Summary:
This blog will discuss version-specific occurrences of the SQL Server Error 3013, the reasons behind the error, and methods to fix it. If you cannot restore the database (DB) from backup, it usually means that the backup (.bak) file is damaged or corrupt. There is no manual method to restore the database from a corrupt .bak file. In that case, use Stellar Repair for MS SQL Technician for backup recovery to recover the DB from the backup (.bak) file.

Contents
- Version-Specific Occurrences of SQL Error 3013
- What Causes SQL Server Error 3013?
- Methods to Fix SQL Server Error 3013
- What if You Cannot Restore SQL Server Database from Backup?
- Conclusion
Sometimes, when performing an SQL Server database (DB) backup to a storage device or trying to restore the DB from backup, you may encounter the following error message:
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
The frequency of this error may vary depending on the versions of SQL Server application you are using.
Version-Specific Occurrences of SQL Error 3013
- SQL Server 7.0: In this SQL version, the error occurs when a clustered index is created in every filegroup of the table. The error message is as follows:
- SQL Server 2000: If the database of volume less than 2 GB is already available and an attempt is made to back up another database having more than the existing volume, it results in 3013 error code. And, you will receive an error message similar to:

- SQL Server 2005: In this version, the error occurs when Backup Administrator tries to restore data files and log files together in a single instance of time. The error message appears as:

What Causes SQL Server Error 3013?
Plausible reasons that result in SQL Server restore database is terminating abnormally error are as follows:
- An attempt to view the Network drive has been made by an unauthorized user.
- The storage device, on which the backup file (.bak) is stored, has failed.
- A write failure has occurred during backup creation.
- When there is not enough storage on the backup drive.
- When an attempt is made to execute backup on transactional logs when Database is in SUSPECT mode.
Methods to Fix SQL Server Error 3013
NOTE: Since backup has terminated abruptly, avoid rewriting the same backup, as it may result in the same error again.
Depending on the version-specific occurrence of SQL Server Error 3013, follow these methods to fix the error:
NOTE: Methods 1, 2, and 3 may resolve the problem, provided the error has not occurred during backup restoration. But, if you have encountered backup failed error 3013 during the restoration process, skip to Method 4.
Method 1 – Check the Security Permission for User
Follow these steps to check if a user is denied permission to take DB backups in SQL Server:
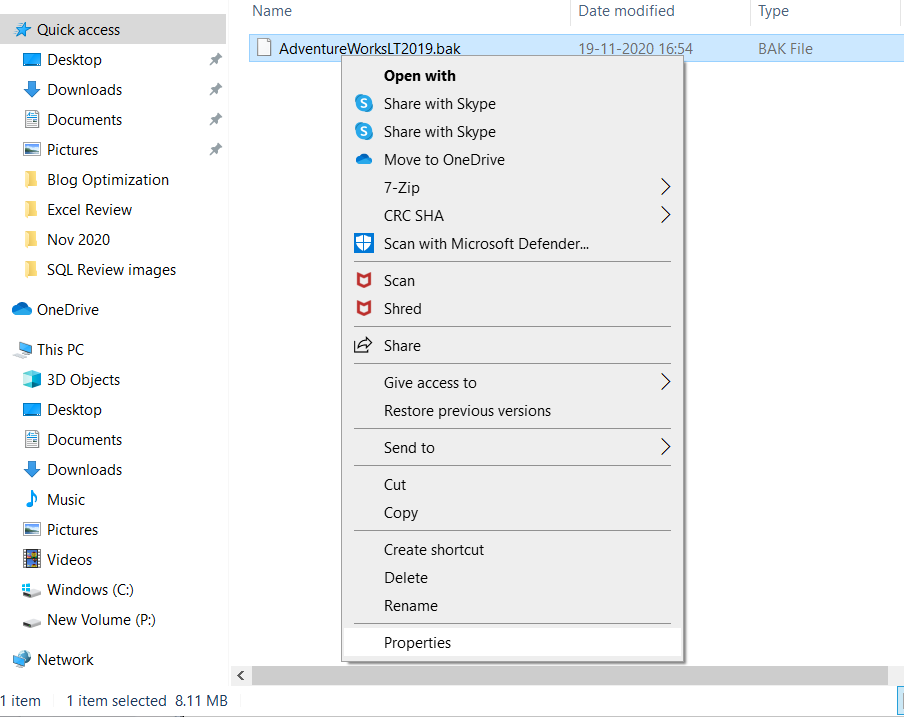
Step 1: Browse the location of the backup folder to find the database ‘.bak’ file.
Step 2: Right-click the backup file, and select Properties.
Step 3: In the Properties window, click the Security Tab.
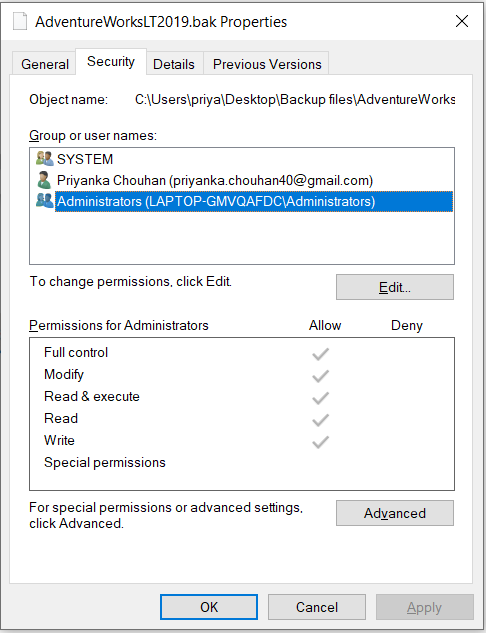
Step 4: Now check the Deny permissions for Authenticated Users.
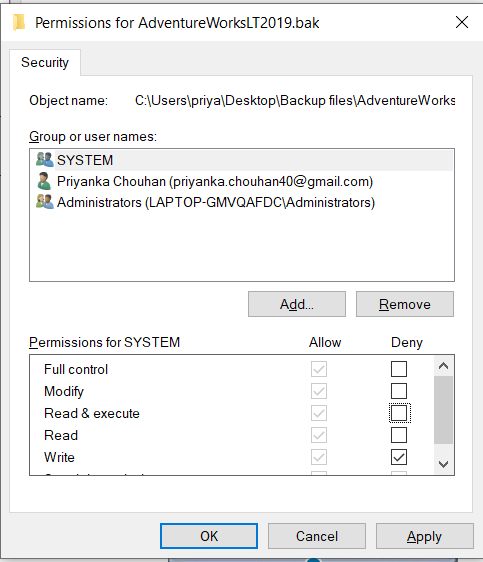
Step 5: Click Edit and remove the denied permission.
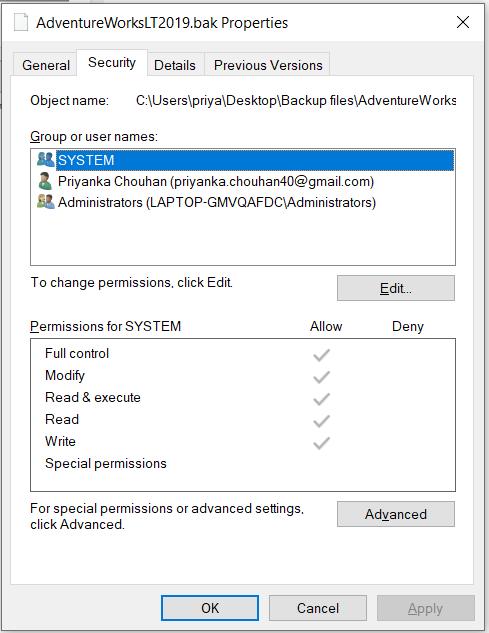
Step 6: Click OK.
Method 2 – Delete the Previous Backup
Manually delete the previous backup and enable the SQL server to execute new backups to the backup device to fix the error. Use the following command for manual deletion of the last backup:
BACKUP DATABASE mydatabase TO DISK= ‘C:Mydatabase.bak’ with formatMethod 3 – Perform Full Backup Restoration
Sometimes, partial restoration is not the solution, try performing a full backup restoration technique. To perform a full backup, first, uninstall the backup application followed by re-installation. Check that the account under which SQL service binds is the member of “Domain User Group” and has been provided with ‘Write’ access to the Windows server.
Method 4 – Try Retrieving another Backup Set
If backup restoration is behind the error, try retrieving other backup sets within the backup device by specifying the file number.
NOTE: The file number signifies the backup set series that needs to be restored.
Run the following command to retrieve the backup set from Query Analyzer:
RESTORE HEADERONLY FROM DISK=’C: MyDatabase.bakNext, specify the particular backup set for retrieval by using the following command:
RESTORE DATABASE mydatabase FROM DISK=’C: MyDatabase.bak WITH FILE = FileNumberThe above command may help you restore some backup sets from the damaged device, but there is a possibility that the backup restoration process is not complete. So, it is mandatory to verify the integrity of the restored database.
You can identify the success or failure of backup operation or restore operation in the SQL Server error log, as well as, from the backup history tables in the MSDB system database.
What if You Cannot Restore SQL Server Database from Backup?
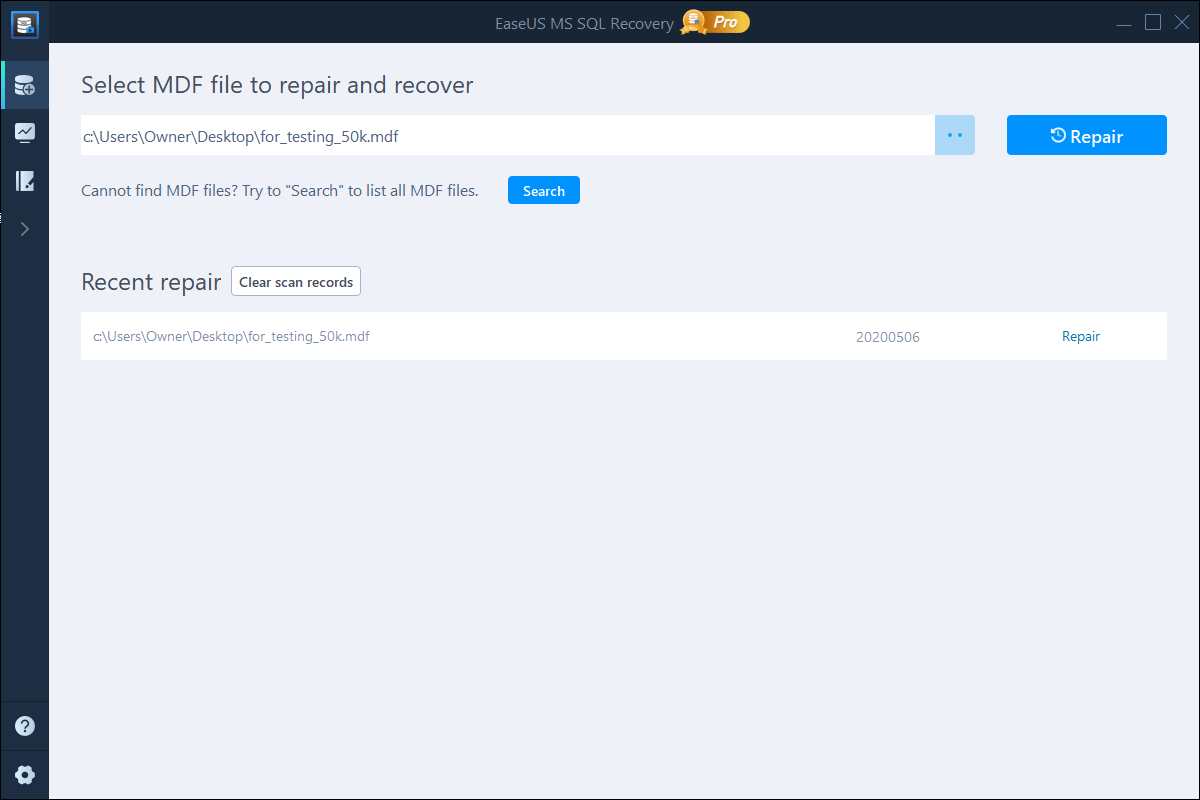
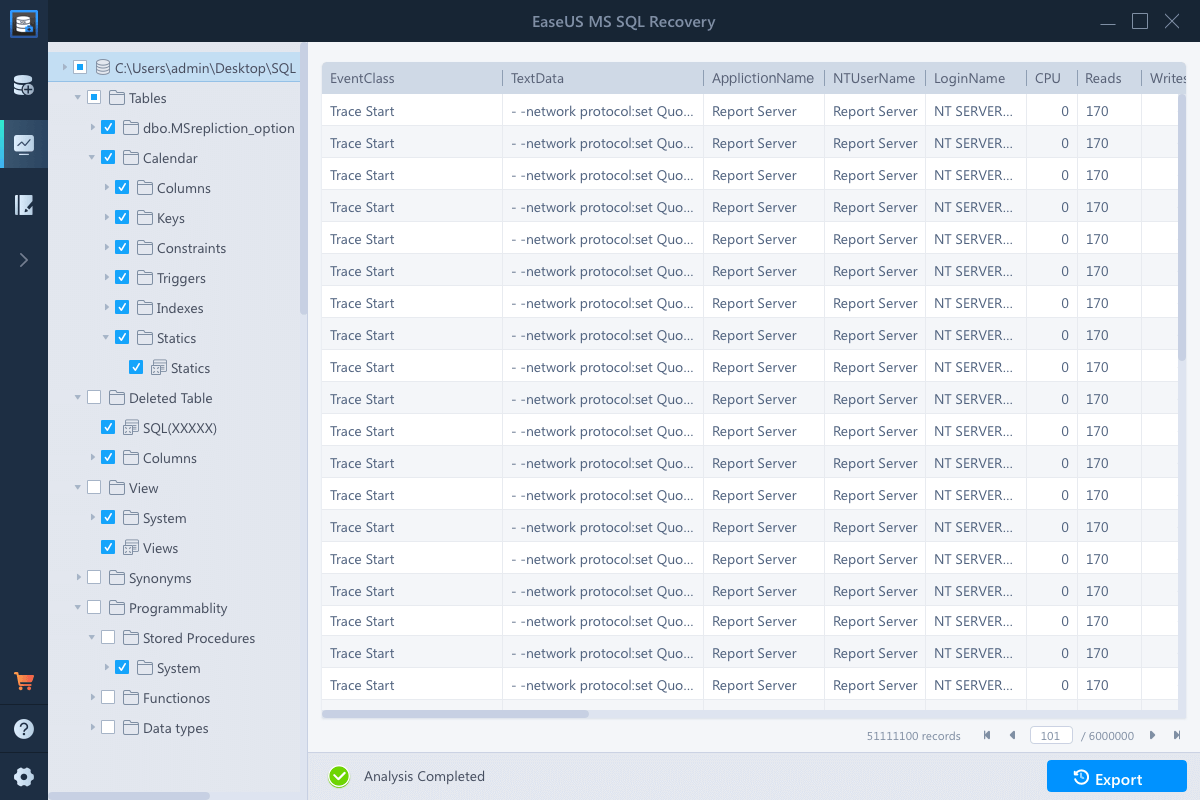
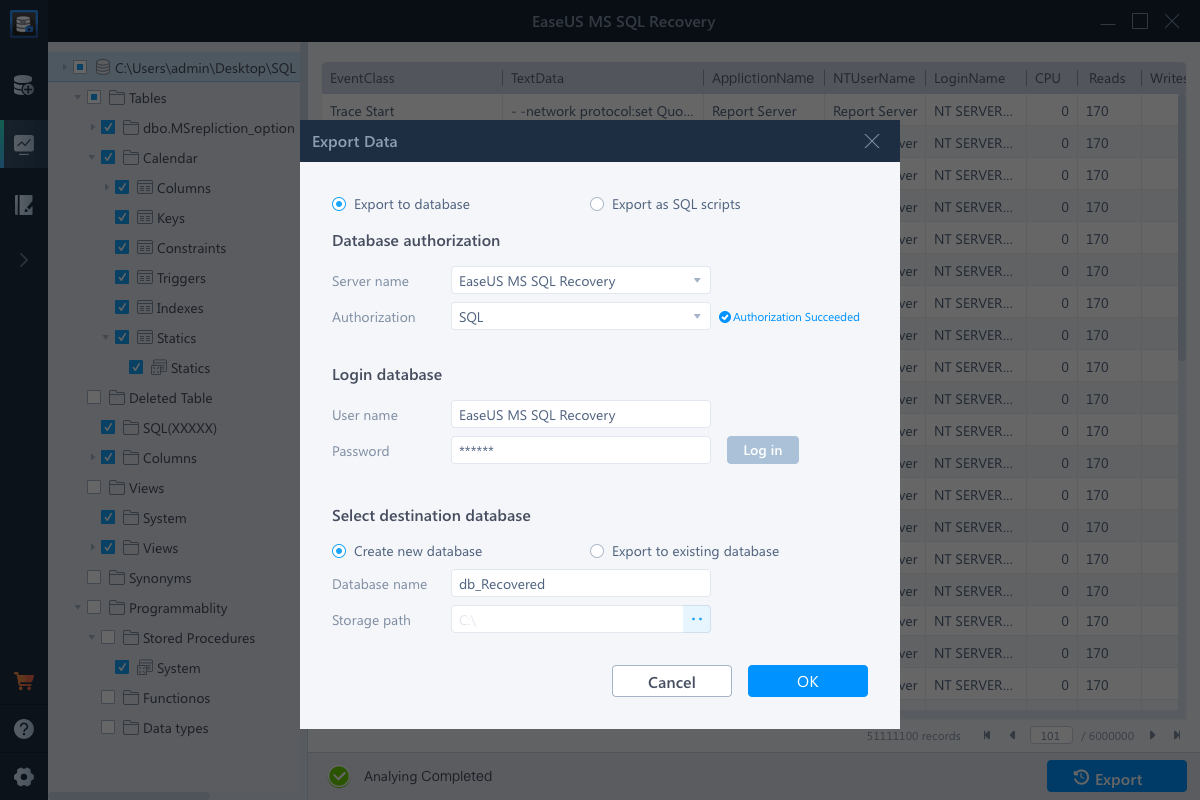
If you’re unable to restore your database from the .bak file, it is likely that the file has turned corrupt. And, you cannot restore from a corrupt .bak file. But, you can try to extract data from the file by using Stellar Repair for MSSQL Technician software. It is trusted by Microsoft MVPs and is a combination of 3 powerful tools that help repair corrupt SQL Server database, extracts database from corrupt .bak file, and reset SQL Server password.

Conclusion
When your backup system is hit with SQL Server Error 3013 before restoring the database, you can try any of these manual methods to fix the error:
- Check for user security permission and change it.
- Try deleting the old data from the backup device and enable SQL Server application to implement a new backup operation.
- Try performing a full backup restoration.
If you get a 3013 error when restoring the DB, check for other backup sets available on the storage device and retrieve them. But, if you’re unable to restore the .bak file, chances are that the file is corrupt. If that’s the case, you can try extracting data from the .bak file by using the Stellar Repair for MS SQL Technician software.
About The Author
Priyanka Chauhan
Priyanka is a technology expert working for key technology domains that revolve around Data Recovery and related software’s. She got expertise on related subjects like SQL Database, Access Database, QuickBooks, and Microsoft Excel. Loves to write on different technology and data recovery subjects on regular basis. Technology freak who always found exploring neo-tech subjects, when not writing, research is something that keeps her going in life.
| title | description | author | ms.author | ms.reviewer | ms.date | ms.service | ms.subservice | ms.topic | helpviewer_keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MSSQLSERVER_3013 |
MSSQLSERVER_3013 |
pijocoder |
jopilov |
sureshka, mathoma |
03/23/2023 |
sql |
supportability |
reference |
3013 (Database Engine error) |
MSSQLSERVER_3013
[!INCLUDE SQL Server]
Details
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Product Name | SQL Server |
| Event ID | 3013 |
| Event Source | MSSQLSERVER |
| Component | SQLEngine |
| Symbolic Name | DMP_ABORT |
| Message Text | BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally /RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally. |
Explanation
This error is a generic error that occurs when a backup or restore operation is interrupted unexpectedly. You see 3013 raised together with other error messages that provide more specific insight into the cause of the backup failure. Examples would include read or writes failure from/to the backup media or other unexpected Win32 API call failures.
Cause
There could be many various causes for an abnormal termination of a backup or a restore in SQL Server. Here’s a list of common reasons:
- Insufficient disk space
- Incorrect path to the backup storage device
- The backup file/device is already open by another program
- Backup media device failure or malfunction
- Database corruption — if the database is corrupt, the backup or restore operation may fail.
- Lack of BACKUP DATABASE, BACKUP LOG or CREATE DATABASE permissions to be able to back up or restore respectively
- SQL Server service account lack of access to the backup device
User action
Examine the SQL Error log for other messages that occur alongside this error for additional information and troubleshooting.
-
For insufficient disk space, ensure sure that the drive where you’re writing the backup has enough free space available or use a different device. See Examples with errors 3203 and 3203
-
For incorrect file path, double-check and correct the path and file name specified in the BACKUP or RESTORE command.
-
For backup media failure, if you’re backing up to a tape drive or other backup device, make sure that the device is functioning properly and isn’t experiencing any hardware errors. See Examples with errors 3203 and 3203 and Example with error 3241
-
For database corruption issues, you’re likely to observe other errors in SQL Server. Run DBCC CHECKDB to identify any errors in the database and resolve. For more information, see Troubleshoot database consistency errors reported by DBCC CHECKDB
-
If your server principal account lacks permissions to do a backup or a restore operation, ensure account that is granted those permissions. See Backup permissions and Restore permissions
-
For SQL Server service account permission issues, ensure that the SQL Server service account has read and write access to the backup device or the file system where the backup file is written. See Backup permissions.
Here are examples of commonly observed errors together with 3013.
Example with error 3241
In this scenario, error 3241 is raised with 3013 and indicates issues with the backup itself.
Msg 3241, Level 16, State 0, Line 2
The media family on device 'G:backupProdDB_backup.bak' is incorrectly formed. SQL Server cannot process this media family.
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
RESTORE FILELIST is terminating abnormally.
Resolution:
This error typically indicates damaged backup(s) or the media that stores or transferred the backups malfunctioned. Find an alternative backup to restore either from different medium or try earlier or later backup.
Also, see KB5014298 for backup/restores of TDE databases — FIX: Error 3241 occurs during executing RESTORE DATABASE OR RESTORE LOG
For more troubleshooting ideas, see Media-related errors when you restore a database from a backup
Examples with errors 3203 and 3203
Errors 3202 and 3203 are backup errors raised when there are I/O-related issues. These two errors indicate whether a read or a write request was performed and show the underlying OS error that resulted from the I/O failure. These examples have been observed:
Msg 3203, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Read on "G:SQLDATAProductionDb.ndf" failed: 483(The request failed due to a fatal device hardware error.)
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Msg 3202, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
Write on "Y:SQLDATAProductionDb.bak" failed: 1117(The request could not be performed because of an I/O device error.)
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Msg 3202, Level 16, State 1, Line 14
Write on "\BackupServerShareProdDb.bak" failed: 112(There is not enough space on the disk.)
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 14
BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Resolution:
-
The examples with OS 483 and 1117 indicate I/O device failure. Check for malfunction or damage of the storage media. Review System event logs, hardware configuration and logs and work with hardware administrator and vendor to address any issues with the media that stores the backups. Here’s an example of a message you may find in the System Event log, which indicates of I/O issues that need to be addressed:
Warning PM,Disk,153,None,The IO operation at logical block address 0xe90525a0 for Disk 3 (PDO name: Device0000017) was retried. -
If OS error 112 is raised indicating space issues, ensure sufficient disk space on the local or remote storage where the backup is sent. If sufficient space is available, ensure reliability of storage media.
Example with 3624
In some cases error 3013 may be raised together with a system assertion. If a backup fails with an assertion, then the main focus is to address the assertion itself. Here’s an example of an issue observed:
Msg 3013, Sev 16, State 1, Line 1
VERIFY DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Msg 3624, Sev 20, State 1, Line 1
A system assertion check has failed. Check the SQL Server error log for details. Typically, an assertion failure is caused by a software bug or data corruption. To check for database corruption, consider running DBCC CHECKDB. If you agreed to send dumps to Microsoft during setup, a mini dump will be sent to Microsoft. An update might be available from Microsoft in the latest Service Pack or in a Hotfix from Technical Support.
Error: 17066, Severity: 16, State: 1.
SQL Server Assertion: File: mediaRead.cpp:429 Expression: !m_ActiveConsumptionList.IsEmpty () || !m_ActiveReads.IsEmpty () || !m_DecodeOutputQ.IsEmpty () || (CFeatureSwitchesMin::GetCurrentInstance ()->FEnableCheckingActiveDecodeQueueEnabled () && !m_ActiveDecodeInput.IsEmpty ()) SPID: 74 Process ID: 25440
Resolution:
Review the SQL Server error log and use the methodology outlined in this article MSSQLSERVER_3624 to troubleshoot the assert failures:
-
Run DBCC CHECKDB on your databases and ensure all components on the I/O path are functioning properly.
-
Lookup part or all of the assert expression online for any known issues. For example in this case if you look up «m_ActiveConsumptionList.IsEmpty» you may find this article:
KB4469554 — FIX: Assertion error occurs during restore of compressed backups in SQL Server 2014, 2016 and 2017
-
Update your SQL Server to a later build (Cumulative update)
-
Ensure no external component is interfering and causing the failure
Example with error 4303
This example illustrates a restore of a transaction log sequence that failed and raised error 3013. The specific error 4303 indicates that either more transaction log restores are missing prior to this one or that the transaction log backup file is damaged. For example, the LSN = 4294967295429496729565535 doesn’t appear to be a valid LSN and that may be a result of a corrupt backup file or media.
Msg 4303, Level 16, State 1, Line 3
The roll forward start point is now at log sequence number (LSN) 8177105000003941300003. Additional roll forward past LSN 4294967295429496729565535 is required to complete the restore sequence.
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 3
RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Resolution:
If you encounter errors such as 4303 together with 3013, find an alternative good backup to restore. Also check the stability of the storage media where backups are placed and repair as necessary.
See also
- Troubleshoot SQL Server backup and restore operations.
Overview of SQL Server Error 3013
One of the most frustrating situations that a user experiences while working with SQL Server is when errors are encountered. These errors disrupt the normal functioning of SQL Server and in worst case scenario may even lead to data loss. Sometimes, SQL Server Backup Detected Corruption In the Database Log. In this write-up, we are going to discuss about one such SQL Error 3013.
Error Description
SQL Server Error 3013 mainly occurs when the backup process to a disk/tape or a restoration process from a disk/tape is under process.
What is «Restore Database Terminating Abnormally» in SQL Error 3013 ?
The error message and the occurrence factors of SQL Server error 3013 vary according to the SQL Server version the user is currently working with.
SQL Server 7.0
In this SQL version, the error is encountered when the clustered index has been created in all the filegroups of the table.
SQL Server 2000
In this case, if the database of size 2 GB already exists and a separate database of size more than 2 GB is restored in the existing database, the error is generated.
SQL Server 2005
In the instance of restoration of both the data and log files at the same time, the Error 3013 is encountered.
Reason behind Its Occurrence
The dominant reason behind the occurrence of this error is the inability of the database to read the filemark present in the backup device or inaccessibility of the filemark itself. Before proceeding further, let us know what filemark actually is.
A filemark in a backup device is the element that does not store user data. In order to organize and unify the storage patterns, the filemarks, divide the partition in smaller segments. Their primary task is splitting data of all the individual files that are stored in the backup device.
The other reasons, which also play an important role in the occurrence of SQL error 3013, are:
- Media failure on the device in which the backup has been stored.
- Write failure whilst the execution of the backup process.
- Connectivity loss during the network backup process.
Workaround
1. The error can be removed by manual deletion of the device and ensuring that the server performs new backup to the device. The command to do so is:
2. In case the restoration process is the reason behind the error occurrence, it is possible to retrieve the other backup data by specifying the file number in the device.
In order to check the presence of multiple backup sets on the device, run the following code:
For indicating a specific set of backup, run the following command:
Note: The FileNumber term is used to represent the file series that the user wants to restore
Conclusion
In the blog, we discussed about the SQL Server Error 3013. With the help of the workarounds mentioned in the above section, the users can easily remove this error and continue with the restoration and backup process. In case if you failed with manual solution then you can also try SQL BAK recovery tool to successfully repair corrupt SQL .bak file.
Fix SQL Server Backup Error – Backup Database is Terminating Abnormally. sqlstate 42000 (Error 3013)
admin ~
Modified: 24-05-2023 ~ SQL Server , Technology ~ 5 Minutes Reading
Let us assume that you are restoring a database backup from any disk or tape. While doing this, you have changed the logical name of the database. And then you may receive the following error message: SQL Server backup error 3013 or Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 Backup database is terminating abnormally
This error is interconnected to restoring the database. Using the statement RESTORE FILELISTONLY, a user can check the backup file. You will notice that the modified logical name of the database is corrupted or damaged and the last character of the name is truncated.
Consider the following user Query: SQL Server Backup Error 3013
Clark Williams: “Hi. The problem is when we tried to backup and restore our database using SQL Server 2008, we got an error. The schedule was to create seven backups of twenty-three databases. The schedule worked fine for some time. But, from the past two days, all the backups failed. The server is showing the following error:
Write on “T:\.bak” failed: 170(The requested resource is in use.)
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Server, Line 1
BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Outcome: Failed
Priyanka Chauhan
Priyanka is a technology expert working for key technology domains that revolve around Data Recovery and related software’s. She got expertise on related subjects like SQL Database, Access Database, QuickBooks, and Microsoft Excel. Loves to write on different technology and data recovery subjects on regular basis. Technology freak who always found exploring neo-tech subjects, when not writing, research is something that keeps her going in life.