What this tutorial is about
This tutorial aims to walk you step by step through creating source code in a Python project, with the use of PyCharm’s code intelligence features. You will see how PyCharm helps keep your source code in perfect shape, with proper indentations, spaces, imports etc. — actually, you’ll see that PyCharm itself is a code quality tool.
Python programming is out of scope of this tutorial. To learn more about the Python language, please refer to the official website.
Before you start
Make sure that:
-
You are working with PyCharm version 5.0 or later. If you still do not have PyCharm, download it from this page. To install PyCharm, follow the instructions, depending on your platform. Refer to the product documentation for details.
-
You have created a Python project (). Refer to the product documentation for details.
-
You have created two directories src and test_dir ( or Alt+Insert).
-
You have added Python files to the src and test_dir directories of your project( or Alt+Insert). To learn about creating files, refer to the section Populate projects.
Highliting code style violations
Create a new Python file src/Solver.py Alt+Insert. The created file immediately opens for editing. The file by default has no contents — this is because the file Solver.py is created by a file template that (in the case of Python files) contains just nothing.
Next, start typing the keyword class. When you just start typing, PyCharm immediately shows the suggestion list to complete your code:
(Refer to Code Completion page of the product documentation for details.)
The red curve marks the next expected entry — in this case, this is the expected identifier. Enter the class name Solver. The red curve moves after the class name. If you hover your mouse pointer over this curve, you see the error description («Colon expected»). Also, mind the red error stripe in the right gutter — it also marks the same error:
OK, type the colon, and press Enter. According to the Python code style, the next statement is indented. If by chance you press space after Enter, you will thus violate the code style settings.
Tuning the PEP8 inspections
However, by default these violation are but weak warnings, and as such, are not visible. So, at first, let’s raise their importance. Click 
Apply changes and close the dialog. Now let’s return to our source code.
Tracking PEP8 rules
Now PyCharm shows its best! It stands on guard to protect your code style integrity. You immediately note that indented space is highlighted, and, when you type the next statement, for example, def demo(self,a,b,c):, PyCharm will show the message from the PEP8 inspection:
So, as you can see, PyCharm supports PEP8 as the official Python style guide. If you explore the list of inspections (Ctrl+Alt+S — Inspections), you will see that PyCharm launches the pep8.py tool on your code, and pinpoints the code style violations.
Code inspections and their settings
Btw, look at the Inspections more attentively. If you have just opened this page, you see the default inspection profile with the default settings: it means that the inspections apply to all the sources of the current project.
Let’s try to customize this profile for two different scopes:
-
In the Test scope, the spelling errors should be marked as typos (green)
-
In the Production scope, the spelling errors should be marked as errors (red) — can we actually produce code with typos?
This is how it’s done…
Creating scopes
First, let’s define the two scopes. To do that, click 

In the Add New Scope dialog box, type the scope name (Test), and then, in the project tree, choose the directory to be included in the Test scope, test_dir. Note that the Pattern field is filled in automatically, as you include the directory:
Repeat this process to create the Production scope.
Creating inspection profile with these scopes
Next, let’s create a copy of the default profile (though this profile is editable… just to be on the safe side):
and give it a new name, for example, MyProjectProfile. This new profile is a copy of the default one, and has the same set of inspections.
With this new profile selected, let’s locate the Spelling inspection and change it. To find the Spelling inspection (we’ve already done it before), just type spel in the search area.
What’s next? Click In All Scopes button and select the Test scope from the list; repeat same for the Production scope
In the scope «Test», the inspection severity is left as-is (a typo); however, the scope «Production» we’ll choose «Error» from the list of severities:
Mind the color code of inspections. They are shown black if unchanged. If they are blue, then it means that they have been changed.
Apply changes and close the dialog…
So, the modified inspection profile is ready. Its name is Project Default (copy), and it has different settings for the Spelling inspection in the Test and Production scopes. Next, let’s inspect code against this profile. To do that, choose on the main menu, and in the dialog box, choose the desired profile and scope:
Do it twice — for Test and Production scopes (if you want to preserve inspection results for further examination and sharing, you can export them). Explore results:
Highlighting errors
Besides coding style violations, PyCharm highlights the other errors too, depending on the selected profile.
For example, if your inspection profile includes Python inspection Unresolved references, and you use a symbol that not yet has been imported, PyCharm underlines the unresolved reference and suggests to add import statement:
Refer to the product documentation.
Generating source code
PyCharm provides lots of possibilities to automatically generate code. You can explore the auto-generation features in the product documentation. Let’s explore the main code generation procedures. To do that, just delete all contents of the file Solver.py, and start from scratch.
First, create an instance of a class:
Next, press Alt+Enter and choose the intention action Create class ‘Solver’:
Great! PyCharm has stubbed out a class:
Next, let’s add a method to the class instance. To do that, type a dot after class instance, and then type the method name. This method does not yet exist, and PyCharm suggests to create one:
Let’s do some manual work — type the source code. When it comes to calculate the discriminant, we have to extract a square root. There is a dedicated function sqrt in the library math, but it is not yet imported. OK, let’s type it anyway, and see how PyCharm copes with it. Press Alt+Enter and choose Import ‘math’:
So, we’ve come to the source code like this:
import math
class Solver(object):
def demo(self,a,b,c):
d = b ** 2 — 4 * a * c
disc = math.sqrt(d)
root1 = (- b + disc) / (2 * a)
root2 = (- b — disc) / (2 * a)
print (root1, root2)
return root1, root2
However, it lacks some significant analysis. We’d like to analyze the radicand d. If it is zero or positive, then the discriminant and the equation roots will be calculated; when the radicand is negative, let’s raise an exception. How PyCharm will help complete this task?
Let’s surround a block of code with if construct. Select the statements to be completed, when d is non-negative, and press Ctrl+Alt+T (or choose on the main menu):
Select if option from the suggestion list. As you see, PyCharm automatically adds if True: and indents the selected lines:
We are not at all interested in a boolean expression, so let’s change the selected True to d >= 0. Next, place the caret at the end of the last line, and press Enter. The caret rests on the next line, with the same indentation as the if statement; type the else: clause here, and see PyCharm reporting about the expected indentation:
When you press Enter again, the caret rests at the indented position. Here you can type the exception expression, using PyCharm’s powerful automatic code completion:
Reformatting code
Let’s look again at our Solver.py file. Its right gutter shows yellow stripes. When you hover your mouse pointer over a stripe, PyCharm shows the description of the corresponding problem in the code:
The good news is that they are but warnings, and won’t affect the results. Bad news is they are too numerous to fix each one by one. Is it possible to make the source code nice and pretty without much fuss?
PyCharm says — yes. This is the code reformatting feature. So let’s try to change formatting of the entire file. To do that, press Ctrl+Alt+L (or choose on the main menu):
Look at the code now — the PEP8-related drawbacks are all gone.
Note that you can define formatting rules yourself. To do that, open the code style settings, select language (in this case, Python), and make the necessary changes:
Adding documentation comments
OK, formatting is fixed now, but there are still some stripes left. The inevitable yellow light bulb shows the possibility to add a docstring comment:
Choose this suggestion and see the docstring comment for a certain parameter added:
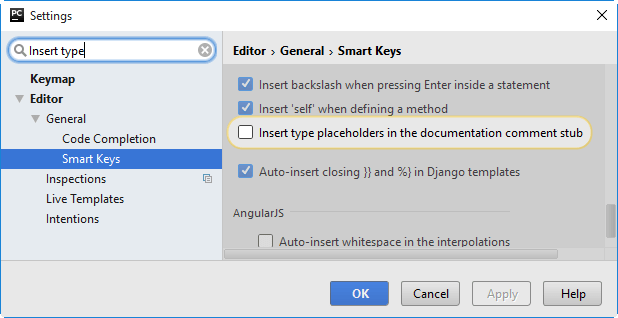
Note that you have to select the checkbox Insert type placeholders in documentation comment strings in the Smart Keys page of the Editor settings:
There are several docstring formats, and the documentation comments are created in the format, which you have selected in the Python Integrated Tools page. If you so wish, you can change the docstring format to, say, Epytext or plain text.
Type hinting
The documentation comments can be used to define the expected types of parameters, return values, or local variables. Why do we need it all? For example, we’d like to keep under control the types of parameters we pass to the demo() method. To do that, let’s add the corresponding information to the documentation comment (By the way, mind code completion in the documentation comments!):
Next, when you look at the method invocation, you see that the wrong parameter is highlighted by the PyCharm’s inspection Type Checker:
Learn more about type hinting in the PyCharm documentation.
Last modified: 11 January 2023
I’ve been having this PEP8 style highlighting issue. The issue is it’s not highlighting obvious style issues, like no blank lines before class definitions, or no empty lines at the end of the file. It could have to do with my VM and vagrant, but the project code is hosted locally so I don’t think that should be an issue.
If I do Code > Run Inspection By Name > PEP 8 coding style violation it says it finds no instances.
Under File > Settings > Editor > Code Style > Python > Blank Lines I have blank lines set around the class. An oddity is that if I change the number of lines «around method», it changes them in real time in the example text on the right, but it doesn’t do the same for lines «around class».
Under File > Settings > Editor > Inspections > Python I have «PEP 8 coding style violation» selected. I’ve tried changing it from warning to error and I still can’t see the highlights in my file.
I don’t have power saver mode on, which I’ve learned is a way to deactivate the background style checking in the editor.
I searched in Help > Show Log in Files for PEP8 and found «Pep8ExternalAnnotator — Found no suitable interpreter», but I don’t know what that means and I couldn’t find any references to it online.
I’m running PyCharms professional 2016.3
PyCharm 2016.3.2
Build #PY-163.10154.50, built on December 28, 2016
Licensed to arbaerbearfaerfa
Subscription is active until October 17, 2017
For educational use only.
JRE: 1.8.0_112-release-408-b6 amd64
JVM: OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM by JetBrains s.r.o
Всем привет.
Можно ли как нибудь в PyCharm по нажатию конопки или комбинации, полностью весь код в файле привестии к PEP8 стандарту. То есть что бы удалились лишние энтеры, перенос строки, импорты лишние убрались и всё в этом духе.
Есть комбинация alt + ctrl + o, но она только импорты лишние дропает.
-
Вопрос заданболее трёх лет назад
-
13059 просмотров
Rui Sun
Ph.D. student
Biomedical Engineering
Carnegie Mellon University
-
GitHub
less than 1 minute read
Taken from https://gist.github.com/StefanoMagrassi/6c78b6f48599377a5c805fd58a5cd93d
- Go to settings, search for Inspections (Under Editor, Code style)
- Find and click PEP8 code style violation. In the right panel, there is ignore errors option.
- Find the error code of interest, e.g. E501 line too long here, and paste the code to Pycharm.
- Ok the setting.
Introduction
Python development uses Pycharm.
Python Coding style warning
Variable in function should be lowercasepep8 indentation is not a multiple of four(appears when changing the Indent size from 4 half-width spaces to 2)
Is annoying everywhere, so I will put the setting method in Pycharm to suppress this on the back of the leaflet.
Setting method
- ** How to remove Variable in function should be lower case **
- Open ʻInspections
withFile→Settingand uncheckPEP 8 coding naming convention viloation` - ** How to erase pep8 indentation is not a multiple of four **
- Open ʻInspections
withFile→Settingand selectPEP 8 coding style viloation` on the search screen in the right pane. - Add ʻE111
to ʻIgnore errorsand execute ʻApply`
Similar warnings in other development environments
- If you use PEP8’s Linter in other development environments, you should usually have a setting to Ignore certain errors. For example, in the case of ATOM PEP8 Linter, if you write
'ignoreErrorCodes':'E111, E501'inconfig.csonLooks good
Supplement about PEP8
About PEP8
- PEP8 is roughly a Python Coding Rule. This article is very helpful
- PEP8 Click here for Japanese translation
- See here for a list of PEP8 Error Codes (http://pep8.readthedocs.org/en/latest/intro.html#error-codes)
Major Coding Rules
-
About Indent
-
It is recommended to make one indent (Tab) with four Spaces
-
If you want to suppress this error, ignore E111 and E114
-
About function names and variable names
-
Function name, variable name: It is recommended to separate all lowercase letters with
_(set_stream_loggeretc.) -
Class name: Upper Camel Case recommended (eg
GetImageLocation) -
Other than Pycharm, Flake8 (PEP8 Wrap library) and [pep8-naming (flake8 plugin)](https://github.com/flintwork/ It seems that you should put pep8-naming) and set it to ignore N802 / N806 etc. (I have not tried it)
-
1 line length
-
Up to 79 characters per line is recommended
-
If you want to suppress this error, ignore E501
-
About Import Declaration
-
1 line 1 library Import recommended
-
If you want to suppress this error, ignore E401
-
Whitespace before and after the operator
-
Insert a space before and after operators such as
=, ==, <,>, is, in, not in -
If you want to suppress this error, ignore E221 and E222
About PEP8 Check Tool
There are two types of tools, pep8 and ʻautopep8`.
- About
pep8 - Tool that tells you where to fix
- Install with
pip install pep8and checkpep8 xxx.py --show-source* If you specify .py, the error code and the corresponding part will be spit out as shown below. - If you want to ignore a particular Error,
pep8 xxx.py --ignore = E111, E114, E501 --show-source
E111 / 114 is ʻIndent Error, E501 isLine Too Long`
xxx.py:4:1: E302 expected 2 blank lines, found 1
def foo():
^
misc_test.py:5:9: E225 missing whitespace around operator
msgs=['Hello','World!!']
^
misc_test.py:5:18: E231 missing whitespace after ','
msgs=['Hello','World!!']
^
misc_test.py:9:10: W292 no newline at end of file
foo()
^
- About ʻautopep8`
- It is a tool that even corrects automatically
- Install with
pip install autopep8and want it to be automatically corrected as ʻautopep8 -i xxx.py` * If you specify .py, the contents of File will be corrected without asking questions (so be careful when executing) is)