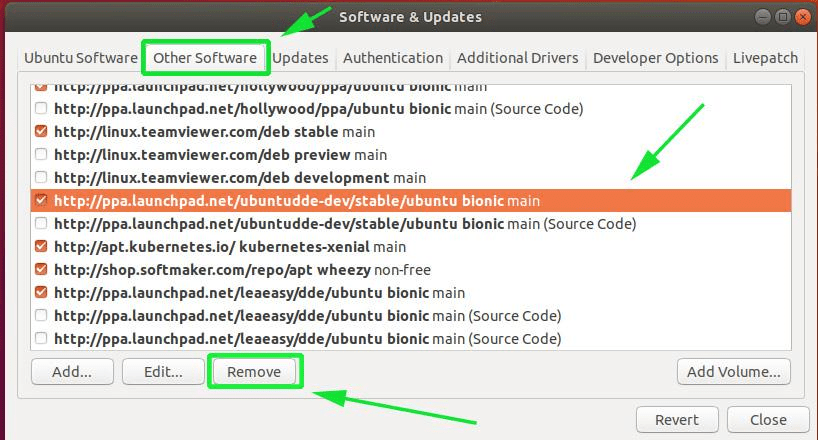
On the ‘Software & Updates‘ window, click on the ‘Other Software‘ tab. Next, click to uncheck and purge the problematic PPAs.
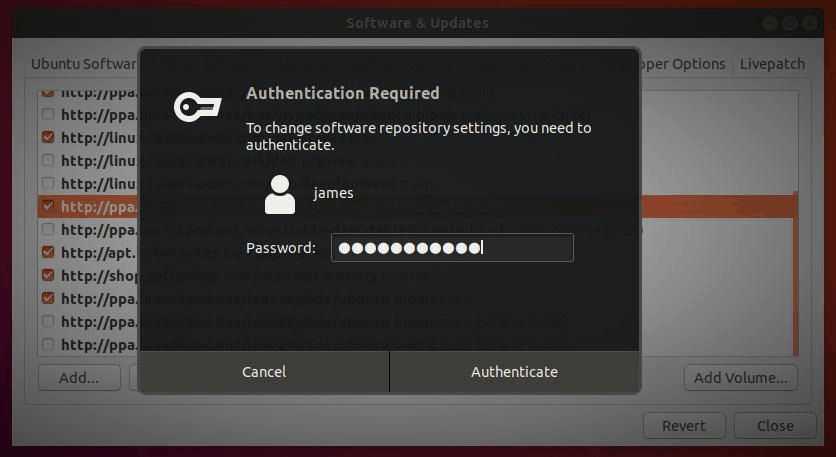
Provide your password to authenticate the removal of the repositories in question.
If you are using the terminal, you can , use the syntax:
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:name/here
For example
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:niko2040/el19
After removing the troublesome PPAs, you should now be able to update/upgrade your system and manage your packages with ease. That’s it, guys. In this guide, we have shown you how to resolve the ‘the repository is not signed’ error on Ubuntu. I do hope that this guide was beneficial.
Одним из нескольких способов установки программного обеспечения в Ubuntu является использование PPA или добавление сторонних репозиториев. Несколько волшебных строк, набранных в терминале, дают вам легкий доступ к программному обеспечению или его более новой версии, которая по умолчанию недоступна в Ubuntu.
Все выглядит здорово и даже великолепно, вы привыкли добавлять дополнительные сторонние репозитории и делаете это с закрытыми глазами, но однажды при обновлении Ubuntu сталкиваетесь с такой ошибкой:
E: The repository ‘http://ppa.launchpad.net/numix/ppa/ubuntu focal Release’ does not have a Release file.
N: Updating from such a repository can’t be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default.
N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.
E: Репозиторий ‘http://ppa.launchpad.net/numix/ppa/ubuntu focal Release’ не имеет файла релиза.
N: Обновление из такого репозитория не может быть сделано безопасно, и поэтому отключено по умолчанию.
N: Посетите страницу мануала apt-secure(8) для создания репозитория и деталей конфигурации пользователя.
В этом руководстве для начинающих пользователей Ubuntu я объясню, что означает эта ошибка, почему вы ее видите и что вам стоит предпринять, чтобы справиться с этой ошибкой?
Понимание сути ошибки «Репозиторий не имеет файла релиза»
Давайте разбираться по порядку. Сообщение об ошибке:
E: Репозиторий ‘http://ppa.launchpad.net/numix/ppa/ubuntu focal release’ не имеет файла релиза.
Важной частью этого сообщения об ошибке является словосочетание «focal release».
Вы, наверное, уже знаете, что у каждого выпуска Ubuntu есть кодовое имя. Для Ubuntu 20.04 кодовое имя — Focal Fossa. «Focal» в сообщении об ошибке указывает на Focal Fossa, которым является Ubuntu 20.04.
Эта ошибка в основном говорит вам, что, хотя вы добавили сторонний репозиторий в список источников вашей системы, этот новый репозиторий недоступен для вашей текущей версии Ubuntu.
Почему так? Потому что, вероятно, вы используете новую версию Ubuntu, а разработчики еще не сделали программное обеспечение доступным для этой новой версии.
На этом этапе я настоятельно рекомендую прочитать мои подробные руководства по репозиториям PPA и Ubuntu. Эти две статьи дадут вам лучшее, более глубокое и детальное понимание темы. Поверь мне, дорогой читатель, ты не будешь разочарован.
Как узнать, доступен ли PPA или сторонний репозиторий для вашей версии Ubuntu [Опционально]
Сначала вы должны проверить версию Ubuntu и его кодовое имя с помощью команды «lsb_release -a»:
abhishek@itsfoss:~$ lsb_release -a No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Release: 20.04 Codename: focal
Следующий шаг, который нам стоит сделать – это посетить сайт соответствующего программного обеспечения.
Следующая часть объяснения возможно не самая доступная для понимания, но все получится стоит приложить чуть-чуть терпения и усилий.
В приведенном здесь примере ошибка жалуется на http://ppa.launchpad.net/numix/ppa/ubuntu. Это репозиторий PPA, и вы можете легко найти его веб-страницу. Как, спросите вы. Вообще изи.
Используйте Google или альтернативную гуглу поисковую систему, например Duck Duck Go, и выполните поиск, по ключевым словам, «ppa numix». Этот запрос первым же результатом выдаст вам ссылку на launchpad.net, который является веб-сайтом, используемым для размещения кода, связанного с PPA.
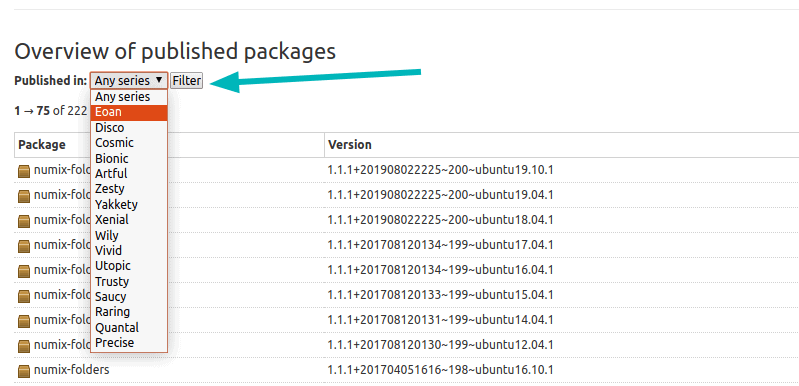
На веб-странице PPA вы можете перейти к разделу «Обзор опубликованных пакетов» и отфильтровать его по кодовому имени вашей версии Ubuntu:
Для сторонних репозиториев, не относящихся к PPA, вам необходимо проверить официальный веб-сайт программного обеспечения и посмотреть, доступен ли репозиторий для вашей версии Ubuntu или нет.
Что делать, если репозиторий недоступен для вашей версии Ubuntu
Если указанный репозиторий недоступен для вашей версии Ubuntu, вот что вы можете сделать:
· Удалите проблемный репозиторий из списка репозиториев, чтобы вы не видели ошибку при каждом запуске обновления.
· Получить программное обеспечение из другого источника (если это возможно).
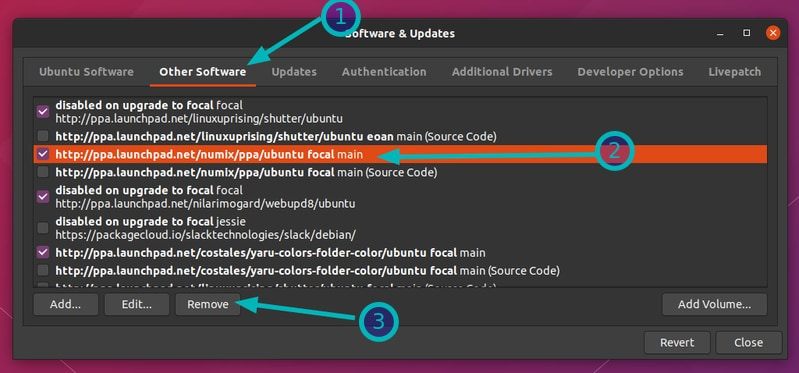
Чтобы удалить проблемный репозиторий, запустите инструмент Software & Updates:
Перейдите на вкладку «Другое программное обеспечение» и найдите нужный репозиторий. Выделите его и нажмите кнопку «Удалить», чтобы удалить его из вашей системы.
Это удалит PPA или репозиторий, о котором идет речь.
Следующим шагом является получение программного обеспечения из какого-то другого источника, и тут все абсолютно субъективно и вариативно. В некоторых случаях вы все равно можете загрузить файл DEB с веб-сайта PPA и использовать программное обеспечение (пошаговую инструкцию я даю в руководстве по PPA). Кроме того, вы можете проверить веб-сайт проекта, на предмет существования Snap / Flatpak или Python версий искомого программного обеспечения.
When installing software on Ubuntu, sometimes you may be required to add third-party PPAs. Adding PPAs enables you to access software packages that have not been included in official Ubuntu repositories. Sometimes, when updating your system or installing software packages, you may run into an error indicating that the added PPA does not have a release file.
This error is quite frustrating as it limits your ability to manage software packages in an efficient manner. In this guide, we will guide you on how you can resolve this issue and go back to using your system without an issue.
So, let’s first understand, what is the meaning of error ‘Repository does not have a release file’ ?
Before we address this issue, it’s prudent that we first understand what this error means. The ‘Repository does not have a release file’ error essentially tells you that the repository that you have just added is not available for your Ubuntu version.
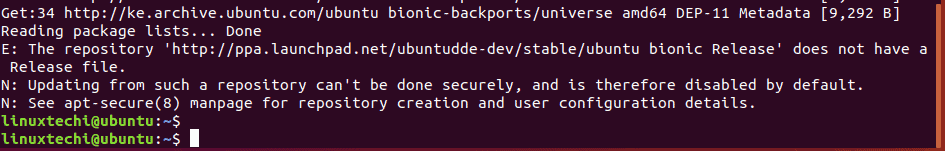
For example, I tried to install Deepin desktop environment on Ubuntu 18.04 using the PPA below which should be used on Ubuntu 20.04 also known as Focal Fossa.
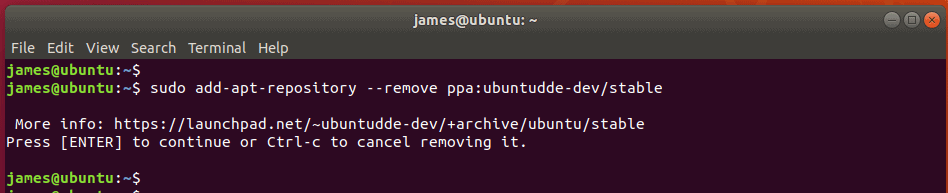
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntudde-dev/stable
This yielded the error shown in the snippet below.
This error prevents you from updating, upgrading and even installing software packages.
How to Fix ‘Repository does not have a release file’ error
Having known what causes the error, let’s now see how you can fix your system. To clear the error, you need to remove the troublesome repository. You can achieve this graphically the ‘Software & Updates’ tool or running commands on the terminal.
To remove the repository graphically, launch the ‘Software & Updates‘ tool as shown.
Click on the ‘Other Software’ tab and then select the PPA to be removed. Finally, click on the ‘Remove’ button at the bottom of the window.
An authentication window will pop up prompting you for your password. Type in your user’s password and press ENTER.
On the command line, you can remove the repository using the syntax shown:
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:name/here
In our case, our command will be:
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:ubuntudde-dev/stable
Then hit ENTER to remove the repository.
And that’s how you resolve the “Repository does not have a release file” error on Ubuntu.
If you use the desktop edition of Ubuntu, you may ultimately run into the issue where apt-get update frequently returns “Failed to obtain 404 Not Found” warnings. The identical issue could also arise when using apt-get install. Not to worry; it will be resolved shortly. In this guide we went through all the commonly known troubleshooting steps that can fix the problem. Other guides are here: Change User Account Type in Windows 10 and How to modify Windows 11 Taskbar via Intune and GPO also How to Change User Account Type in Windows 10 again upgrade from Ubuntu 20.04 LTS to 22.04 LTS and install Rust in a Linux System and Change User Account Type in Windows 10. In this article, you will learn how to Fix 404 Not Found Repository Errors in Ubuntu/Debian distribution.
The Issue “404 Not Found Repository Errors”
When using the apt-get update or apt-get install command, you can encounter messages similar to the ones below. This is due to the short 9-month support period for Ubuntu versions. Releases with LTS (Long Term Support) have support for 5 years. You’ll start receiving those error messages as soon as the version you’re using loses support. Please refer to these exciting guides: VMSA-2022-0026: An arbitrary file read vulnerability in VMware Aria Operations, how to Search Group Policy for a Specific Setting in Windows 10 and Windows 11, and how to Deploy Code from GitHub to Azure App Service from the Command-line.
The default location below is no longer available due to Ubuntu moving the repositories to a different server.
http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dist/rdgmh@raphael:~$ sudo su
[sudo] password for rdgmh:
root@raphael:/home/rdgmh# apt update
Get:1 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease [110 kB]
Ign:2 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease
Ign:3 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease
Ign:4 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease
Hit:5 https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/azure-cli jammy InRelease
Err:6 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy Release
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.124 80]
Ign:7 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu impish-security InRelease
Err:8 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates Release
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.124 80]
Err:9 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu impish-security Release
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.38 80]
Err:10 http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports Release
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.124 80]
Hit:11 http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt jammy-pgdg InRelease
Reading package lists... Done
E: The repository 'http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy Release' does not have a Release file.
N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default.
N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.
E: The repository 'http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates Release' does not have a Release file.
N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default.
N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.
E: The repository 'http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu impish-security Release' does not have a Release file.
N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default.
N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.
E: The repository 'http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports Release' does not have a Release file.
N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default.
N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details.
N: Skipping acquire of configured file 'main/binary-i386/Packages' as repository 'http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt jammy-pgdg InRelease' doesn't support architecture 'i386'
root@raphael:/home/rdgmh#
There are three ways to make your apt commands function properly once more. Upgrade the Ubuntu release first. Second, change the old package repositories’ sources urls. and finally restore the PPA and default repository. The details of the three options are provided below.
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade 
As you can see, this didn’t solve the problem so we will go with option 2. You can alter the sources url for the Ubuntu repository to find the older packages if an immediate distribution upgrade is not an option.
Update Packages Url
To update the sources in /etc/apt/sources, use the sed tool. list file to the new repository location for outdated packages
sudo sed -i -e 's/archive.ubuntu.com|security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list
Use the grep command below to see if there are any other files in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ that require updating.
grep -E 'archive.ubuntu.com|security.ubuntu.com' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/* 
There are a series of steps we need to take further
- open /etc/apt/sources.list with a text editor, in this case, i have chosen to use vim so the command will be as shown below:
vim /etc/apt/sources.list2. We need to comment out extras.ubuntu.com like this below
#extras.ubuntu.com The reason we are commenting it out is because the repo is no longer supported
3. replace main/security repositories with old-releases versions as follows.


this solution too did not work. Even replaced main/security with the archive as shown below

Replace default repository: The only solution that worked!
The majority of the PPAs and repositories in your sources.list are broken and no longer functional. The default repositories should be restored, in my opinion.
So let’s make a directory change into it and write the following code
mkdir ~/solution
cd ~/solution/
cat << EOF > ~/solution/sources.list
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu focal partner
deb-src http://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu focal partner
EOF
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list
sudo cp ~/solution/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list
Remove all the PPAs in your system:
sudo mv /etc/apt/sources.list.d/* ~/solutionrun the command to update again and you will see that the problem has been solved
apt update
Summary
404 Not Found is a common problem in Ubuntu and the only effective way to solve this is to replace the default repository just as we saw in the final step above. I hope you found this blog post helpful on how to Fix 404 Not Found Repository Errors in Ubuntu/Debian distribution. If you have any questions, please let me know in the comment session.
When using the desktop version of Ubuntu you’ll eventually get or probably have the problem that apt-get update throws a lot «Failed to fetch 404 Not Found» errors. Additionally, you may have the same problem when running apt-get install. Don’t worry, it will be fixed in a minute.
The Problem
You may see messages like the ones below when executing apt-get update or apt-get install. That is because Ubuntu releases are only supported for 9 months. LTS (Long Term Support) releases have support for 5 years. Once support is cut for the version you’re using, you’ll see those error messages. Ubuntu moves the repositories to another server and the defined URL to reach the sources are no longer available on default location http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dist/.
$ sudo apt-get update
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring Release.gpg
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-updates Release.gpg
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports Release.gpg
Ign http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security Release.gpg
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring Release
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-updates Release
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports Release
…
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/restricted Sources
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/universe Sources
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/multiverse Sources
404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports/main Translation-en
Ign http://de.archive.ubuntu.com raring-backports/multiverse Translation-en
Err http://security.ubuntu.com raring-security/main amd64 Packages
…
W: Failed to fetch http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/restricted/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 141.30.13.30 80]
W: Failed to fetch http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/universe/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 141.30.13.30 80]
W: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring-security/main/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.92.201 80]
W: Failed to fetch http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/dists/raring/multiverse/source/Sources 404 Not Found [IP: 141.30.13.30 80]
…
E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.
How to Fix The Problem
There are two solutions to get your apt commands working again. First: upgrade the Ubuntu release. Second: update the sources url to the old package repositories. Both solutions are described below in more detail.
Distribution Upgrade
The most simple solution is to upgrade your Ubuntu instance to the newest release:
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
If the distribution upgrade is not an option right now, you can update the sources url for the Ubuntu repositories to find the old packages.
Update Packages Url
You can use the sed command to update the sources in /etc/apt/sources.list file to the new location for old package repositories2.
Run the following command to update archive.ubuntu.com and security.ubuntu.com package repository4 URLs with old-releases.ubuntu.com. Since the normal Ubuntu releases link to the archive.… and security.… URLs, the support will be removed after their live cycle of 9 months and respective repositories3 moved to old-releases.….
sudo sed -i -e 's/archive.ubuntu.com|security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list
**Linux Mint additionally requires the execution of this command:**
sudo sed -i -e 's/archive.ubuntu.com|security.ubuntu.com/old-releases.ubuntu.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/official-package-repositories.list
To check whether there are other files in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ which need to be updated, use the following grep command.
grep -E 'archive.ubuntu.com|security.ubuntu.com' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/*
That’s it. Now you can update your sources again.
sudo apt-get update
Bazinga!
- 1: Myles McNamara’s blog post saved me a lot of time to understand the problem and find a solution
- 2: Ask Ubuntu: Install Software From Old Repositories (sed command)
- 3: Ubuntu Old Releases
- 4: Ubuntu Current Releases