Python is installed in a local directory.
My directory tree looks like this:
(local directory)/site-packages/toolkit/interface.py
My code is in here:
(local directory)/site-packages/toolkit/examples/mountain.py
To run the example, I write python mountain.py, and in the code I have:
from toolkit.interface import interface
And I get the error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "mountain.py", line 28, in ?
from toolkit.interface import interface
ImportError: No module named toolkit.interface
I have already checked sys.path and there I have the directory /site-packages. Also, I have the file __init__.py.bin in the toolkit folder to indicate to Python that this is a package. I also have a __init__.py.bin in the examples directory.
I do not know why Python cannot find the file when it is in sys.path. Any ideas? Can it be a permissions problem? Do I need some execution permission?
alex
6,6449 gold badges52 silver badges103 bronze badges
asked Dec 3, 2008 at 21:26
7
Based on your comments to orip’s post, I guess this is what happened:
- You edited
__init__.pyon windows. - The windows editor added something non-printing, perhaps a carriage-return (end-of-line in Windows is CR/LF; in unix it is LF only), or perhaps a CTRL-Z (windows end-of-file).
- You used WinSCP to copy the file to your unix box.
- WinSCP thought: «This has something that’s not basic text; I’ll put a .bin extension to indicate binary data.»
- The missing
__init__.py(now called__init__.py.bin) means python doesn’t understand toolkit as a package. - You create
__init__.pyin the appropriate directory and everything works… ?
answered Dec 4, 2008 at 0:17
John FouhyJohn Fouhy
41k19 gold badges62 silver badges77 bronze badges
7
I ran into something very similar when I did this exercise in LPTHW; I could never get Python to recognise that I had files in the directory I was calling from. But I was able to get it to work in the end. What I did, and what I recommend, is to try this:
(NOTE: From your initial post, I am assuming you are using an *NIX-based machine and are running things from the command line, so this advice is tailored to that. Since I run Ubuntu, this is what I did)
-
Change directory (cd) to the directory above the directory where your files are. In this case, you’re trying to run the
mountain.pyfile, and trying to call thetoolkit.interface.pymodule, which are in separate directories. In this case, you would go to the directory that contains paths to both those files (or in other words, the closest directory that the paths of both those files share). Which in this case is thetoolkitdirectory. -
When you are in the
toolkitdirectory, enter this line of code on your command line:export PYTHONPATH=.This sets your PYTHONPATH to «.», which basically means that your PYTHONPATH will now look for any called files within the directory you are currently in, (and more to the point, in the sub-directory branches of the directory you are in. So it doesn’t just look in your current directory, but in all the directories that are in your current directory).
-
After you’ve set your PYTHONPATH in the step above, run your module from your current directory (the
toolkitdirectory). Python should now find and load the modules you specified.
starball
15.3k6 gold badges29 silver badges137 bronze badges
answered Apr 22, 2014 at 3:52
SpecteraceSpecterace
1,0357 silver badges7 bronze badges
4
Does
(local directory)/site-packages/toolkit
have a __init__.py?
To make import walk through your directories every directory must have a __init__.py file.
answered Dec 3, 2008 at 21:50
igorgueigorgue
17.8k13 gold badges37 silver badges54 bronze badges
3
On *nix, also make sure that PYTHONPATH is configured correctly, especially that it has this format:
.:/usr/local/lib/python
(Mind the .: at the beginning, so that it can search on the current directory, too.)
It may also be in other locations, depending on the version:
.:/usr/lib/python
.:/usr/lib/python2.6
.:/usr/lib/python2.7 and etc.
answered Mar 4, 2011 at 21:14
RenaudRenaud
16k6 gold badges79 silver badges78 bronze badges
6
You are reading this answer says that your __init__.py is in the right place, you have installed all the dependencies and you are still getting the ImportError.
I was facing a similar issue except that my program would run fine when ran using PyCharm but the above error when I would run it from the terminal. After digging further, I found out that PYTHONPATH didn’t have the entry for the project directory. So, I set PYTHONPATH per Import statement works on PyCharm but not from terminal:
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:`pwd` (OR your project root directory)
There’s another way to do this using sys.path as:
import sys
sys.path.insert(0,'<project directory>') OR
sys.path.append('<project directory>')
You can use insert/append based on the order in which you want your project to be searched.
jww
96.8k90 gold badges408 silver badges878 bronze badges
answered Feb 8, 2019 at 16:57
avpavp
2,86228 silver badges34 bronze badges
4
Using PyCharm (part of the JetBrains suite) you need to define your script directory as Source:
Right Click > Mark Directory as > Sources Root
Neuron
5,0525 gold badges38 silver badges58 bronze badges
answered Jan 4, 2017 at 17:53
MonoThreadedMonoThreaded
11.3k11 gold badges70 silver badges100 bronze badges
2
For me, it was something really stupid. I installed the library using pip3 install but was running my program as python program.py as opposed to python3 program.py.
answered Aug 22, 2019 at 16:02
kevkev
2,7115 gold badges22 silver badges45 bronze badges
1
I solved my own problem, and I will write a summary of the things that were wrong and the solution:
The file needs to be called exactly __init__.py. If the extension is different such as in my case .py.bin then Python cannot move through the directories and then it cannot find the modules. To edit the files you need to use a Linux editor, such as vi or nano. If you use a Windows editor this will write some hidden characters.
Another problem that was affecting it was that I had another Python version installed by the root, so if someone is working with a local installation of python, be sure that the Python installation that is running the programs is the local Python. To check this, just do which python, and see if the executable is the one that is in your local directory. If not, change the path, but be sure that the local Python directory is before than the other Python.
answered Dec 4, 2008 at 1:11
EduardoEduardo
19.8k23 gold badges64 silver badges73 bronze badges
3
To mark a directory as a package you need a file named __init__.py, does this help?
answered Dec 3, 2008 at 21:31
oriporip
72.9k21 gold badges116 silver badges148 bronze badges
8
an easy solution is to install the module using python -m pip install <library-name> instead of pip install <library-name>
you may use sudo in case of admin restrictions
answered Sep 18, 2017 at 15:30
Badr BellajBadr Bellaj
11.4k2 gold badges42 silver badges44 bronze badges
3
To all those who still have this issue. I believe Pycharm gets confused with imports. For me, when i write ‘from namespace import something’, the previous line gets underlined in red, signaling that there is an error, but works. However »from .namespace import something’ doesn’t get underlined, but also doesn’t work.
Try
try:
from namespace import something
except NameError:
from .namespace import something
answered May 11, 2019 at 19:34
AKJAKJ
9402 gold badges13 silver badges18 bronze badges
1
Yup. You need the directory to contain the __init__.py file, which is the file that initializes the package. Here, have a look at this.
The __init__.py files are required to make Python treat the directories as containing packages; this is done to prevent directories with a common name, such as string, from unintentionally hiding valid modules that occur later on the module search path. In the simplest case, __init__.py can just be an empty file, but it can also execute initialization code for the package or set the __all__ variable, described later.
answered Jan 7, 2009 at 14:22
miyamiya
1,0591 gold badge11 silver badges20 bronze badges
If you have tried all methods provided above but failed, maybe your module has the same name as a built-in module. Or, a module with the same name existing in a folder that has a high priority in sys.path than your module’s.
To debug, say your from foo.bar import baz complaints ImportError: No module named bar. Changing to import foo; print foo, which will show the path of foo. Is it what you expect?
If not, Either rename foo or use absolute imports.
answered May 2, 2017 at 6:41
liushuaikobeliushuaikobe
2,1321 gold badge23 silver badges26 bronze badges
1
- You must have the file __ init__.py in the same directory where it’s the file that you are importing.
- You can not try to import a file that has the same name and be a file from 2 folders configured on the PYTHONPATH.
eg:
/etc/environment
PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:/opt/folder1:/opt/folder2
/opt/folder1/foo
/opt/folder2/foo
And, if you are trying to import foo file, python will not know which one you want.
from foo import … >>> importerror: no module named foo
answered Jan 9, 2014 at 19:45
Iasmini GomesIasmini Gomes
6971 gold badge9 silver badges14 bronze badges
0
My two cents:
Spit:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "bashbash.py", line 454, in main
import bosh
File "Wrye Bash Launcher.pyw", line 63, in load_module
mod = imp.load_source(fullname,filename+ext,fp)
File "bashbosh.py", line 69, in <module>
from game.oblivion.RecordGroups import MobWorlds, MobDials, MobICells,
ImportError: No module named RecordGroups
This confused the hell out of me — went through posts and posts suggesting ugly syspath hacks (as you see my __init__.py were all there). Well turns out that game/oblivion.py and game/oblivion was confusing python
which spit out the rather unhelpful «No module named RecordGroups». I’d be interested in a workaround and/or links documenting this (same name) behavior -> EDIT (2017.01.24) — have a look at What If I Have a Module and a Package With The Same Name? Interestingly normally packages take precedence but apparently our launcher violates this.
EDIT (2015.01.17): I did not mention we use a custom launcher dissected here.
answered Sep 6, 2014 at 11:17
Mr_and_Mrs_DMr_and_Mrs_D
31.9k38 gold badges178 silver badges358 bronze badges
2
Fixed my issue by writing print (sys.path) and found out that python was using out of date packages despite a clean install. Deleting these made python automatically use the correct packages.
answered Jul 21, 2016 at 18:51
dukevindukevin
22.3k36 gold badges81 silver badges110 bronze badges
In my case, because I’m using PyCharm and PyCharm create a ‘venv’ for every project in project folder, but it is only a mini env of python. Although you have installed the libraries you need in Python, but in your custom project ‘venv’, it is not available. This is the real reason of ‘ImportError: No module named xxxxxx’ occurred in PyCharm.
To resolve this issue, you must add libraries to your project custom env by these steps:
- In PyCharm, from menu ‘File’->Settings
- In Settings dialog, Project: XXXProject->Project Interpreter
- Click «Add» button, it will show you ‘Available Packages’ dialog
- Search your library, click ‘Install Package’
- Then, all you needed package will be installed in you project custom ‘venv’ folder.
Enjoy.
answered Feb 18, 2019 at 3:35
YuanhuiYuanhui
4595 silver badges15 bronze badges
For me, running the file as a module helped.
Instead of
python myapp/app.py
using
python -m myapp.app
It’s not exactly the same but it might be a better approach in some cases.
answered Apr 28, 2022 at 13:59
juanignaciosljuanignaciosl
3,4252 gold badges27 silver badges28 bronze badges
1
Linux: Imported modules are located in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages
If you’re using a module compiled in C, don’t forget to chmod the .so file after sudo setup.py install.
sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/*.so
answered May 30, 2014 at 22:50
KrisWebDevKrisWebDev
9,3124 gold badges39 silver badges59 bronze badges
0
In my case, the problem was I was linking to debug python & boost::Python, which requires that the extension be FooLib_d.pyd, not just FooLib.pyd; renaming the file or updating CMakeLists.txt properties fixed the error.
answered Sep 4, 2013 at 2:52
peter karasevpeter karasev
2,5581 gold badge28 silver badges38 bronze badges
My problem was that I added the directory with the __init__.py file to PYTHONPATH, when actually I needed to add its parent directory.
answered Mar 27, 2018 at 12:41
RichRich
6621 gold badge6 silver badges14 bronze badges
0
If you are using a setup script/utility (e.g. setuptools) to deploy your package, don’t forget to add the respective files/modules to the installer.
When supported, use find_packages() or similar to automatically add new packages to the setup script. This will absolutely save you from a headache, especially if you put your project aside for some time and then add something later on.
import setuptools
setuptools.setup(
name="example-pkg",
version="0.0.1",
author="Example Author",
author_email="author@example.com",
description="A small example package",
packages=setuptools.find_packages(),
classifiers=[
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
"Operating System :: OS Independent",
],
python_requires='>=3.6',
)
(Example taken from setuptools documentation)
answered Oct 17, 2020 at 11:36
michael-slxmichael-slx
6558 silver badges15 bronze badges
I had the same problem (Python 2.7 Linux), I have found the solution and i would like to share it. In my case i had the structure below:
Booklet
-> __init__.py
-> Booklet.py
-> Question.py
default
-> __init_.py
-> main.py
In ‘main.py’ I had tried unsuccessfully all the combinations bellow:
from Booklet import Question
from Question import Question
from Booklet.Question import Question
from Booklet.Question import *
import Booklet.Question
# and many othet various combinations ...
The solution was much more simple than I thought. I renamed the folder «Booklet» into «booklet» and that’s it. Now Python can import the class Question normally by using in ‘main.py’ the code:
from booklet.Booklet import Booklet
from booklet.Question import Question
from booklet.Question import AnotherClass
From this I can conclude that Package-Names (folders) like ‘booklet’ must start from lower-case, else Python confuses it with Class names and Filenames.
Apparently, this was not your problem, but John Fouhy’s answer is very good and this thread has almost anything that can cause this issue. So, this is one more thing and I hope that maybe this could help others.
answered May 27, 2018 at 23:49
ioaniatrioaniatr
2774 silver badges15 bronze badges
In linux server try dos2unix script_name
(remove all (if there is any) pyc files with command find . -name '*.pyc' -delete)
and re run in the case if you worked on script on windows
answered Jan 17, 2020 at 15:07
PoliPoli
7710 bronze badges
In my case, I was using sys.path.insert() to import a local module and was getting module not found from a different library. I had to put sys.path.insert() below the imports that reported module not found. I guess the best practice is to put sys.path.insert() at the bottom of your imports.
answered Mar 10, 2020 at 9:55
I’ve found that changing the name (via GUI) of aliased folders (Mac) can cause issues with loading modules. If the original folder name is changed, remake the symbolic link. I’m unsure how prevalent this behavior may be, but it was frustrating to debug.
answered Feb 17, 2021 at 18:47
GhotiGhoti
7374 silver badges19 bronze badges
another cause makes this issue
file.py
#!/bin/python
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
- if your default
pythonispyyhon2
$ file $(which python)
/sbin/python: symbolic link to python2
file.pyneedpython3, for this case(bs4)- you can not execute this module with
python2like this:
$ python file.py
# or
$ file.py
# or
$ file.py # if locate in $PATH
- Tow way to fix this
error,
# should be to make python3 as default by symlink
$ rm $(which python) && ln -s $(which python3) /usr/bin/python
# or use alias
alias python='/usr/bin.../python3'
or change shebang in file.py to
#!/usr/bin/...python3
answered Aug 2, 2022 at 23:05
After just suffering the same issue I found my resolution was to delete all pyc files from my project, it seems like these cached files were somehow causing this error.
Easiest way I found to do this was to navigate to my project folder in Windows explorer and searching for *.pyc, then selecting all (Ctrl+A) and deleting them (Ctrl+X).
Its possible I could have resolved my issues by just deleting the specific pyc file but I never tried this
sina72
4,9113 gold badges35 silver badges36 bronze badges
answered Aug 8, 2014 at 8:36
SayseSayse
42.5k14 gold badges77 silver badges146 bronze badges
0
I faced the same problem: Import error. In addition the library’ve been installed 100% correctly. The source of the problem was that on my PC 3 version of python (anaconda packet) have been installed). This is why the library was installed no to the right place. After that I just changed to the proper version of python in the my IDE PyCharm.
answered Dec 5, 2015 at 7:21
RocketqRocketq
5,29823 gold badges75 silver badges125 bronze badges
I had the same error. It was caused by somebody creating a folder in the same folder as my script, the name of which conflicted with a module I was importing from elsewhere. Instead of importing the external module, it looked inside this folder which obviously didn’t contain the expected modules.
answered Dec 13, 2016 at 11:45
Toivo SäwénToivo Säwén
1,6942 gold badges14 silver badges33 bronze badges
В Python может быть несколько причин возникновения ошибки ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ...:
- Модуль Python не установлен.
- Есть конфликт в названиях пакета и модуля.
- Есть конфликт зависимости модулей Python.
Рассмотрим варианты их решения.
Модуль не установлен
В первую очередь нужно проверить, установлен ли модуль. Для использования модуля в программе его нужно установить. Например, если попробовать использовать numpy без установки с помощью pip install будет следующая ошибка:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numpy'Для установки нужного модуля используйте следующую команду:
pip install numpy
# или
pip3 install numpyИли вот эту если используете Anaconda:
conda install numpyУчтите, что может быть несколько экземпляров Python (или виртуальных сред) в системе. Модуль нужно устанавливать в определенный экземпляр.
Конфликт имен библиотеки и модуля
Еще одна причина ошибки No module named — конфликт в названиях пакета и модуля. Предположим, есть следующая структура проекта Python:
demo-project
└───utils
__init__.py
string_utils.py
utils.pyЕсли использовать следующую инструкцию импорта файла utils.py, то Python вернет ошибку ModuleNotFoundError.
>>> import utils.string_utils
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:demo-projectutilsutils.py", line 1, in
import utils.string_utils
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'utils.string_utils';
'utils' is not a package
В сообщении об ошибке сказано, что «utils is not a package». utils — это имя пакета, но это также и имя модуля. Это приводит к конфликту, когда имя модуля перекрывает имя пакета/библиотеки. Для его разрешения нужно переименовать файл utils.py.
Иногда может существовать конфликт модулей Python, который и приводит к ошибке No module named.
Следующее сообщение явно указывает, что _numpy_compat.py в библиотеке scipy пытается импортировать модуль numpy.testing.nosetester.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:demo-projectvenv
Libsite-packages
scipy_lib_numpy_compat.py", line 10, in
from numpy.testing.nosetester import import_nose
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numpy.testing.nosetester'Ошибка ModuleNotFoundError возникает из-за того, что модуль numpy.testing.nosetester удален из библиотеки в версии 1.18. Для решения этой проблемы нужно обновить numpy и scipy до последних версий.
pip install numpy --upgrade
pip install scipy --upgrade Что означает ошибка ModuleNotFoundError: No module named
Python ругается, что не может найти нужный модуль
Python ругается, что не может найти нужный модуль
Ситуация: мы решили заняться бигдатой и обработать большой массив данных на Python. Чтобы было проще, мы используем уже готовые решения и находим нужный нам код в интернете, например такой:
import numpy as np
x = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
nums = np.array([2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
type(nums)
zeros = np.zeros((5, 4))
lin = np.linspace(1, 10, 20)Копируем, вставляем в редактор кода и запускаем, чтобы разобраться, как что работает. Но вместо обработки данных Python выдаёт ошибку:
❌ModuleNotFoundError: No module named numpy
Странно, но этот код точно правильный: мы его взяли из блога разработчика и, по комментариям, у всех всё работает. Откуда тогда ошибка?
Что это значит: Python пытается подключить библиотеку, которую мы указали, но не может её найти у себя.
Когда встречается: когда библиотеки нет или мы неправильно написали её название.
Что делать с ошибкой ModuleNotFoundError: No module named
Самый простой способ исправить эту ошибку — установить библиотеку, которую мы хотим подключить в проект. Для установки Python-библиотек используют штатную команду pip или pip3, которая работает так: pip install <имя_библиотеки>. В нашем случае Python говорит, что он не может подключить библиотеку Numpy, поэтому пишем в командной строке такое:
pip install numpy
Это нужно написать не в командной строке Python, а в командной строке операционной системы. Тогда компьютер скачает эту библиотеку, установит, привяжет к Python и будет ругаться на строчку в коде import numpy.
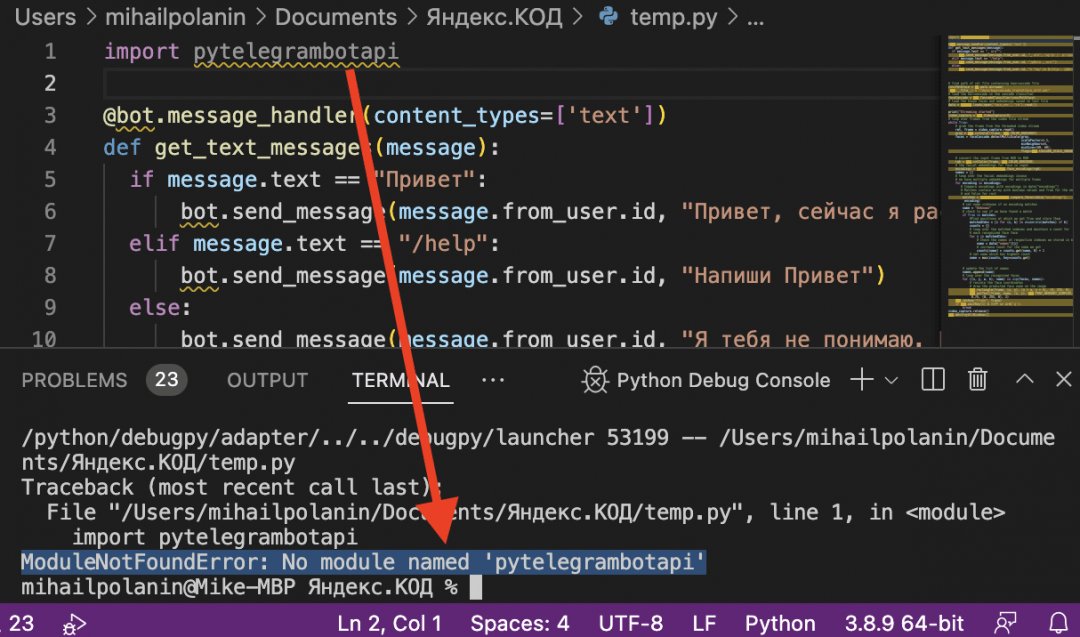
Ещё бывает такое, что библиотека называется иначе, чем указано в команде pip install. Например, для работы с телеграм-ботами нужна библиотека telebot, а для её установки надо написать pip install pytelegrambotapi. Если попробовать подключить библиотеку с этим же названием, то тоже получим ошибку:
А иногда такая ошибка — это просто невнимательность: пропущенная буква в названии библиотеки или опечатка. Исправляем и работаем дальше.
Вёрстка:
Кирилл Климентьев
When you try to import a module in a Python file, Python tries to resolve this module in several ways. Sometimes, Python throws the ModuleNotFoundError afterward. What does this error mean in Python?
As the name implies, this error occurs when you’re trying to access or use a module that cannot be found. In the case of the title, the «module named Python» cannot be found.
Python here can be any module. Here’s an error when I try to import a numpys module that cannot be found:
import numpys as np
Here’s what the error looks like:
Here are a few reasons why a module may not be found:
- you do not have the module you tried importing installed on your computer
- you spelled a module incorrectly (which still links back to the previous point, that the misspelled module is not installed)…for example, spelling
numpyasnumpysduring import - you use an incorrect casing for a module (which still links back to the first point)…for example, spelling
numpyasNumPyduring import will throw the module not found error as both modules are «not the same» - you are importing a module using the wrong path
How to fix the ModuleNotFoundError in Python
As I mentioned in the previous section, there are a couple of reasons a module may not be found. Here are some solutions.
1. Make sure imported modules are installed
Take for example, numpy. You use this module in your code in a file called «test.py» like this:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(arr)
If you try to run this code with python test.py and you get this error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named "numpy"
Then it’s most likely possible that the numpy module is not installed on your device. You can install the module like this:
python -m pip install numpy
When installed, the previous code will work correctly and you get the result printed in your terminal:
[1, 2, 3]
2. Make sure modules are spelled correctly
In some cases, you may have installed the module you need, but trying to use it still throws the ModuleNotFound error. In such cases, it could be that you spelled it incorrectly. Take, for example, this code:
import nompy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(arr)
Here, you have installed numpy but running the above code throws this error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named "nompy"
This error comes as a result of the misspelled numpy module as nompy (with the letter o instead of u). You can fix this error by spelling the module correctly.
3. Make sure modules are in the right casing
Similar to the misspelling issue for module not found errors, it could also be that you are spelling the module correctly, but in the wrong casing. Here’s an example:
import Numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(arr)
For this code, you have numpy installed but running the above code will throw this error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'Numpy'
Due to casing differences, numpy and Numpy are different modules. You can fix this error by spelling the module in the right casing.
4. Make sure you use the right paths
In Python, you can import modules from other files using absolute or relative paths. For this example, I’ll focus on absolute paths.
When you try to access a module from the wrong path, you will also get the module not found here. Here’s an example:
Let’s say you have a project folder called test. In it, you have two folders demoA and demoB.
demoA has an __init__.py file (to show it’s a Python package) and a test1.py module.
demoA also has an __init__.py file and a test2.py module.
Here’s the structure:
└── test
├── demoA
├── __init__.py
│ ├── test1.py
└── demoB
├── __init__.py
├── test2.py
Here are the contents of test1.py:
def hello():
print("hello")
And let’s say you want to use this declared hello function in test2.py. The following code will throw a module not found error:
import demoA.test as test1
test1.hello()
This code will throw the following error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'demoA.test'
The reason for this is that we have used the wrong path to access the test1 module. The right path should be demoA.test1. When you correct that, the code works:
import demoA.test1 as test1
test1.hello()
# hello
Wrapping up
For resolving an imported module, Python checks places like the inbuilt library, installed modules, and modules in the current project. If it’s unable to resolve that module, it throws the ModuleNotFoundError.
Sometimes you do not have that module installed, so you have to install it. Sometimes it’s a misspelled module, or the naming with the wrong casing, or a wrong path. In this article, I’ve shown four possible ways of fixing this error if you experience it.
I hope you learned from it 
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named in Python occurs when:
- The name of the module is incorrect
- The path of the module is incorrect
- The Library is not installed
- The module is unsupported
- Python 2 instead of Python 3
In this article, We’ll discuss the reasons and the solutions for the ModuleNotFoundError error.
1. The name of the module is incorrect
The first reason for ModuleNotFoundError: No module named is the module name is incorrect. For example, let’s try to import the os module with double «s» and see what will happen:
>>> import oss
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'oss'As you can see, we got ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘oss.’ To solve the error, make sure that you use the correct module name.
Let’s import the module with the correct name.
>>> import os
>>> As you can see, the error is solved.
2. The path of the module is incorrect
The Second reason is the path of the local module you want to import is incorrect. for example, let’s see a directory structure
Project structure:
core.py
folder_1
---my_module.py
In this folder, we’ve:
- core.py: is the file that will execute
- folder_1: folder contains my_module.py
Now in core.py, let’s try to import my_module.py
core.py
import my_module #incorrect
Output:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'my_module'As you can see, we got the error because my_module.py is not in the path that we’ve executed core.py. We need to define the module’s path in the following example to solve the error.
core.py
import folder_1.my_module #correct
Output:
...Program finished with exit code 0
Now we’ve imported m_module successfully.
3. The library is not installed
Also, you can get the ModuleNotFoundError: No module named issue if you are trying to import a library module that is not installed in your virtual environment or computer.
So before importing a library’s module, you need to install it with any package-management system.
For example, let’s try to import the Beautifulsoup4 library that’s not installed in my virtual environment.
>>> from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'bs4'Now, let’s install the library and try to re-import it:
pip install beautifulsoup4
Collecting beautifulsoup4
Using cached https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d1/41/e6495bd7d3781cee623ce23ea6ac73282a373088fcd0ddc809a047b18eae/beautifulsoup4-4.9.3-py3-none-any.whl
Requirement already satisfied: soupsieve>1.2; python_version >= "3.0" in /home/py/Desktop/seo_pro/seo_env/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from beautifulsoup4) (1.9.5)
Installing collected packages: beautifulsoup4
Successfully installed beautifulsoup4-4.9.3Re-importing:
>>> from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
>>> As you can see, after installing the package, the program is working.
4. The module is unsupported
When a library releases a new update, new modules are added, and others are dropped to support it.
If you try to import a module that is n unsupported by the library, you will get ModuleNotFoundError: No module named.
To ensure the module is supported, go to the package documentation and check if the module is available or not.
5. Python 2 instead of Python 3
As you know, Some Python libraries no longer support Python 2. For that reason, you’ll get the ModuleNotFoundError error if you execute a module that does not support Python 2 with Python 2.
To solve the error:
First, let’s check our python version using these two commands:
python -V
# Python 2.7.18
python3 -V
# Python 3.9.5
In my case, Python 3 is on the python3 command, So I will execute the program using python3. If Python3 is not found on your device, Install Python on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Conclusion
In conclusion, To solve the ModuleNotFoundError: No module named:
- Ensure the name of the module is incorrect
- Ensure the path of the module is incorrect
- Ensure the Library is installed
- Ensure the module is supported
- Ensure using Python 3
Finally, I hope your problem has been fixed.




![ModuleNotFoundError: no module named Python Error [Fixed]](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/content/images/size/w2000/2022/09/module-not-found-error.png)
