Техническая оптимизация — основа основ в продвижении сайта. Если у вашего ресурса есть проблемы с безопасностью и защитой данных, вам будет очень сложно двигаться в ТОП выдачи.
Ранее мы писали о базовых правилах безопасности сайта и важности перехода на HTTPS. В этой статье мы расскажем о настройке SSL-/TLS-сертификата и типичных ошибках, которые могут навредить сайту.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) и TLS (Transport Layer Security) — стандартизированная технология шифрования, которая защищает передаваемые сайтом и сайту данные. Она напрямую связана с HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): если сайт использует HTTPS-подключение, это значит, что данные передаются по протоколу SSL или TLS.
SSL была представлена в 1995 году и обновлена до TLS в 1999-м — технология видоизменялась, реагируя на новые уязвимости. Протоколы постоянно обновляются и большинство их предыдущих версий считаются устаревшими. Важно следить за обновлениями и использовать самую актуальную версию SSL/TLS.
Как SSL/TLS влияет на продвижение
Для Google безопасность всегда среди главных приоритетов: поисковик учитывает наличие HTTPS при ранжировании с 2014 года и постоянно обновляет требования к SSL-/TLS-сертификатам.
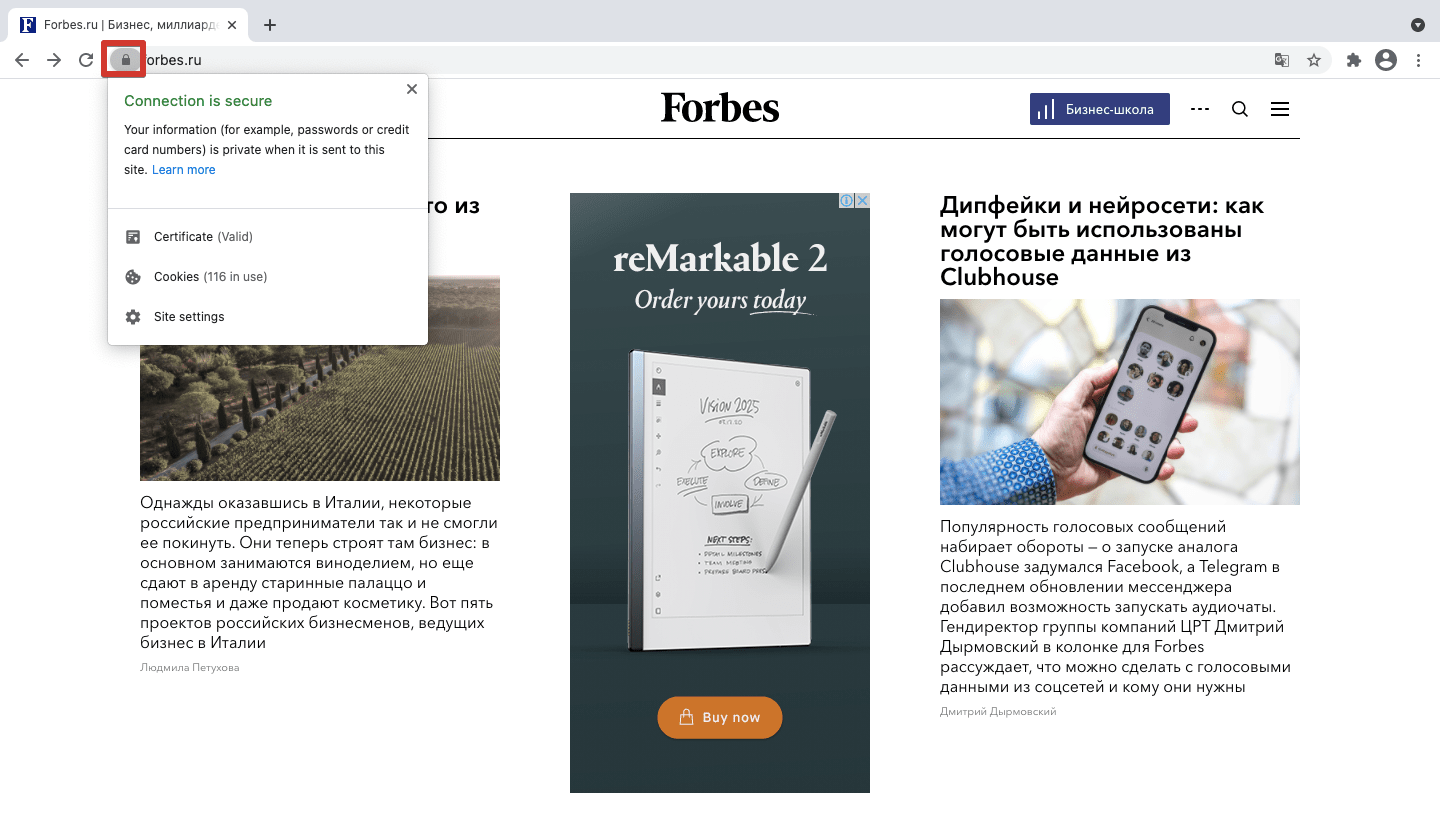
Большинство браузеров маркируют незащищенные страницы — проверить безопасность соединения можно по значку замка в адресной строке. Safari показывает этот значок, только если сайт использует адекватное шифрование; Firefox показывает перечеркнутый замок при недостаточном уровне защиты на сайтах, которые используют пользовательские данные; Chrome показывает красный треугольник при проблемах с безопасностью и значок замка при безопасном соединении.
Хоть преимущества технологии SSL/TLS довольно очевидны, многие сайты до сих пор не перешли на HTTPS или же используют недостаточно надежные версии протоколов. Статистика 2019 года говорит о том, что 20% крупнейших сайтов в мире не используют безопасный протокол, а по данным на начало 2020 года, только 18% доменных имен в зоне .ru используют узлы HTTPS.
Многие владельцы сайтов не хотят заморачиваться с покупкой и обновлением SSL-/TLS-сертификата или считают, что он им не нужен, если ресурс не собирает пользовательские данные. Но в современных реалиях ваш сайт будет попросту терять клиентов и позиции в поиске, если вы не перейдете на HTTPS и не будете следить за актуальностью шифрования. Для вашего удобства существует множество инструментов для настройки и мониторинга SSL-/TLS-сертификатов, в том числе бесплатные, как Let’s Encrypt.
Как исправлять типичные ошибки SSL/TLS
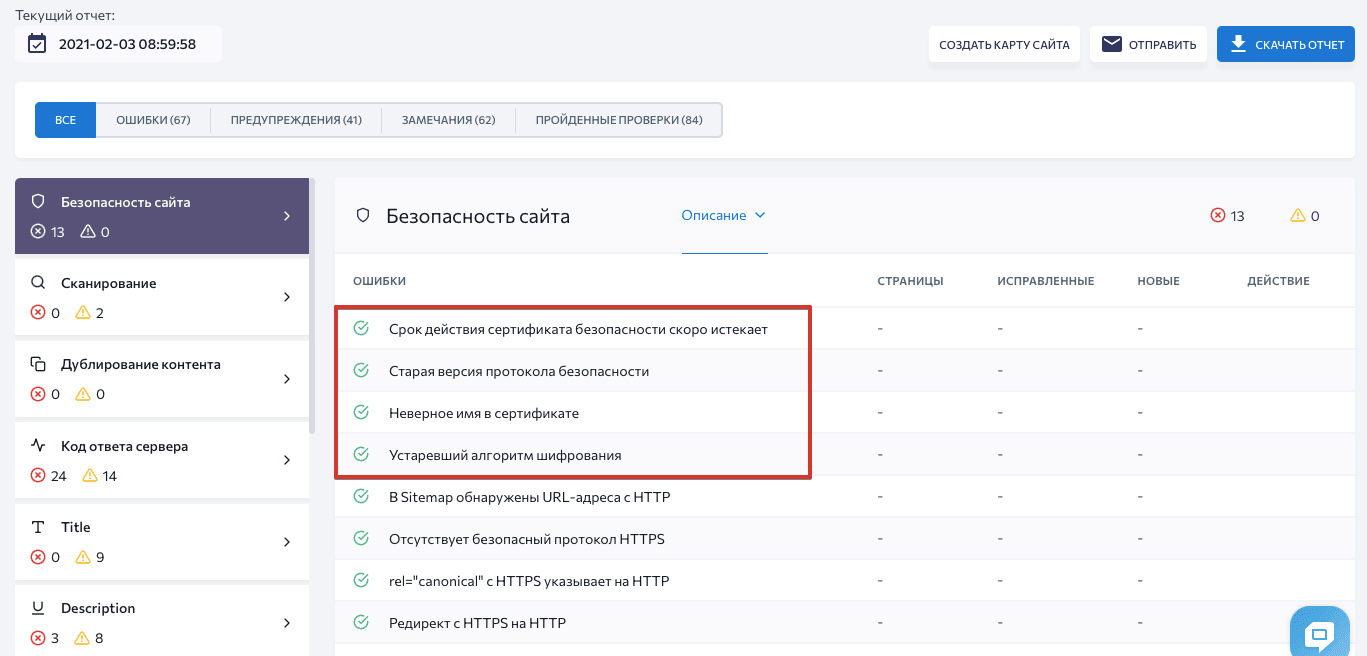
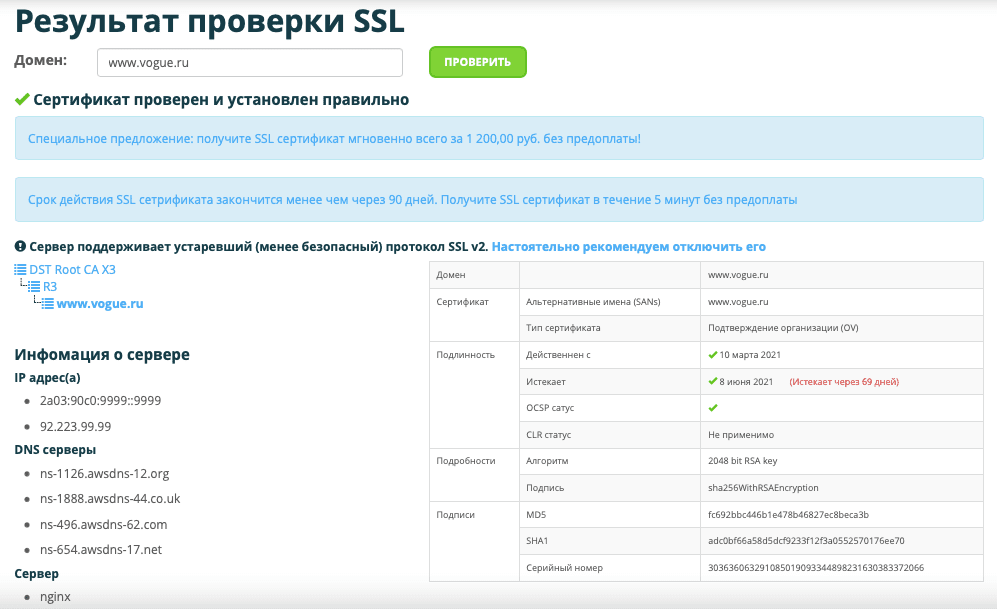
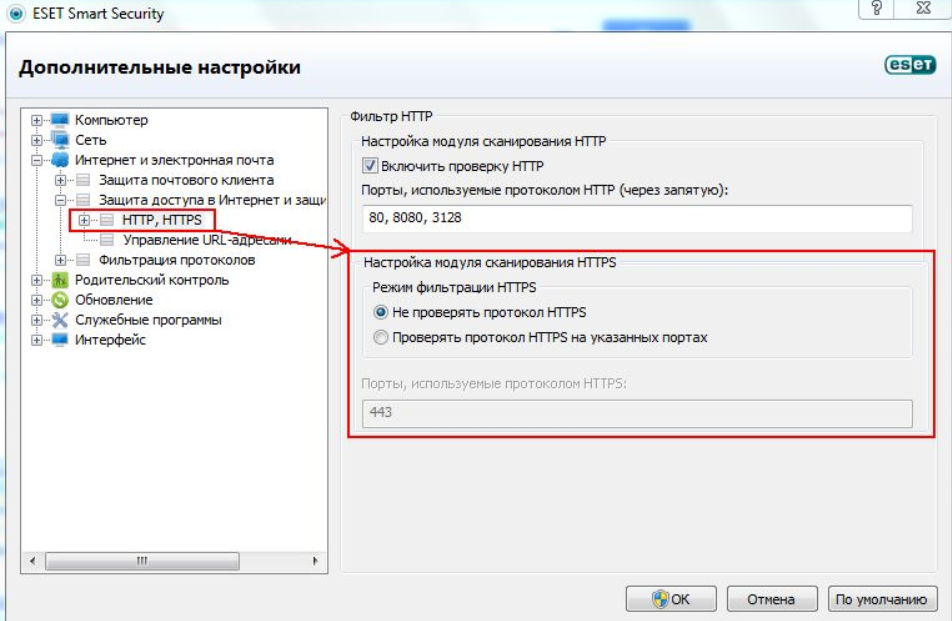
Если у вас уже есть SSL-/TLS-сертификат, он требует регулярного обновления и мониторинга. Чтобы избежать ошибок, проверяйте свой сайт на наличие проблем с SSL/TLS. Вы можете быстро обнаружить возможные ошибки с помощью «Аудита сайта» SE Ranking — для этого перейдите в раздел «Отчет об ошибках» и секцию «Безопасность сайта»:
Давайте рассмотрим 4 частые ошибки SSL-/TLS-сертификатов и объясним, как их исправить.
1. Недействительный сертификат
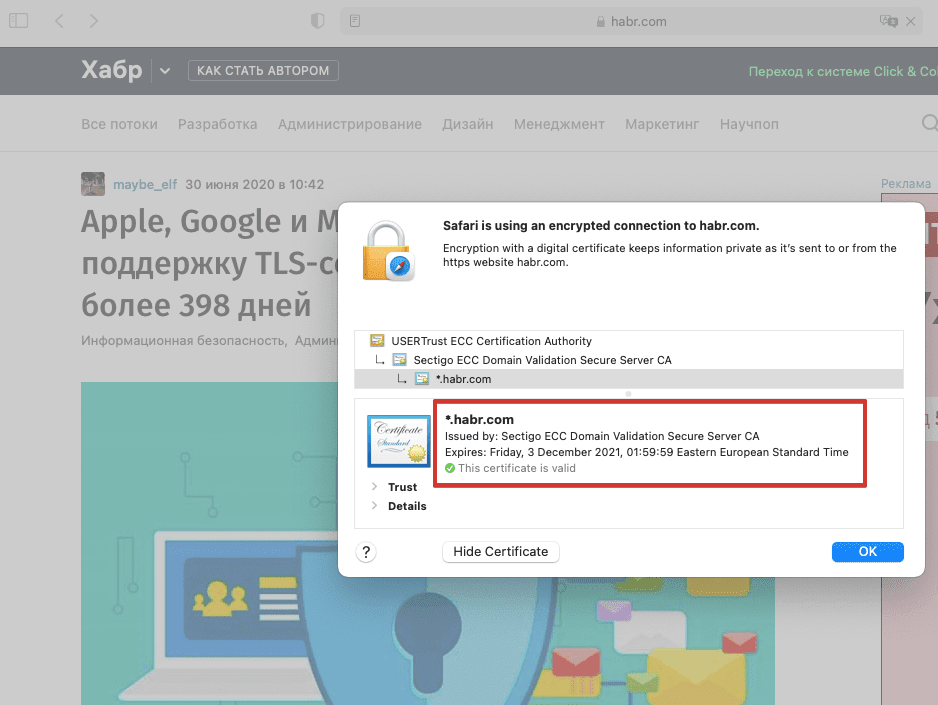
У сертификата безопасности есть определенный срок действия. Он постоянно уменьшался: до 5 лет в 2011-м, до 3 лет в 2015-м, до 2 лет в 2018-м. Сейчас сертификаты действительны только 398 дней (13 месяцев) — с 2020 года Safari, Chrome и Mozilla прекратили поддержку сертификатов с большим сроком действия.
Информация о дате истечения действия сертификата доступна в браузере:
Что же происходит, если SSL-/TLS-сертификат устаревает? Сайт становится недоступен — пользователи увидят сообщение о небезопасности в браузере. Результат — существенные потери трафика и, соответственно, прибыли.
Поэтому стоит знать дату истечения действия сертификата и вовремя его обновлять. Помогут вам в этом автоматизированные решения типа Let’s Encrypt, AWS Certificate Manager. Также существуют инструменты, которые несколько раз оповещают вас перед окончанием срока действия сертификата. Иногда и вовсе ничего делать не нужно, ведь многие центры сертификации предлагают автоматическое обновление.
Если вы все же оказались в ситуации недействительного сертификата, нужно вручную его обновить или приобрести новый. Что именно нужно сделать:
- Выбрать тип сертификата. Большинство центров сертификации предлагает несколько вариантов, покрывающих потребности сайтов разного масштаба. Если вы только обновляете существующий сертификат и не хотите поменять его тип, этот шаг у вас уже выполнен (иногда логично переключиться на более мощный тип сертификата — например, приобрести Wildcard-сертификат, если у вашего сайта появились поддомены). Покупая новый сертификат, внимательно проверяйте авторитетность производителя. Вы можете настроить CAA-запись, чтобы ограничить круг удостоверяющих центров, имеющих право выпускать сертификаты для вашего домена. Среди самых популярных центров сертификации — GlobalSign, Digicert, Sectigo, Thawte.
- Сгенерировать запрос на получение сертификата. После покупки нужно сгенерировать CSR (certificate signing request) у хостинг-провайдера. В результате вы получите файл ключа и сам запрос для загрузки в настройках сертификата.
- Активировать и валидировать сертификат. Далее нужно подтвердить свои права на домен через email, CNAME-запись или подтверждающий файл. Как и в предыдущем процессе, особенности настройки зависят от выбранного провайдера.
- Проверить корректность работы сертификата. После установки сертификата проверьте его с помощью онлайн-инструмента. Например:
Если это ваша первая покупка SSL-/TLS-сертификата, вам также следует добавить HTTPS-версию сайта в сервисы для вебмастеров и перенаправить на нее HTTP-трафик. Узнайте больше о правильном переезде на HTTPS из нашей статьи.
Рекомендуем использовать инструменты мониторинга и настраивать напоминания об окончании срока действия — так вам не придется разбираться с последствиями, если срок действия сертификата истечет.
2. Устаревшая версия протокола безопасности
Технологии шифрования совершенствуются, но и хакерские атаки становятся все изощреннее. Постоянно растущие риски — одна из причин сокращения срока действия SSL-/TLS-сертификатов и обновления протокола.
Протокол TLS был представлен как апгрейд SSL (версии 3.0 на тот момент), поэтому любая версия TLS более безопасна чем SSL. Самый актуальный протокол — TLS 1.3, выпущенный в 2018 году, — имеет усовершенствованный криптографический алгоритм и позволяет браузеру быстрее подсоединиться к серверу сайта. С 2020 года все основные браузеры не поддерживают устаревшие версии TLS (1.0 и 1.1), а значит не пускают пользователей на сайты, использующие эти версии.
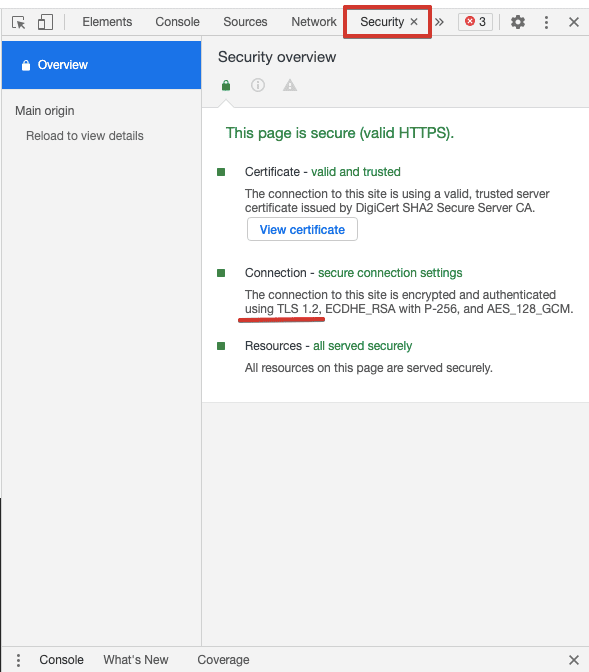
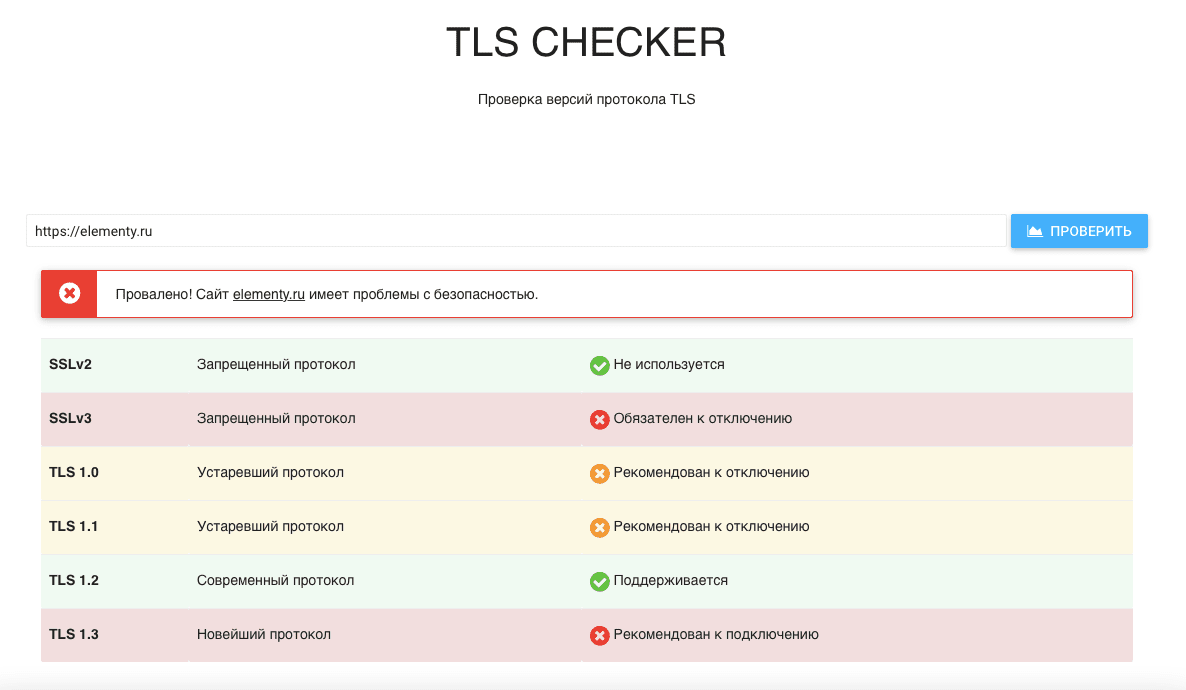
Важно использовать актуальную версию протокола безопасности и отключать все предыдущие версии. Существует несколько способов проверить, какой протокол у сайта:
- Во вкладке Security в Chrome DevTools:
- В онлайн-инструментах, проверяющих, какие версии TLS и SSL включены на сайте. Например:
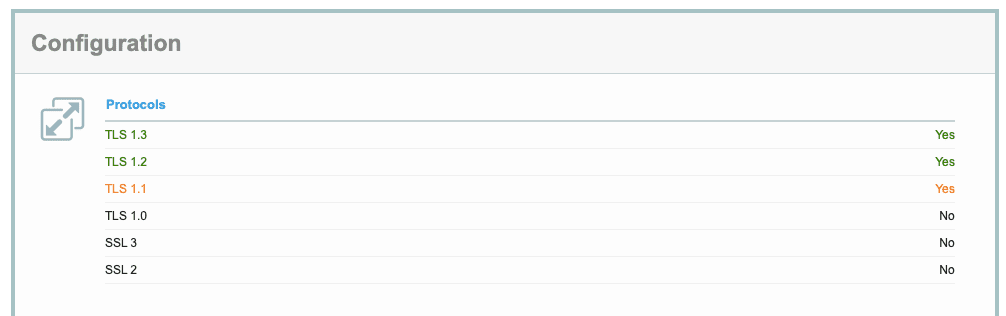
Чтобы включить последнюю версию TLS, прежде всего убедитесь, что ваш сайт поддерживает ее. Запустите серверную проверку — например, в SSL Labs — и просмотрите результаты конфигурации:
После этого свяжитесь со своим хостинг-провайдером, чтоб узнать, как именно подключить актуальную версию протокола. Вам нужно будет указать правильную версию в файле конфигураций сервера.
Скажем, ваш сайт размещен на сервере Nginx. Вам нужно отредактировать файл nginx.conf, указав в нем установленную версию TLS. Также удалите из файла все ранее используемые версии, которые признаны устаревшими. Строка конфигурации будет выглядеть так:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
Если же окажется, что ваш сайт не поддерживает TLS 1.2 или 1.3, стоит обратиться к провайдеру и по возможности сменить тариф (или провайдера).
3. Несоответствие имени сертификата
Ошибка неверного имени сертификата вызвана тем, что доменное имя, указанное в SSL-/TLS-сертификате, не соответствует введенному в адресной строке. Пользователи в таком случае не смогут зайти на сайт.
Причины несоответствия имени SSL-/TLS-сертификата:
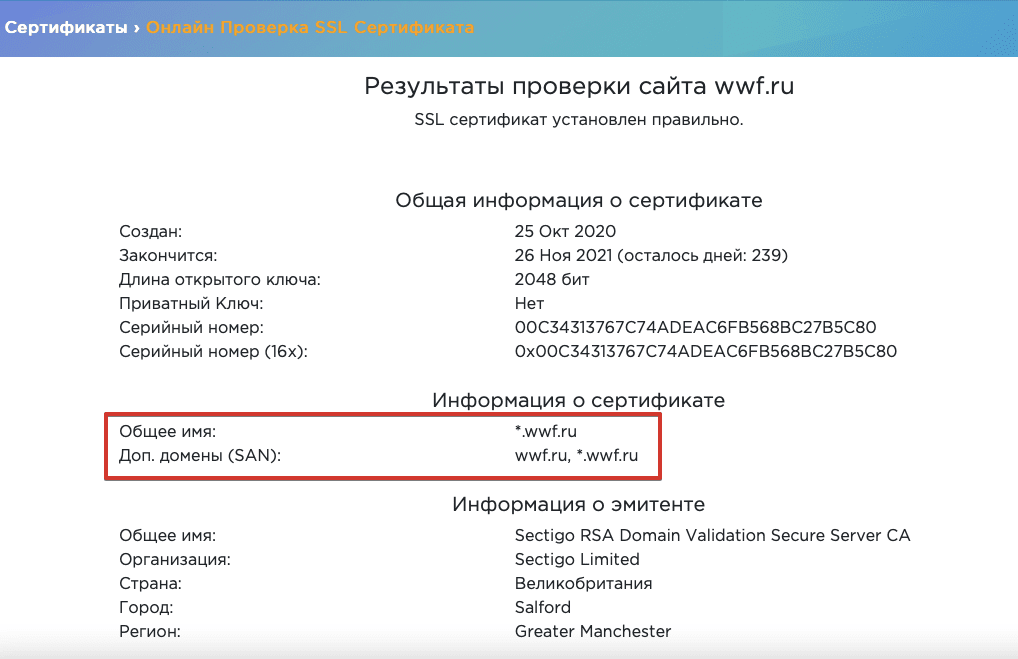
- На сайт заходят через внутреннее доменное имя, не указанное в сертификате. Например, вы вводите в адресную строку vashsajt.localhost, тогда как ваш сертификат содержит только vashsajt.com. Вы можете решить эту проблему с помощью сертификата с альтернативным именем субъекта SAN — такой тип позволяет включать целый ряд имен хостов. Проверяйте наличие сертификатов SAN у разных удостоверяющих центров.
- Сайт доступен и с префиксом www, и без, тогда как в сертификате указана только одна версия. Вам нужно решить, хотите ли вы использовать www в доменном имени, перенаправить весь трафик сайта на соответствующую версию и указать ее в SSL-/TLS-сертификате. Мы детальнее разбираем этот вопрос в статье о префиксе www и его влиянии на SEO.
- Сайт делит IP-адрес с другими и не имеет отдельного протокола. Для большинства сайтов необязателен отдельный IP-адрес, а использование совместного экономит бюджет. Если у вашего сайта общий IP, укажите доменное имя в расширении протокола SNI. С помощью SNI сервер будет выбирать уникальный для вашего имени хоста TLS-сертификат и соответствующий ключ. Без такого расширения сервер будет использовать шаблонный сертификат, общий для нескольких сайтов, и он может быть слабее установленного вами протокола.
- Хостинг-провайдер сайта использует шаблонные настройки, которые предопределяют SSL/TLS для доменного имени. Чтобы решить эту проблему, нужно связаться с провайдером и узнать, как заменить их сертификат на ваш, или же поменять провайдера.
В онлайн-инструментах можно проверить, какие доменные имена включены в ваш SSL-/TLS-сертификат:
4. Устаревший алгоритм шифрования
Когда пользователь заходит на сайт, происходит процесс «рукопожатия»: клиент (браузер) и сервер идентифицируют друг друга, браузер при этом проверяет подлинность SSL-/TLS-сертификата. Набор алгоритмов шифрования очень важен для этого процесса: браузер сообщает, какие комбинации шифров он поддерживает, и сервер выбирает лучшую из подходящих. Если набор алгоритмов шифрования, используемый в конкретном сертификате, недостаточно надежный, браузер выдаст предупреждение об устаревшей криптографии.
Набор алгоритмов шифрования состоит из нескольких шифров, отвечающих за разные функции. Перед разработкой TLS 1.3 самой надежной была такая комбинация:
- Алгоритм для обмена ключами между сервером и браузером (ECDHE)
- Цифровая подпись, удостоверяющая сертификат (ECDSA)
- Шифр для обмена данными (AES-256-GCM)
- Алгоритм для аутентификации сообщений (SHA384)
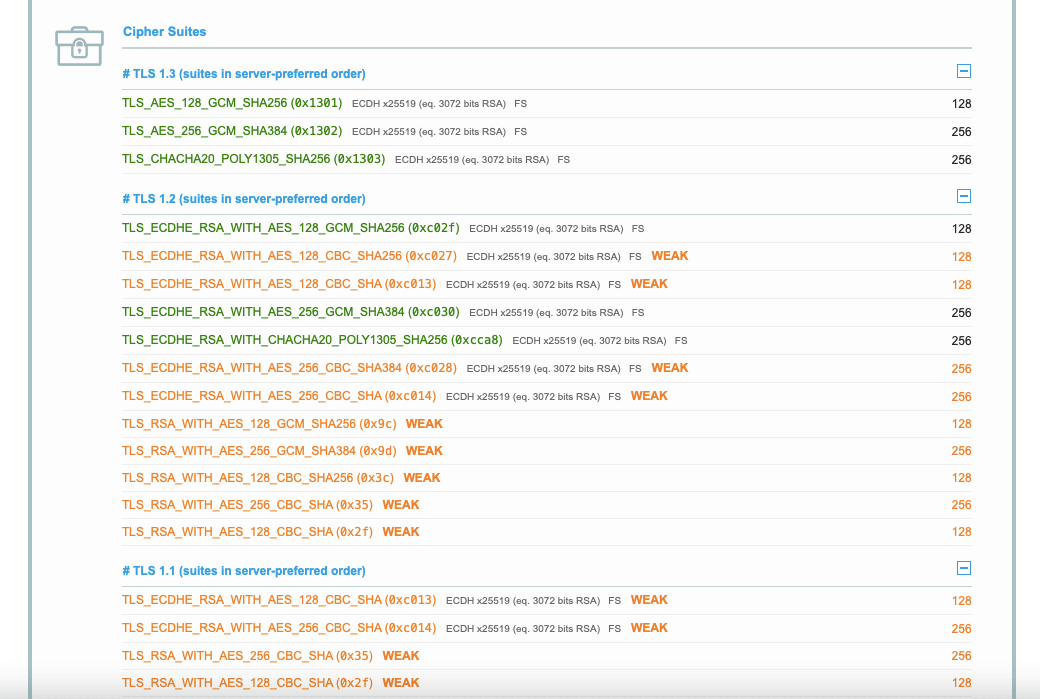
Комбинация в TLS 1.3 содержит только два последних шифра и по умолчанию не поддерживает устаревшие алгоритмы для обмена ключами и аутентификации сертификата.
Версия TLS 1.2 до сих пор считается достаточно надежной, но у нее есть уязвимости из-за большей вариативности алгоритмов шифрования и их качества. С TLS 1.3 выбор шифров ограничен самыми безопасными и весь процесс «рукопожатия» происходит проще и быстрее.
Если вы не знаете, какие шифры поддерживаются вашим сертификатом, стоит проверить их актуальность. Можно запустить онлайн-тест:
Если вы обнаружите устаревшие алгоритмы, нужно отключить их в настройках сервера. Кроме того, можно проанализировать рейтинг шифров и указать приоритетный порядок, чтобы браузеры выбирали самый надежный из поддерживаемых в вашем сертификате.
Обеспечьте сайту бескомпромиссную защиту
Продвигать сайт без заботы о его безопасности не получится. Чтобы защитить свой сайт от кибератак и уязвимости данных, нужен надежный SSL-/TLS-сертификат с самыми актуальными настройками. Мы рекомендуем использовать последнюю версию TLS, поставить напоминания о дате истечения срока действия, подключить самые надежные алгоритмы шифрования и регулярно проверять состояние протокола.
Анастасия — контент-маркетолог и редактор в SE Ranking, пишет про SEO, маркетинг и цифровые технологии. Кроме текстов для блога SE Ranking, Анастасия пишет музыку, а также любит старые фильмы и свою собаку.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): It is an internet security protocol based on encryption. It was developed in the year 1996 by Netscape to ensure privacy, authentication, and data integrity. It is the predecessor to TLS encryption. It provides a secure channel between two devices or machines communicating over the Internet or even an internal network. SSL is also used to secure communication between web browsers and web servers. This can be seen when a site’s address has HTTPS, where the ‘S’ stands for ‘secure’. It is also a transparent protocol and requires little to no interaction from the end user in establishing a secure session. Some examples of services protected by SSL are online payments, webmail servers, and system logins.
Transport Layer Security (TLS): It can be described as a more secure and updated version of SSL. It is a cryptographic protocol that allows end-to-end security of data exchanged between different applications over the Internet. It was specifically based on SSL 3.0 and was developed in the year 1999 by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). As SSL has not been updated since the year 1996, TLS has been considered the industry standard for over 20 years. TLS is implemented on top of TCP to encrypt Application Layer protocols like HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and IMAP. It can also be implemented on UDP, DCCP, and SCTP. The main use of TLS is to encrypt the communication between web applications and servers. For example, web browsers loading a website.
An SSL/ TLS handshake error occurs when the client and server can’t establish communication over the SSL/TLS protocol (usually due to a protocol mismatch).
Some common fixes to the SSL/TLS handshake failed error:
1. Correcting System Time: It is one of the easiest and most obvious fixes. If the system date and time on your device are incorrect, it can cause an SSL/TLS handshake failed error. This error happens because the correct date and time are essential for SSL certificates; as they have finite lifespans and have an expiration date.
2. Using a different Browser: Sometimes, the browser in use can cause the SSL/TLS handshake failure. It may be due to a browser misconfiguration or a browser plugin, which can cause problems in connecting to legitimate websites. As finding out the exact misconfiguration can be time-consuming, you can simply try another browser. If you still face the SSL/TLS handshake failure even after changing the browser, the issue usually lies with the browser plugins. To verify whether this is the case, disable all installed plugins and check again.
3. Add website to allowlist: It may be possible that your firewall is intercepting your request for inspection, causing an SSL/TLS handshake failure. To fix this, add the website to your allowlist. For Google Chrome,
- Open the admin console homepage and go to Devices→Chrome.
- Settings→Users & browsers.
- Leave the top organizational unit selected (which it should be by default). This applies the setting to all users and enrolled browsers.
- Scroll down to URL Blocking and enter the website you want to access, under Blocked URL Exceptions.
- Hit Save.
4. Update browser to the latest SSL protocol: To check if your browser is using the latest SSL protocol:
- Visit SSL Labs.
- Click on Projects.
- Click on SSL Client Test.
- Under Protocol Support, check whether your browser supports the latest version of TLS.
Advantages of SSL/TLS:
- Improved Security.
- Easily deployed.
- Ability to use HTTP/2.
Disadvantages of SSL/TLS:
- Speed degradation.
- Allows insecure encryption.
- Plugin incompatibility.
Last Updated :
28 Jul, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
In last blog, I introduced how SSL/TLS connections are established and how to verify the whole handshake process in network packet file. However capturing network packet is not always supported or possible for certain scenarios. Here in this blog, I will introduce 5 handy tools that can test different phases of SSL/TLS connection so that you can narrow down the cause of SSL/TLS connection issue and locate root cause.
curl
Suitable scenarios: TLS version mismatch, no supported CipherSuite, network connection between client and server.
curl is an open source tool available on Windows 10, Linux and Unix OS. It is a tool designed to transfer data and supports many protocols. HTTPS is one of them. It can also used to test TLS connection.
Examples:
1. Test connection with a given TLS version.
curl -v https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380 —tlsv1.0
2. Test with a given CipherSuite and TLS version
curl -v https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380 —ciphers ECDHE-RSA-NULL-SHA —tlsv1.2
Success connection example:
curl -v https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380 --tlsv1.2
* Rebuilt URL to: https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380/
* Trying 13.75.94.86...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net (13.75.94.86) port 6380 (#0)
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 1/3)
* schannel: checking server certificate revocation
* schannel: sending initial handshake data: sending 202 bytes...
* schannel: sent initial handshake data: sent 202 bytes
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 2/3)
* schannel: failed to receive handshake, need more data
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 2/3)
* schannel: encrypted data got 4096
* schannel: encrypted data buffer: offset 4096 length 4096
* schannel: received incomplete message, need more data
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 2/3)
* schannel: encrypted data got 1024
* schannel: encrypted data buffer: offset 5120 length 5120
* schannel: received incomplete message, need more data
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 2/3)
* schannel: encrypted data got 496
* schannel: encrypted data buffer: offset 5616 length 6144
* schannel: sending next handshake data: sending 3791 bytes...
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 2/3)
* schannel: encrypted data got 51
* schannel: encrypted data buffer: offset 51 length 6144
* schannel: SSL/TLS handshake complete
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 3/3)
* schannel: stored credential handle in session cacheFail connection example due to either TLS version mismatch. Not supported ciphersuite returns similar error.
curl -v https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380 --tlsv1.0
* Rebuilt URL to: https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380/
* Trying 13.75.94.86...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net (13.75.94.86) port 6380 (#0)
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 1/3)
* schannel: checking server certificate revocation
* schannel: sending initial handshake data: sending 144 bytes...
* schannel: sent initial handshake data: sent 144 bytes
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 2/3)
* schannel: failed to receive handshake, need more data
* schannel: SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380 (step 2/3)
* schannel: failed to receive handshake, SSL/TLS connection failed
* Closing connection 0
* schannel: shutting down SSL/TLS connection with pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380
* Send failure: Connection was reset
* schannel: failed to send close msg: Failed sending data to the peer (bytes written: -1)
* schannel: clear security context handle
curl: (35) schannel: failed to receive handshake, SSL/TLS connection failedFailed due to network connectivity issue.
curl -v https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380 --tlsv1.2
* Rebuilt URL to: https://pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net:6380/
* Trying 13.75.94.86...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* connect to 13.75.94.86 port 6380 failed: Timed out
* Failed to connect to pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380: Timed out
* Closing connection 0
curl: (7) Failed to connect to pingrds.redis.cache.windows.net port 6380: Timed outopenssl
Suitable scenarios: TLS version mismatch, no supported CipherSuite, network connection between client and server.
openSSL is an open source tool and its s_client acts as SSL client to test SSL connection with a remote server. This is helpful to isolate the cause of client.
- On majority Linux machines, OpenSSL is there already. On Windows, you can download it from this link: https://chocolatey.org/packages/openssl
- Run Open SSL
- Windows: open the installation directory, click /bin/, and then double-click openssl.exe.
- Mac and Linux: run openssl from a terminal.
- Issue s_client -help to find all options.
Command examples:
1. Test a particular TLS version:
s_client -host sdcstest.blob.core.windows.net -port 443 -tls1_1
2. Disable one TLS version
s_client -host sdcstest.blob.core.windows.net -port 443 -no_tls1_2
3. Test with a given ciphersuite:
s_client -host sdcstest.blob.core.windows.net -port 443 -cipher ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
4. Verify if remote server’s certificates are trusted.
Success connection example:
CONNECTED(000001A0)
depth=1 C = US, O = Microsoft Corporation, CN = Microsoft RSA TLS CA 02
verify error:num=20:unable to get local issuer certificate
verify return:1
depth=0 CN = *.blob.core.windows.net
verify return:1
---
Certificate chain
0 s:CN = *.blob.core.windows.net
i:C = US, O = Microsoft Corporation, CN = Microsoft RSA TLS CA 02
1 s:C = US, O = Microsoft Corporation, CN = Microsoft RSA TLS CA 02
i:C = IE, O = Baltimore, OU = CyberTrust, CN = Baltimore CyberTrust Root
---
Server certificate
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIINtDCCC5ygAwIBAgITfwAI6NfesKGuQGWPYQAAAAjo1zANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsF
ADBPMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEeMBwGA1UEChMVTWljcm9zb2Z0IENvcnBvcmF0aW9u
pK8hqxL0zc4NQLRTq9RNpdPwnNmGn5SZ4Nu5ktUgWokR97THzgs6a/ErHH2tigLF
jwkgB8UuV/hhu3vEa0jxstSBgbjQPgSNexAl7XwgawaucIF+wkRpPW2w0VTcDWtT
1bGtFCpewAo=
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
subject=CN = *.blob.core.windows.net
issuer=C = US, O = Microsoft Corporation, CN = Microsoft RSA TLS CA 02
---
No client certificate CA names sent
Peer signing digest: MD5-SHA1
Peer signature type: RSA
Server Temp Key: ECDH, P-256, 256 bits
---
SSL handshake has read 5399 bytes and written 293 bytes
Verification error: unable to get local issuer certificate
---
New, TLSv1.0, Cipher is ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
Server public key is 2048 bit
Secure Renegotiation IS supported
Compression: NONE
Expansion: NONE
No ALPN negotiated
SSL-Session:
Protocol : TLSv1.1
Cipher : ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
Session-ID: B60B0000F51FFB7C9DDB4E58CD20DC20987C13CFD31386BE435D612CF5EFDBF9
Session-ID-ctx:
Master-Key: DA402F6E301B4E4981B7820CAF6E0AF3C633290E85E2998BFAB081788488D3807ABD3FF41FF48DA55DB56281C024C4F4
PSK identity: None
PSK identity hint: None
SRP username: None
Start Time: 1615557502
Timeout : 7200 (sec)
Verify return code: 20 (unable to get local issuer certificate)
Extended master secret: yesFail connection example due to TLS mismatch:
OpenSSL> s_client -host sdcstest.blob.core.windows.net -port 443 -tls1_3
CONNECTED(0000017C)
write:errno=10054
---
no peer certificate available
---
No client certificate CA names sent
---
SSL handshake has read 0 bytes and written 254 bytes
Verification: OK
---
New, (NONE), Cipher is (NONE)
Secure Renegotiation IS NOT supported
Compression: NONE
Expansion: NONE
No ALPN negotiated
Early data was not sent
Verify return code: 0 (ok)
---
error in s_client
Fail connection example due to network connectivity:
OpenSSL> s_client -host sdcstest.blob.core.windows.net -port 7780
30688:error:0200274C:system library:connect:reason(1868):crypto/bio/b_sock2.c:110:
30688:error:2008A067:BIO routines:BIO_connect:connect error:crypto/bio/b_sock2.c:111:
connect:errno=0
error in s_client
Online tool
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/
Suitable scenarios: TLS version mismatch, no supported CipherSuite.
This is a free online service performs a deep analysis of the configuration of any SSL web server on the public Internet. It can list all supported TLS versions and ciphers of a server. And auto detect if server works fine in different types of client, such as web browsers, mobile devices, etc.
Please note, this only works with public access website. For internal access website will need to run above curl or openssl from an internal environment. And it only supports domain name and does not work with IP address.
Web Browser:
Suitable scenarios: Verify if server certificate chain is trusted on client.
Web Browser can be used to verify if remote server’s certificate is trusted or not locally:
- Access the url from web browser.
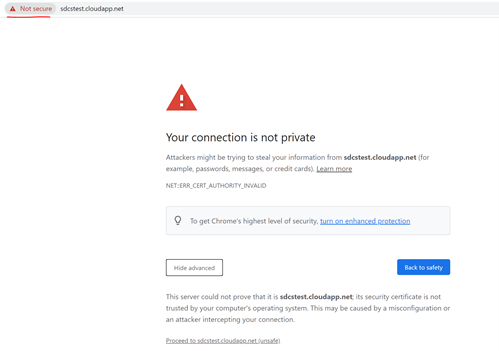
- It does not matter if the page can be load or not. Before loading anything from the remote sever, web browser tried to establish SSL connection.
- If you see below error returned, it means certificate is not trusted on current machine.
Certutil
Suitable scenarios: Verify if server certificate on client, verify client certificate on server.
Certutil is a tool available on windows. It is useful to verify a given certificate. For example verify server certificate from client end. If mutual authentication is implemented, this tool can also be used to verify client certificate on server.
The command auto verifies trusted certificate chain and certificate revocation list (CRL).
Command:
certutil -verify -urlfetch <client cert file path>
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/certutil#-verify
Next blog, I will introduce solutions for common causes of SSL/TLS connection issues.
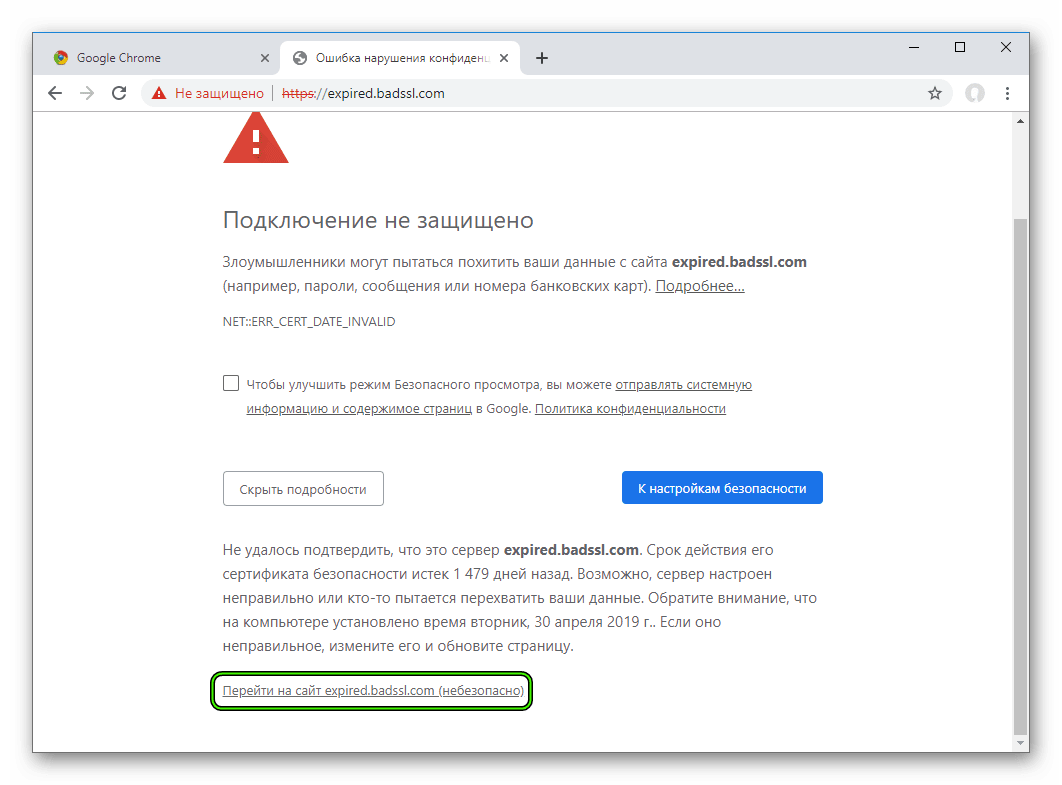
При открытии сайтов в браузере иногда возникают ошибки – домен в адресной строке выделяется красным с зачеркиванием или ресурс вообще не открывается. Типовая причина скрывается в сбоях работы сертификата SSL. Исправить их может только администратор сайта, но перед обращением к нему стоит проверить собственный компьютер.
Что такое SSL
Текущие тенденции сайтостроения предполагают высокую безопасность соединения пользователя с веб-ресурсом. Это необходимо для защиты персональных данных, секретных номеров банковских карт и информации о проводимых сделках. Организуется безопасность подключением протокола шифрования Secure Sockets Layer (сокращенно SSL).
Особенности сертификата:
- Сертификат выпускается доверенным центром Certification Authority (CA).
- После выдачи он подключается к домену средствами провайдера хостинга.
- Срок его действия ограничен 1 годом, после чего требуется продление.
Работа сайта возможна и без SSL, но поисковые системы «не доверяют» таким ресурсам и помечают их в браузере как неблагонадежные. Поэтому лучше разобраться, как решить проблему с защитой и полноценно пользоваться протоколом HTTPS. Сертификат актуален на сайтах, где присутствует регистрация, предлагается покупка товаров или онлайн-оплата различных сервисов.
При появлении любых сомнений в исправности защиты регистрироваться на сайте или вводить ранее выданные логин и пароль не рекомендуется. Тем более не стоит осуществлять онлайн-оплату с банковских карт или электронных кошельков, ведь не исключено, что проблема возникла из-за взлома ресурса злоумышленниками.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Причины появления ошибок SSL
Существует всего две причины, почему браузер отображает ошибку сертификата SSL со стороны сервера. Первая заключается в окончании срока активации, вторая – это покупка сертификата у поставщика без достаточных полномочий для выдачи «полноценной защиты». Например, виной может быть выбор самоподписанного сертификата, лишь эмулирующего работу реального протокола.
Остальные проблемы обычно скрываются на локальном компьютере:
- Произошел сброс системного времени.
- Неправильно настроена антивирусная программа.
- Сбоит браузер или установленное расширение.
- Срабатывает вредоносный скрипт.
Чтобы выяснить настоящую причину, пользователю браузера рекомендуется проверить все перечисленные факторы. При том же заражении компьютерными вирусами возможно проявление сразу нескольких симптомов – от изменения текущего времени и блокировки антивирусом до подключения перенаправления страниц в браузере и других неприятностей.
Изредка встречаются ситуации, когда проблема возникла со стороны администратора, если он ошибся при подключении нового сертификата или забыл продлить его действие. Обычно такие неполадки устраняются быстро, потому что после активации сайт проверяется и, в случае неработоспособности сертификата, проводится повторное подключение вплоть до получения положительного результата.
Время и дата
Сертификат SSL имеет четко обозначенный срок действия с датой активации и деактивации. Такой подход отчасти дает дополнительную защиту, потому что в случае технического сбоя в системных часах компьютера сайты перестают открываться. Сброс времени обычно происходит «назад», на дату изготовления материнской платы, на что и реагирует система.
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Вручную внести корректную дату и время, после чего обновить страницу в браузере.
- Воспользоваться функцией синхронизации через интернет, встроенной в Windows.
- Заменить батарейку на памяти BIOS. При первом запуске ПК нужно внести корректные данные.
Каждый раз после изменения времени рекомендуется ручное обновление страницы или перезапуск браузера. Такой шаг активирует повторное соединение с сервером и позволяет зайти на сайт «с нуля», но уже с правильным временем, соответствующим сроку действия сертификата SSL (после активации и до ее завершения).
Настройки антивируса и брандмауэра
Программы для защиты компьютера от вирусов и хакерских атак иногда блокируют и «полезные» соединения, например, определенные домены или сразу весь протокол HTTPS, используемый при подключении сертификата SSL. Большинство антивирусов и брандмауэров проверяют его работу, и это становится причиной блокировки сайта как «злоумышленника, пытающего украсть данные».
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Отключить режим «проверка протокола HTTPS». После этого зайти на сайт заново.
- Полностью выключить антивирусную программу. Перезагрузить ПК, открыть страницу.
- Сбросить настройки брандмауэра. Опять проводится перезапуск компьютера и веб-ресурса.
Функция временного отключения имеется в любой защитной программе, даже интегрированной в операционную систему Windows. Но это не гарантирует полную деактивацию приложения. В этом случае разобраться в ситуации поможет открытие сайта на другом компьютере или запуск безопасного режима (актуально для проводного подключения к интернету).
Браузер и операционная система
Наличие проблемы с браузером проще всего определить открытием сайта на другом устройстве или в другой программе. Иногда решение заключается в банальном обновлении версии приложения до актуальной. То же относится к операционной системе, если используется интегрированный браузер вроде Edge. Пакеты обновлений для того и выпускаются, чтобы устранять неполадки в ПО.
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Полностью очистить историю браузера вместе с кэшем и другими данными.
- Временно отключить все ранее установленные и активные расширения.
- Переустановить программу после ее полной деинсталляции.
Остается еще один вариант – сбросить настройки браузера до состояния «по умолчанию». Способ аналогичен переустановке, но экономит время. Правда, он неэффективен, если проблема возникла из-за сбоя в одном из служебных файлов программы. Отдельное внимание стоит уделить расширению, выполняющему функции антивирусной защиты, ведь оно часто блокирует даже безопасное соединение.
Заражение компьютерными вирусами
Выдачей ошибки SSL браузер, вероятно, предупреждает о попытке его подмены, переадресации на сайт-клон или иной угрозе. В это случае рекомендуется провести полную проверку компьютера на наличие вирусов. Если присутствуют другие признаки заражения, стоит скачать парочку программ со свежими антивирусными базами (например, CureIt).
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Временно отключить все программы из автозагрузки.
- Провести очистку диска от временных файлов.
- Перезагрузить компьютер после предыдущих шагов.
Выполняются перечисленные действия программами типа CCleaner. Они дают прямой доступ как к автозагрузке операционной системе, так и к списку расширений установленных браузеров. Также в таких программах обычно есть функция удаления ненужных системных файлов, в которых запросто может быть тело компьютерного вируса.
Если предложенные способы устранения ошибки SSL не помогли, остается ждать, пока проблему устранит администратор, или воспользоваться любым другим тематическим сайтом с аналогичным контентом.
I finally found the answer (I haven’t noted my source but it was from a search);
While the code works in Windows XP, in Windows 7, you must add this at the beginning:
// using System.Net;
ServicePointManager.Expect100Continue = true;
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls12;
// Use SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3 if needed for compatibility reasons
And now, it works perfectly.
ADDENDUM
As mentioned by Robin French; if you are getting this problem while configuring PayPal, please note that they won’t support SSL3 starting by December, 3rd 2018. You’ll need to use TLS. Here’s Paypal page about it.
answered May 25, 2010 at 13:18
Simon DugréSimon Dugré
17.7k11 gold badges56 silver badges73 bronze badges
25
The solution to this, in .NET 4.5 is
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls12;
If you don’t have .NET 4.5 then use
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = (SecurityProtocolType)3072;
answered Feb 22, 2018 at 14:46
5
Make sure the ServicePointManager settings are made before the HttpWebRequest is created, else it will not work.
Works:
ServicePointManager.Expect100Continue = true;
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls
| SecurityProtocolType.Tls11
| SecurityProtocolType.Tls12
| SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3;
HttpWebRequest request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create("https://google.com/api/")
Fails:
HttpWebRequest request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create("https://google.com/api/")
ServicePointManager.Expect100Continue = true;
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls
| SecurityProtocolType.Tls11
| SecurityProtocolType.Tls12
| SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3;
soccer7
3,4193 gold badges29 silver badges49 bronze badges
answered Jun 21, 2018 at 21:39
hogarth45hogarth45
3,3471 gold badge22 silver badges27 bronze badges
8
Note: Several of the highest voted answers here advise setting ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol, but Microsoft explicitly advises against doing that. Below, I go into the typical cause of this issue and the best practices for resolving it.
One of the biggest causes of this issue is the active .NET Framework version. The .NET framework runtime version affects which security protocols are enabled by default.
- In ASP.NET sites, the framework runtime version is often specified in web.config. (see below)
- In other apps, the runtime version is usually the version for which the project was built, regardless of whether it is running on a machine with a newer .NET version.
There doesn’t seem to be any authoritative documentation on how it specifically works in different versions, but it seems the defaults are determined more or less as follows:
| Framework Version | Default Protocols |
|---|---|
| 4.5 and earlier | SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0 |
| 4.6.x | TLS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 |
| 4.7+ | System (OS) Defaults |
For the older versions, your mileage may vary somewhat based on which .NET runtimes are installed on the system. For example, there could be a situation where you are using a very old framework and TLS 1.0 is not supported, or using 4.6.x and TLS 1.3 is not supported.
Microsoft’s documentation strongly advises using 4.7+ and the system defaults:
We recommend that you:
- Target .NET Framework 4.7 or later versions on your apps. Target .NET Framework 4.7.1 or later versions on your WCF apps.
- Do not specify the TLS version. Configure your code to let the OS decide on the TLS version.
- Perform a thorough code audit to verify you’re not specifying a TLS or SSL version.
For ASP.NET sites: check the targetFramework version in your <httpRuntime> element, as this (when present) determines which runtime is actually used by your site:
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5" />
Better:
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.7" />
answered Oct 2, 2019 at 6:02
JLRisheJLRishe
99k19 gold badges131 silver badges169 bronze badges
6
I had this problem trying to hit https://ct.mob0.com/Styles/Fun.png, which is an image distributed by CloudFlare on its CDN that supports crazy stuff like SPDY and weird redirect SSL certs.
Instead of specifying Ssl3 as in Simons answer I was able to fix it by going down to Tls12 like this:
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls12;
new WebClient().DownloadData("https://ct.mob0.com/Styles/Fun.png");
InteXX
6,0636 gold badges41 silver badges77 bronze badges
answered Oct 15, 2014 at 17:42
Bryan LegendBryan Legend
6,7601 gold badge59 silver badges60 bronze badges
3
After many long hours with this same issue I found that the ASP.NET account the client service was running under didn’t have access to the certificate. I fixed it by going into the IIS Application Pool that the web app runs under, going into Advanced Settings, and changing the Identity to the LocalSystem account from NetworkService.
A better solution is to get the certificate working with the default NetworkService account but this works for quick functional testing.
answered Dec 4, 2014 at 16:31
Nick GotchNick Gotch
9,15714 gold badges70 silver badges97 bronze badges
3
The error is generic and there are many reasons why the SSL/TLS negotiation may fail. The most common is an invalid or expired server certificate, and you took care of that by providing your own server certificate validation hook, but is not necessarily the only reason. The server may require mutual authentication, it may be configured with a suites of ciphers not supported by your client, it may have a time drift too big for the handshake to succeed and many more reasons.
The best solution is to use the SChannel troubleshooting tools set. SChannel is the SSPI provider responsible for SSL and TLS and your client will use it for the handshake. Take a look at TLS/SSL Tools and Settings.
Also see How to enable Schannel event logging.
answered May 18, 2010 at 18:14
Remus RusanuRemus Rusanu
287k40 gold badges437 silver badges567 bronze badges
3
The approach with setting
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls12
Seems to be okay, because Tls1.2 is latest version of secure protocol. But I decided to look deeper and answer do we really need to hardcode it.
Specs: Windows Server 2012R2 x64.
From the internet there is told that .NetFramework 4.6+ must use Tls1.2 by default. But when I updated my project to 4.6 nothing happened.
I have found some info that tells I need manually do some changes to enable Tls1.2 by default
https://support.microsoft.com/en-in/help/3140245/update-to-enable-tls-1-1-and-tls-1-2-as-default-secure-protocols-in-wi
But proposed windows update doesnt work for R2 version
But what helped me is adding 2 values to registry. You can use next PS script so they will be added automatically
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:SOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoft.NetFrameworkv4.0.30319' -Name 'SchUseStrongCrypto' -Value '1' -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:SOFTWAREMicrosoft.NetFrameworkv4.0.30319' -Name 'SchUseStrongCrypto' -Value '1' -Type DWord
That is kind of what I was looking for. But still I cant answer on question why NetFramework 4.6+ doesn’t set this …Protocol value automatically?
answered Oct 28, 2019 at 20:58
simply goodsimply good
9711 gold badge12 silver badges26 bronze badges
5
Another possible cause of the The request was aborted: Could not create SSL/TLS secure channel error is a mismatch between your client PC’s configured cipher_suites values, and the values that the server is configured as being willing and able to accept. In this case, when your client sends the list of cipher_suites values that it is able to accept in its initial SSL handshaking/negotiation «Client Hello» message, the server sees that none of the provided values are acceptable, and may return an «Alert» response instead of proceeding to the «Server Hello» step of the SSL handshake.
To investigate this possibility, you can download Microsoft Message Analyzer, and use it to run a trace on the SSL negotiation that occurs when you try and fail to establish an HTTPS connection to the server (in your C# app).
If you are able to make a successful HTTPS connection from another environment (e.g. the Windows XP machine that you mentioned — or possibly by hitting the HTTPS URL in a non-Microsoft browser that doesn’t use the OS’s cipher suite settings, such as Chrome or Firefox), run another Message Analyzer trace in that environment to capture what happens when the SSL negotiation succeeds.
Hopefully, you’ll see some difference between the two Client Hello messages that will allow you to pinpoint exactly what about the failing SSL negotiation is causing it to fail. Then you should be able to make configuration changes to Windows that will allow it to succeed. IISCrypto is a great tool to use for this (even for client PCs, despite the «IIS» name).
The following two Windows registry keys govern the cipher_suites values that your PC will use:
- HKLMSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftCryptographyConfigurationSSL0010002
- HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlCryptographyConfigurationLocalSSL0010002
Here’s a full writeup of how I investigated and solved an instance of this variety of the Could not create SSL/TLS secure channel problem: http://blog.jonschneider.com/2016/08/fix-ssl-handshaking-error-in-windows.html
answered Aug 31, 2016 at 4:33
Jon SchneiderJon Schneider
25.5k23 gold badges140 silver badges168 bronze badges
3
Something the original answer didn’t have. I added some more code to make it bullet proof.
ServicePointManager.Expect100Continue = true;
ServicePointManager.DefaultConnectionLimit = 9999;
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls | SecurityProtocolType.Tls11 | SecurityProtocolType.Tls12 | SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3;
answered Jun 1, 2016 at 15:05
SpoiledTechie.comSpoiledTechie.com
10.5k21 gold badges77 silver badges99 bronze badges
5
The top-voted answer will probably be enough for most people. However, in some circumstances, you could continue getting a «Could not create SSL/TLS secure channel» error even after forcing TLS 1.2. If so, you may want to consult this helpful article for additional troubleshooting steps. To summarize: independent of the TLS/SSL version issue, the client and server must agree on a «cipher suite.» During the «handshake» phase of the SSL connection, the client will list its supported cipher-suites for the server to check against its own list. But on some Windows machines, certain common cipher-suites may have been disabled (seemingly due to well-intentioned attempts to limit attack surface), decreasing the possibility of the client & server agreeing on a cipher suite. If they cannot agree, then you may see «fatal alert code 40» in the event viewer and «Could not create SSL/TLS secure channel» in your .NET program.
The aforementioned article explains how to list all of a machine’s potentially-supported cipher suites and enable additional cipher suites through the Windows Registry. To help check which cipher suites are enabled on the client, try visiting this diagnostic page in MSIE. (Using System.Net tracing may give more definitive results.) To check which cipher suites are supported by the server, try this online tool (assuming that the server is Internet-accessible). It should go without saying that Registry edits must be done with caution, especially where networking is involved. (Is your machine a remote-hosted VM? If you were to break networking, would the VM be accessible at all?)
In my company’s case, we enabled several additional «ECDHE_ECDSA» suites via Registry edit, to fix an immediate problem and guard against future problems. But if you cannot (or will not) edit the Registry, then numerous workarounds (not necessarily pretty) come to mind. For example: your .NET program could delegate its SSL traffic to a separate Python program (which may itself work, for the same reason that Chrome requests may succeed where MSIE requests fail on an affected machine).
answered Jun 1, 2019 at 6:16
APWAPW
3544 silver badges6 bronze badges
1
This one is working for me in MVC webclient
public string DownloadSite(string RefinedLink)
{
try
{
Uri address = new Uri(RefinedLink);
ServicePointManager.ServerCertificateValidationCallback = delegate { return true; };
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3;
System.Net.ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls11 | SecurityProtocolType.Tls12;
using (WebClient webClient = new WebClient())
{
var stream = webClient.OpenRead(address);
using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(stream))
{
var page = sr.ReadToEnd();
return page;
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
log.Error("DownloadSite - error Lin = " + RefinedLink, e);
return null;
}
}
soccer7
3,4193 gold badges29 silver badges49 bronze badges
answered Oct 4, 2017 at 7:14
Arun Prasad E SArun Prasad E S
9,3438 gold badges73 silver badges86 bronze badges
3
«The request was aborted: Could not create SSL/TLS secure channel» exception can occur if the server is returning an HTTP 401 Unauthorized response to the HTTP request.
You can determine if this is happening by turning on trace-level System.Net logging for your client application, as described in this answer.
Once that logging configuration is in place, run the application and reproduce the error, then look in the logging output for a line like this:
System.Net Information: 0 : [9840] Connection#62912200 - Received status line: Version=1.1, StatusCode=401, StatusDescription=Unauthorized.
In my situation, I was failing to set a particular cookie that the server was expecting, leading to the server responding to the request with the 401 error, which in turn led to the «Could not create SSL/TLS secure channel» exception.
answered Aug 19, 2014 at 19:55
Jon SchneiderJon Schneider
25.5k23 gold badges140 silver badges168 bronze badges
1
Another possibility is improper certificate importation on the box. Make sure to select encircled check box. Initially I didn’t do it, so code was either timing out or throwing same exception as private key could not be located.
answered Jul 11, 2012 at 22:27
SherlockSherlock
1,0228 silver badges19 bronze badges
1
Doing this helped me:
System.Net.ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls12;
answered Jan 26, 2021 at 22:39
Merlyn007Merlyn007
4341 gold badge7 silver badges21 bronze badges
0
Finally found solution for me.
Try this adding below line before calling https url (for .Net framework 4.5):
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls12;
Luis Teijon
4,7517 gold badges36 silver badges57 bronze badges
answered Jun 16, 2021 at 5:24
0
I had this problem because my web.config had:
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5.2" />
and not:
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.6.1" />
answered Aug 15, 2017 at 10:47
Terje SolemTerje Solem
8061 gold badge10 silver badges25 bronze badges
1
In my case, the service account running the application did not have permission to access the private key. Once I gave this permission, the error went away
- mmc
- certificates
- Expand to personal
- select cert
- right click
- All tasks
- Manage private keys
- Add the service account user
answered Nov 13, 2017 at 21:24
Dinesh RajanDinesh Rajan
2,35623 silver badges19 bronze badges
1
As you can tell there are plenty of reasons this might happen. Thought I would add the cause I encountered …
If you set the value of WebRequest.Timeout to 0, this is the exception that is thrown. Below is the code I had… (Except instead of a hard-coded 0 for the timeout value, I had a parameter which was inadvertently set to 0).
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(@"https://myservice/path");
webRequest.ContentType = "text/html";
webRequest.Method = "POST";
string body = "...";
byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(body);
webRequest.ContentLength = bytes.Length;
var os = webRequest.GetRequestStream();
os.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length);
os.Close();
webRequest.Timeout = 0; //setting the timeout to 0 causes the request to fail
WebResponse webResponse = webRequest.GetResponse(); //Exception thrown here ...
answered Apr 25, 2014 at 20:50
TCCTCC
2,5461 gold badge24 silver badges35 bronze badges
1
The root of this exception in my case was that at some point in code the following was being called:
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Ssl3;
This is really bad. Not only is it instructing .NET to use an insecure protocol, but this impacts every new WebClient (and similar) request made afterward within your appdomain. (Note that incoming web requests are unaffected in your ASP.NET app, but new WebClient requests, such as to talk to an external web service, are).
In my case, it was not actually needed, so I could just delete the statement and all my other web requests started working fine again. Based on my reading elsewhere, I learned a few things:
- This is a global setting in your appdomain, and if you have concurrent activity, you can’t reliably set it to one value, do your action, and then set it back. Another action may take place during that small window and be impacted.
- The correct setting is to leave it default. This allows .NET to continue to use whatever is the most secure default value as time goes on and you upgrade frameworks. Setting it to TLS12 (which is the most secure as of this writing) will work now but in 5 years may start causing mysterious problems.
- If you really need to set a value, you should consider doing it in a separate specialized application or appdomain and find a way to talk between it and your main pool. Because it’s a single global value, trying to manage it within a busy app pool will only lead to trouble. This answer: https://stackoverflow.com/a/26754917/7656 provides a possible solution by way of a custom proxy. (Note I have not personally implemented it.)
answered Sep 16, 2016 at 23:54
1
If you are running your code from Visual Studio, try running Visual Studio as administrator. Fixed the issue for me.
answered Feb 27, 2018 at 16:59
handleshandles
7,63117 gold badges63 silver badges85 bronze badges
1
System.Net.WebException: The request was aborted: Could not create
SSL/TLS secure channel.
In our case, we where using a software vendor so we didn’t have access to modify the .NET code. Apparently .NET 4 won’t use TLS v 1.2 unless there is a change.
The fix for us was adding the SchUseStrongCrypto key to the registry. You can copy/paste the below code into a text file with the .reg extension and execute it. It served as our «patch» to the problem.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv4.0.30319]
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv4.0.30319]
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
answered Jul 26, 2018 at 14:35
capdragoncapdragon
14.5k24 gold badges106 silver badges153 bronze badges
3
I have struggled with this problem all day.
When I created a new project with .NET 4.5 I finally got it to work.
But if I downgraded to 4.0 I got the same problem again, and it was irreversable for that project (even when i tried to upgrade to 4.5 again).
Strange no other error message but «The request was aborted: Could not create SSL/TLS secure channel.» came up for this error
answered Dec 2, 2015 at 16:08
aghostaghost
1922 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
In case that the client is a windows machine, a possible reason could be that the tls or ssl protocol required by the service is not activated.
This can be set in:
Control Panel -> Network and Internet -> Internet Options -> Advanced
Scroll settings down to «Security» and choose between
- Use SSL 2.0
- Use SSL 3.0
- Use TLS 1.0
- Use TLS 1.1
- Use TLS 1.2
answered May 10, 2017 at 7:05
cnomcnom
2,9914 gold badges29 silver badges60 bronze badges
4
none of this answer not working for me , the google chrome and postman work and handshake the server but ie and .net not working. in google chrome in security tab > connection show that encrypted and authenticated using ECDHE_RSA with P-256 and AES_256_GCM cipher suite to handshake with the server.
i install IIS Crypto and in cipher suites list on windows server 2012 R2 ican’t find ECDHE_RSA with P-256 and AES_256_GCM cipher suite. then i update windows to the last version but the problem not solve. finally after searches i understood that windows server 2012 R2 not support GSM correctly and update my server to windows server 2016 and my problem solved.
answered May 31, 2020 at 5:46
I was having this same issue and found this answer worked properly for me. The key is 3072. This link provides the details on the ‘3072’ fix.
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = (SecurityProtocolType)3072;
XmlReader r = XmlReader.Create(url);
SyndicationFeed albums = SyndicationFeed.Load(r);
In my case two feeds required the fix:
https://www.fbi.gov/feeds/fbi-in-the-news/atom.xml
https://www.wired.com/feed/category/gear/latest/rss
Stephen Rauch♦
47.5k31 gold badges106 silver badges135 bronze badges
answered May 27, 2018 at 14:02
joeydoodjoeydood
511 silver badge4 bronze badges
1
None of the answers worked for me.
This is what worked:
Instead of initializing my X509Certifiacte2 like this:
var certificate = new X509Certificate2(bytes, pass);
I did it like this:
var certificate = new X509Certificate2(bytes, pass, X509KeyStorageFlags.MachineKeySet | X509KeyStorageFlags.PersistKeySet | X509KeyStorageFlags.Exportable);
Notice the X509KeyStorageFlags.Exportable !!
I didn’t change the rest of the code (the WebRequest itself):
// I'm not even sure the first two lines are necessary:
ServicePointManager.Expect100Continue = true;
ServicePointManager.SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocolType.Tls12;
request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(string.Format("https://{0}.sii.cl/cvc_cgi/dte/of_solicita_folios", server));
request.Method = "GET";
request.Referer = string.Format("https://hercules.sii.cl/cgi_AUT2000/autInicio.cgi?referencia=https://{0}.sii.cl/cvc_cgi/dte/of_solicita_folios", servidor);
request.UserAgent = "Mozilla/4.0";
request.ClientCertificates.Add(certificate);
request.CookieContainer = new CookieContainer();
using (HttpWebResponse response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse())
{
// etc...
}
In fact I’m not even sure that the first two lines are necessary…
answered Apr 30, 2019 at 17:58
sportssports
7,81314 gold badges71 silver badges129 bronze badges
2
Another possibility is that the code being executed doesn’t have the required permissions.
In my case, I got this error when using Visual Studio debugger to test a call to a web service. Visual Studio wasn’t running as Administrator, which caused this exception.
answered Oct 30, 2019 at 10:11
OfirDOfirD
8,9235 gold badges45 silver badges88 bronze badges
This fixed for me, add Network Service to permissions.
Right click on the certificate > All Tasks > Manage Private Keys… > Add… > Add «Network Service».
answered Apr 6, 2018 at 6:27
jayasurya_jjayasurya_j
1,4991 gold badge14 silver badges22 bronze badges
1