Source (Py v2.7.3) for traceback.format_exception() and called/related functions helps greatly. Embarrassingly, I always forget to Read the Source. I only did so for this after searching for similar details in vain. A simple question, «How to recreate the same output as Python for an exception, with all the same details?» This would get anybody 90+% to whatever they’re looking for. Frustrated, I came up with this example. I hope it helps others. (It sure helped me! 
import sys, traceback
traceback_template = '''Traceback (most recent call last):
File "%(filename)s", line %(lineno)s, in %(name)s
%(type)s: %(message)sn''' # Skipping the "actual line" item
# Also note: we don't walk all the way through the frame stack in this example
# see hg.python.org/cpython/file/8dffb76faacc/Lib/traceback.py#l280
# (Imagine if the 1/0, below, were replaced by a call to test() which did 1/0.)
try:
1/0
except:
# http://docs.python.org/2/library/sys.html#sys.exc_info
exc_type, exc_value, exc_traceback = sys.exc_info() # most recent (if any) by default
'''
Reason this _can_ be bad: If an (unhandled) exception happens AFTER this,
or if we do not delete the labels on (not much) older versions of Py, the
reference we created can linger.
traceback.format_exc/print_exc do this very thing, BUT note this creates a
temp scope within the function.
'''
traceback_details = {
'filename': exc_traceback.tb_frame.f_code.co_filename,
'lineno' : exc_traceback.tb_lineno,
'name' : exc_traceback.tb_frame.f_code.co_name,
'type' : exc_type.__name__,
'message' : exc_value.message, # or see traceback._some_str()
}
del(exc_type, exc_value, exc_traceback) # So we don't leave our local labels/objects dangling
# This still isn't "completely safe", though!
# "Best (recommended) practice: replace all exc_type, exc_value, exc_traceback
# with sys.exc_info()[0], sys.exc_info()[1], sys.exc_info()[2]
print
print traceback.format_exc()
print
print traceback_template % traceback_details
print
In specific answer to this query:
sys.exc_info()[0].__name__, os.path.basename(sys.exc_info()[2].tb_frame.f_code.co_filename), sys.exc_info()[2].tb_lineno
Обработка ошибок увеличивает отказоустойчивость кода, защищая его от потенциальных сбоев, которые могут привести к преждевременному завершению работы.
Прежде чем переходить к обсуждению того, почему обработка исключений так важна, и рассматривать встроенные в Python исключения, важно понять, что есть тонкая грань между понятиями ошибки и исключения.
Ошибку нельзя обработать, а исключения Python обрабатываются при выполнении программы. Ошибка может быть синтаксической, но существует и много видов исключений, которые возникают при выполнении и не останавливают программу сразу же. Ошибка может указывать на критические проблемы, которые приложение и не должно перехватывать, а исключения — состояния, которые стоит попробовать перехватить. Ошибки — вид непроверяемых и невозвратимых ошибок, таких как OutOfMemoryError, которые не стоит пытаться обработать.
Обработка исключений делает код более отказоустойчивым и помогает предотвращать потенциальные проблемы, которые могут привести к преждевременной остановке выполнения. Представьте код, который готов к развертыванию, но все равно прекращает работу из-за исключения. Клиент такой не примет, поэтому стоит заранее обработать конкретные исключения, чтобы избежать неразберихи.
Ошибки могут быть разных видов:
- Синтаксические
- Недостаточно памяти
- Ошибки рекурсии
- Исключения
Разберем их по очереди.
Синтаксические ошибки (SyntaxError)
Синтаксические ошибки часто называют ошибками разбора. Они возникают, когда интерпретатор обнаруживает синтаксическую проблему в коде.
Рассмотрим на примере.
a = 8
b = 10
c = a b
File "", line 3
c = a b
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
Стрелка вверху указывает на место, где интерпретатор получил ошибку при попытке исполнения. Знак перед стрелкой указывает на причину проблемы. Для устранения таких фундаментальных ошибок Python будет делать большую часть работы за программиста, выводя название файла и номер строки, где была обнаружена ошибка.
Недостаточно памяти (OutofMemoryError)
Ошибки памяти чаще всего связаны с оперативной памятью компьютера и относятся к структуре данных под названием “Куча” (heap). Если есть крупные объекты (или) ссылки на подобные, то с большой долей вероятности возникнет ошибка OutofMemory. Она может появиться по нескольким причинам:
- Использование 32-битной архитектуры Python (максимальный объем выделенной памяти невысокий, между 2 и 4 ГБ);
- Загрузка файла большого размера;
- Запуск модели машинного обучения/глубокого обучения и много другое;
Обработать ошибку памяти можно с помощью обработки исключений — резервного исключения. Оно используется, когда у интерпретатора заканчивается память и он должен немедленно остановить текущее исполнение. В редких случаях Python вызывает OutofMemoryError, позволяя скрипту каким-то образом перехватить самого себя, остановить ошибку памяти и восстановиться.
Но поскольку Python использует архитектуру управления памятью из языка C (функция malloc()), не факт, что все процессы восстановятся — в некоторых случаях MemoryError приведет к остановке. Следовательно, обрабатывать такие ошибки не рекомендуется, и это не считается хорошей практикой.
Ошибка рекурсии (RecursionError)
Эта ошибка связана со стеком и происходит при вызове функций. Как и предполагает название, ошибка рекурсии возникает, когда внутри друг друга исполняется много методов (один из которых — с бесконечной рекурсией), но это ограничено размером стека.
Все локальные переменные и методы размещаются в стеке. Для каждого вызова метода создается стековый кадр (фрейм), внутрь которого помещаются данные переменной или результат вызова метода. Когда исполнение метода завершается, его элемент удаляется.
Чтобы воспроизвести эту ошибку, определим функцию recursion, которая будет рекурсивной — вызывать сама себя в бесконечном цикле. В результате появится ошибка StackOverflow или ошибка рекурсии, потому что стековый кадр будет заполняться данными метода из каждого вызова, но они не будут освобождаться.
def recursion():
return recursion()
recursion()
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RecursionError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
----> 1 recursion()
in recursion()
1 def recursion():
----> 2 return recursion()
... last 1 frames repeated, from the frame below ...
in recursion()
1 def recursion():
----> 2 return recursion()
RecursionError: maximum recursion depth exceeded
Ошибка отступа (IndentationError)
Эта ошибка похожа по духу на синтаксическую и является ее подвидом. Тем не менее она возникает только в случае проблем с отступами.
Пример:
for i in range(10):
print('Привет Мир!')
File "", line 2
print('Привет Мир!')
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
Исключения
Даже если синтаксис в инструкции или само выражение верны, они все равно могут вызывать ошибки при исполнении. Исключения Python — это ошибки, обнаруживаемые при исполнении, но не являющиеся критическими. Скоро вы узнаете, как справляться с ними в программах Python. Объект исключения создается при вызове исключения Python. Если скрипт не обрабатывает исключение явно, программа будет остановлена принудительно.
Программы обычно не обрабатывают исключения, что приводит к подобным сообщениям об ошибке:
Ошибка типа (TypeError)
a = 2
b = 'PythonRu'
a + b
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
1 a = 2
2 b = 'PythonRu'
----> 3 a + b
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'str'
Ошибка деления на ноль (ZeroDivisionError)
10 / 0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZeroDivisionError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
----> 1 10 / 0
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
Есть разные типы исключений в Python и их тип выводится в сообщении: вверху примеры TypeError и ZeroDivisionError. Обе строки в сообщениях об ошибке представляют собой имена встроенных исключений Python.
Оставшаяся часть строки с ошибкой предлагает подробности о причине ошибки на основе ее типа.
Теперь рассмотрим встроенные исключения Python.
Встроенные исключения
BaseException
+-- SystemExit
+-- KeyboardInterrupt
+-- GeneratorExit
+-- Exception
+-- StopIteration
+-- StopAsyncIteration
+-- ArithmeticError
| +-- FloatingPointError
| +-- OverflowError
| +-- ZeroDivisionError
+-- AssertionError
+-- AttributeError
+-- BufferError
+-- EOFError
+-- ImportError
| +-- ModuleNotFoundError
+-- LookupError
| +-- IndexError
| +-- KeyError
+-- MemoryError
+-- NameError
| +-- UnboundLocalError
+-- OSError
| +-- BlockingIOError
| +-- ChildProcessError
| +-- ConnectionError
| | +-- BrokenPipeError
| | +-- ConnectionAbortedError
| | +-- ConnectionRefusedError
| | +-- ConnectionResetError
| +-- FileExistsError
| +-- FileNotFoundError
| +-- InterruptedError
| +-- IsADirectoryError
| +-- NotADirectoryError
| +-- PermissionError
| +-- ProcessLookupError
| +-- TimeoutError
+-- ReferenceError
+-- RuntimeError
| +-- NotImplementedError
| +-- RecursionError
+-- SyntaxError
| +-- IndentationError
| +-- TabError
+-- SystemError
+-- TypeError
+-- ValueError
| +-- UnicodeError
| +-- UnicodeDecodeError
| +-- UnicodeEncodeError
| +-- UnicodeTranslateError
+-- Warning
+-- DeprecationWarning
+-- PendingDeprecationWarning
+-- RuntimeWarning
+-- SyntaxWarning
+-- UserWarning
+-- FutureWarning
+-- ImportWarning
+-- UnicodeWarning
+-- BytesWarning
+-- ResourceWarning
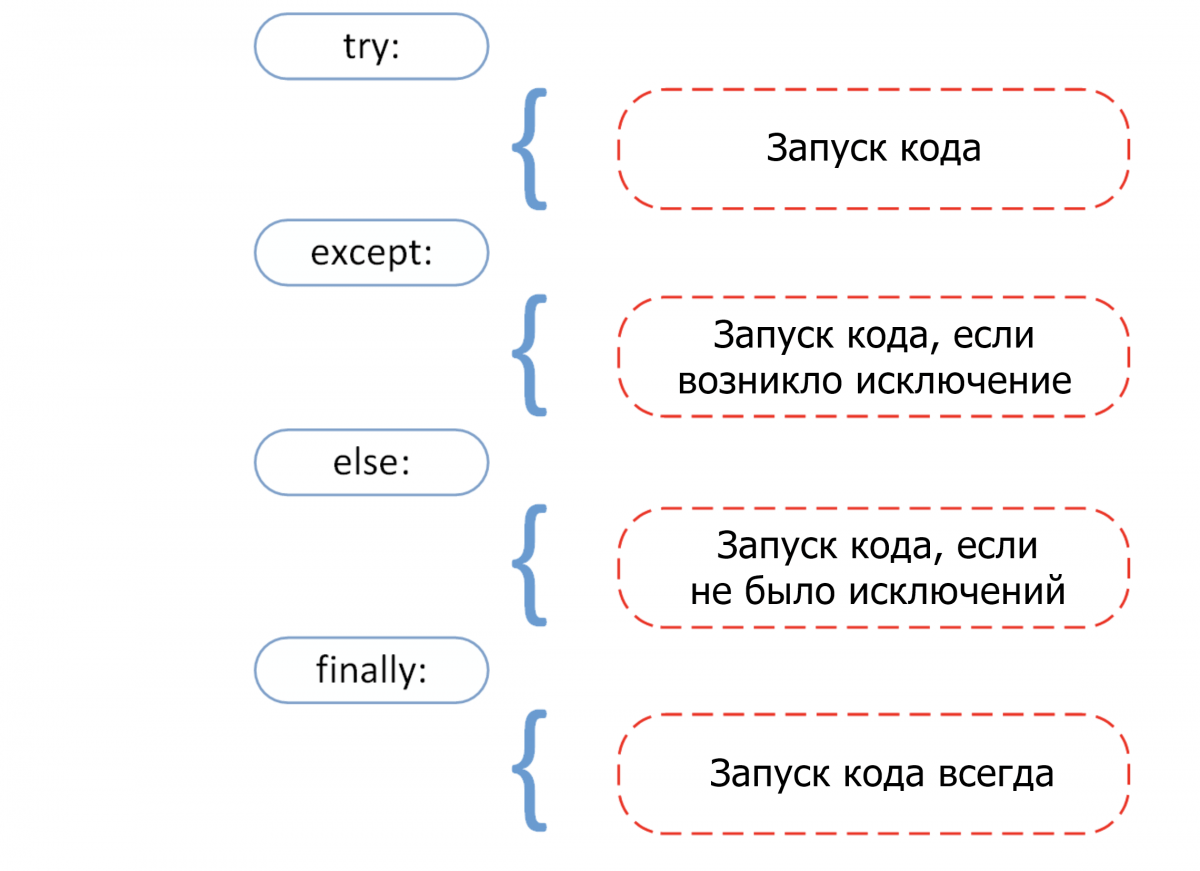
Прежде чем переходить к разбору встроенных исключений быстро вспомним 4 основных компонента обработки исключения, как показано на этой схеме.
Try: он запускает блок кода, в котором ожидается ошибка.Except: здесь определяется тип исключения, который ожидается в блокеtry(встроенный или созданный).Else: если исключений нет, тогда исполняется этот блок (его можно воспринимать как средство для запуска кода в том случае, если ожидается, что часть кода приведет к исключению).Finally: вне зависимости от того, будет ли исключение или нет, этот блок кода исполняется всегда.
В следующем разделе руководства больше узнаете об общих типах исключений и научитесь обрабатывать их с помощью инструмента обработки исключения.
Ошибка прерывания с клавиатуры (KeyboardInterrupt)
Исключение KeyboardInterrupt вызывается при попытке остановить программу с помощью сочетания Ctrl + C или Ctrl + Z в командной строке или ядре в Jupyter Notebook. Иногда это происходит неумышленно и подобная обработка поможет избежать подобных ситуаций.
В примере ниже если запустить ячейку и прервать ядро, программа вызовет исключение KeyboardInterrupt. Теперь обработаем исключение KeyboardInterrupt.
try:
inp = input()
print('Нажмите Ctrl+C и прервите Kernel:')
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('Исключение KeyboardInterrupt')
else:
print('Исключений не произошло')
Исключение KeyboardInterrupt
Стандартные ошибки (StandardError)
Рассмотрим некоторые базовые ошибки в программировании.
Арифметические ошибки (ArithmeticError)
- Ошибка деления на ноль (Zero Division);
- Ошибка переполнения (OverFlow);
- Ошибка плавающей точки (Floating Point);
Все перечисленные выше исключения относятся к классу Arithmetic и вызываются при ошибках в арифметических операциях.
Деление на ноль (ZeroDivisionError)
Когда делитель (второй аргумент операции деления) или знаменатель равны нулю, тогда результатом будет ошибка деления на ноль.
try:
a = 100 / 0
print(a)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Исключение ZeroDivisionError." )
else:
print("Успех, нет ошибок!")
Исключение ZeroDivisionError.
Переполнение (OverflowError)
Ошибка переполнение вызывается, когда результат операции выходил за пределы диапазона. Она характерна для целых чисел вне диапазона.
try:
import math
print(math.exp(1000))
except OverflowError:
print("Исключение OverFlow.")
else:
print("Успех, нет ошибок!")
Исключение OverFlow.
Ошибка утверждения (AssertionError)
Когда инструкция утверждения не верна, вызывается ошибка утверждения.
Рассмотрим пример. Предположим, есть две переменные: a и b. Их нужно сравнить. Чтобы проверить, равны ли они, необходимо использовать ключевое слово assert, что приведет к вызову исключения Assertion в том случае, если выражение будет ложным.
try:
a = 100
b = "PythonRu"
assert a == b
except AssertionError:
print("Исключение AssertionError.")
else:
print("Успех, нет ошибок!")
Исключение AssertionError.
Ошибка атрибута (AttributeError)
При попытке сослаться на несуществующий атрибут программа вернет ошибку атрибута. В следующем примере можно увидеть, что у объекта класса Attributes нет атрибута с именем attribute.
class Attributes(obj):
a = 2
print(a)
try:
obj = Attributes()
print(obj.attribute)
except AttributeError:
print("Исключение AttributeError.")
2
Исключение AttributeError.
Ошибка импорта (ModuleNotFoundError)
Ошибка импорта вызывается при попытке импортировать несуществующий (или неспособный загрузиться) модуль в стандартном пути или даже при допущенной ошибке в имени.
import nibabel
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ModuleNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
----> 1 import nibabel
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'nibabel'
Ошибка поиска (LookupError)
LockupError выступает базовым классом для исключений, которые происходят, когда key или index используются для связывания или последовательность списка/словаря неверна или не существует.
Здесь есть два вида исключений:
- Ошибка индекса (
IndexError); - Ошибка ключа (
KeyError);
Ошибка ключа
Если ключа, к которому нужно получить доступ, не оказывается в словаре, вызывается исключение KeyError.
try:
a = {1:'a', 2:'b', 3:'c'}
print(a[4])
except LookupError:
print("Исключение KeyError.")
else:
print("Успех, нет ошибок!")
Исключение KeyError.
Ошибка индекса
Если пытаться получить доступ к индексу (последовательности) списка, которого не существует в этом списке или находится вне его диапазона, будет вызвана ошибка индекса (IndexError: list index out of range python).
try:
a = ['a', 'b', 'c']
print(a[4])
except LookupError:
print("Исключение IndexError, индекс списка вне диапазона.")
else:
print("Успех, нет ошибок!")
Исключение IndexError, индекс списка вне диапазона.
Ошибка памяти (MemoryError)
Как уже упоминалось, ошибка памяти вызывается, когда операции не хватает памяти для выполнения.
Ошибка имени (NameError)
Ошибка имени возникает, когда локальное или глобальное имя не находится.
В следующем примере переменная ans не определена. Результатом будет ошибка NameError.
try:
print(ans)
except NameError:
print("NameError: переменная 'ans' не определена")
else:
print("Успех, нет ошибок!")
NameError: переменная 'ans' не определена
Ошибка выполнения (Runtime Error)
Ошибка «NotImplementedError»
Ошибка выполнения служит базовым классом для ошибки NotImplemented. Абстрактные методы определенного пользователем класса вызывают это исключение, когда производные методы перезаписывают оригинальный.
class BaseClass(object):
"""Опередляем класс"""
def __init__(self):
super(BaseClass, self).__init__()
def do_something(self):
# функция ничего не делает
raise NotImplementedError(self.__class__.__name__ + '.do_something')
class SubClass(BaseClass):
"""Реализует функцию"""
def do_something(self):
# действительно что-то делает
print(self.__class__.__name__ + ' что-то делает!')
SubClass().do_something()
BaseClass().do_something()
SubClass что-то делает!
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
14
15 SubClass().do_something()
---> 16 BaseClass().do_something()
in do_something(self)
5 def do_something(self):
6 # функция ничего не делает
----> 7 raise NotImplementedError(self.__class__.__name__ + '.do_something')
8
9 class SubClass(BaseClass):
NotImplementedError: BaseClass.do_something
Ошибка типа (TypeError)
Ошибка типа вызывается при попытке объединить два несовместимых операнда или объекта.
В примере ниже целое число пытаются добавить к строке, что приводит к ошибке типа.
try:
a = 5
b = "PythonRu"
c = a + b
except TypeError:
print('Исключение TypeError')
else:
print('Успех, нет ошибок!')
Исключение TypeError
Ошибка значения (ValueError)
Ошибка значения вызывается, когда встроенная операция или функция получают аргумент с корректным типом, но недопустимым значением.
В этом примере встроенная операция float получат аргумент, представляющий собой последовательность символов (значение), что является недопустимым значением для типа: число с плавающей точкой.
try:
print(float('PythonRu'))
except ValueError:
print('ValueError: не удалось преобразовать строку в float: 'PythonRu'')
else:
print('Успех, нет ошибок!')
ValueError: не удалось преобразовать строку в float: 'PythonRu'
Пользовательские исключения в Python
В Python есть много встроенных исключений для использования в программе. Но иногда нужно создавать собственные со своими сообщениями для конкретных целей.
Это можно сделать, создав новый класс, который будет наследовать из класса Exception в Python.
class UnAcceptedValueError(Exception):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
def __str__(self):
return repr(self.data)
Total_Marks = int(input("Введите общее количество баллов: "))
try:
Num_of_Sections = int(input("Введите количество разделов: "))
if(Num_of_Sections < 1):
raise UnAcceptedValueError("Количество секций не может быть меньше 1")
except UnAcceptedValueError as e:
print("Полученная ошибка:", e.data)
Введите общее количество баллов: 10
Введите количество разделов: 0
Полученная ошибка: Количество секций не может быть меньше 1
В предыдущем примере если ввести что-либо меньше 1, будет вызвано исключение. Многие стандартные исключения имеют собственные исключения, которые вызываются при возникновении проблем в работе их функций.
Недостатки обработки исключений в Python
У использования исключений есть свои побочные эффекты, как, например, то, что программы с блоками try-except работают медленнее, а количество кода возрастает.
Дальше пример, где модуль Python timeit используется для проверки времени исполнения 2 разных инструкций. В stmt1 для обработки ZeroDivisionError используется try-except, а в stmt2 — if. Затем они выполняются 10000 раз с переменной a=0. Суть в том, чтобы показать разницу во времени исполнения инструкций. Так, stmt1 с обработкой исключений занимает больше времени чем stmt2, который просто проверяет значение и не делает ничего, если условие не выполнено.
Поэтому стоит ограничить использование обработки исключений в Python и применять его в редких случаях. Например, когда вы не уверены, что будет вводом: целое или число с плавающей точкой, или не уверены, существует ли файл, который нужно открыть.
import timeit
setup="a=0"
stmt1 = '''
try:
b=10/a
except ZeroDivisionError:
pass'''
stmt2 = '''
if a!=0:
b=10/a'''
print("time=",timeit.timeit(stmt1,setup,number=10000))
print("time=",timeit.timeit(stmt2,setup,number=10000))
time= 0.003897680000136461
time= 0.0002797570000439009
Выводы!
Как вы могли увидеть, обработка исключений помогает прервать типичный поток программы с помощью специального механизма, который делает код более отказоустойчивым.
Обработка исключений — один из основных факторов, который делает код готовым к развертыванию. Это простая концепция, построенная всего на 4 блоках: try выискивает исключения, а except их обрабатывает.
Очень важно поупражняться в их использовании, чтобы сделать свой код более отказоустойчивым.
One has pretty much control on which information from the traceback to be displayed/logged when catching exceptions.
The code
with open("not_existing_file.txt", 'r') as text:
pass
would produce the following traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "exception_checks.py", line 19, in <module>
with open("not_existing_file.txt", 'r') as text:
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'not_existing_file.txt'
Print/Log the full traceback
As others already mentioned, you can catch the whole traceback by using the traceback module:
import traceback
try:
with open("not_existing_file.txt", 'r') as text:
pass
except Exception as exception:
traceback.print_exc()
This will produce the following output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "exception_checks.py", line 19, in <module>
with open("not_existing_file.txt", 'r') as text:
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'not_existing_file.txt'
You can achieve the same by using logging:
try:
with open("not_existing_file.txt", 'r') as text:
pass
except Exception as exception:
logger.error(exception, exc_info=True)
Output:
__main__: 2020-05-27 12:10:47-ERROR- [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'not_existing_file.txt'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "exception_checks.py", line 27, in <module>
with open("not_existing_file.txt", 'r') as text:
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'not_existing_file.txt'
Print/log error name/message only
You might not be interested in the whole traceback, but only in the most important information, such as Exception name and Exception message, use:
try:
with open("not_existing_file.txt", 'r') as text:
pass
except Exception as exception:
print("Exception: {}".format(type(exception).__name__))
print("Exception message: {}".format(exception))
Output:
Exception: FileNotFoundError
Exception message: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'not_existing_file.txt'
|
vargor 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 26.07.2016 Сообщений: 17 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
26.08.2016, 22:45. Показов 11524. Ответов 4 Метки номер, ошибки, с, Строки (Все метки)
Собственно само решение. Казалось бы просто, а готовых решений не нашел.
0 |
|
mmm_corp 103 / 91 / 32 Регистрация: 30.05.2015 Сообщений: 594 |
||||
|
26.08.2016, 23:23 |
2 |
|||
нагуглил, не проверял Добавлено через 14 секунд Добавлено через 19 секунд
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 26.07.2016 Сообщений: 17 |
|
|
26.08.2016, 23:42 [ТС] |
3 |
|
Хз, куда я нигмил
0 |
|
103 / 91 / 32 Регистрация: 30.05.2015 Сообщений: 594 |
|
|
27.08.2016, 22:43 |
4 |
|
баян но…. правильно заданный гуглу вопрос — половина как минимум ответа
0 |
|
alex925 2740 / 2339 / 620 Регистрация: 19.03.2012 Сообщений: 8,830 |
||||
|
27.08.2016, 23:20 |
5 |
|||
|
vargor, все просто
0 |
|
IT_Exp Эксперт 87844 / 49110 / 22898 Регистрация: 17.06.2006 Сообщений: 92,604 |
27.08.2016, 23:20 |
|
5 |
In this Python Tutorial let us learn about the 3 different pieces of information that you can extract and use from the Exceptions caught on your except clauses, and see the best ways to use each of these pieces in our Python programs.
Let us start by learning what the 3 pieces of information are.
What kind of information can you get from Exceptions?
You can get the following 3 pieces of data from exceptions
- Exception Type,
- Exception Value a.k.a Error Message, and
- Stack-trace or Traceback Object.
All three of the above information is printed out by the Python Interpreter when our program crashes due to an exception as shown in the following example
>> my_list = [1,2]
>> print (my_list[3])
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-35-63c7f9106be5>", line 1, in <module>
print (my_list[3])
IndexError: list index out of rangeLines 3,4,5,6 shows the Stack-trace
Line 7 shows the Exception type and Error Message.
Our focus in this article is to learn how to extract the above 3 pieces individually in our except clauses and print them out as needed.
Hence, the rest of the article is all about answering the following questions
- what does each of the information in the above list mean,
- how to extract each of these 3 pieces individually and
- how to use these pieces in our programs.
Piece#1: Printing Exception Type
The Exception Type refers to the class to which the Exception that you have just caught belongs to.
Extracting Piece#1 (Exception Type)
Let us improve our Example 1 above by putting the problematic code into try and except clauses.
try:
my_list = [1,2]
print (my_list[3])
except Exception as e:
print(type(e))Here, in the try clause, we have declared a List named my_list and initialized the list with 2 items. Then we have tried to print the 3rd/non-existent item in the list.
The except clause catches the IndexError exception and prints out Exception type.
On running the code, we will get the following output
<class 'IndexError'>As you can see we just extracted and printed out the information about the class to which the exception that we have just caught belongs to!
But how exactly did we do that?
If you have a look at the except clause. In the line
except Exception as e:what we have done is, we have assigned the caught exception to an object named “e”. Then by using the built-in python function type(), we have printed out the class name that the object e belongs to.
print(type(e))Where to get more details about Exception Types
Now that we have the “Exception Type”, next we will probably need to get some information about that particular type so that we can get a better understanding of why our code has failed. In order to do that, the best place to start is the official documentation.
For built in exceptions you can have a look at the Python Documentation
For Exception types that come with the libraries that you use with your code, refer to the documentation of your library.
Piece#2: Printing Exception Value a.k.a Error message
The Exception type is definitely useful for debugging, but, a message like IndexError might sound cryptic and a good understandable error-message will make our job of debugging easier without having to look at the documentation.
In other words, if your program is to be run on the command line and you wish to log why the program just crashed then it is better to use an “Error message” rather than an “Exception Type”.
The example below shows how to print such an Error message.
try:
my_list = [1,2]
print (my_list[3])
except Exception as e:
print(e)This will print the default error message as follows
list index out of rangeEach Exception type comes with its own error message. This can be retrieved using the built-in function print().
Say your program is going to be run by a not-so-tech-savvy user, in that case, you might want to print something friendlier. You can do so by passing in the string to be printed along with the constructor as follows.
try:
raise IndexError('Custom message about IndexError')
except Exception as e:
print(e)This will print
Custom message about IndexErrorTo understand how the built-in function print() does this magic, and see some more examples of manipulating these error messages, I recommend reading my other article in the link below.
Python Exception Tutorial: Printing Error Messages (5 Examples!)
If you wish to print both the Error message and the Exception type, which I recommend, you can do so like below.
try:
my_list = [1,2]
print (my_list[3])
except Exception as e:
print(repr(e))This will print something like
IndexError('list index out of range')Now that we have understood how to get control over the usage of Pieces 1 and 2, let us go ahead and look at the last and most important piece for debugging, the stack-trace which tells us where exactly in our program have the Exception occurred.
Piece#3: Printing/Logging the stack-trace using the traceback object
Stack-trace in Python is packed into an object named traceback object.
This is an interesting one as the traceback class in Python comes with several useful methods to exercise complete control over what is printed.
Let us see how to use these options using some examples!
import traceback
try:
my_list = [1,2]
print (my_list[3])
except Exception:
traceback.print_exc()This will print something like
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-38-f9a1ee2cf77a>", line 5, in <module>
print (my_list[3])
IndexError: list index out of rangewhich contains the entire error messages printed by the Python interpreter if we fail to handle the exception.
Here, instead of crashing the program, we have printed this entire message using our exception handler with the help of the print_exc() method of the traceback class.
The above Example-6 is too simple, as, in the real-world, we will normally have several nested function calls which will result in a deeper stack. Let us see an example of how to control the output in such situations.
def func3():
my_list = [1,2]
print (my_list[3])
def func2():
print('calling func3')
func3()
def func1():
print('calling func2')
func2()
try:
print('calling func1')
func1()
except Exception as e:
traceback.print_exc()Here in the try clause we call func1(), which in-turn calls func2(), which in-turn calls func3(), which produces an IndexError. Running the code above we get the following output
calling func1
calling func2
calling func3
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-42-2267707e164f>", line 15, in <module>
func1()
File "<ipython-input-42-2267707e164f>", line 11, in func1
func2()
File "<ipython-input-42-2267707e164f>", line 7, in func2
func3()
File "<ipython-input-42-2267707e164f>", line 3, in func3
print (my_list[3])
IndexError: list index out of rangeSay we are not interested in some of the above information. Say we just want to print out the Traceback and skip the error message and Exception type (the last line above), then we can modify the code like shown below.
def func3():
my_list = [1,2]
print (my_list[3])
def func2():
func3()
def func1():
func2()
try:
func1()
except Exception as e:
traceback_lines = traceback.format_exc().splitlines()
for line in traceback_lines:
if line != traceback_lines[-1]:
print(line)Here we have used the format_exc() method available in the traceback class to get the traceback information as a string and used splitlines() method to transform the string into a list of lines and stored that in a list object named traceback_lines
Then with the help of a simple for loop we have skipped printing the last line with index of -1 to get an output like below
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-43-aff649563444>", line 3, in <module>
func1()
File "<ipython-input-42-2267707e164f>", line 11, in func1
func2()
File "<ipython-input-42-2267707e164f>", line 7, in func2
func3()
File "<ipython-input-42-2267707e164f>", line 3, in func3
print (my_list[3])Another interesting variant of formatting the information in the traceback object is to control the depth of stack that is actually printed out.
If your program uses lots of external library code, odds are the stack will get very deep, and printing out each and every level of function call might not be very useful. If you ever find yourself in such a situation you can set the limit argument in the print_exc() method like shown below.
traceback.print_exc(limit=2, file=sys.stdout)This will limit the number of levels to 2. Let us use this line of code in our Example and see how that behaves
def func3():
my_list = [1,2]
print (my_list[3])
def func2():
func3()
def func1():
func2()
try:
func1()
except Exception as e:
traceback.print_exc(limit=2)This will print
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-44-496132ff4faa>", line 12, in <module>
func1()
File "<ipython-input-44-496132ff4faa>", line 9, in func1
func2()
IndexError: list index out of rangeAs you can see, we have printed only 2 levels of the stack and skipped the 3rd one, just as we wanted!
You can do more things with traceback like formatting the output to suit your needs. If you are interested to learn even more things to do, refer to the official documentation on traceback here
Now that we have seen how to exercise control over what gets printed and how to format them, next let us have a look at some best practices on when to use which piece of information
Best Practices while Printing Exception messages
When to Use Which Piece
- Use Piece#1 only on very short programs and only during the development/testing phase to get some clues on the Exceptions without letting the interpreter crash your program. Once finding out, implement specific handlers to do something about these exceptions. If you are not sure how to handle the exceptions have a look at my other article below where I have explained 3 ways to handle Exceptions
Exceptions in Python: Everything You Need To Know! - Use Piece#2 to print out some friendly information either for yourself or for your user to inform them what exactly is happening.
- Use all 3 pieces on your finished product, so that if an exception ever occurs while your program is running on your client’s computer, you can log the errors and have use that information to fix your bugs.
Where to print
One point worth noting here is that the default file that print() uses is the stdout file stream and not the stderr stream. To use stderr instead, you can modify the code like this
import sys
try:
#some naughty statements that irritate us with exceptions
except Exception as e:
print(e, file=sys.stderr)The above code is considered better practice, as errors are meant to go to stderr and not stdout.
You can always print these into a separate log file too if that is what you need. This way, you can organize the logs collected in a better manner by separating the informational printouts from the error printouts.
How to print into log files
If you are going to use a log file I suggest using python’s logging module instead of print() statements, as described here
If you are interested in learning how to manually raise exceptions, and what situations you might need to do that you can read this article below
Python: Manually throw/raise an Exception using the “raise” statement
If you are interested in catching and handling multiple exception in a single except clause, you can this article below
Python: 3 Ways to Catch Multiple Exceptions in a single “except” clause
And with that, I will conclude this article!
I hope you enjoyed reading this article and got some value out of it!
Feel free to share it with your friends and colleagues!