В Microsoft SQL Server есть возможность обращения к различным источникам данных, которые расположены вне SQL сервера, это возможно благодаря технологии связанных серверов и сегодня мы с Вами рассмотрим пример настройки связанного сервера с СУБД Oracle.
Подробно о том, что такое связанный сервер, а также простые примеры настройки связанных серверов мы с Вами рассматривали в материале – Связанные серверы в MS SQL Server 2014.
Сейчас как я уже сказал, мы будем настраивать связанный сервер, источником данных которого будет выступать СУБД Oracle.
Примечание! Для примера я буду использовать Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Express, а версия Oracle у меня Oracle Database Express Edition 11g.
Прежде чем начать хотелось бы сказать, что для настройки связанных серверов используются так называемые «Провайдеры» или «Поставщики», которых на самом деле много. Для связи с Oracle существует несколько поставщиков, например:
- Microsoft OLE DB Provider for Oracle (MSDAORA) – как не трудно догадаться его разработчиком является компания Microsoft;
- Oracle Provider for OLE DB (OraOLEDB.Oracle) – данный провайдер разработала сама компания Oracle для связи со своей СУБД.
Все рекомендуют использовать провайдер от Oracle, в том числе и я, основываясь на собственном опыте. Так как OraOLEDB.Oracle более оптимизирован для работы с Oracle, например, как-то раз при использовании провайдера MSDAORA текстовые данные на русском языке (VARCHAR2) с сервера Oracle приходили мне в виде «?????», после недолгого шаманства пришлось сменить провайдера.
Поэтому сегодня мы будем рассматривать пример настройки связанного сервера с использованием Oracle Provider for OLE DB (OraOLEDB.Oracle) от компании Oracle.
Практически для любого поставщика требуются какие-то инструменты, чтобы он функционировал, в том числе и для OraOLEDB.Oracle.
Для того чтобы провайдер OraOLEDB.Oracle работал его необходимо установить, предварительно скачав с официального сайта Oracle.
Содержание
- Как скачать Oracle Provider for OLE DB (OraOLEDB.Oracle)?
- Установка Oracle Data Access Components (ODAC)
- Шаг 1
- Шаг 2
- Шаг 3
- Шаг 4
- Шаг 5
- Шаг 6
- Проверка работы провайдера OraOLEDB.Oracle
- Создание связанного сервера с использованием провайдера OraOLEDB.Oracle
- Устранение возможных ошибок при создании связанного сервера с Oracle в Microsoft SQL Server
- Ошибка 7302
- Ошибка 7303
- Ошибка 7314
- Ошибка 7356
- Ошибка 7357
Как скачать Oracle Provider for OLE DB (OraOLEDB.Oracle)?
Oracle Provider for OLE DB на текущий момент распространяется в составе инструмента для разработчиков ODAC.
Oracle Data Access Components (ODAC) – это набор компонентов для разработчиков, который предоставляет им доступ к данным Oracle.
Чтобы его скачать, необходимо зарегистрироваться на сайте Oracle или если Вы уже зарегистрированы, то войти в аккаунт. Затем переходите на страницу загрузки ODAC вот она.
Потом в зависимости от Вашей системы (т.е. на которой установлен MS SQL Server), Вы выбираете 32 битную версию или 64 битную. У меня система 64 битная, поэтому я нажимаю на ссылку 64-bit ODAC Downloads.
После перехода на следующую страницу сразу соглашаетесь с условиями лицензионного соглашения, т.е. отмечаете пункт «Accept License Agreement».
Далее Вы выбираете версию ODAC, которая соответствует версии СУБД Oracle.
При этом название файлов с префиксом «Xcopy» означает, что установка будет осуществляться посредством пакетных файлов (батников). Если такого префикса нет, то в данном архиве присутствует некий дистрибутив с графическим интерфейсом.
Итак, как я уже сказал у меня версия Oracle Express Edition 11g, поэтому я выбираю 64-bit ODAC 11.2 Release 5 (11.2.0.3.20) for Windows x64 – это вариант с установкой через графический интерфейс.
В итоге у меня загрузился файл ODAC1120320_x64.zip
Установка Oracle Data Access Components (ODAC)
Распаковываем архив и запускам файл setup.exe.
Шаг 1
Запустится программа установки ODAC, на первом окне мы нажимаем «Next».
Шаг 2
Затем оставляем по умолчанию, т.е. нам нужна установка клиентской части, жмем «Next».
Шаг 3
Далее, если хотите, можете указать каталог для установки ODAC, я предварительно создал папку «OracleOleDB» на диске C специально для этих целей, поэтому я ее и выбираю, жмем «Next».
Шаг 4
Теперь нам необходимо выбрать компоненты, которые мы хотим установить, в нашем случае нам нужен только Oracle Provider for OLE DB и, конечно же, Oracle Instant Client, с остальных компонентов снимаем галочку и жмем «Next».
Шаг 5
Проверяем все параметры установки и жмем «Install».
В итоге начнется процесс установки.
Он будет завершен, когда появится следующее сообщение, жмем «Exit».
Шаг 6
После того как установился провайдер Oracle Provider for OLE DB нам необходимо в каталог «C:OracleOleDBproduct11.2.0client_1NetworkAdmin» (в моем случае) скопировать файл tnsnames.ora с сервера Oracle (из каталога …networkADMIN) или создать самим такой файлик и вписать в него настройки подключения, которые нам сообщит администратор Oracle, например, у меня для Express Edition они вот такие.
XE =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = TestComp)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = XE)
)
)
EXTPROC_CONNECTION_DATA =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SID = PLSExtProc)
(PRESENTATION = RO)
)
)
ORACLR_CONNECTION_DATA =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SID = CLRExtProc)
(PRESENTATION = RO)
)
)
В данном каталоге есть папка Sample, в которой есть пример заполнения файла tnsnames.ora.
После установки Oracle Provider for OLE DB необходимо перезагрузить сервер.

Проверка работы провайдера OraOLEDB.Oracle
Перед тем как переходить к созданию связанного сервера на Microsoft SQL Server необходимо проверить правильно ли мы установили провайдера. Это можно сделать следующим образом. Создайте на рабочем столе простой текстовый файл, например, TestConnect.txt, затем измените его расширение на TestConnect.udl
Запустите его, и у Вас откроется окно «Свойства канала передачи данных». Далее Вам необходимо на вкладке «Поставщик данных» выбрать поставщика, т.е. в нашем случае это «Oracle Provider for OLE DB» и нажать «Далее».
После чего Вы перейдете на вкладку «Соединение», где нужно заполнить параметры подключения:
- Источник данных — адрес сервера Oracle;
- Пользователь – это пользователь для подключения к СУБД Oracle;
- Пароль – соответственно пароль для подключения к СУБД Oracle.
И для проверки связи нажимаем «Проверить соединение».
Если у Вас появилось сообщение «Проверка соединения выполнена», то можете переходить к созданию связанного сервера, если нет, то у Вас что-то с провайдером или с сервером Oracle.
Создание связанного сервера с использованием провайдера OraOLEDB.Oracle
Для того чтобы создать связанный сервер в Microsoft SQL Server запустите среду Management Studio.
Сначала давайте у провайдера изменим один параметр под названием «AllowInProcess» или «Допускать в ходе процесса», так как этого требует провайдер OraOLEDB.Oracle. В остальных случаях не рекомендуется использовать данную опцию, так как в этом случае если произойдет сбой провайдера, то и весь SQL сервер даст сбой.
Для этого в обозревателе объектов найдите контейнер «Объекты сервера -> Связанные серверы-> Поставщики», откройте его и найдите наш провайдер OraOLEDB.Oracle. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и откройте «Свойства».
Отметьте вышеуказанный параметр, т.е. «Допускать в ходе процесса» и нажмите «ОК».
Теперь переходим непосредственно к созданию так называемого Linked-сервера.
Щелкаем правой кнопкой мыши по контейнеру «Связанные серверы» и выбираем «Создать связанный сервер».
Затем вводим параметры связанного сервера, а именно:
- Связанный сервер – имя сервера, т.е. название объекта к которому мы будем обращаться из своих SQL инструкций;
- Поставщик – провайдер, т.е. Oracle Provider for OLE DB;
- Название продукта – Oracle;
- Источник данных – это SID, к которому мы будем подключаться на сервере Oracle (должен быть прописан в файле TNSNAMES.ORA);
Потом переходим на вкладку «Безопасность», выбираем пункт «Устанавливать с использованием следующего контекста безопасности» и вводим логин и пароль от СУБД Oracle. Жмем «ОК».
Все готово, связанный сервер мы создали, и он у нас отобразился в списке связанных серверов в Management Studio. Теперь мы можем обращаться (посылать запросы) к этому связанному серверу, например, у меня на сервере Oracle есть таблица ORACLETABLE, которая содержит просто какой-то список товаров, и для того чтобы осуществить выборку данных из этой таблицы с помощью Management Studio SQL сервера, можно использовать следующие запросы.
SELECT * FROM ORACLEDB..ORACLEUSER.ORACLETABLE
--Или так
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(ORACLEDB,
'SELECT * FROM ORACLETABLE')
Если Вы предпочитаете пользоваться SQL инструкциями, то ниже представлена инструкция, которая делает ровно то же самое что и мы чуть ранее в графическом интерфейсе SSMS.
USE [master]
GO
EXEC sp_MSset_oledb_prop N'OraOLEDB.Oracle', N'AllowInProcess', 1
GO
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'ORACLEDB',
@srvproduct=N'Oracle',
@provider=N'OraOLEDB.Oracle',
@datasrc=N'XE'
GO
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname = N'ORACLEDB',
@locallogin = NULL ,
@useself = N'False',
@rmtuser = N'ORACLEUSER',
@rmtpassword = N'Pa$$w0rd'
GO
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(ORACLEDB,
'SELECT * FROM ORACLETABLE')
Ошибка 7302
«Не удалось создать экземпляр поставщика OLE DB «OraOLEDB.Oracle» для связанного сервера …»
Возможно, отсутствует (или некорректный) путь к каталогу с Instant Client (каталог в который Вы установили ODAC) в системной переменной PATH. Необходимо его прописать и перезапустить SQL сервер. Также возможно параметр ORACLE_HOME задан неверно.
Ошибка 7303
Данная ошибка возвращается SQL сервером в случае, когда не удалось проинициализировать объект источника данных поставщика OLE DB, например, в нашем случае «OraOLEDB.Oracle». Причин, по которым она появляется много, поэтому нам необходимо смотреть ошибку, которую вернул сам провайдер.
Ошибки при инициализации провайдера OraOLEDB.Oracle
| Описание ошибки | Возможные причины, устранение |
| ORA-01017: invalid username/password; logon denied | Неправильно указан логин и пароль к БД Oracle. |
| ORA-12154: TNS:could not resolve the connect identifier specified | Файл tnsnames.ora отсутствует или в нем указан несуществующий SID и SERVICE_NAME. Также возможно Вы неправильно ввели его при создании связанного сервера в строке «Источник данных». |
| ORA-12514: TNS:listener does not currently know of service requested in connect descriptor | В файле tnsnames.ora неправильно введен SERVICE_NAME |
| ORA-12533: TNS:illegal ADDRESS parameters | Некорректное название параметров в файле tnsnames.ora (например, ADDRESS). |
| ORA-12541: TNS:no listener | Ошибка означает, что у Вас в файле tnsnames.ora неправильно указан PORT, на котором работает сервер Oracle. Необходимо узнать на каком порту работает сервер Oracle, и указать его в этом параметре. |
| ORA-12545: Connect failed because target host or object does not exist | Данная ошибка возвращается тогда, когда в файле tnsnames.ora неправильно указан (или просто недоступен) сервер Oracle, т.е. параметр HOST. В данном случае необходимо: проверить данный параметр, проверить доступность сервера. |
В случае если у Вас в каких-нибудь сообщениях выскакивает провайдер OLE DB «MSDAORA» (или любой другой провайдер или вообще он не указан), то это означает, что Вы неправильно выбрали провайдера при создании связанного сервера. MSDAORA – это провайдер от компании Microsoft. OraOLEDB.Oracle – от компании Oracle, как я говорил, рекомендовано использовать провайдер от Oracle.
Теперь давайте рассмотрим несколько ошибок, которые могут возникнуть уже после создания связанного сервера, т.е. связанный сервер создан, но при обращении к его объектам возникает ошибка.
Ошибка 7314
«Поставщик OLE DB «OraOLEDB.Oracle» для связанного сервера «Название сервера» не содержит таблицы «Название таблицы». Таблица либо не существует, либо текущий пользователь не имеет разрешения на доступ к ней.»
Здесь Вы, наверное, ошиблись в написании самого объекта, например, написали имя объекта в неправильном регистре. Oracle чувствителен к регистру, если к нему обращаться через ссылку связанного сервера, например
SELECT * FROM ORACLEDB..ORACLEUSER.OracleTable
В этом случае если таблица OracleTable на сервере Oracle создана как ORACLETABLE, у Вас возникнет ошибка. Чтобы этого избежать, можно указать правильный регистр или использовать конструкцию OPENQUERY, например
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(ORACLEDB, 'SELECT * FROM OracleTable')
Также не исключено что объекта действительно нет или у Вас отсутствуют необходимые разрешения.
Для того чтобы посмотреть, какие объекты и в каком регистре есть на сервере (т.е. узнать точное имя) можно использовать процедуру sp_tables_ex, например
EXEC sp_tables_ex @table_server=«Имя связанного сервера», @table_schema='«Имя пользователя»'
Ошибка 7356
«Поставщик OLE DB «MSDAORA» для связанного сервера «Название сервера» предоставил несогласованные метаданные для столбца.»
Данную ошибку я встречал у поставщика MSDAORA, когда пытался обратиться к таблице, в которой нет данных, т.е. она пустая (нет строк). Эту ошибку можно избежать, если использовать конструкцию OPENQUERY.
Ошибка 7357
«Не удалось обработать объект «Название объекта». Поставщик OLE DB «OraOLEDB.Oracle» для связанного сервера «Название сервера» обнаружил, что у объекта либо нет ни одного столбца, либо текущий пользователь не имеет разрешения на доступ к объекту.»
В данном случае скорей всего Вы пытаетесь обратиться к таблице (или другому объекту) от имени пользователя, который не имеет разрешения на доступ к ней. Другими словами, у пользователя, которого Вы указывали при создании связанного сервера, нет необходимых прав.
Заметка! Если Вас интересует язык SQL, рекомендую почитать мою книгу «SQL код», которая ориентирована на изучение SQL как стандарта, после прочтения книги Вы сможете писать SQL запросы в любой системе управления базами данных.
На этом у меня все, пока!
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hi All,
I am trying to connect linked Server with name given IP,Port ( 10.156.58.59,5986) format with SQL login which has R/access on certain databases. Connecting from SQL 2012 to SQL 2008 R2 . and getting below error.
IT is named instance. SQL browser is running.
what else i am missing to check?
————-
The OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI10» for linked server reported an error. Authentication failed.
Cannot initialize the data source object of OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI10» for linked server.
OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI10» for linked server returned message «Invalid authorization specification». (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 7399)——————————-
TCP Provider: No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it.
OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI10» for linked server «TEST» returned message «Login timeout expired».
OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI10» for linked server returned message «A network-related or instance-specific error has occurred while establishing a connection to SQL Server. Server is not found or not accessible.
OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI10» for linked server «TEST» returned message «Invalid connection string attribute». (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 10061)—————————
Any help would greatly appreciated.
Thank you.
Thank you very much for your time and effort to answer this post. Please Mark As Answer if it is helpful. \Aim To Inspire Rather to Teach Best -Ankit
-
Edited by
Tuesday, February 20, 2018 8:59 PM
-
Edited by
Answers
-
So, what is the error you see when trying this connection string?
10.156.58.59IT,5986
Does an error get written to SQL Log on target server? (SQL server you are linking to)
Try scripted way to create Linked Server:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N‘TEST’, @srvproduct=N‘SQLNCLI’,@provider=N‘SQLNCLI’, @datasrc=N‘10.156.58.59,5986’,
@catalog = N‘yourdatabase’
If that doesn’t work, try including FQDN like this:
EXEC
master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N‘TEST’, @srvproduct=N‘SQLNCLI’,@provider=N‘SQLNCLI’, @datasrc=N‘10.156.58.59.companydomain.com,5986’,
@catalog = N‘yourdatabase’(replace companydomain.com with you’re real domain)
HTH,
Phil Streiff, MCDBA, MCITP, MCSA
-
Edited by
philfactor
Wednesday, February 21, 2018 4:31 PM -
Marked as answer by
-kit
Monday, February 26, 2018 2:54 PM
-
Edited by
-
Do you have Security configured for your SQL account in the Linked Server?
Do you have ‘allow remote connections to this server’ enabled, on the target server?
Are you trying the Link Server to hostname instead of IP address?
hostnameIT,5986
-or-
hostname.companydomain.comIT,5986
HTH,
Phil Streiff, MCDBA, MCITP, MCSA
-
Edited by
philfactor
Wednesday, February 21, 2018 6:50 PM -
Marked as answer by
-kit
Monday, February 26, 2018 2:54 PM
-
Edited by
-
It is irrelevant if you can connect to both A and B from your laptop. What it interesting is if you can RDP into A and then, on the A RDP session connect to B using SSMS.
Tibor Karaszi, SQL Server MVP (Web
Blog)-
Marked as answer by
-kit
Monday, February 26, 2018 2:54 PM
-
Marked as answer by
I’m trying to pull in data from a remote SQL Server. I can access the remote server using SQL authentication; I haven’t had any luck using the same credentials with sp_addlinkedserver.
I’m trying something like this:
Exec sp_dropserver 'Remote', 'droplogins'
go
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver
@server='Remote',
@srvproduct='',
@provider='SQLNCLI',
@datasrc='0.0.0.0'
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
@useself='FALSE',
@rmtsrvname='Remote',
@rmtuser='User',
@rmtpassword='Secret'
Select Top 10 * from Remote.DatabaseName.dbo.TableName
Here’s what I get:
OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI" for linked server "Remote" returned message "Login timeout expired". OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI" for linked server "Remote" returned message "An error has occurred while establishing a connection to the server. When connecting to SQL Server 2005, this failure may be caused by the fact that under the default settings SQL Server does not allow remote connections.". Msg 53, Level 16, State 1, Line 0 Named Pipes Provider: Could not open a connection to SQL Server [53].
Again, I can access the server directly (in SQL Management Studio) using these exact credentials, so it’s not a problem with my network or credentials.
Most of the examples I’ve seen online seem to involve Windows domain accounts, as opposed to SQL security logins. Does this not work with SQL authentication?
Loading…
Abstract
This article details the use of «Execute AT LinkedServer» clause. It’s best in some ways when you are trying to run dynamic complex queries across heterogeneous data source. There are many instances that OpenQuery/OpenRowSet and four-part qualifier calling
might not work in the complex SQL design. The limitation of a linked server will explode when are trying to manipulate data and write complex queries with heterogeneous data sources.
↑ Return to Top
Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Pre-requisites
- Known Errors
- Error 1: Th e object has no columns or the current user does not have permissions on that object
- Error 2: Unable to begin Distributed transaction
- Error 3: The Transaction Manager has disabled its support for remote/network transactions
- Conclusion
- References
- Further Reading
↑ Return to Top
Introduction
We recently ended up in calling a remote stored procedure(“X”) from a remote machine (“Y”) and the script needed to pull data and store into a remote server(“Z”). We set up the linked server and everything was working great. Executing queries to pull the
data to my machine was fine, but a problem arose when we needed to execute a stored procedure which houses complex SQL queries from the other remote server.
The three methods we have tried to execute the SP on remote server are:
- Calling with four-part naming convention
- Using OpenQuery and OpenRowSet
- Execute At LinkedServer
The first method was not successful since there is a dependency on inbound and outbound transactions. It was successful in the execution of the SP using Execute(‘SQL’) AT LinkedServer. The details are illustrated in this article.
↑ Return to Top
Pre-requisites
- Make sure RPC and RPC Out parameters are set to TRUE
- MSDTC is enabled to run distributed queries
Syntax
Execute a pass-through command against a linked server
{ EXEC | EXECUTE }
( { @string_variable | [ N ]
'command_string [ ? ]'
} [ + ...n ]
[ { , { value | @variable [ OUTPUT ] } } [ ...n ] ]
)
[ AS { LOGIN | USER } =
' name ' ]
[ AT linked_server_name ]
[;]
E xample,
DECLARE @Script nvarchar(max) =
N'
<dynamic sql script>
';
EXECUTE (@Script) AT <linked_server_name>
INSERT <table> (columns)
EXECUTE (@Script) AT <linked server>;
SQL could be a single query or a sequence of statements, dynamic SQL, or be entirely static. The linked server could be an instance of SQL, Oracle, DB2, etc. The use of Openquery, Openrowset and four-part calling stored procedure might work in simple
cases. When you are working with distributed queries with heterogeneous data source the use of EXECUTE … AT LinkedServer works best. The SQL Server extends the EXECUTE statement so that it can be used to send pass-through commands to linked servers. Additionally,
the context in which a string or command is executed can be explicitly set.
↑ Return to Top
Known Errors
Error 1: The object has no columns or the current user does not have permissions on that object
"Cannot process the object "<query text>".The OLE DB provider "<provider>" for linked Server "<server>" indicates that either the object has
no columns or the current user does not have permissions on that object"
The OpenQuery and OpenRowset are often best used with the simple SELECT statement. By adding ‘SET FMTONLY OFF; SET NOCOUNT ON;’ to SQL string will ignore validating the output format and it will return the data as is. The OPENROWSET command operates
the same as the OPENQUERY command but OpenRowSet provides a flexibility in creating dynamic connections.
SELECT
* FROM
OPENQUERY(ADDBSP18,'SET FMTONLY ON; exec MES_DW2_PROD.dbo.SPTrans_Tracs_Pull_Prashanth ''7/1/2016'',''7/31/2016''')
The reason for the error is that when you execute a stored procedure on a linked server, the provider first tries to determine the shape of the resulting row set. It does this by issuing SET FMTONLY ON; There are multiple ways to handle this type of situations
within the SP itself that is avoiding the use temp tables.
Error 2: Unable to begin Distributed transaction
«The operation could not be performed because OLE DB provider «SQLNCLI» for linked server «X» was unable to begin a distributed transaction»
To re-enable the RCP commands for the linked server:
exec sp_serveroption @server='SERVERNAME1', @optname='rpc', @optvalue='true'
exec sp_serveroption @server='SERVERNAME1', @optname='rpc out', @optvalue='true'
Calling remote SP with four-part qualifier name.
EXEC ADBSP18.DW_PROD.dbo. [trans_Tracs_Pull]'7/1/2016','7/31/2016'
Error 3: The Transaction Manager has disabled its support for remote/network transactions
“The operation could not be performed OLD DB provider “SQLNCLI10” for linked server “MYSERVER” was unable to begin a distributed transaction.The transaction manager
has disabled its support for remote/network transactions.“
To enable inbound and outbound transaction setting on MSDTC, follow the steps given below. Do the same setting on both servers(Local and Remote Server).
In this case, the remote server was configured with IBM I-Series driver.
- Open “Component Services” Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Component Services
- In Component Services, right click “My Computer” and select “Properties” Console Root > Component Services > Computers > My Computer
- Select the “MSDTC” tab (Select appropriate MSDTC if it’s clustered) and click “Security Configuration” in the “Transaction Configuration”
Enable Allow inbound and Allow outbound.
- Restart the DTC service (should do so automatically).
The below example shows the execution of distributed query executed on the remote server which fetches the data and writes it an another remote SQL instance.
↑ Return to Top
Conclusion
You can safely use Linked Servers in a production setting but do your research and test before settling on a solution. In many cases, the simple approach may ease out the problem.
The OPENQUERY/OPENROWSET guarantees the SQL will execute on the remote server and only bring back the results from that query to the local server.In many cases, this can be used for simple SQL statements and it row set doesn’t
hold in any temporary tables. When the SQL is getting complex and needs to query heterogeneous data source, It may get little cumbersome. EXEC() AT is similar to OPENQUERY/OPENQUERY in that the static SQL/dynamic SQL will always execute on the remote server
except that you cannot use the results locally within a JOIN but you can use them, however, to INSERT them into a local table. Also, EXEC() AT allows you to provide SQL in a variable whereas OPENQUERY will not accept a variable which many times forces the
use of dynamic SQL.
As usual, any feedback is welcome. Hope that this article was helpful to you!
↑ Return to Top
References
Technet
EXECUTE (Transact-SQL)
- https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188332(v=sql.100).aspx
Further Reading
- http://dba.stackexchange.com/questions/46289/which-one-is-more-efficient-select-from-linked-server-or-insert-into-linked-ser/46302#46302
↑ Return to Top
Problem:
You created a linked server on SQL Server to a PostgreSQL database. You can open and navigate the linked server on SSMS up to listing the tables, but can not perform select to certain tables, returning the below errors:
The OLE DB provider “MSDASQL” for linked server “LinkedServername” returned message “Requested conversion is not supported.”.
Msg 7341, Level 16, State 2, Line 43
Cannot get the current row value of column “[MSDASQL].ColumnName” from OLE DB provider “MSDASQL” for linked server “LinkedServername”.
Msg 7356, Level 16, State 1, Line 53
The OLE DB provider “MSDASQL” for linked server “pLinkedServername” supplied inconsistent metadata for a column. The column “ColumnName” (compile-time ordinal 15) of object “”DatabaseName”.”SchemaName”.”ColumnName”” was reported to have a “DBCOLUMNFLAGS_ISLONG” of 128 at compile time and 0 at run time.
The data type throwing the error can either be a varchar, text, or Boolean. It also happens whether the specific column is included in the select statement or not.
Cause:
This happens because of a mismatch with the length of the data type or an incorrect conversion from the source data type in PostgreSQL and SQL Server.
Workaround:
You can work around this issue by force casting the selected column to a specific data type. This solution will work for data types that have different lengths on Postgresql and SQL Server. It will not work for incorrect conversions. eg. the column in PostgreSQL is a Boolean and the linked server want to receive it as a char value. For the proper solution, refer to to the section below.
Solution:
To address the issue properly, it all comes down to creating your Linked server correctly. Here are the proper steps for creating a SQL Server linked server to a PostgreSQL database:
1. Download and install the latest ODBC driver for the PostgreSQL version that you are using. There used to be a lot of third party ODBC for PostgreSQL since they didn’t come out of one for 64 bit – and most SQL Server deployments out there are 64 bit. But now PostgreSQL has released their own. You can download the drivers here.
2. After installing the driver, create a 64 bit ODBC System DSN pointing to your PostgreSQL. Launch the ODBC Data Source Administrator on the server where the SQL Server is. If you want the DSN to be available for everyone which you should if you are going to use it for the linked server, go to the System DSN tab. Click Add.
3. Now there are two drivers that the Postgres has added. One for Unicode and a default one. The Unicode driver is for modern applications that have wider character sets and for Postgresql databases that are encoded with UTF-8/Unicode. You should likely be using this. The other details are self-explanatory. Those are the details for your PostgreSQL, database, server, user name, SSL Mode, port, password, description for the DSN, and the data source which will be the name of your DSN. You can click test after filling out the details to verify the connectivity.
4. Now this is the important part if you are receiving the conversion errors mentioned in this post. Under Options, click on Datasource. This will launch the Advanced Options window for the Datasource. From here you can set how the DSN will treat the data being retrieved from the source.
5. You can set how it will treat certain data types. For this scenario/issue, you’ll need to uncheck the “Bools as Char” under data type options and treat Text as LongVarChar. You can also set Unknown Sizes to Maximum. The Max Varchar and MaxLongVarChar values can be left as default. But if you are hitting issues with length for varchar data types, you may adjust them accordingly.
6. Now that you have your ODBC DSN set correctly, you can recreate/create your Linked Server. You can use SSMS GUI. Log in to your SQL Server and navigate to Server Objects -> Right click Linked Servers and choose New Linked Servers.
7. Key in the name you want for your linked server. Choose Other Data source on server type and choose Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers. You can put PostgreSQL on Product Name for clarity, then on Data Source input the DSN Name you created earlier.
8. Choose Security on the Left tab to configure the security for the linked server. Choose “Be made using this security context” and key in your username and password.
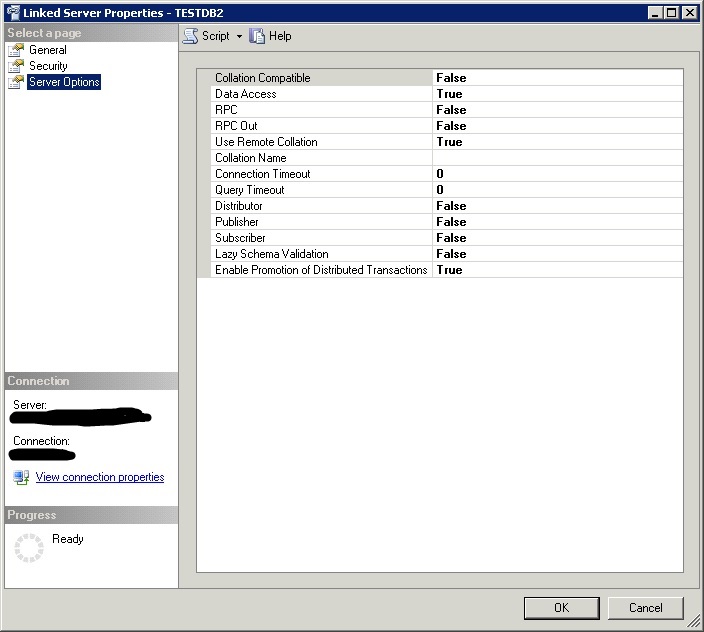
9. Choose Server Options on the left tab to change some settings as shown below. Note the changes on RPC settings.
10. Click OK. Now it will attempt to connect first. If all is well, it will be able to save and appear on your Linked Server list. If it can’t connect currently it will tell you.
11. Now try selecting again. You should be able to select properly without encountering the errors.
12. You can also create the SQL Server Linked Server using the TSQL script below:
USE [master]
go
EXEC master.dbo.Sp_addlinkedserver @server = N’LinkedServerName’, @srvproduct=N’Postgresql’, @provider=N’MSDASQL’,
@datasrc=N’DSN.Name’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’collation compatible’, @optvalue=N’false’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’data access’, @optvalue=N’true’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’dist’, @optvalue=N’false’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’pub’, @optvalue=N’false’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’rpc’, @optvalue=N’true’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’rpc out’, @optvalue=N’false’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’sub’, @optvalue=N’false’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’connect timeout’, @optvalue=N’0′
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’collation name’, @optvalue=NULL
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’lazy schema validation’, @optvalue=N’false’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’query timeout’, @optvalue=N’0′
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’use remote collation’, @optvalue=N’true’
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_serveroption @server=N’LinkedServerName’, @optname=N’remote proc transaction promotion’, @optvalue=N’true’
goUSE [master]
goEXEC master.dbo.Sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname = N’LinkedServerName’, @locallogin = NULL, @useself = N’False’, @rmtuser = N’pgsqlUserName’, @rmtpassword = N’pgsqlUserNamePasswordHere’
go
This should address the conversion issues and you’ll be able to select without any issue.
Want to talk with an expert? Schedule a call with our team to get the conversation started.
Your error here is
server not found
This is because you used @srvproduct=N'SQL Server', in this case you should use SQL Server’s pc name in case of default instance, i.e. this connection string would be correct in case of default instance:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_pc_name', @srvproduct=N'SQL Server'
or use this one in case of named instance:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_pc_nameinst_name', @srvproduct=N'SQL Server'
If you want to use any other name, even just IP (or IP,port in case of named instance, use @provider=N'SQLNCLI':
for default instance
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_linked_server_name_as_I_want_it', @srvproduct=N'', @provider=N'SQLNCLI', @datasrc=N'10.237.69.11'
for named instance:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_linked_server_name_as_I_want_it', @srvproduct=N'', @provider=N'SQLNCLI', @datasrc=N'10.237.69.11,your_port'
If you want to use GUI (SSMS), or change server name to your pc name, or use another radio button position, for ex. SQL Native Client (other than SQL Server)
Normally, it is easy enough to setup a Linked Server on SQL Server to other data sources. Problems are usually caused by one of the usual culprits that have to be addressed
- SQL Logins simply do not work well when trying to do this type of setup
- The Windows login has to have permissions to the file (on a drive or network share)
- The appropriate drivers have to be setup (64 bit / 32 bit)
- …will add more here based on user comments to this post
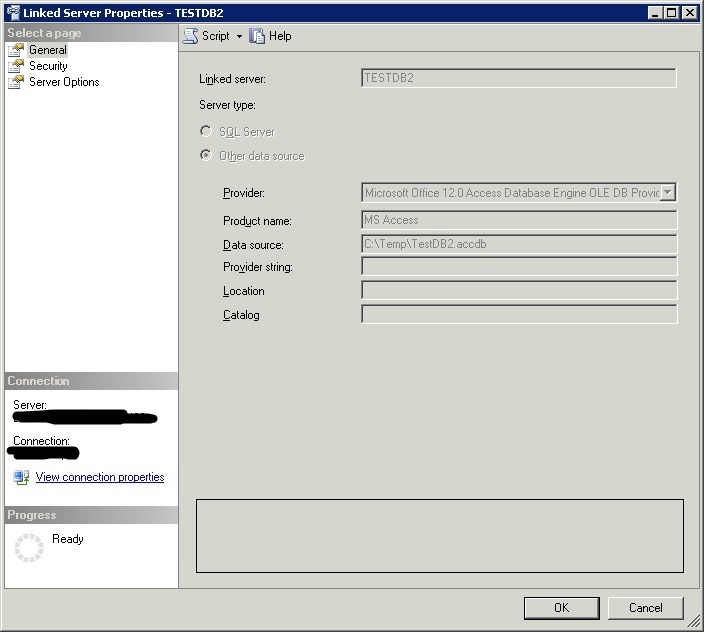
After creating my Linked Server to MS Access, using my admin account (Windows login is part of local administrators), everything was fine. However, when the user tried to access it, he ran into errors.
Let us begin with how I setup the Linked Server:
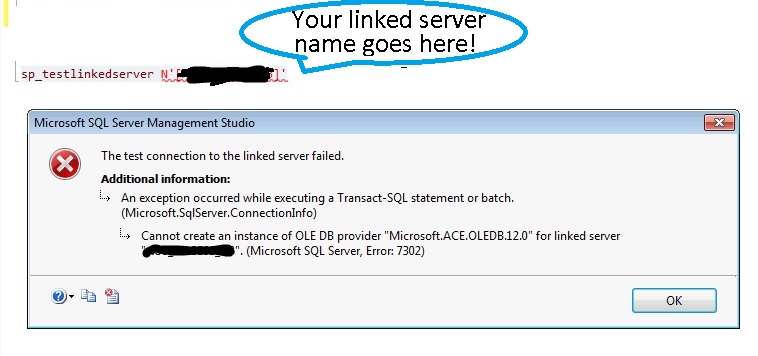
The first error was:
I searched and found this solution to fix the issue:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_MSset_oledb_prop
N'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0',
N'AllowInProcess',
1
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_MSset_oledb_prop
N'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0',
N'DynamicParameters',
1
GO
It works on my machine moment!
At this point, as an Windows admin user, I was able to test the link and query it fine and run queries against my Linked Server without any issues.
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([TESTDB], 'SELECT * FROM Table1')
However, non-Windows admin users were running into this error when they tried to use the same Linked Server.
TITLE: Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
——————————The test connection to the linked server failed.
——————————
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:An exception occurred while executing a Transact-SQL statement or batch. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
——————————
Cannot initialize the data source object of OLE DB provider “Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0” for linked server “TESTDB2”.
OLE DB provider “Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0” for linked server “TESTDB2” returned message “Unspecified error”. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 7303)For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft%20SQL%20Server&ProdVer=12.00.2000&EvtSrc=MSSQLServer&EvtID=7303&LinkId=20476
——————————
BUTTONS:OK
——————————
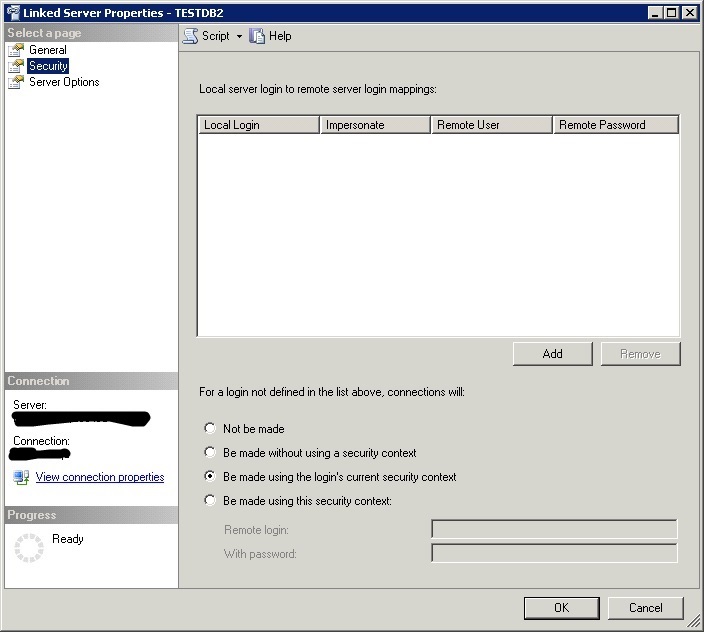
I figured that it had to do with permissions to the MS Access file/folder but that was not it. I tried the different security options for the user in the “security” tab of the Linked Server properties but that nothing helped.
So, I reached out to my fellow DBA’s to see if they had seen anything like it and one of them suggested this solution based on an error in the Event Log
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/dataaccesstechnologies/2011/09/28/troubleshooting-cannot-create-an-instance-of-ole-db-provider/
Event log message was:
The machine-default permission settings do not grant Local Activation permission for the COM Server application with CLSID
{2206CDB0-19C1-11D1-89E0-00C04FD7A829}
and APPID
{2206CDB0-19C1-11D1-89E0-00C04FD7A829}
to the user [******] SID (S-1-5-21-1935393997-861567501-725345543-90175) from address LocalHost (Using LRPC). This security permission can be modified using the Component Services administrative tool.
However, this did not work either!
The Solution:
At my behest, another DBA fought through the issue and discovered that giving read/write privileges to the Temp folder of the SQL service account user is what fixes the issue. Keep reading for the details..
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/814398
Here it is in his own words:
We got this working…. It turns out the user running the query needs to have R/W access to the temp directory of the SQL Server service account. This seems like a very silly and very insecure thing to me.
I came across this discussion below and gave my non-admin account RW access to the SQL Server Service account’s default temp folder and it worked. I’ve granted RW access to non-admin user who was experiencing issues.
https://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/sqlserver/en-US/6f663ab8-c75d-419b-a4bf-bb6c0f5b84c4/ole-db-provider-microsoftaceoledb120-for-linked-server-null-returned-message-unspecified?forum=transactsql
I just added Read/Write Rights on the folder C:Users\AppDataLocalTemp and everything started to work. Please note this is different from what most articles recommend doing which is to give Read/Write rights to folder C:WindowsServiceProfilesNetworkServiceAppDataLocalTemp folder
The link below also has the two solutions that I tried but I found it after I fixed the issue:
http://sqlish.com/msg-7302-level-16-state-1-line-1-cannot-create-an-instance-of-ole-db-provider-%E2%80%9Cmicrosoft-ace-oledb-12-0%E2%80%9D-for-linked-server-%E2%80%9Cnull%E2%80%9D/
At the least, this post will act as a reference for myself. At best, it will fix your MS Access Linked Server problem for you. In any case, please leave feedback that might help other readers. What should have been a simple 10 minute thing, turned into a day or two thing for me!
Creating a new Linked Server in MSSQL seems to be one of the easiest DBA’s tasks. It might however happen that some problems occur. How to deal with a failed connection test? Let me describe the issue I faced and how I solved it.
What is a Linked Server?
Linked Servers are used to enable one SQL Server Database Engine to read data from another remote datasource and execute T-SQL statements on remote database objects. The remote data source does not have to necessarily be only another SQL Server instance, the provider might be i.a. Oracle database or Azure CosmosDB. The purpose of creating a Linked Server is to enable quick and seamless data integration between various data sources
Required Permissions
Let’s imagine that our internal client asks us to join a short 15-minute meeting and expects us to create a Linked Server during that call. We are informed that it’s a very typical implementation, which has already been introduced on another internal environment and we will be provided will all necessary information. The only reason we are needed on that call is that because we obey the security rules and do not grant sysadmin rights to anyone outside our DBA team, which helps us keep an eye on all significant events on our DB environment.
Linked Server successfully created but connection test failed
So coming back to our case study, the stakeholder provided us with the query which was used on another instance and they claim that it should work with no issues. Our job was just to click “Execute” on the supposedly-perfect query from our admin account and to report success. Well, the Linked Server has beed created, but the simple test connection failed. Why? Let’s discover.
Please note that for this article’s purpose I’ll show the GUI troubleshooting path, not the T-SQL query.
So we’ve been provided with the Linked Server name, data source Provider, source server address (Data source) and the database name (Catalog).
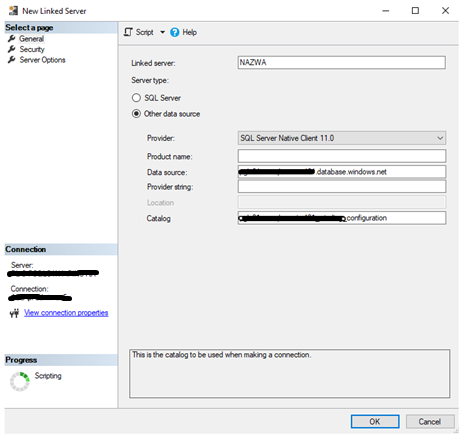
Want to talk with an expert? Schedule a call with our team to get the conversation started.
Your error here is
server not found
This is because you used @srvproduct=N'SQL Server', in this case you should use SQL Server’s pc name in case of default instance, i.e. this connection string would be correct in case of default instance:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_pc_name', @srvproduct=N'SQL Server'
or use this one in case of named instance:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_pc_nameinst_name', @srvproduct=N'SQL Server'
If you want to use any other name, even just IP (or IP,port in case of named instance, use @provider=N'SQLNCLI':
for default instance
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_linked_server_name_as_I_want_it', @srvproduct=N'', @provider=N'SQLNCLI', @datasrc=N'10.237.69.11'
for named instance:
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'my_linked_server_name_as_I_want_it', @srvproduct=N'', @provider=N'SQLNCLI', @datasrc=N'10.237.69.11,your_port'
If you want to use GUI (SSMS), or change server name to your pc name, or use another radio button position, for ex. SQL Native Client (other than SQL Server)
Normally, it is easy enough to setup a Linked Server on SQL Server to other data sources. Problems are usually caused by one of the usual culprits that have to be addressed
- SQL Logins simply do not work well when trying to do this type of setup
- The Windows login has to have permissions to the file (on a drive or network share)
- The appropriate drivers have to be setup (64 bit / 32 bit)
- …will add more here based on user comments to this post
After creating my Linked Server to MS Access, using my admin account (Windows login is part of local administrators), everything was fine. However, when the user tried to access it, he ran into errors.
Let us begin with how I setup the Linked Server:
The first error was:
I searched and found this solution to fix the issue:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_MSset_oledb_prop
N'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0',
N'AllowInProcess',
1
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_MSset_oledb_prop
N'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0',
N'DynamicParameters',
1
GO
It works on my machine moment!
At this point, as an Windows admin user, I was able to test the link and query it fine and run queries against my Linked Server without any issues.
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY([TESTDB], 'SELECT * FROM Table1')
However, non-Windows admin users were running into this error when they tried to use the same Linked Server.
TITLE: Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
——————————The test connection to the linked server failed.
——————————
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:An exception occurred while executing a Transact-SQL statement or batch. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
——————————
Cannot initialize the data source object of OLE DB provider “Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0” for linked server “TESTDB2”.
OLE DB provider “Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0” for linked server “TESTDB2” returned message “Unspecified error”. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 7303)For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft%20SQL%20Server&ProdVer=12.00.2000&EvtSrc=MSSQLServer&EvtID=7303&LinkId=20476
——————————
BUTTONS:OK
——————————
I figured that it had to do with permissions to the MS Access file/folder but that was not it. I tried the different security options for the user in the “security” tab of the Linked Server properties but that nothing helped.
So, I reached out to my fellow DBA’s to see if they had seen anything like it and one of them suggested this solution based on an error in the Event Log
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/dataaccesstechnologies/2011/09/28/troubleshooting-cannot-create-an-instance-of-ole-db-provider/
Event log message was:
The machine-default permission settings do not grant Local Activation permission for the COM Server application with CLSID
{2206CDB0-19C1-11D1-89E0-00C04FD7A829}
and APPID
{2206CDB0-19C1-11D1-89E0-00C04FD7A829}
to the user [******] SID (S-1-5-21-1935393997-861567501-725345543-90175) from address LocalHost (Using LRPC). This security permission can be modified using the Component Services administrative tool.
However, this did not work either!
The Solution:
At my behest, another DBA fought through the issue and discovered that giving read/write privileges to the Temp folder of the SQL service account user is what fixes the issue. Keep reading for the details..
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/814398
Here it is in his own words:
We got this working…. It turns out the user running the query needs to have R/W access to the temp directory of the SQL Server service account. This seems like a very silly and very insecure thing to me.
I came across this discussion below and gave my non-admin account RW access to the SQL Server Service account’s default temp folder and it worked. I’ve granted RW access to non-admin user who was experiencing issues.
https://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/sqlserver/en-US/6f663ab8-c75d-419b-a4bf-bb6c0f5b84c4/ole-db-provider-microsoftaceoledb120-for-linked-server-null-returned-message-unspecified?forum=transactsql
I just added Read/Write Rights on the folder C:Users\AppDataLocalTemp and everything started to work. Please note this is different from what most articles recommend doing which is to give Read/Write rights to folder C:WindowsServiceProfilesNetworkServiceAppDataLocalTemp folder
The link below also has the two solutions that I tried but I found it after I fixed the issue:
http://sqlish.com/msg-7302-level-16-state-1-line-1-cannot-create-an-instance-of-ole-db-provider-%E2%80%9Cmicrosoft-ace-oledb-12-0%E2%80%9D-for-linked-server-%E2%80%9Cnull%E2%80%9D/
At the least, this post will act as a reference for myself. At best, it will fix your MS Access Linked Server problem for you. In any case, please leave feedback that might help other readers. What should have been a simple 10 minute thing, turned into a day or two thing for me!
Creating a new Linked Server in MSSQL seems to be one of the easiest DBA’s tasks. It might however happen that some problems occur. How to deal with a failed connection test? Let me describe the issue I faced and how I solved it.
What is a Linked Server?
Linked Servers are used to enable one SQL Server Database Engine to read data from another remote datasource and execute T-SQL statements on remote database objects. The remote data source does not have to necessarily be only another SQL Server instance, the provider might be i.a. Oracle database or Azure CosmosDB. The purpose of creating a Linked Server is to enable quick and seamless data integration between various data sources
Required Permissions
Let’s imagine that our internal client asks us to join a short 15-minute meeting and expects us to create a Linked Server during that call. We are informed that it’s a very typical implementation, which has already been introduced on another internal environment and we will be provided will all necessary information. The only reason we are needed on that call is that because we obey the security rules and do not grant sysadmin rights to anyone outside our DBA team, which helps us keep an eye on all significant events on our DB environment.
Linked Server successfully created but connection test failed
So coming back to our case study, the stakeholder provided us with the query which was used on another instance and they claim that it should work with no issues. Our job was just to click “Execute” on the supposedly-perfect query from our admin account and to report success. Well, the Linked Server has beed created, but the simple test connection failed. Why? Let’s discover.
Please note that for this article’s purpose I’ll show the GUI troubleshooting path, not the T-SQL query.
So we’ve been provided with the Linked Server name, data source Provider, source server address (Data source) and the database name (Catalog).
In the Security tab we’re to choose the fourth option – the connection will be made using this security option – all we have to do is just to enter the username and password we’ve received from the client.
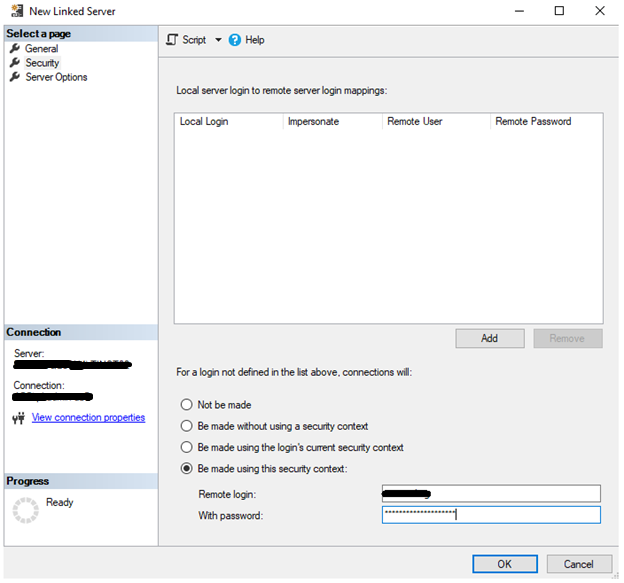
And that’s it. We know the source server address, the source database name and we have a user’s credentials which has proper access scope. We’re clicking OK. What could go wrong?
Yikes! The error dialog appears:
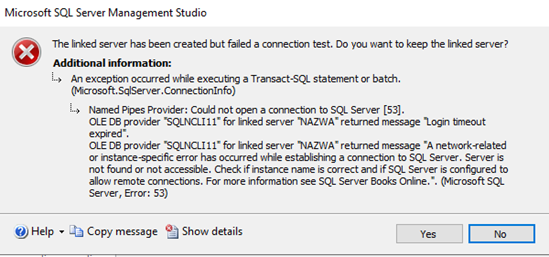
Unfortunately, something went wrong. Let’s cautiously read what the error message says, it might be help us chose what to do next:
- Could not open a connection to SQL Server,
- Login timeout expired,
- A network-related or instance-specific error has occured while establishing a connection to SQL Server. Serves is not found or not accessible – It’s a very common Error 53, suggesting that the server address is either incorrect or it does not allow remote connections.
Solve your problem with these steps
I’ll provide the troubleshooting path which I followed and finally found out how to successfully establish connection between my server and the one we’re trying to link to. If my solution does not fit for you, I’d suggest firstly contacting the source server’s DBA and asking him to confirm if they do allow remote connections. This can be verified by opening SQL Server’s instance properties > Connections tab.
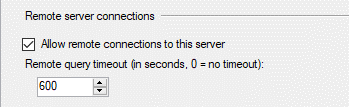
Before contacting another DBA, the steps I’ve taken were:
1. Check for typos and pinged the source server
Obvious – but worth checking. Double-check if you’ve properly entered/pasted the server address, database name, user’s credentials. Try pinging the server you’re supposed to connect to. Ping request could not find host <hostname> might be alarming
2. Check the user’s permissions
A simple verification we may do is to try to log in with the provided credentials to the source server.
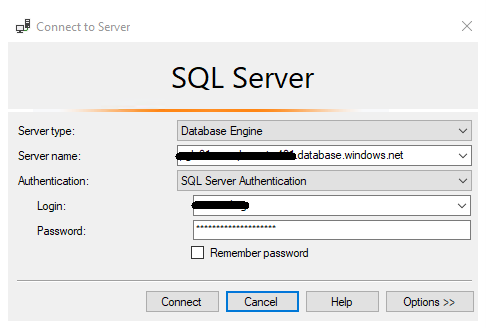
The error I got is clear: my machine is not able to recognize the host we’re trying to connect to.
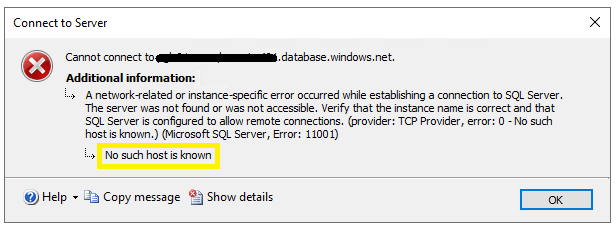
Perfect, then we are almost there. No woder why ping request could not find the host if we’re trying to connect to an external domain (we should’ve asked the stakeholder to describe the source server’s parameters more precisely). Anyway, the solution is very simple – we have to edit the hosts file and help our local machine connect to an external source.
3. Add the server IP and DNS in the hosts file
On the server where your SQL Server engine is installed go to the following file: C:Windowssystem32driversetchosts.
Before changing any system file – don’t forget to save its copy somewhere else – just in case. Let’s open the hosts file in the Notepad and add in the last row the IP address and DNS name of the desired server.
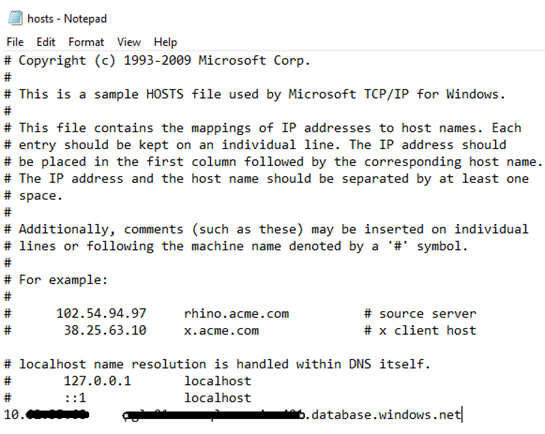
Just to remind – the “#” symbol serves for commenting out the rest of the row. In our case we do not want the hash at the beginning of our entry. After entering the correct value, save the file and go back to SQL Server Management Studio.
4. Repeat step 2 – try to connect with the user’s credentials
Let’s try connecting again to check if the error message has changed.
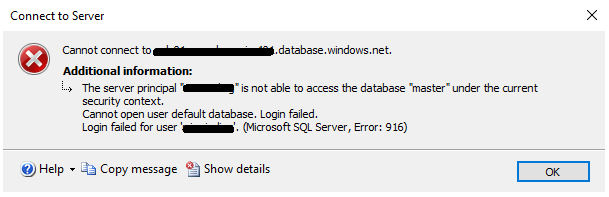
The message “no such host known” does not appear anymore! In my case the error says that the user does not have access to the master database which is its default database. In our case it’s not a problem, since the Linked Server is configured to connect to a particular database. Step 5 is optional – if you don’t have time to satisfy your curiosity, go directly to step 6.
5. Connect to a non-default database
Choose the SQL Server Authentication option, enter the server name and user credentials and do not click automatically Connect but click Options >> in the right bottom corner.
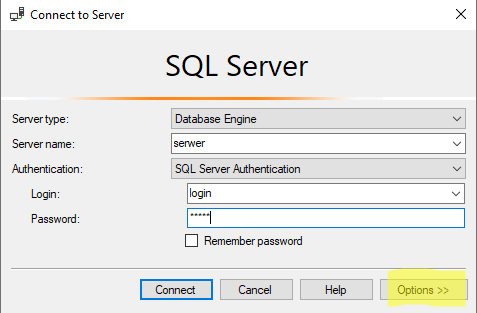
Next change the database name from <default> to the one you want to connect to.
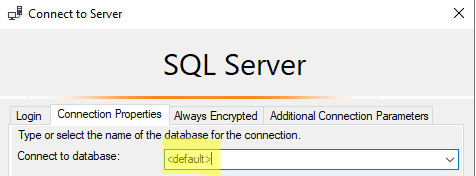
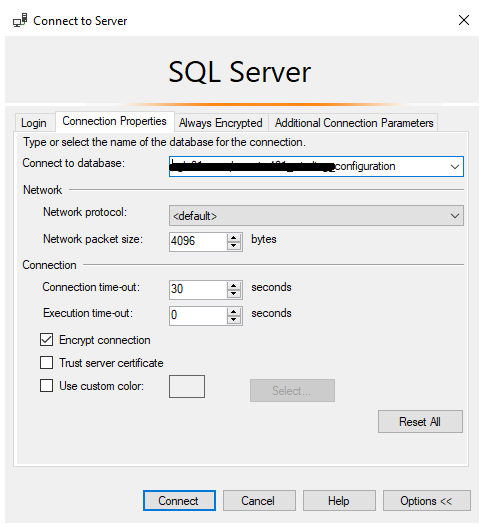
After clicking Connect we’ve been successfully logged on the source server:
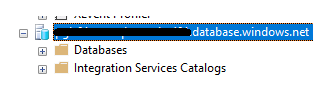
Then we can get back to the Linked Server creation.
6. Create the Linked Server
Finally, let’s re-enter the parameters the customer provided us with and try to create the Linked Server again. In my case no error message appeared and the Linked Server object has been successfully created.
Right-click on the newly created Linked Server and choose Test Connection.
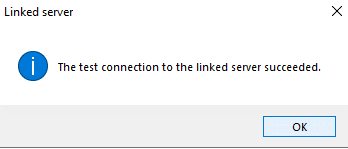
The reply we get is that the test connection was successful. The job is done!
The reason we failed to create the Linked Server immediately with the information provided by the requestor was not due to insufficient data from the client nor incorrect credentials. What we missed was asking ourselves (or the client) – where is the source server located. As it was not in our corporate domain, it was our duty to help our local machine connect to an external source by adding a row in the hosts file.
Any questions on how to configure a Linked Server? Are you wondering how such solution may boost your business?
Schedule a free consultation. Consult your company needs with our experts. Learn about solutions that will help your company improve business processes and ensure data security.