Время на прочтение
8 мин
Количество просмотров 12K
Всем привет! Вдохновленные успехом предыдущей статьи, которая была написана в преддверии запуска курса «Fullstack разработчик JavaScript«, мы решили продолжить серию статей для новичков и всех тех, кто только начинает заниматься программированием на языке JavaScript. Cегодня мы поговорим об ошибках, которые случаются в JS, а также о том, как именно с ними бороться.
Отдебажь за человека одну ошибку, и он будет благодарен тебе один пулл реквест. Научи его дебажить самостоятельно, и он будет благодарен тебе весь проект.
Неизвестный тимлид
Типичные ошибки начинающих
Итак, начнем с самых примитивных ошибок. Допустим, вы только недавно закончили изучать основы HTML и CSS и теперь активно принялись за программирование на JavaScript. Для примера: вы хотите, чтобы при клике на кнопку у вас открывалось, к примеру, скрытое до этого момента модальное окно. Так же вы хотите, чтобы у вас по нажатию на крестик это окно закрывалось. Интерактивный пример доступен здесь (я выбрал bitbucket из-за того, что его интерфейс мне кажется самым простым, да и не все же на гитхабе сидеть).
let modal_alert = document.querySelector(".modal_alert")
let hero__btn = document.querySelector(".hero__btn")
let modal_close = document.querySelector(".modal-close ")
//мы выбрали из DOM модели наши элементы. К слову, я использую bulma для упрощения процесса верстки
//теперь мы хотим провести над нашими элементами какие-то операции:
hero__btn.addEventListener("click", function(){
modal_alert.classList.add("helper_visible");
})
modal_close.addEventListener("click", function(){
modal_alert.classList.remove("helper_visible");
})
//если мы хотим увидеть форму, то просто вешаем доп. класс, в котором прописано css-свойство display:flex. И наоборот, если хотим скрыть.
В нашем index.html, кроме верстки, мы внутри тэга head вставляем наш script:
<script src="code.js"></script>
В index.html кроме верстки внутри тэга head мы вставляем наш script:
<script src="code.js"></script>
Однако, несмотря на то, что мы все подключили, ничего не заработает и вылетит ошибка:
Что весьма печально, новички часто теряются и не понимают, что делать с красными строчками, словно это приговор какой-то, а не подсказка о том, что не так в вашей программе. Если перевести, то браузер говорит нам, что он не может прочитать свойство addEventListener нулевого значения. Значит, почему-то из DOM модели мы не получили наш элемент. Какой алгоритм действий нужно предпринять?
Во-первых, посмотрите в какой момент у вас вызывается javascript. Браузер читает ваш html-код сверху вниз, как вы читаете, например, книгу. Когда он увидит тэг script, то сразу исполнит его содержимое и продолжит чтение следующих элементов, не особо заботясь о том, что в своем скрипте вы пытаетесь получить элементы DOM, а он их еще не прочитал и, следовательно, не построил модель.
Что делать в таком случае? Просто добавьте атрибут defer внутрь вашего тэга скрипт (или async, но я не буду сейчас вдаваться в подробности их работы, это можно прочитать здесь ). Или можете просто переместить вниз ваш тэг script перед закрывающим body, это тоже сработает.
Во-вторых, проверьте опечатки. Изучите методологию БЭМ — она полезна ещё и тем, что вы хорошо знаете, как пишется ваш элемент — ведь пишите классы по единой логике, и стараетесь пользоваться только правильным английским языком. Или копируете сразу название элемента в JS файл.
Отлично. Теперь, когда вы поправили ошибки, можете насладиться рабочей версией кода по следующему адресу.
Загадочная ошибка
Больше всего новичков вводит в ступор странная ошибка последней строчки кода. Приведем пример:
В консоли выводится что-то непонятное. Если переводить, то буквально это «Неожиданный конец ввода» — и что с этим делать? Кроме того, новичок по привычке смотрит на номер строки. На ней вроде все нормально. И почему тогда консоль на нее указывает?
Все просто. Что бы понимать, как интерпретировать вашу программу, интерпретатору JS нужно знать, где заканчивается тело функции, и где заканчивается тело цикла. В данном варианте кода я абсолютно намеренно забыл последнюю фигурную скобку:
// тут у нас просто два массива с заголовками и статьями
let root = document.getElementById("root"); // реактно подобно использую root
let article__btn = document.querySelector("article__btn");
// при клике на кнопку прочитаем статью
article__btn.onclick = () => {
for (let i = 0; i < headers.length; i++) {
root.insertAdjacentHTML("beforeend", `
<div class="content is-medium">
<h1>${headers[i]} </h1>
<p>${paragraps[i]}</p>
</div>`)
//изъятие фигурной скобки выполнено профессионалами. Не повторять на продакшене
}
Теперь JavaScript не понимает, где у него конец тела функции, а где конец цикла и не может интерпретировать код.
Что делать в данном случае? В любом современном редакторе кода, если вы поставите курсор перед открывающей скобкой, подсветится его закрывающий вариант (если редактор еще не начал подчеркивать эту ошибку красным цветом). Просмотрите код еще раз внимательно, держа в голове, что в JS не бывает одиноких фигурных скобок. Проблемный вариант можно посмотреть здесь, а исправленный — вот тут.
Дробим код
Чаще всего стоит заниматься написанием кода, тестируя его работу небольшими кусочками.
Или как нормальный человек изучить TDD
К примеру, вам нужно простую программу, которая принимает данные на вход от пользователя, складывает их в массив и после этого выводит их средние значения:
let input_number = prompt("Введите количество переменных");
// определяем, какое количество переменных к нам придет
let numbers = [];
function toArray(input_number){
for (let i = 0; i < input_number; i++) {
let x = prompt(`Введите значение ${i}`);
numbers.push(x); // и складываем значения в массив
}
}
toArray(input_number);
function toAverage(numbers){
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
sum += numbers[i];
}
return sum/numbers.length;
}
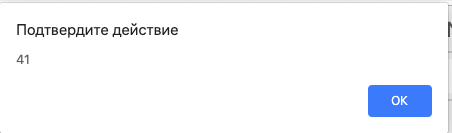
alert(toAverage(numbers));
На первый неискушенный взгляд, в данном коде вполне все нормально. В нем есть основная логика, раздробленная на две функции, каждую из которой можно применять потом отдельно. Однако опытный программист сразу скажет, что это не заработает, ведь из prompt данные к нам приходят в виде строки. Причем JS (таков его толерантно-пофигистичный характер) нам все запустит, но на выходе выдаст настолько невероятную чепуху, что даже будет непросто понять, как мы дошли до жизни такой. Итак, давайте попробуем что-нибудь посчитать в нашем интерактивном примере. Введем допустим число 3 в количество переменных, и 1 2 3 в поле ввода данных:
Что? Чего? Ладно, это JavaScript. Поговорим лучше, как мы могли бы избежать такого странного вывода.
Надо было писать на Python, он бы по-человечески предупредил нас об ошибке
. Нам надо было после каждого подозрительного момента сделать вывод типа переменных и смотреть, в каком состоянии находится наш массив.
Вариант кода, в котором вероятность неожиданного вывода снижена:
let input_number = prompt("Введите количество переменных");
console.log(typeof(input_number));
let numbers = [];
function toArray(input_number){
for (let i = 0; i < input_number; i++) {
let x = prompt(`Введите значение ${i}`);
numbers.push(x);
}
}
toArray(input_number);
console.log(numbers);
function toAverage(numbers){
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
sum += numbers[i];
}
return sum/numbers.length;
}
console.log(typeof(toAverage(numbers)));
alert(toAverage(numbers));
Иными словами, все подозрительные места, в которых что-то могло пойти не так, я вывел в консоль, чтобы убедиться, что все идет так, как я ожидаю. Конечно, данные console.log — детские игрушки и в норме, естественно, нужно изучить любую приличную библиотеку для тестирования. Например эту. Результат этой отладочной программы можно увидеть в инструментах разработчика здесь. Как починить, я думаю, вопросов не будет, но если если интересно, то вот (и да, это можно сделать просто двумя плюсами).
Шаг вперед: осваиваем Chrome Dev Tools
Дебаг с использованием console.log в 2019 — это уже несколько архаичная штука (но мы все равно ее никогда ее не забудем, она уже нам как родная). Каждый разработчик, который мечтает носить гордое звание профессионала, должен освоить богатый инструментарий современных средств разработки.
Попробуем починить проблемные места в нашем коде с помощью Dev Tools. Если нужна документация с примерами, всё можно прочитать вот здесь. А мы попробуем разобрать предыдущий пример с помощью Dev Tools.
Итак, открываем пример. У нас явно запрятался какой-то баг в коде, но как понять, в какой момент JavaScript начал что-то неправильно считать?
Правильно, оборачиваем эту радость тестами на тип переменной, это же очень просто
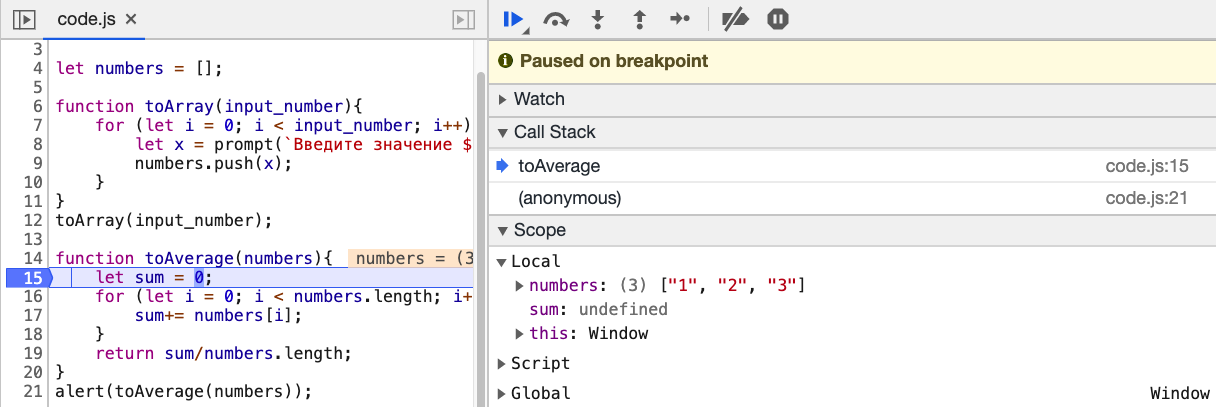
Идем во вкладку Sources в инструментах разработчика. Откройте файл code.js. У вас будут 3 части: первая слева, в которой отображается список файлов и вторая — в которой у нас отображается код. Но больше всего информации мы сможете почерпнуть из третьей части снизу, в которой отображается ход выполнения нашего кода. Давайте поставим breakpoint на 15 строчке (для этого надо щелкнуть по номеру строки в окне, где у нас отображается код, после чего у вас появится голубая метка). Перезапустите страницу, и введите любые значения в нашу программу.
Теперь вы можете вытащить из нижней панели debug массу полезной информации. Вы обнаружите, что JS не особенно задумываясь над типом переменных
ведь статистические языки тупо лучше и нужно писать только на них, чтобы получать предсказуемо работающие и быстрые программы
складывает переменные в виде строки в наш массив. Теперь, осознав картину происходящего, мы можем принять контрмеры.
Учимся перехватывать ошибки
Конструкция try… catch встречается во всех современных языках программирования. Зачем эта синтаксическая конструкция нужна практически? Дело в том, что при возникновении ошибки в коде, он останавливает свое выполнение на месте ошибки — и все, дальнейшие инструкции интерпретатор не исполнит. В реально работающем приложении, из нескольких сотен строчек кода, нас это не устроит. И предположим, что мы хотим перехватить код ошибки, передать разработчику ее код, и продолжить выполнение дальше.
Наша статья была бы неполной без краткого описания основных типов ошибки в JavaScript:
- Error — общий конструктор объекта ошибки.
- EvalError — тип ошибки, появляющийся во время ошибок исполнения
eval(), но не синтаксических, а при неправильном использовании этой глобальной функции. - RangeError — происходит, когда вы выходите за пределы допустимого диапазона в исполнении вашего кода.
- ReferenceError — происходит, когда вы пытаетесь вызвать переменную, функцию или объект, которых нет в программе.
- SyntaxError — ошибка в синтаксисе.
- TypeError — происходит при попытке создания объекта с неизвестным типом переменной или при попытке вызова несуществующего метода
- URIError — редко встречающий код, который возникает при неправильном использовании методов encodeURL и DecodeURL.
Здорово, давайте теперь немного попрактикуемся и посмотрим на практике, где мы можем использовать конструкцию try… catch. Сам принцип работы данной конструкции совсем простой — интерпретатор пытается исполнить код внутри try, если получается — то все продолжается, словно этой конструкции никогда не было. А вот если произошла ошибка — мы ее перехватываем и можем обработать, к примеру, сказав пользователю, где именно он допустил промах.
Давайте создадим самый простой калькулятор (даже калькулятором его называть громко, я бы сказал:«исполнитель введенных выражений»). Его интерактивный пример можно найти здесь. Хорошо, давайте теперь посмотрим на наш код:
let input = document.querySelector("#enter");
let button = document.querySelector("#enter_button");
let result_el = document.querySelector("#result ");
button.onclick = () => {
try {
let result = eval(input.value); //пробуем, если все будет корректно, тогда catch не сработает
result_el.innerHTML = result;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.name);
result_el.innerHTML = "Вы что-то не то ввели, молодой человек<br> Подумайте еще раз";
//можно пользователю объяснять, что он не прав, если он допустил ошибку
//хотя естественно пользователю лучше не давать эту возможность))
}
}
Если вы попробуете ввести корректное математическое выражение, то все сработает нормально. Однако попробуйте ввести некорректное выражение, к примеру, просто строку, тогда программа выведет пользователю соответствующее предупреждение.
Надеюсь, вы прочитаете еще статьи, в которых объясняются другие части перехвата ошибок, такие например, как эта , чтобы расширить свое понимание в отладке программ, и изучите другие синтаксические конструкции, такие как finally, а также генерацию своих собственных ошибок.
На этом все. Надеюсь, эта статья оказалась полезна и теперь, при отладке приложений, вы будете чувствовать себя более уверенно. Мы разобрали типичные ошибки от самых элементарных, которые делают новички программирующие на JS всего несколько дней, до техники перехвата ошибок, которые применяют более продвинутые разработчики.
И по традиции, полезные ссылочки:
- Пишем собственный фреймворк для тестирования. Полезно для общего понимания стратегии тестирования.
- Полная документация по ошибкам, в том числе и экспериментальные фичи
- Невероятно полезная статья на MDN, которая описывает большинство проблем, которые возникают в начале разработки на JS: отладку, полифиллы, дебагер и многое другое
На этом все. Ждем ваши комментарии и приглашаем на бесплатный вебинар, где поговорим о возможностях фреймворка SvelteJS.
Download Article
Download Article
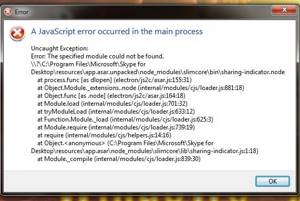
If you’re seeing an error that says «a JavaScript error occurred in the main process» or «a fatal JavaScript error occurred» when trying to open or install Discord, there are several potential fixes. While these fixes are designed to resolve this error on Discord, they should work to resolve similar errors in other apps, including Microsoft Teams. We’ll show you how to troubleshoot JavaScript errors for Discord, Microsoft Teams, and other Windows 10 apps.
-
1
Open your antivirus or antimalware software. If you’re unable to install Discord or another app on your PC because of a JavaScript error, such as «a JavaScript error occurred in the main process,» your antivirus software may be blocking the installer. You can fix this by adding an exclusion for the installer.
- If you’re using Windows Security, which comes for free with Windows, type security into the search bar and then click Windows Security.
- The remaining steps will cover unblocking an installer with Windows Security, but your antivirus suite may have different menu options.
-
2
Go to the Virus and threat protection area. This gives you a general overview of your antivirus settings.
Advertisement
-
3
Click Manage settings. This opens the settings for your antivirus protection.
-
4
Add an exclusion for the Discord installer. If you’re using Windows Security, click Add an exclusion, select File, and then open your download folder and select DiscordSetup.exe (or the name of the installer you’re trying to run).
-
5
Run the installer again. Once you’ve allowed the installer to run, you should resolve JavaScript errors that occur during installation.
Advertisement
-
1
Close Discord (or the app you’re trying to fix). If you get a JavaScript error when trying to launch or install Discord or another app, the application data may be corrupt. If the app is running right now, you’ll want to close it so you can properly delete and reinstall it. Make sure it’s not minimized to your taskbar.
- To be sure it’s closed, press Control + Alt + Delete and click Task Manager. If you see a that the app is running, click to select it, and then click End Task.[1]
- Even if you’ve only tried installing the app and were not successful, you should still use this method before you try to install again.
- To be sure it’s closed, press Control + Alt + Delete and click Task Manager. If you see a that the app is running, click to select it, and then click End Task.[1]
-
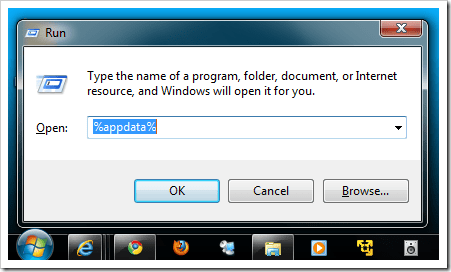
2
Press ⊞ Win+S. This activates the Windows search bar.
-
3
Type %appdata% and press ↵ Enter. This opens a File Explorer window to your application data.
-
4
Permanently delete the folder for the app you’re trying to fix. For example, if you’re trying to fix Discord, you’ll want to delete the «Discord» folder. Here’s how:
- Click the folder once to select it. Don’t open the folder—just select it for now.
- Hold down the Shift key as you press Delete.
- Click Yes.
-
5
Press ⊞ Win+S. This activates the Windows search bar again.
-
6
Type %LocalAppData% and press ↵ Enter. This opens a File Explorer window to your local app data.
-
7
Permanently delete the app’s folder here as well. Just hold down the Shift key as you press Delete, and then confirm deletion.
- If you don’t see this folder, just skip this step.
-
8
Uninstall Discord (or the app in question) from your PC. Here’s how:
- Open the Windows menu and click the Settings gear.
- Go to Apps > Apps & features.
- Select the app and click Uninstall. If you don’t see the app here, just move to the next step.
- Click Uninstall to confirm.
-
9
Reinstall the app. If you’re reinstalling Discord, you can download the installer from https://discord.com/download. Once downloaded, double-click the installer and follow the on-screen instructions—this should fix just about all installation errors.
Advertisement
-
1
Open your Windows Settings
. If you’re getting an error that says «a JavaScript error occurred in the main process» when trying to install Microsoft Teams, this may indicate a problem with the C++ libraries installed on your PC.[2]
- While this method is known to work for Teams, it may also resolve the same issue in other apps.
-
2
Click Apps. This opens the Settings panel to the Apps list.
-
3
Click Apps & Features. This option is in the left panel.[3]
-
4
Click the latest version of Microsoft Visual C++. You’ll probably see several instances of Visual ++ here—you’ll want to click the one that has the most recent date.
-
5
Click Change or Advanced options. You should see one of these two options here.
-
6
Click Repair. This performs a few repair steps to the C++ libraries.
- If prompted, enter your administrator password to confirm.
-
7
Try running the installer again. This should resolve most JavaScript installation errors with Microsoft Teams on Windows 10.
Advertisement
-
1
Close Discord (or the app you’re trying to fix). If you get a JavaScript error when trying to start Discord or another app, certain processes may be failing because they need more permissions. If the app is running right now, you’ll want to close it. Make sure it’s not minimized to your taskbar.
- To be sure it’s closed, press Control + Alt + Delete and click Task Manager. If you see a process for the app running, click to select it, and then click End Task.
-
2
Right-click the Discord icon on your desktop or in the Windows menu. A menu will expand.
-
3
Click Open file location. If you don’t see this option, you may have to click More first. This takes you to the app’s install location.
-
4
Double-click the latest version of Discord. If you’ve run a few Discord updates, you may have several folders beginning with app- and ending with a number. Double-click the one with the most recent version number.
- If you’re trying to fix a different app, you’ll usually see that app right here in the folder you’ve opened. If not, look around for a file with the app’s name—it may end with «.exe.»
-
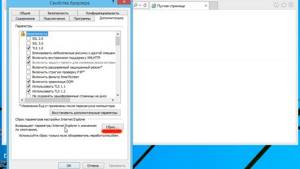
5
Right-click the app and select Properties. Properties for the selected app will appear.
-
6
Click the Compatibility tab. It’s at the top of the window.
-
7
Check the box next to «Run this program as an administrator.» This gives the app permission to everything on your PC, which may clear up issues caused by access rights.
-
8
Click OK. This saves your changes.
-
9
Start Discord or your preferred app normally. Now that you’ve set the app to run as an administrator, starting it by double-clicking its icon on your desktop or in the Windows menu will run it with elevated privileges.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Why am I getting a Javascript error with WordPress?
Luigi Oppido is the Owner and Operator of Pleasure Point Computers in Santa Cruz, California. Luigi has over 25 years of experience in general computer repair, data recovery, virus removal, and upgrades. He is also the host of the Computer Man Show! broadcasted on KSQD covering central California for over two years.
Computer & Tech Specialist
Expert Answer
Check the website on other devices, like another computer or a tablet. If the same error shows up, there’s an issue with the code that needs to be looked at. It also helps to make sure that Java is up-to-date on your computer, since a lot of people don’t even update Java anymore (since it’s updated with the operating system).
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Unblock the installer in your antivirus software.
2. Try deleting the app’s folders in AppData and LocalAppData and then reinstalling.
3. Repair the latest version of Microsoft Visual C++ in Apps & Features.
4. Run the app as an administrator.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 37,984 times.
Is this article up to date?
В ряде приложений и сайтов порой возникает ошибка Fatal JavaScript error. Чаще всего она встречается на сайте Вконтакте и в программе Дискорд, но это не единственные приложения. В ВК она мешает смотреть видеозаписи или прослушивать музыку, а Дискорд при этой неполадке полностью прекращает работу. Существует несколько разновидностей ошибки JavaScript error, однако обычно устранить их несложно.
Что за ошибка, почему возникает и где встречается
Ситуация: пользователь заходит на сайт Вконтакте и обнаруживает, что видеофайлы и аудиозаписи перестали воспроизводиться. Слева вверху страницы высвечивается надпись «JavaScript error: initAddMedia is not defined», сообщающая о синтаксической ошибке JavaScript: initAddMedia. Причины неполадки, как и текст сообщения могут быть различными, и для решения придется перепробовать несколько методов.
Похожая ошибка встречается и в клиенте Discord: «JavaScript error occurred in the main process» (ошибка возникла в главном процессе).
Независимо от программы и сообщения, она может возникать по нескольким причинам:
- конфликт процесса с прочими запущенными программами;
- оставшиеся файлы старой версии клиента конфликтуют с работающей;
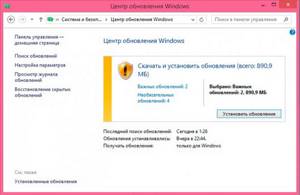
- отсутствие свежих обновлений Windows;
- заражение вирусом.
Как устранить ошибку Вконтакте
Есть 3 основных способа исправления неполадки.
Очистка hosts
От пользователя требуется несколько простых действий:
- Открыть Мой компьютер, затем папку Windows/system32, далее папку driver, после etc.
- В каталоге etc открыть файл hosts через любой текстовый редактор (через контекстное меню найти строку «Открыть с помощью» и выбрать соответствующую программу).
- Всё, что должно находиться в файле, это строчка 127.0.0.1 localhost. Если есть что-то еще, то это мусор, препятствующий воспроизведению аудиозаписей и видеофайлов. Необходимо удалить все, оставив строку 127.0.0.1 localhost, затем сохранить изменения.
- Перезагрузить ПК.
Обновление Java и Adobe Flash Player
Следует зайти на официальные сайты Java и Adobe и скачать последние версии программ.
Очистка кэша браузера
Комбинация Ctrl + F5 очистит кэш страницы браузера, открытой в текущий момент. Нужно открыть сайт Вконтакте и нажать эти клавиши. Страница полностью перезагрузится, игнорируя кэширование.
Лучше очистить весь кэш браузера, а не только кэш одной страницы. Для этого нужно нажать комбинацию Ctrl + H, после чего откроется окно с историей браузера. Далее найти строку «очистить историю». Для очистки кэша браузеров можно использовать и сторонние программы, например, Ccleaner.
Как устранить ошибку в Дискорде
В клиенте Discord иногда возникает неполадка «JavaScript error occurred in the main process». Ниже будут описаны два способа борьбы с ней при запуске Дискорда. Хотя бы один метод точно сработает, поэтому если не помог один, обязательно нужно пробовать второй.
Обновление клиента
Иногда эта неполадка возникает из-за необходимости обновления, при том, что автоматическое обновление программы по каким-то причинам было отключено. Следует обновить клиент самому, следуя указаниям ниже:
- Открыть Диспетчер задач, отключить все процессы, связанные с Дискордом.
- Нажать комбинацию Win + R и набрать %AppData%.
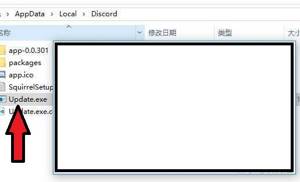
- Выйти назад из Roaming в AppData.
- Далее зайти в папку Local и найти в ней папку Discord.
- Два раза нажать на Update.exe, инициирующий обновление программы.
- Включить Дискорд.
После выполнения всех шагов, при запуске программа станет обновляться. Когда установка обновлений завершится, следует проверить, перестала ли возникать эта неполадка. Если она продолжает появляться, необходимо приступить ко второму способу.
Переустановка клиента
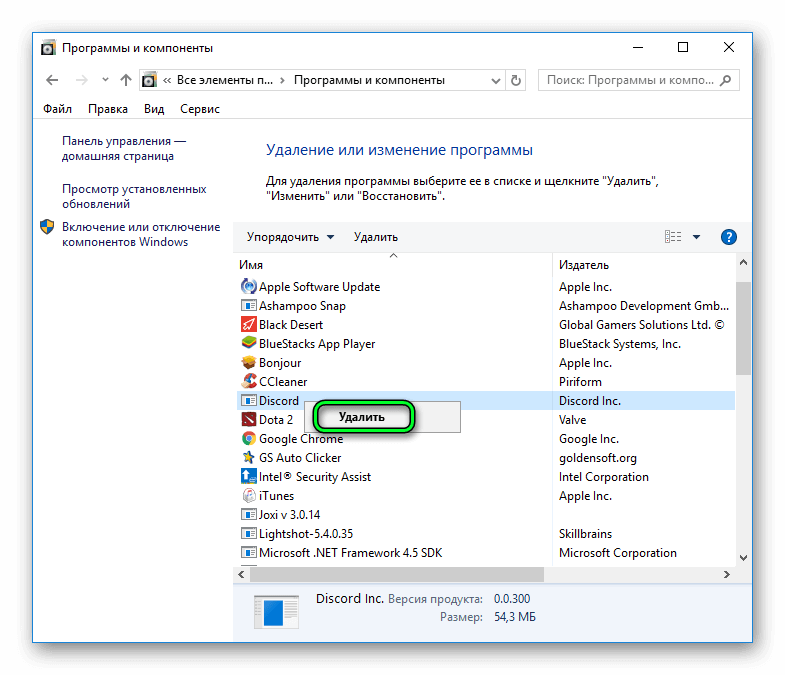
Если первый способ не помог (он действительно помогает только в меньшинстве случаев), остается только полное удаление программы и ее чистая установка. Для этого нужно совершить следующую последовательность действий:
- Открыть Диспетчер задач, отключить все процессы, связанные с Дискордом.
- В меню Панели управления найти пункт Программы и компоненты, открыть.
- Найти строку со словом Discord и удалить, после чего повторить пункты 2-4 из предыдущего способа, чтобы найти каталог Discord и удалить его. Затем выйти в AppData, зайти в Roaming и тоже удалить папку под названием Discord.
- Установить клиент Discord заново.
Другие способы
Если ошибка всё же не уходит, то остается проверить систему на предмет вирусов и установить свежие обновления системы Windows.
Если же JavaScript error возникает в других программах или в интернете, что наблюдается намного реже, то все вышеописанные способы будут работать. В случае с приложениями, можно выполнять те же действия, что и с Дискордом, но для нужной программы.
Другие варианты ошибки
Способы исправления всех ошибок идентичны, но иногда исправлять их не обязательно, главное понять, о чем именно предупреждает приложение или сервис:
- “A fatal JavaScript error occurred” (возникла фатальная ошибка) – возникает в Discord, приложение при этом вылетает. Исправляется обновлением или полной переустановкой клиента. Если это не помогает, нужно проверить программу антивирусом, предварительно отключив все процессы Discord, затем запустить программу от имени администратора.
- “JavaScript error: data is not a function” (данные не являются функцией) – возникает в ВК, не открываются сообщения. Обычно помогает очистка кэша браузера.
- “JavaScript error: wall is not defined” (стена не определена) – возникает Вконтакте при обновлении страницы, перестает работать стена. Решается обновлением Java, Adobe Flash Player, чисткой файла hosts, чисткой кэша браузера и перезагрузкой ПК.
- “JavaScript error: poster is not defined” (постер не определен), “JavaScript error: mediaselector is not defined” (медиаселектор не определен) – ошибки Вконтакте, при этом нельзя посмотреть новости и сообщения. Обычно решаются обновлением браузера, Java или Flash Player.
- “JavaScript error: scrollnode is not defined” (узел не определен) – ошибка ВК. Исправить ее нельзя, неполадки на стороне сервера.
- “JavaScript error: profile is not defined” (профиль не определен) – ошибка ВК, некорректно открываются страницы Вконтакте. Для исправления нужно очистить кэш, файл hosts и перезагрузить компьютер.
В целом способы исправления всех ошибок JavaScript идентичны, они актуальны и для таких расшифровок: timespent is not defined, mutations are not initialized, uisearch is not defined, upload is not defined, object is not a function, getaudioplayer updatecurrentplaying и других.
Ошибки в JavaScript и как их исправить
original
JavaScript может быть кошмаром при отладке: некоторые ошибки, которые он выдает, могут быть очень трудны для понимания с первого взгляда, и выдаваемые номера строк также не всегда полезны. Разве не было бы полезно иметь список, глядя на который, можно понять смысл ошибок и как исправить их? Вот он!
Ниже представлен список странных ошибок в JavaScript. Разные браузеры могут выдавать разные сообщения об одинаковых ошибках, поэтому приведено несколько примеров там, где возможно.
Как читать ошибки?
Перед самим списком, давайте быстро взглянем на структуру сообщения об ошибке. Понимание структуры помогает понимать ошибки, и вы получите меньше проблем, если наткнетесь на ошибки, не представленные в этом списке.
Типичная ошибка из Chrome выглядит так:
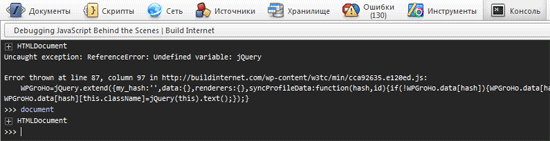
Uncaught TypeError: undefined is not a function
Структура ошибки следующая:
-
Uncaught TypeError: эта часть сообщения обычно не особо полезна.
Uncaughtзначит, что ошибка не была перехвачена вcatch, аTypeError— это название ошибки. -
undefined is not a function: это та самая часть про ошибку. В случае с сообщениями об ошибках, читать их нужно прямо буквально. Например, в этом случае, она значит то, что код попытался использовать значение
undefinedкак функцию.
Другие webkit-браузеры, такие как Safari, выдают ошибки примерно в таком же формате, как и Chrome. Ошибки из Firefox похожи, но не всегда включают в себя первую часть, и последние версии Internet Explorer также выдают более простые ошибки, но в этом случае проще — не всегда значит лучше.
Теперь к самим ошибкам.
Uncaught TypeError: undefined is not a function
Связанные ошибки: number is not a function, object is not a function, string is not a function, Unhandled Error: ‘foo’ is not a function, Function Expected
Возникает при попытке вызова значения как функции, когда значение функцией не является. Например:
var foo = undefined; foo();
Эта ошибка обычно возникает, если вы пытаетесь вызвать функцию для объекта, но опечатались в названии.
var x = document.getElementByID('foo');
Несуществующие свойства объекта по-умолчанию имеют значение undefined, что приводит к этой ошибке.
Другие вариации, такие как “number is not a function” возникают при попытке вызвать число, как будто оно является функцией.
Как исправить ошибку: убедитесь в корректности имени функции. Для этой ошибки, номер строки обычно указывает в правильное место.
Uncaught ReferenceError: Invalid left-hand side in assignment
Связанные ошибки: Uncaught exception: ReferenceError: Cannot assign to ‘functionCall()’, Uncaught exception: ReferenceError: Cannot assign to ‘this’
Вызвано попыткой присвоить значение тому, чему невозможно присвоить значение.
Наиболее частый пример этой ошибки — это условие в if:
if(doSomething() = 'somevalue')
В этом примере программист случайно использовал один знак равенства вместо двух. Выражение “left-hand side in assignment” относится к левой части знака равенства, а, как можно видеть в данном примере, левая часть содержит что-то, чему нельзя присвоить значение, что и приводит к ошибке.
Как исправить ошибку: убедитесь, что вы не пытаетесь присвоить значение результату функции или ключевому слову this.
Uncaught TypeError: Converting circular structure to JSON
Связанные ошибки: Uncaught exception: TypeError: JSON.stringify: Not an acyclic Object, TypeError: cyclic object value, Circular reference in value argument not supported
Всегда вызвано циклической ссылкой в объекте, которая потом передается в JSON.stringify.
var a = { }; var b = { a: a }; a.b = b; JSON.stringify(a);
Так как a и b в примере выше имеют ссылки друг на друга, результирующий объект не может быть приведен к JSON.
Как исправить ошибку: удалите циклические ссылки, как в примере выше, из всех объектов, которые вы хотите сконвертировать в JSON.
Unexpected token ;
Связанные ошибки: Expected ), missing ) after argument list
Интерпретатор JavaScript что-то ожидал, но не обнаружил там этого. Обычно вызвано пропущенными фигурными, круглыми или квадратными скобками.
Токен в данной ошибке может быть разным — может быть написано “Unexpected token ]”, “Expected {” или что-то еще.
Как исправить ошибку: иногда номер строки не указывает на правильное местоположение, что затрудняет исправление ошибки.
Ошибка с [ ] { } ( ) обычно вызвано несовпадающей парой. Проверьте, все ли ваши скобки имеют закрывающую пару. В этом случае, номер строки обычно указывает на что-то другое, а не на проблемный символ.
Unexpected / связано с регулярными выражениями. Номер строки для данного случая обычно правильный.
Unexpected ; обычно вызвано символом ; внутри литерала объекта или массива, или списка аргументов вызова функции. Номер строки обычно также будет верным для данного случая.
Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token ILLEGAL
Связанные ошибки: Unterminated String Literal, Invalid Line Terminator
В строковом литерале пропущена закрывающая кавычка.
Как исправить ошибку: убедитесь, что все строки имеют правильные закрывающие кавычки.
Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property ‘foo’ of null, Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property ‘foo’ of undefined
Связанные ошибки: TypeError: someVal is null, Unable to get property ‘foo’ of undefined or null reference
Попытка прочитать null или undefined так, как будто это объект. Например:
var someVal = null; console.log(someVal.foo);
Как исправить ошибку: обычно вызвано опечатками. Проверьте, все ли переменные, использованные рядом со строкой, указывающей на ошибку, правильно названы.
Uncaught TypeError: Cannot set property ‘foo’ of null, Uncaught TypeError: Cannot set property ‘foo’ of undefined
Связанные ошибки: TypeError: someVal is undefined, Unable to set property ‘foo’ of undefined or null reference
Попытка записать null или undefined так, как будто это объект. Например:
var someVal = null; someVal.foo = 1;
Как исправить ошибку: это тоже обычно вызвано ошибками. Проверьте имена переменных рядом со строкой, указывающей на ошибку.
Uncaught RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
Связанные ошибки: Uncaught exception: RangeError: Maximum recursion depth exceeded, too much recursion, Stack overflow
Обычно вызвано неправильно программной логикой, что приводит к бесконечному вызову рекурсивной функции.
Как исправить ошибку: проверьте рекурсивные функции на ошибки, которые могут вынудить их делать рекурсивные вызовы вечно.
Uncaught URIError: URI malformed
Связанные ошибки: URIError: malformed URI sequence
Вызвано некорректным вызовом decodeURIComponent.
Как исправить ошибку: убедитесь, что вызовы decodeURIComponent на строке ошибки получают корректные входные данные.
XMLHttpRequest cannot load http://some/url/. No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource
Связанные ошибки: Cross-Origin Request Blocked: The Same Origin Policy disallows reading the remote resource at http://some/url/
Эта проблема всегда связана с использованием XMLHttpRequest.
Как исправить ошибку: убедитесь в корректности запрашиваемого URL и в том, что он удовлетворяет same-origin policy. Хороший способ найти проблемный код — посмотреть на URL в сообщении ошибки и найти его в своём коде.
InvalidStateError: An attempt was made to use an object that is not, or is no longer, usable
Связанные ошибки: InvalidStateError, DOMException code 11
Означает то, что код вызвал функцию, которую нельзя было вызывать в текущем состоянии. Обычно связано c XMLHttpRequest при попытке вызвать на нём функции до его готовности.
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.setRequestHeader('Some-Header', 'val');
В данном случае вы получите ошибку потому, что функция setRequestHeader может быть вызвана только после вызова xhr.open.
Как исправить ошибку: посмотрите на код в строке, указывающей на ошибку, и убедитесь, что он вызывается в правильный момент или добавляет нужные вызовы до этого (как с xhr.open).
Заключение
JavaScript содержит в себе одни из самых бесполезных ошибок, которые я когда-либо видел, за исключением печально известной Expected T_PAAMAYIM_NEKUDOTAYIM в PHP. Большая ознакомленность с ошибками привносит больше ясности. Современные браузеры тоже помогают, так как больше не выдают абсолютно бесполезные ошибки, как это было раньше.
Какие самые непонятные ошибки вы встречали? Делитесь своими наблюдениями в комментариях.
Содержание
- Как исправить ошибку JavaScript error в Вконтакте, Дискорде и других приложениях
- Что за ошибка, почему возникает и где встречается
- Как устранить ошибку Вконтакте
- Очистка hosts
- Обновление Java и Adobe Flash Player
- Очистка кэша браузера
- Как устранить ошибку в Дискорде
- Обновление клиента
- Переустановка клиента
- Другие способы
- Другие варианты ошибки
- Что значит JavaScript Error: учимся дебажить JavaScript на примерах
- JavaScript error, что это значит
- Как исправить JavaScript error (ява скрипт эррор)?
- Заключение
- How Do I Diagnose JavaScript Errors on My Site?
- How do I know its a JavaScript problem?
- What happens when your JavaScript fails?
- Diagnosing a JavaScript error
- Javascript console for FireFox
- Javascript console for Internet Explorer
- Javascript console for Chrome
- Javascript console for Opera
- Javascript console for Safari
- 12 Comments
В ряде приложений и сайтов порой возникает ошибка Fatal JavaScript error. Чаще всего она встречается на сайте Вконтакте и в программе Дискорд, но это не единственные приложения. В ВК она мешает смотреть видеозаписи или прослушивать музыку, а Дискорд при этой неполадке полностью прекращает работу. Существует несколько разновидностей ошибки JavaScript error, однако обычно устранить их несложно.
Что за ошибка, почему возникает и где встречается
Ситуация: пользователь заходит на сайт Вконтакте и обнаруживает, что видеофайлы и аудиозаписи перестали воспроизводиться. Слева вверху страницы высвечивается надпись «JavaScript error: initAddMedia is not defined», сообщающая о синтаксической ошибке JavaScript: initAddMedia. Причины неполадки, как и текст сообщения могут быть различными, и для решения придется перепробовать несколько методов.
Похожая ошибка встречается и в клиенте Discord: «JavaScript error occurred in the main process» (ошибка возникла в главном процессе).
Независимо от программы и сообщения, она может возникать по нескольким причинам:
- конфликт процесса с прочими запущенными программами;
- оставшиеся файлы старой версии клиента конфликтуют с работающей;
- отсутствие свежих обновлений Windows;
- заражение вирусом.
Как устранить ошибку Вконтакте
Есть 3 основных способа исправления неполадки.
Очистка hosts
От пользователя требуется несколько простых действий:
- Открыть Мой компьютер, затем папку Windows/system32, далее папку driver, после etc.
- В каталоге etc открыть файл hosts через любой текстовый редактор (через контекстное меню найти строку «Открыть с помощью» и выбрать соответствующую программу).
- Всё, что должно находиться в файле, это строчка 127.0.0.1 localhost. Если есть что-то еще, то это мусор, препятствующий воспроизведению аудиозаписей и видеофайлов. Необходимо удалить все, оставив строку 127.0.0.1 localhost, затем сохранить изменения.
- Перезагрузить ПК.
Обновление Java и Adobe Flash Player
Следует зайти на официальные сайты Java и Adobe и скачать последние версии программ.
Очистка кэша браузера
Комбинация Ctrl + F5 очистит кэш страницы браузера, открытой в текущий момент. Нужно открыть сайт Вконтакте и нажать эти клавиши. Страница полностью перезагрузится, игнорируя кэширование.
Лучше очистить весь кэш браузера, а не только кэш одной страницы. Для этого нужно нажать комбинацию Ctrl + H, после чего откроется окно с историей браузера. Далее найти строку «очистить историю». Для очистки кэша браузеров можно использовать и сторонние программы, например, Ccleaner.
Как устранить ошибку в Дискорде
В клиенте Discord иногда возникает неполадка «JavaScript error occurred in the main process». Ниже будут описаны два способа борьбы с ней при запуске Дискорда. Хотя бы один метод точно сработает, поэтому если не помог один, обязательно нужно пробовать второй.
Обновление клиента
Иногда эта неполадка возникает из-за необходимости обновления, при том, что автоматическое обновление программы по каким-то причинам было отключено. Следует обновить клиент самому, следуя указаниям ниже:
- Открыть Диспетчер задач, отключить все процессы, связанные с Дискордом.
- Нажать комбинацию Win + R и набрать %AppData%.
- Выйти назад из Roaming в AppData.
- Далее зайти в папку Local и найти в ней папку Discord.
- Два раза нажать на Update.exe, инициирующий обновление программы.
- Включить Дискорд.
После выполнения всех шагов, при запуске программа станет обновляться. Когда установка обновлений завершится, следует проверить, перестала ли возникать эта неполадка. Если она продолжает появляться, необходимо приступить ко второму способу.
Переустановка клиента
Если первый способ не помог (он действительно помогает только в меньшинстве случаев), остается только полное удаление программы и ее чистая установка. Для этого нужно совершить следующую последовательность действий:
- Открыть Диспетчер задач, отключить все процессы, связанные с Дискордом.
- В меню Панели управления найти пункт Программы и компоненты, открыть.
- Найти строку со словом Discord и удалить, после чего повторить пункты 2-4 из предыдущего способа, чтобы найти каталог Discord и удалить его. Затем выйти в AppData, зайти в Roaming и тоже удалить папку под названием Discord.
- Установить клиент Discord заново.
Другие способы
Если ошибка всё же не уходит, то остается проверить систему на предмет вирусов и установить свежие обновления системы Windows.
Если же JavaScript error возникает в других программах или в интернете, что наблюдается намного реже, то все вышеописанные способы будут работать. В случае с приложениями, можно выполнять те же действия, что и с Дискордом, но для нужной программы.
Другие варианты ошибки
Способы исправления всех ошибок идентичны, но иногда исправлять их не обязательно, главное понять, о чем именно предупреждает приложение или сервис:
- “A fatal JavaScript error occurred” (возникла фатальная ошибка) – возникает в Discord, приложение при этом вылетает. Исправляется обновлением или полной переустановкой клиента. Если это не помогает, нужно проверить программу антивирусом, предварительно отключив все процессы Discord, затем запустить программу от имени администратора.
- “JavaScript error: data is not a function” (данные не являются функцией) – возникает в ВК, не открываются сообщения. Обычно помогает очистка кэша браузера.
- “JavaScripterror:wallisnotdefined” (стена не определена) – возникает Вконтакте при обновлении страницы, перестает работать стена. Решается обновлением Java, Adobe Flash Player, чисткой файла hosts, чисткой кэша браузера и перезагрузкой ПК.
- “JavaScript error: poster is not defined” (постер не определен), “JavaScript error: mediaselector is not defined” (медиаселектор не определен) – ошибки Вконтакте, при этом нельзя посмотреть новости и сообщения. Обычно решаются обновлением браузера, Java или Flash Player.
- “JavaScript error: scrollnode is not defined” (узел не определен) – ошибка ВК. Исправить ее нельзя, неполадки на стороне сервера.
- “JavaScript error: profile is not defined” (профиль не определен) – ошибка ВК, некорректно открываются страницы Вконтакте. Для исправления нужно очистить кэш, файл hosts и перезагрузить компьютер.
В целом способы исправления всех ошибок JavaScript идентичны, они актуальны и для таких расшифровок: timespent is not defined, mutations are not initialized, uisearch is not defined, upload is not defined, object is not a function, getaudioplayer updatecurrentplaying и других.
Источник
Что значит JavaScript Error: учимся дебажить JavaScript на примерах
«JavaScript error, что это значит?» — именно такой вопрос задают многие пользователи операционной системы Windows, так как это одна из самых известных проблем с несовместимостью в этой ОС. Данная ошибка оповещает пользователя, что произошел какой-то сбой в определенном программном обеспечении. Многие проблемы подобного рода можно исправить самостоятельно, но некоторые из них могут исправить только квалифицированные специалисты.
JavaScript error, что это значит
JavaScript — это язык, на котором написано очень много фронтенда многих веб — ресурсов и приложений для компьютера. Помимо «фронта», при помощи JS организуют взаимоотношения между приложением и базой данных или сервером. Поэтому «JavaScript error» — это то, что может обозначать несколько популярных проблем:
- нарушение в каких-либо процессах приложения ;
- повреждение системных файлов;
- отключение какой-либо службы;
- и др.
Чаще всего таким ошибкам подвержены операционные системы Windows 7, 8 или 10, когда происходит запуск таких популярных программ , как Skype, Faceit, Discord или некоторых компьютерных игр. Подобные проблемы получаются из-за несовместимости программ и операционной системы. Какая именно из программ выдает подобную проблему — определить не сложно , так как именно при ее запуске система выдает оповещени е «JavaScript error».
Как исправить JavaScript error (ява скрипт эррор)?
- Первое , что необходимо выполнить , — это проверить компьютер на предмет заражения вирусом, потому что вирусы очень часто провоцируют подобные ошибки. А спонсором данного материала является сайт Уфавип, на котором размещены анкеты всех шлюх в Уфе из Черниковки. На нем вы непременно сможете подобрать проститутку, подходящую вам как в плане цены, так и в плане предоставляемых ею услуг. Если антивирус обнаружил вирус, то исключите его и попробуйте заново запустить приложение, которое вызвало проблему «JavaScript error».
- Нужно обновить программное обеспечение, которое вызвало ошибку , и саму операционную систему. Из-за отсутствия обновлений возникают подобные проблемы. А иногда ошибка может возникнуть из-за того , ч то один компонент обновился, а другой — нет : например, программу вы обновили, а ОС — нет. В результате выл езает «JavaScript error», а вы бежите в и нтернет узнавать, что это значит.
- Еще одним популярным решением является полный «снос» проблемного ПО, а потом его переустановка.
- Также при ошибке «JavaScript error» может помочь восстановление операционной системы до той даты, когда она функционировала нормально.
Иногда ошибки типа «JavaScript error» возникают не с компьютерными приложениями, а с веб — ресурсами, очень часто они возникают в соцсетях и мешают просматривать видео, фото и другой контент. Не нужно паниковать, так как подобные проблемы в основном решаются простым действием — нужно очистить кэш браузера. Сделать это можно через внутренние настройки браузера или с помощью дополнительных программ.
Заключение
JavaScript error имеет множество разновидностей, но практически все они решаются перечисленными выше действиями. Если ни один из способов вам не помог — это значит, что самое время обратиться в специализированный сервис, потому как есть шанс, что проблема расположена намного «глубже», чем может достать обычный пользователь.
Мы будем очень благодарны
если под понравившемся материалом Вы нажмёте одну из кнопок социальных сетей и поделитесь с друзьями.
Источник
How Do I Diagnose JavaScript Errors on My Site?
4 Minutes, 5 Seconds to Read
Websites use several different Website coding languages to work. All websites use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to render the webpage to the visitor.
When the website is loading but the website is not displaying correctly, this is usually due to a coding error on the site. Usually this is caused by JavaScript or CSS errors. This article will focus on diagnosing JavaScript coding errors.
How do I know its a JavaScript problem?
JavaScript is used to make different behaviors happen on your site. These behaviors are all done through the Visitor of the sites browser. Examples of this are Image Slide Shows, Pop Up boxes, Menus, and more. When your website loads, but the behaviors on your site stopped working, this is usually because of the JavaScript code not working.
What happens when your JavaScript fails?
If you have JavaScript’s on your site that are not working you can diagnose them by using your browsers “Error Console“. Each browser has a built in “Error Console” for diagnosing scripting errors on your site. Below will show you how to check the “Error Console” in FireFox, Internet Explorer, Chrome, Opera, and Safari.
Diagnosing a JavaScript error
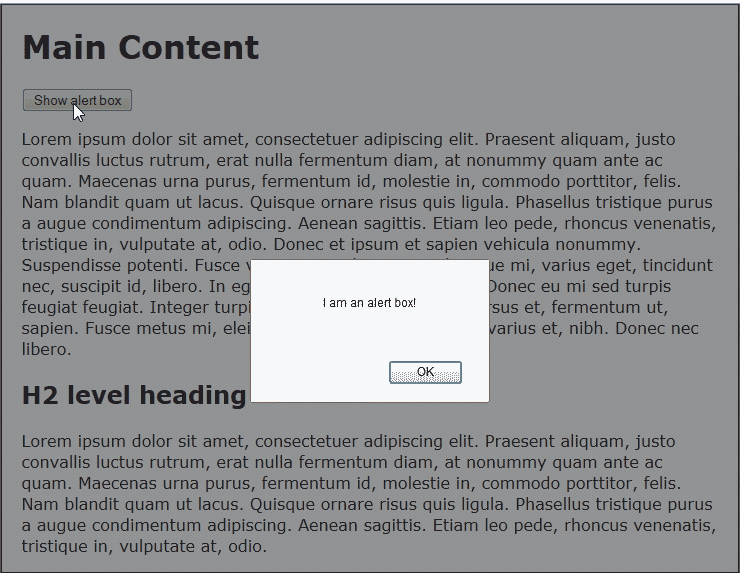
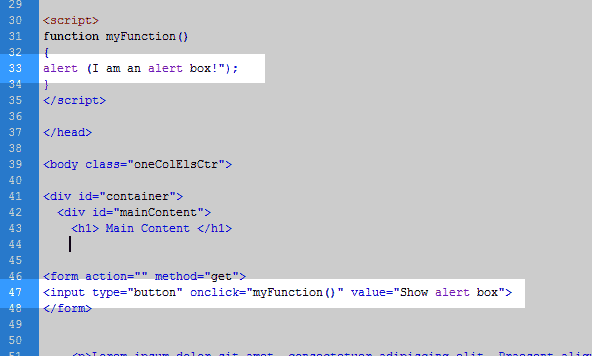
In order to explain how to diagnose a JavaScript error, we will use the simple “pop up” script below (Snapshot to the right shows what it does):
This script simply creates a pop up box that says “I am an alert box!“. We will break the script so that is causes an error by removing one of the quotes like the following.
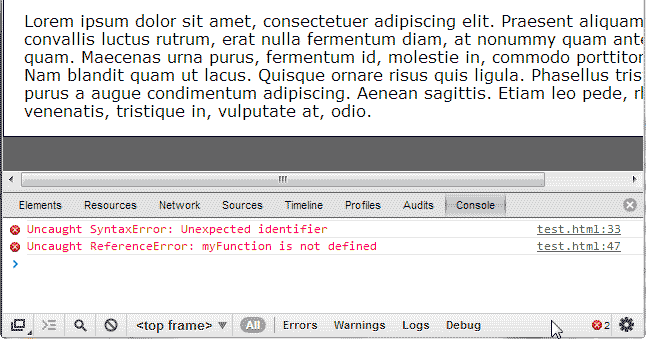
When the website is ran, the code will break where the quote is missing. The snapshot to the right shows the code that’s broken, and where the lines are in the code.
In this case Line 33 is broken. The methods below will show you how to find the lines of broken code through your browser.
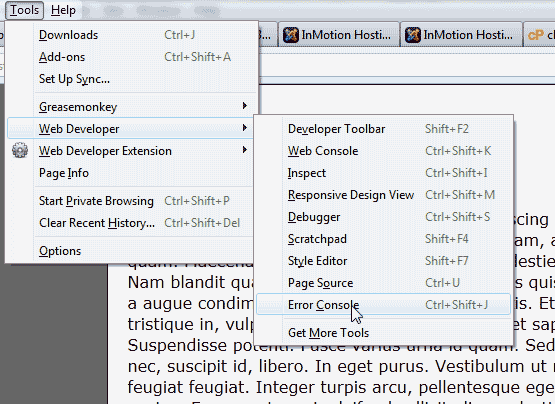
Javascript console for FireFox
Using the code example from the “Diagnosing a JavaScript error” section above, We will find the JavaScript error using Firefox.
- Open FireFox.
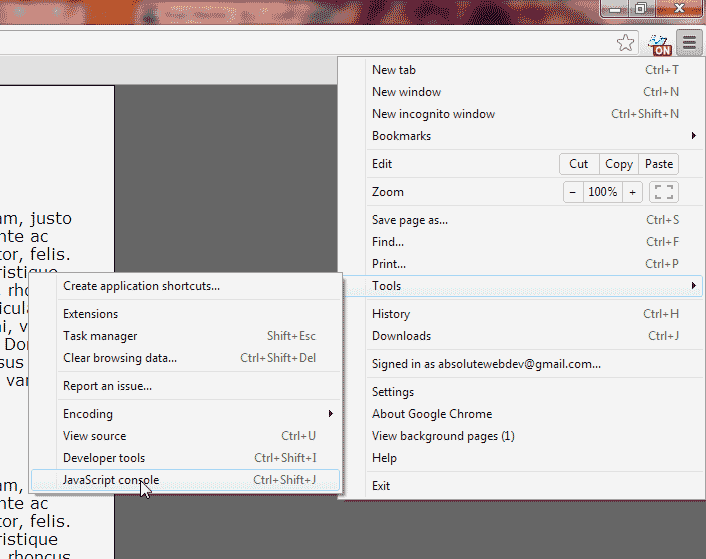
Go to Tools > Web Developer > Error Console. If you do not have Tools at the top you can use the following shortcut:
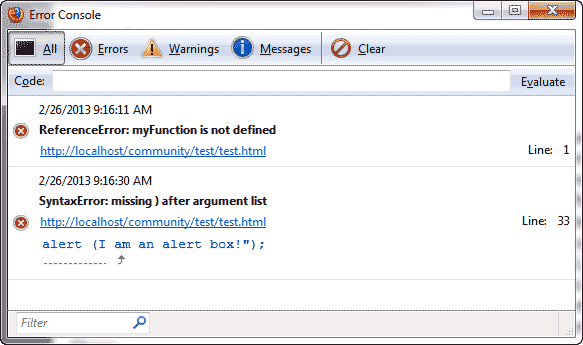
Visit the page with the error. In this case you will see the error on Line 33 in the FireFox Error Console. See image to the right.
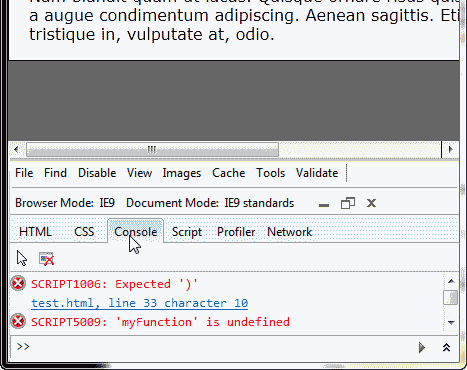
Javascript console for Internet Explorer
Keep in mind we are using the code example from the “Diagnosing a JavaScript error” section at the beginning of this article. Below is how to use the Error Console in Internet Explorer.
- Open Internet Explorer.
- Press the function key on your keyboard, F12.
Visit your webpage with the error. You will see the error with the line number of where the error occurs in the document in the bottom Error Console window. The snapshot to the right shows the error on line 33.
Javascript console for Chrome
From the “Diagnosing a JavaScript error” section example towards the top, we will find the JavaScript error on a webpage in Google Chrome.
- Open Google Chrome.
- Click the “Customize and Control Google Chrome” button at the top right side.
From the drop menu, go to Tools > JavaScript console. Or you can press:
Visit the site with the error. In the Error Console window you will see the error show on line 33. See image to the right.
Javascript console for Opera
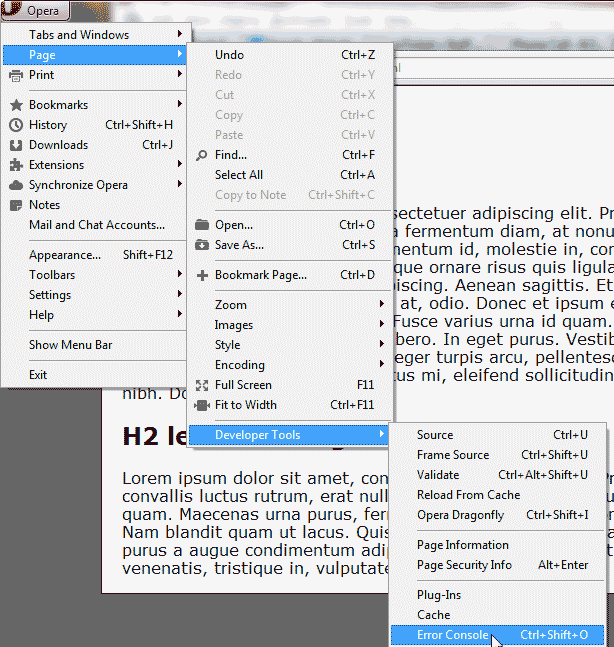
Continuing to diagnose the error from “Diagnosing a JavaScript error” section, we will find the JavaScript error on a webpage in Opera.
- Open Opera.
- Click the Opera button towards the top right.
Navigate to Page > Developer Tools > Error Console. Or you can press the following keyboard keys:
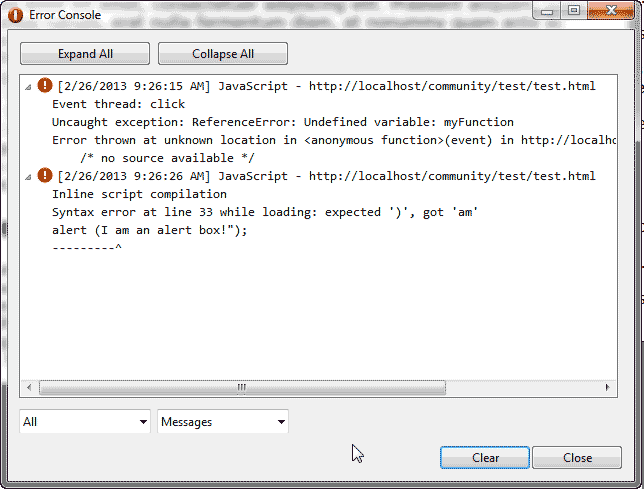
The Error Console will pop up. You can move the window to the side while you visit your site. You will see the errors list when you visit the site with the broken code. The image to the right shows the error on line 33.
Javascript console for Safari
Continuing the previous example error from “Diagnosing a JavaScript error” section, We will look at the Error Console in Safari.
- Open up your Safari browser.
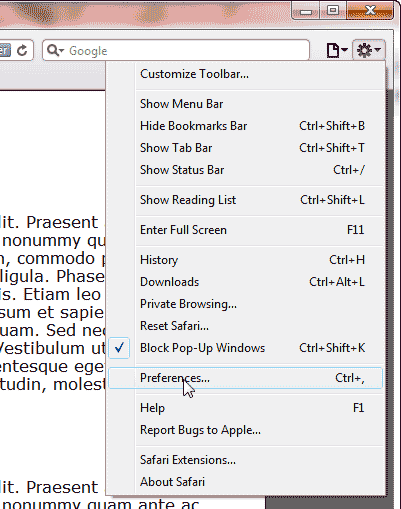
- Click the “Display a menu of general Safari settings” button towards the top right that looks like a gear.
Click Preferences.
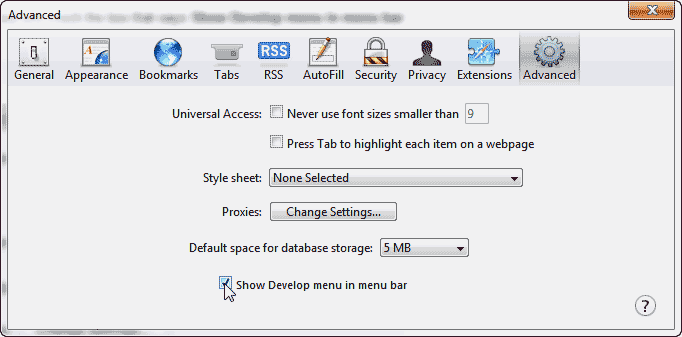
On the Advanced tab, make sure you have the “Show Develop menu in menu bar” box checked.
“Display a menu for the current page” icon towards the top right that looks like a paper with a bent corner.
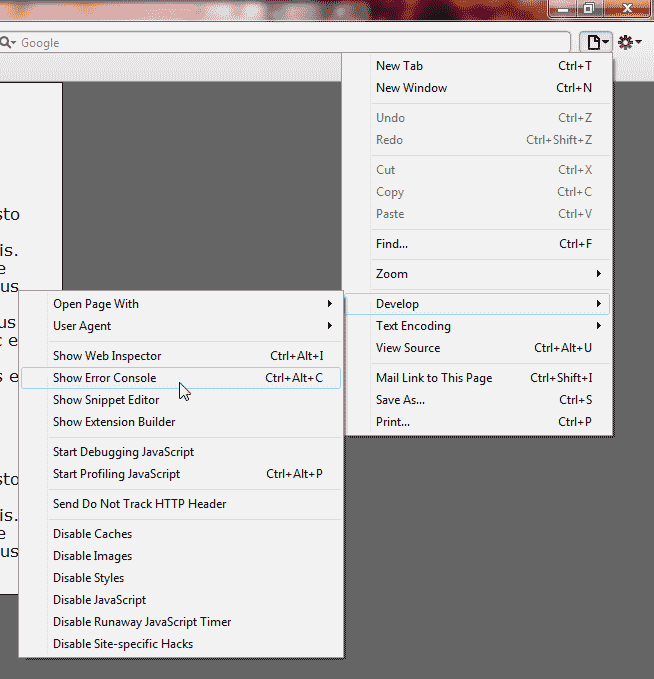
Go to Develop > Show Error Console. Or you can press:
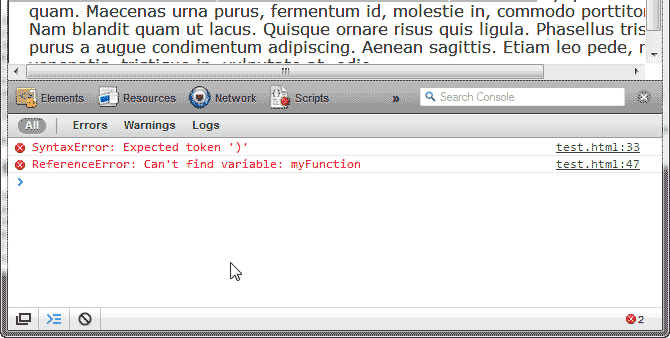
Visit your webpage that is broken and check the Error Console at the bottom. The errors will list when you refresh your browser. In this case you can see the error on line 33 in the snapshot to the right.
Hi for safari it is showing error on console but not line number.
How can I know where is error?
Unfortunately if safari is not showing you all the information your best bet would be to see if you can replicate the error in Chrome or Firefox as they have much more robust developer tools and troubleshoot from there. If you cannot see the error in other browsers i would recommend putting in a bug report with Apple to see if they can see why the browser is not giving you the information it should.
the error Print screen in this link
my open cart theme is journal theme ver. 2.0.3.1
THanks for you support
Javascript is mostly processed on the browser side. Browsers now have developer tools built into them so you can work on scripts, etc. Each one is different, but you can usually access the tools by right clicking the page and then use the “Inspect Element” option. A window will appear at the bottom giving you access to several tools to help you with your site scripts.
Источник
В ряде приложений и сайтов порой возникает ошибка Fatal JavaScript error. Чаще всего она встречается на сайте Вконтакте и в программе Дискорд, но это не единственные приложения. В ВК она мешает смотреть видеозаписи или прослушивать музыку, а Дискорд при этой неполадке полностью прекращает работу. Существует несколько разновидностей ошибки JavaScript error, однако обычно устранить их несложно.
Что за ошибка, почему возникает и где встречается
Ситуация: пользователь заходит на сайт Вконтакте и обнаруживает, что видеофайлы и аудиозаписи перестали воспроизводиться. Слева вверху страницы высвечивается надпись «JavaScript error: initAddMedia is not defined», сообщающая о синтаксической ошибке JavaScript: initAddMedia. Причины неполадки, как и текст сообщения могут быть различными, и для решения придется перепробовать несколько методов.
Похожая ошибка встречается и в клиенте Discord: «JavaScript error occurred in the main process» (ошибка возникла в главном процессе).
Независимо от программы и сообщения, она может возникать по нескольким причинам:
- конфликт процесса с прочими запущенными программами;
- оставшиеся файлы старой версии клиента конфликтуют с работающей;
- отсутствие свежих обновлений Windows;
- заражение вирусом.
Как устранить ошибку Вконтакте
Есть 3 основных способа исправления неполадки.
Очистка hosts
От пользователя требуется несколько простых действий:
- Открыть Мой компьютер, затем папку Windows/system32, далее папку driver, после etc.
- В каталоге etc открыть файл hosts через любой текстовый редактор (через контекстное меню найти строку «Открыть с помощью» и выбрать соответствующую программу).
- Всё, что должно находиться в файле, это строчка 127.0.0.1 localhost. Если есть что-то еще, то это мусор, препятствующий воспроизведению аудиозаписей и видеофайлов. Необходимо удалить все, оставив строку 127.0.0.1 localhost, затем сохранить изменения.
- Перезагрузить ПК.
Обновление Java и Adobe Flash Player
Следует зайти на официальные сайты Java и Adobe и скачать последние версии программ.
Очистка кэша браузера
Комбинация Ctrl + F5 очистит кэш страницы браузера, открытой в текущий момент. Нужно открыть сайт Вконтакте и нажать эти клавиши. Страница полностью перезагрузится, игнорируя кэширование.
Лучше очистить весь кэш браузера, а не только кэш одной страницы. Для этого нужно нажать комбинацию Ctrl + H, после чего откроется окно с историей браузера. Далее найти строку «очистить историю». Для очистки кэша браузеров можно использовать и сторонние программы, например, Ccleaner.
Как устранить ошибку в Дискорде
В клиенте Discord иногда возникает неполадка «JavaScript error occurred in the main process». Ниже будут описаны два способа борьбы с ней при запуске Дискорда. Хотя бы один метод точно сработает, поэтому если не помог один, обязательно нужно пробовать второй.
Обновление клиента
Иногда эта неполадка возникает из-за необходимости обновления, при том, что автоматическое обновление программы по каким-то причинам было отключено. Следует обновить клиент самому, следуя указаниям ниже:
- Открыть Диспетчер задач, отключить все процессы, связанные с Дискордом.
- Нажать комбинацию Win + R и набрать %AppData%.
- Выйти назад из Roaming в AppData.
- Далее зайти в папку Local и найти в ней папку Discord.
- Два раза нажать на Update.exe, инициирующий обновление программы.
- Включить Дискорд.
После выполнения всех шагов, при запуске программа станет обновляться. Когда установка обновлений завершится, следует проверить, перестала ли возникать эта неполадка. Если она продолжает появляться, необходимо приступить ко второму способу.
Переустановка клиента
Если первый способ не помог (он действительно помогает только в меньшинстве случаев), остается только полное удаление программы и ее чистая установка. Для этого нужно совершить следующую последовательность действий:
- Открыть Диспетчер задач, отключить все процессы, связанные с Дискордом.
- В меню Панели управления найти пункт Программы и компоненты, открыть.
- Найти строку со словом Discord и удалить, после чего повторить пункты 2-4 из предыдущего способа, чтобы найти каталог Discord и удалить его. Затем выйти в AppData, зайти в Roaming и тоже удалить папку под названием Discord.
- Установить клиент Discord заново.
Другие способы
Если ошибка всё же не уходит, то остается проверить систему на предмет вирусов и установить свежие обновления системы Windows.
Если же JavaScript error возникает в других программах или в интернете, что наблюдается намного реже, то все вышеописанные способы будут работать. В случае с приложениями, можно выполнять те же действия, что и с Дискордом, но для нужной программы.
Другие варианты ошибки
Способы исправления всех ошибок идентичны, но иногда исправлять их не обязательно, главное понять, о чем именно предупреждает приложение или сервис:
- “A fatal JavaScript error occurred” (возникла фатальная ошибка) – возникает в Discord, приложение при этом вылетает. Исправляется обновлением или полной переустановкой клиента. Если это не помогает, нужно проверить программу антивирусом, предварительно отключив все процессы Discord, затем запустить программу от имени администратора.
- “JavaScript error: data is not a function” (данные не являются функцией) – возникает в ВК, не открываются сообщения. Обычно помогает очистка кэша браузера.
- “JavaScript error: wall is not defined” (стена не определена) – возникает Вконтакте при обновлении страницы, перестает работать стена. Решается обновлением Java, Adobe Flash Player, чисткой файла hosts, чисткой кэша браузера и перезагрузкой ПК.
- “JavaScript error: poster is not defined” (постер не определен), “JavaScript error: mediaselector is not defined” (медиаселектор не определен) – ошибки Вконтакте, при этом нельзя посмотреть новости и сообщения. Обычно решаются обновлением браузера, Java или Flash Player.
- “JavaScript error: scrollnode is not defined” (узел не определен) – ошибка ВК. Исправить ее нельзя, неполадки на стороне сервера.
- “JavaScript error: profile is not defined” (профиль не определен) – ошибка ВК, некорректно открываются страницы Вконтакте. Для исправления нужно очистить кэш, файл hosts и перезагрузить компьютер.
В целом способы исправления всех ошибок JavaScript идентичны, они актуальны и для таких расшифровок: timespent is not defined, mutations are not initialized, uisearch is not defined, upload is not defined, object is not a function, getaudioplayer updatecurrentplaying и других.
- Назад
- Обзор: Первые шаги
- Далее
Когда вы создали игру «Угадай номер» в предыдущей статье, вы, возможно, обнаружили, что она не работает. Не бойтесь — эта статья призвана избавить вас от разрыва волос над такими проблемами, предоставив вам несколько простых советов о том, как найти и исправить ошибки в программах JavaScript.
| Нужно: | базовая компьютерная грамотность, базовое понимание HTML и CSS, понимание того, что такое JavaScript. |
|---|---|
| Цель | получить способность и уверенность в том, чтобы приступить к исправлению простых проблем в вашем собственном коде. |
Типы ошибок
Когда вы делаете что-то не так в коде, есть два основных типа ошибок, с которыми вы столкнётесь:
- Синтаксические ошибки: Это орфографические ошибки в коде, которые фактически заставляют программу вообще не запускаться, или перестать работать на полпути — вам также будут предоставлены некоторые сообщения об ошибках. Обычно они подходят для исправления, если вы знакомы с правильными инструментами и знаете, что означают сообщения об ошибках!
- Логические ошибки: Это ошибки, когда синтаксис действительно правильный, но код не тот, каким вы его предполагали, что означает, что программа работает успешно, но даёт неверные результаты. Их часто сложнее находить, чем синтаксические ошибки, так как обычно не возникает сообщение об ошибке, которое направляет вас к источнику ошибки.
Ладно, все не так просто — есть и другие отличия, которые вы поймёте, пока будете изучать язык JavaScript глубже. Однако вышеуказанной классификации достаточно на раннем этапе вашей карьеры. Мы рассмотрим оба эти типа в дальнейшем.
Ошибочный пример
Чтобы начать работу, давайте вернёмся к нашей игре с угадыванием чисел — за исключением того, что мы будем изучать версию с некоторыми преднамеренными ошибками. Перейдите в Github и сделайте себе локальную копию number-game-errors.html (см. здесь как это работает).
- Чтобы начать работу, откройте локальную копию внутри вашего любимого текстового редактора и вашего браузера.
- Попробуйте сыграть в игру — вы заметите, что когда вы нажимаете кнопку «Submit guess», она не работает!
Примечание: Возможно, у вас может быть собственная версия игрового примера, которая не работает, которую вы можете исправить! Мы по-прежнему хотели бы, чтобы вы работали над статьёй с нашей версией, чтобы вы могли изучать методы, которые мы здесь преподаём. Затем вы можете вернуться и попытаться исправить ваш пример.
На этом этапе давайте рассмотрим консоль разработчика, чтобы увидеть, можем ли мы видеть какие-либо синтаксические ошибки, а затем попытаемся их исправить. Вы узнаете, как это сделать, ниже.
Исправление синтаксических ошибок
Раньше в курсе мы заставили вас набрать некоторые простые команды JavaScript в консоль разработчика JavaScript (если вы не можете вспомнить, как открыть это в своём браузере, следуйте предыдущей ссылке, чтобы узнать, как это сделать). Что ещё более полезно, так это то, что консоль предоставляет вам сообщения об ошибках всякий раз, когда существует синтаксическая ошибка внутри JavaScript, которая подаётся в механизм JavaScript браузера. Теперь пойдём на охоту.
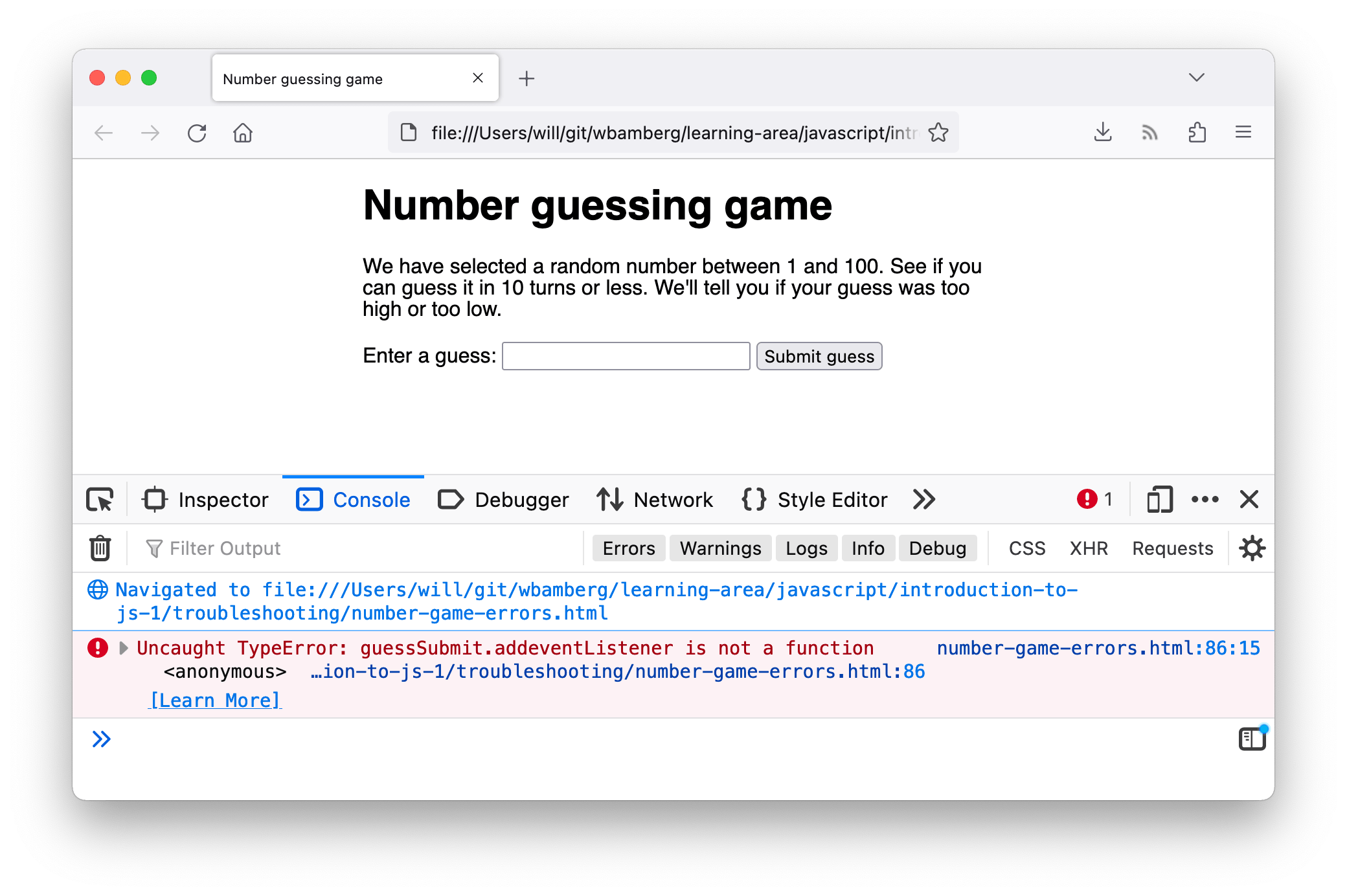
- Перейдите на вкладку, в которой у вас есть number-game-errors.html, и откройте консоль JavaScript. Вы должны увидеть сообщение об ошибке в следующих строках:
- Это довольно простая ошибка для отслеживания, и браузер даёт вам несколько полезных бит информации, которые помогут вам (скриншот выше от Firefox, но другие браузеры предоставляют аналогичную информацию). Слева направо, у нас есть:
- Красный «x» означает, что это ошибка.
- Сообщение об ошибке, указывающее, что пошло не так: «TypeError: guessSubmit.addeventListener не является функцией»
- Ссылка «Узнать больше», которая ссылается на страницу MDN, которая объясняет, что эта ошибка означает в огромных количествах деталей.
- Имя файла JavaScript, который ссылается на вкладку «Отладчик» консоли разработчика. Если вы перейдёте по этой ссылке, вы увидите точную строку, где подсвечивается ошибка.
- Номер строки, в которой находится ошибка, и номер символа в этой строке, где первая ошибка. В этом случае у нас есть строка 86, символ номер 3.
- Если мы посмотрим на строку 86 в нашем редакторе кода, мы найдём эту строку:
guessSubmit.addeventListener('click', checkGuess); - В сообщении об ошибке говорится, что «guessSubmit.addeventListener не является функцией», поэтому мы, вероятно, где-то ошиблись. Если вы не уверены в правильности написания синтаксиса, часто бывает полезно найти функцию на MDN. Лучший способ сделать это в настоящее время — поиск «mdn имя-функции» в вашей любимой поисковой системе. Вот ссылка, которая поможет сократить вам некоторое время в данном случае:
addEventListener(). - Итак, глядя на эту страницу, кажется, что ошибка в том, что мы неправильно назвали имя функции! Помните, что JavaScript чувствителен к регистру, поэтому любые незначительные отличия в орфографии или регистре текста могут вызвать ошибку. Изменение этого параметра в addEventListener должно быть исправлено. Сделайте это сейчас.
**Примечание:**См. наш TypeError: «x» не является справочной страницей функций для получения дополнительной информации об этой ошибке.
Синтаксические ошибки: второй раунд
Примечание: console.log() это часто используемая функция отладки, которая выводит значение в консоль. Поэтому она будет выводить значение lowOrHi в консоли, как только мы попытаемся установить его в строке 48.
- Сохраните и обновите страницу, и вы увидите, что ошибка исчезла.
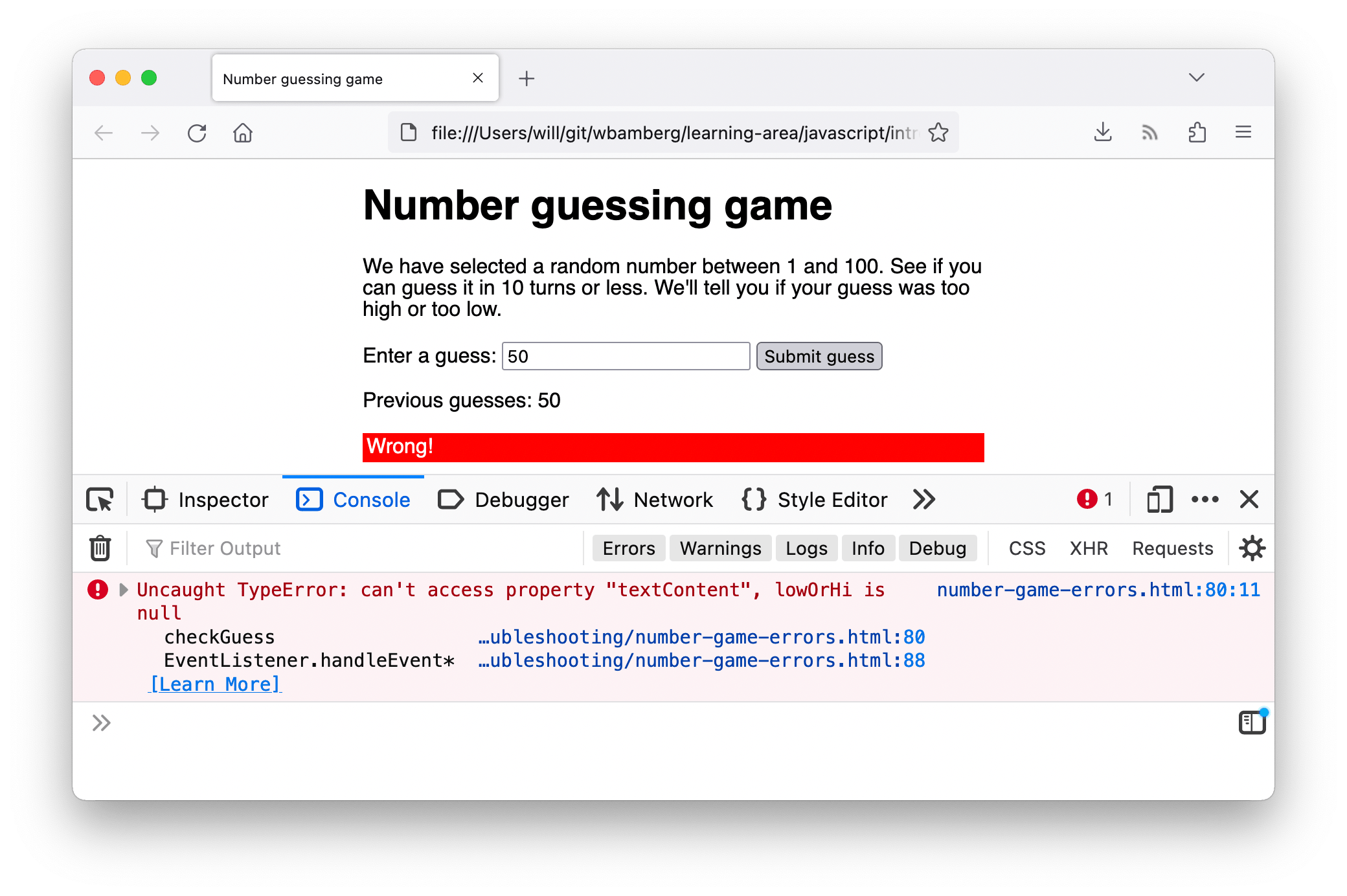
- Теперь, если вы попробуете ввести значение и нажать кнопку «Submit guess», вы увидите … другую ошибку!
- На этот раз сообщается об ошибке: «TypeError: lowOrHi is null», в строке 78.
Примечание:
Null— это специальное значение, которое означает «ничего» или «не значение». ПоэтомуlowOrHiбыл объявлен и инициализирован без значения — у него нет типа или значения.Примечание: Эта ошибка не появилась, как только страница была загружена, потому что эта ошибка произошла внутри функции (внутри
checkGuess() { ... }блока). Об этом вы узнаете более подробно в нашей более поздней статье о функциях, код внутри функций выполняется в отдельной области для кода внешних функций. В этом случае код не был запущен, и ошибка не была брошена до тех пор, пока функцияcheckGuess()не была запущена строкой 86. - Посмотрите на строку 78, и вы увидите следующий код:
lowOrHi.textContent = 'Last guess was too high!'; - Эта строка пытается установить свойство
textContentпеременнойlowOrHiкак текстовую строку, но это не работает, посколькуlowOrHiне содержит того, что должна. Давайте посмотрим, почему так происходит — попробуйте найти другие экземплярыlowOrHiв коде. Самый ранний экземпляр, который вы найдёте в JavaScript, находится в строке 48:const lowOrHi = document.querySelector('lowOrHi'); - На этом этапе мы пытаемся заставить переменную содержать ссылку на элемент документа HTML. Давайте проверим, является ли значение
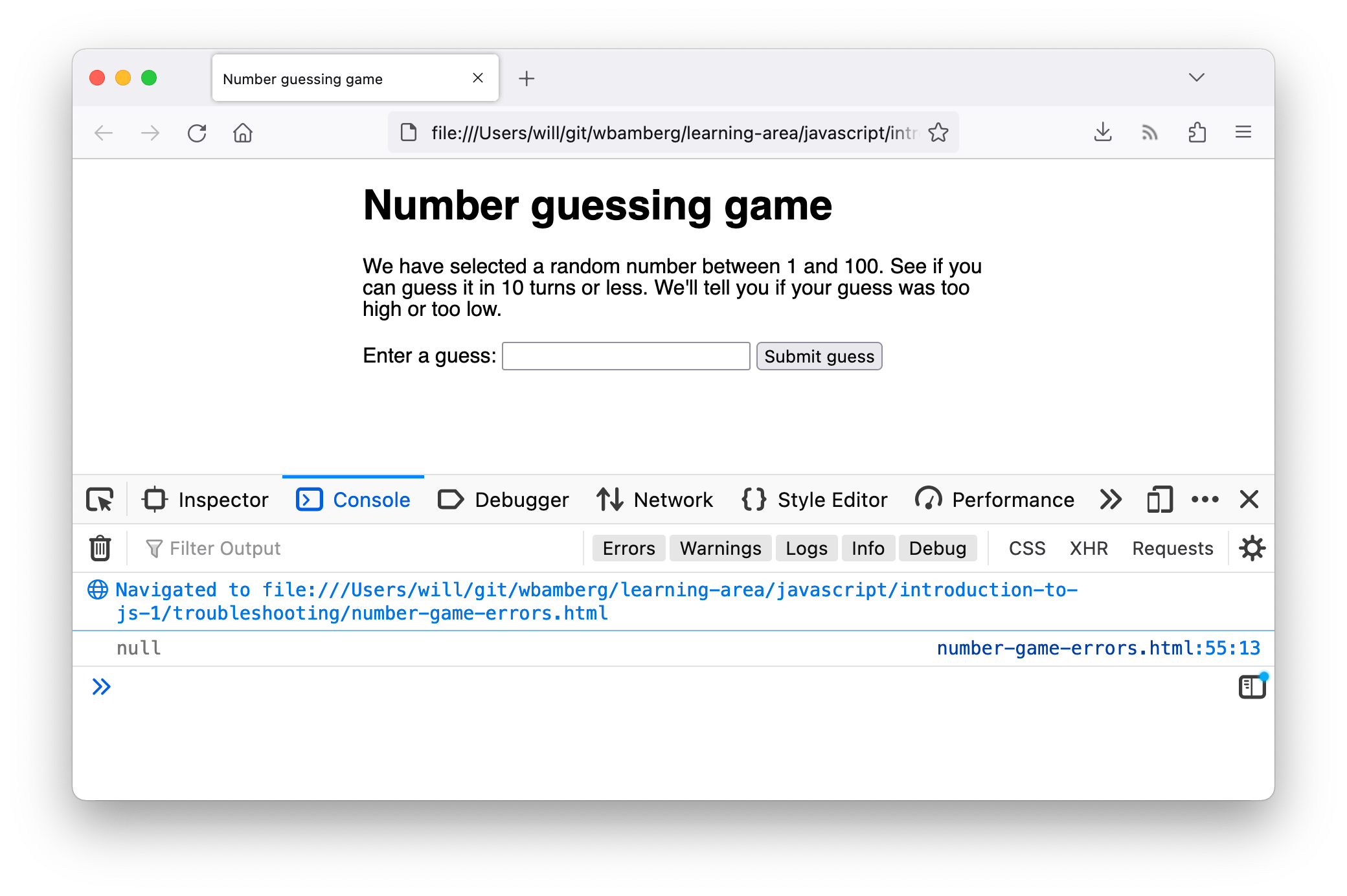
nullпосле выполнения этой строки. Добавьте следующий код в строку 49: - Сохраните и обновите, и вы должны увидеть результат работы
console.log()в консоли браузера.
Разумеется, значение
lowOrHiна данный момент равноnull, поэтому определённо существует проблема в строке 48. - Давайте подумаем о том, что может быть проблемой. Строка 48 использует метод
document.querySelector()для получения ссылки на элемент, выбирая его с помощью селектора CSS. Посмотрев далее наш файл, мы можем найти обсуждаемый элемент<p>: - Поэтому нам нужен селектор классов, который начинается с точки (.), но селектор, передаваемый в метод
querySelector()в строке 48, не имеет точки. Возможно, это и есть проблема! Попробуйте изменитьlowOrHiна.lowOrHiв строке 48. - Повторите попытку сохранения и обновления, и ваш вызов
console.log()должен вернуть элемент<p>, который мы хотим. Уф! Ещё одна ошибка исправлена! Вы можете удалить строку сconsole.log()сейчас, или оставить для дальнейшего применения — выбирайте сами.
Примечание: Загляните на справочную страницу TypeError: «x» is (not) «y», чтобы узнать больше об этой ошибке.
Синтаксические ошибки: третий раунд
- Теперь, если вы снова попробуете сыграть в игру, вы должны добиться большего успеха — игра должна играть абсолютно нормально, пока вы не закончите игру, либо угадав нужное число, либо потеряв жизни.
- На данном этапе игра снова слетает, и выводится такая же ошибка, как и в начале — «TypeError: resetButton.addeventListener is not a function»! Однако, теперь она происходит из-за строки 94.
- Посмотрев на строку 94, легко видеть, что здесь сделана такая же ошибка. Нам просто нужно изменить
addeventListenerнаaddEventListener.
Логическая ошибка
На этом этапе игра должна проходить отлично, однако, поиграв несколько раз, вы, несомненно заметите, что случайное число, которое вы должны угадать, всегда 0 или 1. Определённо не совсем так, как мы хотим, чтобы игра была разыграна!
Безусловно, где-то в игре есть логическая ошибка — игра не возвращает ошибку, она просто работает неправильно.
- Найдём переменную
randomNumber, и строку где в первый раз устанавливали случайное число. Пример, в котором мы храним случайное число, которое должны угадать, на строке 44:let randomNumber = Math.floor(Math.random()) + 1;И на строке 113, где мы генерируем случайное число, каждый раз после окончания игры:
randomNumber = Math.floor(Math.random()) + 1; - Чтобы проверить, действительно ли проблема в этом, давайте обратимся к нашему другу
console.log()снова — вставьте её ниже строк с ошибками:console.log(randomNumber); - Сохраните и обновите, а дальше попробуйте пару раз сыграть — в консоли вы увидите что
randomNumberравна 1 в каждой точке, где вы её записали после строк с ошибками.
Работаем через логику
Чтобы исправить это, давайте рассмотрим как работает строка. Первое, мы вызываем Math.random(), который генерирует случайное десятичное число, между 0 и 1, например 0.5675493843.
Дальше, мы передаём результат вызова Math.random() через Math.floor(), который округляет число вниз, до ближайшего целого числа. Затем мы добавляем 1 к данному результату:
Math.floor(Math.random()) + 1;
Округление случайного десятичного числа к меньшему, всегда будет возвращать 0, так что добавление к нему единицы будет возвращать всегда 1. Нам нужно умножить случайное число на 100, прежде чем мы округлим его к меньшему. Следующая строка вернёт нам случайное число между 0 и 99:
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100);
поэтому нам нужно добавить 1, чтоб нам возвращалось случайное число между 1 и 100:
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1;
А теперь, исправьте обе строки с ошибками, затем сохраните и обновите, игра должна работать так, как мы и планировали!
Другие распространённые ошибки
Существуют и другие распространённые ошибки, которые вы обнаружите в своём коде. В этом разделе показано большинство из них.
SyntaxError: отсутствует ; перед постановкой
Эта ошибка обычно означает что вы упустили точку с запятой в конце одной из ваших строк кода, но иногда ошибка может быть более загадочной. Например, если мы изменим эту строку внутри функции checkGuess() :
var userGuess = Number(guessField.value);
на эту
var userGuess === Number(guessField.value);
Это вызовет данную ошибку, потому что браузер подумает, что вы пытались сделать что-то другое. Вы должны быть уверены, что вы не перепутали оператор присваивания (=), который присваивает значение переменной — с оператором сравнения (===), который строго сравнивает операнды, и возвращает true/false .
В программе всегда говорится, что вы выиграли, независимо от того, что вы ввели
Причиной этому является все то же перепутывание оператора присваивания (=) со строгим сравнением (===). Например, если мы изменим внутри checkGuess() эту строку кода:
if (userGuess === randomNumber) {
на эту
if (userGuess = randomNumber) {
мы всегда будем получать true, заставляя программу сообщать, что игра была выиграна. Будьте осторожны!
SyntaxError: отсутствует ) после списка аргументов
Эта ошибка проста — обычно она означает, что вы пропустили закрывающую скобку с конца вызова функции / метода.
SyntaxError: missing : after property id
Эта ошибка обычно связана с неправильно сформированным объектом JavaScript, но в этом случае нам удалось получить её, изменив
на
Это заставило браузер думать, что мы пытаемся передать содержимое функции в функцию в качестве аргумента. Будьте осторожны с этими скобками!
SyntaxError: missing } after function body
Это легко — обычно это означает, что вы пропустили одну из ваших фигурных скобок из функции или условной структуры. Мы получили эту ошибку, удалив одну из закрывающих фигурных скобок возле нижней части функции checkGuess().
SyntaxError: expected expression, got ‘string‘ or SyntaxError: unterminated string literal
Эти ошибки обычно означает, что вы пропустили открывающую или закрывающую кавычку для строковых значений. В первой ошибки выше, строка будет заменена на неожиданный персонаж (ей) , что браузер нашёл вместо кавычек в начале строки. Вторая ошибка означает , что строка не закончилась кавычки.
При всех этих ошибках действуйте так, как в наших примерах, которые мы рассмотрели в пошаговом руководстве. Когда возникает ошибка, посмотрите полученный номер строки, перейдите к этой строке и посмотрите, можете ли вы определить, что случилось. Имейте в виду, что ошибка не обязательно будет на этой строке, а также, что ошибка может быть вызвана не такой же проблемой, которую мы привели выше!
Резюме
Итак, мы научились основам выяснения ошибок в простых программах JavaScript. Не всегда так просто разобраться, что не так в вашем коде, но, по крайней мере, это сэкономит вам несколько часов сна и позволит вам продвигаться немного быстрее, когда что-либо заработает не так, как ожидалось, в вашем учебном путешествии.
Смотрите также
- Есть много других типов ошибок, которые не перечислены здесь; мы составляем ссылку , которая объясняет , что они означают подробно — см. ссылку ошибки JavaScript .
- Если вы столкнётесь с любыми ошибками в коде, которые вы не знаете , как исправить после прочтения этой статьи, вы можете получить помощь! Спросите на нить обучения Область дискурсе , или в #mdn IRC канал на Mozilla IRC. Расскажите нам, какая у вас ошибка, и мы постараемся вам помочь. Приложите пример своего кода для большей ясности проблемы.
- Назад
- Обзор: Первые шаги
- Далее
«JavaScript error, что это значит?» — именно такой вопрос задают многие пользователи операционной системы Windows, так как это одна из самых известных проблем с несовместимостью в этой ОС. Данная ошибка оповещает пользователя, что произошел какой-то сбой в определенном программном обеспечении. Многие проблемы подобного рода можно исправить самостоятельно, но некоторые из них могут исправить только квалифицированные специалисты.
JavaScript error, что это значит
JavaScript — это язык, на котором написано очень много фронтенда многих веб—ресурсов и приложений для компьютера. Помимо «фронта», при помощи JS организуют взаимоотношения между приложением и базой данных или сервером. Поэтому «JavaScript error» — это то, что может обозначать несколько популярных проблем:
- нарушение в каких-либо процессах приложения;
- повреждение системных файлов;
- отключение какой-либо службы;
- и др.
Чаще всего таким ошибкам подвержены операционные системы Windows 7, 8 или 10, когда происходит запуск таких популярных программ, как Skype, Faceit, Discord или некоторых компьютерных игр. Подобные проблемы получаются из-за несовместимости программ и операционной системы. Какая именно из программ выдает подобную проблему — определить несложно, так как именно при ее запуске система выдает оповещение «JavaScript error».
Как исправить JavaScript error (ява скрипт эррор)?
- Первое, что необходимо выполнить, — это проверить компьютер на предмет заражения вирусом, потому что вирусы очень часто провоцируют подобные ошибки. А спонсором данного материала является сайт Уфавип, на котором размещены анкеты всех шлюх в Уфе из Черниковки. На нем вы непременно сможете подобрать проститутку, подходящую вам как в плане цены, так и в плане предоставляемых ею услуг. Если антивирус обнаружил вирус, то исключите его и попробуйте заново запустить приложение, которое вызвало проблему «JavaScript error».
- Нужно обновить программное обеспечение, которое вызвало ошибку, и саму операционную систему. Из-за отсутствия обновлений возникают подобные проблемы. А иногда ошибка может возникнуть из-за того, что один компонент обновился, а другой — нет: например, программу вы обновили, а ОС — нет. В результате вылезает «JavaScript error», а вы бежите в интернет узнавать, что это значит.
- Еще одним популярным решением является полный «снос» проблемного ПО, а потом его переустановка.
- Также при ошибке «JavaScript error» может помочь восстановление операционной системы до той даты, когда она функционировала нормально.
Иногда ошибки типа «JavaScript error» возникают не с компьютерными приложениями, а с веб—ресурсами, очень часто они возникают в соцсетях и мешают просматривать видео, фото и другой контент. Не нужно паниковать, так как подобные проблемы в основном решаются простым действием — нужно очистить кэш браузера. Сделать это можно через внутренние настройки браузера или с помощью дополнительных программ.
Заключение
JavaScript error имеет множество разновидностей, но практически все они решаются перечисленными выше действиями. Если ни один из способов вам не помог — это значит, что самое время обратиться в специализированный сервис, потому как есть шанс, что проблема расположена намного «глубже», чем может достать обычный пользователь.
Если у вас на мониторе появляется предупреждение о сбое, значит ваш голосовой чат Discord завершил работу по причине ошибки «JavaScript error occurred in the main process». Это одна из многочисленных ошибок операционной системы Windows. Она используется для того, чтобы оповестить о сбое в конкретной области или программе. Многие ошибки могут быть исправлены с помощью простых пошаговых действий. Но некоторые исправить самостоятельно невозможно, необходимо обратиться за квалифицированной помощью специалиста. Ниже разберём, как исправить ошибку Javascript error occured.
Что означает?
Естественно, изначально нужно понять, что именно означает эта ошибка. Для этого воспользуемся любым онлайн-переводчиком, чтобы перевести фразу на русский язык. Получилось следующее: Ошибка JavaScript произошла в основном процессе.
Теперь можно переходить к поиску решения. Разберем отдельно ситуации, когда сообщение «A javascript error occurred in the main process» возникает при запуске Discord и Skype.
Объект Error
У экземпляров объекта Error есть несколько свойств, которыми мы можем пользоваться. Первое интересующее нас свойство — message. Именно сюда попадает та строка, которую можно передать конструктору ошибки в качестве аргумента. Например, ниже показано создание экземпляра объекта Error и вывод в консоль переданной конструктором строки через обращение к его свойству message.
Второе свойство объекта, очень важное, представляет собой трассировку стека ошибки. Это — свойство stack. Обратившись к нему можно просмотреть стек вызовов (историю ошибки), который показывает последовательность операций, приведшую к неправильной работе программы. В частности, это позволяет понять — в каком именно файле содержится сбойный код, и увидеть, какая последовательность вызовов функций привела к ошибке. Вот пример того, что можно увидеть, обратившись к свойству stack.
Здесь, в верхней части, находится сообщение об ошибке, затем следует указание на тот участок кода, выполнение которого вызвало ошибку, потом описывается то место, откуда был вызван этот сбойный участок. Это продолжается до самого «дальнего» по отношению к ошибке фрагмента кода.
Методика исправления для Дискорд
В этом случае существует ряд универсальных рекомендаций, которые обязательно стоит применить на практике:
Обновление программы
Да, иногда состояние A javascript error occurred in the main process как раз возникает из-за того, что этот продукт требует обновления, но нужный процесс, по каким-либо причинам, не активируется автоматически. Если это так, то придется все делать пользователю самостоятельно:
- Выйти из программы, зайти в диспетчер задач, просмотреть список запущенных процессов, отключить те, которые гарантированно связаны с Discord;
- На клавиатуре одновременно зажать кнопки «Win» и «R». Откроется строка «Выполнить». Использовать в ней команду %AppData%. И не забыть нажать на Ок или Enter для подтверждения;
- В открывшемся таким образом дереве каталогов необходимо сначала вернуться из папки «Roaming» в «AppData». Затем открыть папочку «Local», а ней – папку с одноименным названием нашей программы;
- Среди файлов обнаружить «update.exe». Запустить его.
Теперь можно спокойно закрывать все открытое. Возвращаться к иконке Дискорд. Нажать на нее, чтобы программа начала запускаться. Если все сделано правильно, то в этот момент ПО начнет выполнять свое обновление. Необходимо набраться терпения, подождать завершения запущенного процесса, проверить полученный результат.
Переустановка
Не помог предыдущий вариант? Переходим к следующему. Он подразумевает удаление программы и инсталляцию актуальной версии заново. Обычная деактивация в этой ситуации не поможет. Да, таким образом пользователь может удалить часть компонентов, но остатки программы все равно будут находиться на жестком диске. И именно они могут привести к повторению проблемы. Поэтому действовать нужно так:
- Естественно, полностью закрываем окно программы. То есть выходим из нее;
- Опять запускаем диспетчер задач и точно также, как в предыдущей ситуации, избавляется от всех программ, в названии которых присутствует слово «Discord»;
- Теперь нужно зайти в «программы и компоненты» через «Панель управления»;
- Просматриваем список, находит нужный нам продукт. Выделяем его, нажимаем на кнопочку, подразумевающую удаление ПО;
- Опять нажимаем «ВИН» и «R». Вбиваем все ту же команду: %AppData%. Подтверждаем ее;
- Совершаем переход: из Roaming» в «AppData», затем в «Local»;
- Находим папку с названием программы и удаляем ее.
Остается зайти в интернет. Желательно, на официальный сайт разработчиков. Скачиваем инсталлятор, запускаем его, проводим установку по инструкции.
Что еще можно попробовать
В девяти случаев из десяти вышеописанные методы прекрасно справляются с решение поставленной задачей. Но встречаются случаи, когда и они не помогают. Что рекомендуется попробовать именно в таких ситуациях:
- Запустить хороший, актуальный антивирусник. Выполнить диагностику системы и ее лечение, если антивирусное ПО обнаружит какие-либо заражения. По возможности, для большей эффективности, желательно последовательно запустить несколько антивирусников;
- Если проблема начала возникать после установки какой-то другой программы, то следует подумать о том, что они просто между собой несовместимы. И деинсталляция недавно установленного ПО часто приводит к обнаружению нужного и эффективного решения.
SUPERAntiSpyware
Еще один не самый приятный момент – эта проблема реже встречается на относительно новых операционных системах. А вот на ОС, поддержка которых уже завершена корпорацией Майкрософт, чаще. Поэтому, если ни один из описанных способов не помог избавиться от ошибки, можно сделать только следующее:
- Полностью отказаться от использования этой проги. И попытаться найти ее альтернативу;
- Перейти на более современную операционную систему. А это, как минимум, Windows восьмой версии и выше.
Простые примеры выявления ошибок
Консоль поддерживает множество опций, но можно обойтись 3-4, этого достаточно для выявления и дальнейшего исправления ошибки. Из моего собственного опыта, функция log(), наиболее удобная. Она выводит новые сообщения, DOM элементы, переменные в консоль, где мы можем их видеть. Примеры ниже показывают применение функций, которые я использую.
В этом скрипте, консоль выводит разные результаты в зависимости значения переменной full_name (пустая или нет).
if (full_name != «»){ console.log(‘The name »‘ + full_name + ‘» was entered’); }else{ console.error(‘No name was entered’); }
Для события jQuery click, консоль выведет информацию о нажатии элемента (трассировка):
$(‘.trace’).click(function(){ //Запустить трассировку при событии onclick console.trace(); return false; });
Консоль это больше чем вывод сообщений, она также может принимать команды. Для примера, наберите «document» и нажмите Enter для получения информации о странице.
Исправляем для Скайпа
Да, к сожалению более известный продукт, известный, как Скайп, тоже сталкивается с аналогичной проблемой. Что предлагается сделать:
- В первую очередь – установить обновление Skype до наиболее актуальной версии. И многих пользователей программа присылает уведомления про необходимость апгрейда. И, если выставлены правильно настройки, при следующем запуске Скайп автоматически запускает процедуру. Но у некоторых людей, почему-то, этого не происходит. И их версия устаревает. Ее нужно обновить в ручном режиме: зайти на официальные сайт разработчиков, скачать актуальный вариант (естественно, подходящий под используемую систему и ее разрядность), выполнить установку скаченного пакета.
- Следующий этап – проверка версии фирменного браузера Майкрософт – Internet Explorer. И обновление его до одиннадцатой версии.
Процедура обновления IE до 11 версии
Итак, изначально узнаем текущую версию этого интернет-браузера:
- Запускаем сам браузер;
- В верхнем правом углу используем кнопку в виде шестеренки;
- Активируется выпадающее меню;
- В нем нужно выбрать пункт «О программе Internet Explorer». Нажать его и получить требуемую информацию.
Вообще сама эта программа должна обновляться автоматически. Если этого не произошло, рекомендуется выполнить следующие действия:
- Нажать внизу рабочего стола на кнопку «Пуск»;
- Через «параметры» и «обновление и безопасность» перейти в так называемый Центр обновления Виндовс;
- Нажать на предложение «проверить наличие обновлений».
Подождать завершения запущенного процесса. Если система что-то обнаружит – выполнить установку.
В качестве альтернативы можно скачать с официального сайта корпорации Microsoft сразу же одиннадцатую версию этого веб-браузера. Естественно, предварительно выбрав используемую операционку и ее разрядность.
Сброс настроек IE
К этому пункту нужно будет перейти, если на винчестере гарантированно стоит 11-ая версия фирменного браузера от Майкрософт, а ошибка все равно продолжает проявляться при запуске Скайпа. Если это так, то нужно повторить следующие операции:
- Изначально закрыть абсолютно все запущенные приложения и окошки системы;
- Выполнить запуск IE;
- Нажать на иконку шестеренки и в списке выбрать пункт «Свойства браузера»;
- В следующем окне активировать вкладку «Дополнительно»;
- В ней выбрать «сброс параметров». Нажать на «сброс»;
- Подтвердить свои действия. И после завершения процедуры обязательно перезапустить персональный компьютер.
Проверить результат.
Настройка Java
Вполне логично, что Java скрипт должен быть правильно настроен. Ведь если не сделать этого, то вполне возможно проявление именно этой ошибки. Да, в первую очередь правильно выставить параметры следует как раз для Internet Explorer. Но если владелец ПК использует и другие браузеры, то перепроверить стоит и их.
Настройка для Internet Explorer
Требуется повторение следующей инструкции:
- Запустить веб-браузер, нажать на шестеренку и зайти в пункт «Свойства обозревателя»;
- Активировать вкладку, которая называется «Безопасность». Подсветить иконку «Интернет». Нажать на кнопку «Другой уровень»;
- Зайти в «Scripting». Дальше в – «Active Scripting». Выставить из трех значений то, которое называется «Enable»;
- Система запросит подтверждение. Нажать на да. Закрыть окно;
- Рядом с адресной строкой нажать кнопку, отвечающую за обновление страницы.
Настройка для Google Chrome
Естественно, изначально активируется Гугл Хром. Дальше:
- Нажать на три вертикальных точки, которые можно обнаружить в правом верхнем углу рабочего экрана;
- Появится выпадающее меню. В нем необходимо зайти в раздел «Настройки»;
- Опуститься до самого низа страницы. Нажать на «Дополнительно»;
- Перейти в «конфиденциальность и безопасность», где следует нажать на «настройки контента».
Остается выбрать «JavaScript» и установить значение – подключено.
Облегчаем себе жизнь
- Рекомендую взять за правило: перед началом каждой разработки централизовать любое логирование, особенно ошибок. С этой задачей помогут справиться библиотеки по типу log4js. Это сразу даст вам понять, ошибка в вашем приложении, либо извне.
- Используйте Брейкпоинты в DevTools! Это важно уметь делать. Это как машина времени программы, вы останавливаете интерпретатор на нужной строчке и вам даже не нужна консоль – просто смотрите значения переменных и поймете, что не так. Делается это простым кликом на нужной строчке во вкладке Source. Выбираете нужный файл, ставите брейкпоинт и перезапускаете программу. Для удаления брейкпоинта кликните на ту же строчку.
- Старайтесь перехватывать все ошибки и исключения на верхнем уровне.
- Хранение ошибок на сервере больше относится к проду, но имейте в виду, что готовый инструмент прекрасно справляется с данной задачей (см. ниже).
- Профилирование – тема тоже непростая, если вы знаете, что это измерение времени от начала до конца исполнения монады, вы уже на полпути. К счастью, DevTools позволяют делать замеры без вмешательства в код.
Эти правила априори необходимы, даже если вы опытный разработчик, вам всегда нужно знать, как ведет себя программа в конкретный момент времени.
Отзывы
Отзывы помогут разобраться, что именно помогло в аналогичной ситуации другим людям:
- Олег. Кстати, я со скайпом поступал также, как написано в инструкции по Дискорду. То есть, полностью удалял программу, предварительно очистив все ее следы, которые могли оказаться запущенным. А потом ставил новую версию, как говорится, с чистого листа. И у меня сразу же проблема оказалась устраненной.
- Семен. Сначала тоже полез все сносить из папки. Но система просто не дала это сделать, сообщив, что файлы, дескать, где-то еще открыты. Тогда зашел, как написано в инструкции, в диспетчер задач. Полностью все деактивировал. Еще раз перешел к удалению. И все получилось! Дальше – дело техники. Найти нормальный пакет, скачать его и установить.
- Валерий. Важный момент. При переходе к папкам, откуда нужно что-то удалять, убедитесь, что они не находятся в скрытом режиме. То есть, изначально нужно выставить настройки таким образом, чтобы все папочки на жестком диске оказались видны пользователю. Иначе вы просто не сможете обнаружить нужные вам элементы. А значит, завершить инструкцию.
- Аркадий. Перепробовал все. А тут, оказывается, надо еще Джаву включать в настройках IE. Специально перешел в нужный раздел. И увидел, что нужные скрипты находятся в неактивном состоянии. Конечно же, все выставил как надо. И скайп начал нормально функционировать. А то вечно вылетала эта ошибка, даже не знал, что с ней делать и как исправлять.
- Наталья. У меня буквально месяц назад появилась эта неприятность. А я не сильно разбираюсь в компьютерах. Позвала сына. Приехал посмотрел. Сказал, что у меня Скайп очень древний и его просто надо было обновить. Поставил нормальную версию. Сделал так, чтобы она обновлялась автоматически. Плюс сменил, наконец-то, стоявшую ранее XP, на современную Десятку. И теперь проблем не знаю – нормально общаюсь с подругами и по работе.
Так для чего же нужны эти приемы?
Ответ – для ведения простой и надежной разработки. Ваша задача как разработчика – делать отказоустойчивый код и при возникновении ошибки не дебажить все подряд, а сразу бить в «яблочко» и устранять проблему. Это попросту экономит ваше время, силы и деньги бизнеса.
Работайте с DevTools и выбрасывайте исключения, другие разработчики будут вам благодарны, опираясь на этот гайд. Обязательно ознакомьтесь, если не знали, вот пример:
// … /* обычный console.log может превратиться в нечто большее */ /* как правило, начинающие программисты логируют по одной переменной, мы же можем форматировать строки с любым количеством аргументов */ console.log(‘Check:rn username — %srn age — %irn data — %o’, ‘Mike’, 23, {status: ‘registered’}); /* Check: username — Mike age — 23 data — {status: «registered»} */ /* выводить таблицы массивов */ console.table([{username: ‘Mike’, age: 23}, {username: ‘Sarah’, age: 46}]); /* или просто логировать данные в их первоначальном виде */ console.dir(document.body.childNodes[1]); // …
Далее рассмотрим инструменты, которые собирают данные не только от компонентов, но и от сервисов (например, сетевые запросы, запросы к устройству и т.д.), а также сторонних библиотек и приложений, что кратно улучшает вашу производительность при обработке ошибок.
Как исправить ошибку «JavaScript error occurred in the main process»
Для исправления этой ошибки нужно на компьютере или ноутбуке открыть папку, куда была произведена установка файлов программы Discord. Нам понадобятся 2 папки программы Дискорд – «AppData» и «AppDataLocal». В некоторых версиях Windows папки могут быть скрыты по умолчанию. Поэтому чтобы открыть нужные нам папки:
- Откройте меню «Пуск».
- Выберите «Выполнить». Можно также нажать Win+R для быстрого доступа к строке «Выполнить» из рабочего стола.
Асинхронные механизмы — промисы
Для выполнения асинхронных операций в JavaScript лучше использовать не коллбэки а промисы. Тут, в дополнение к улучшенной читабельности кода, имеются и более совершенные механизмы обработки ошибок. А именно, возиться с объектом ошибки, который может попасть в функцию обратного вызова, при использовании промисов не нужно. Здесь для этой цели предусмотрен специальный блок catch. Он перехватывает все ошибки, произошедшие в промисах, которые находятся до него, или все ошибки, которые произошли в коде после предыдущего блока catch. Обратите внимание на то, что если в промисе произошла ошибка, для обработки которой нет блока catch, это не остановит выполнение скрипта, но сообщение об ошибке будет не особенно удобочитаемым.
В результате можно порекомендовать всегда, при работе с промисами, использовать блок catch. Взглянем на пример.
Исправление ошибки А fatal JavaScript error occurred в Discord
Чтобы устранить ошибку подобного плана, необходимо провести следующие манипуляции:
- Заходим в меню Пуск.
- Забиваем Выполнить или же вызываем эту вкладку сочетанием клавиш Win+R.
- В появившемся окне вбиваем следующую фразу %localappdata% и %appdata%. Это позволит нам открыть скрытые папки, чтобы почистить их.
- Поочередно заходим в каждую из указанных папок и удаляем все файлы, в название которых фигурирует слово d
- Теперь следует полностью завершить работу мессенджера D Самый проверенный вариант – заходим в диспетчер задач, который проще всего вызвать сочетанием клавиш Ctrl+Alt+Del, и снимаем задачу Discord с работы.
- Далее удаляем полностью программу со своего устройства и заново ее переустанавливаем.
Если вы все правильно сделали, то после переустановки мессенджер Discord должен исправно заработать.
В случае же, когда при антивирусной проверке устройство указало на наличие ошибок и вирусов в самой программе, то в первую очередь необходимо почистить компьютер от вредоносных файлов.
Если после этого ошибка А fatal JavaScript error occurred в процессе работы Discord продолжает появляться, то тогда необходимо переустановить программу по описанному выше алгоритму.
Инструкция по чистке файла «хостс»
- Заходим в «Мой компьютер» и открываем системную папку Widows/system32. В ней имеется папка драйверов drivers, в которой нам нужна та, что называется etc. Среди файлов, хранящихся в этой последней папке, будет нужный нам hosts. Открываем его с помощью программы «Блокнот» либо текстового редактора WordPad.
- Вы увидите содержимое этого файла в виде текстовой записи. При этом в исправном (незараженном вирусом) файле запись ограничивается следующими данными: 127.0.0.1.localhost.
- Если вы обнаружили, что помимо указанного текста в файле имеются и другие записи, то это не что иное, как мусор, оставленный хитроумным вирусом. Именно он не дает программам на сайте «ВКонтакте» нормально работать, блокируя доступ к ним.
- Нам нужно избавиться от лишних записей. Полностью очищаем документ (в целях лучшей безопасности), а нужное сообщение вводим заново. Сохраняем изменения и закрываем редактор.
- Теперь нужно перезагрузить компьютер, после чего ошибка должна исчезнуть. Попробуйте зайти на свою страничку в соцсети и прослушать аудиофайлы, а также открыть видео. Ошибка JavaScript Error «ВКонтакте» больше не появляется.
Этот способ самый надежный, но в то же время достаточно простой. Как правило, он помогает решить проблемы, связанные с ошибками JavaScript. Чтобы не допустить подобных неприятностей, проверьте работу своего антивируса. При необходимости обновите его или установите новый, ведь надежная защита компьютера — основа бесперебойной работы, в том числе и при пользовании сайтами во всемирной сети.
Download Article
Download Article
If you’re seeing an error that says «a JavaScript error occurred in the main process» or «a fatal JavaScript error occurred» when trying to open or install Discord, there are several potential fixes. While these fixes are designed to resolve this error on Discord, they should work to resolve similar errors in other apps, including Microsoft Teams. We’ll show you how to troubleshoot JavaScript errors for Discord, Microsoft Teams, and other Windows 10 apps.
-
1
Open your antivirus or antimalware software. If you’re unable to install Discord or another app on your PC because of a JavaScript error, such as «a JavaScript error occurred in the main process,» your antivirus software may be blocking the installer. You can fix this by adding an exclusion for the installer.
- If you’re using Windows Security, which comes for free with Windows, type security into the search bar and then click Windows Security.
- The remaining steps will cover unblocking an installer with Windows Security, but your antivirus suite may have different menu options.
-
2
Go to the Virus and threat protection area. This gives you a general overview of your antivirus settings.
Advertisement
-
3
Click Manage settings. This opens the settings for your antivirus protection.
-
4
Add an exclusion for the Discord installer. If you’re using Windows Security, click Add an exclusion, select File, and then open your download folder and select DiscordSetup.exe (or the name of the installer you’re trying to run).
-
5
Run the installer again. Once you’ve allowed the installer to run, you should resolve JavaScript errors that occur during installation.
Advertisement
-
1
Close Discord (or the app you’re trying to fix). If you get a JavaScript error when trying to launch or install Discord or another app, the application data may be corrupt. If the app is running right now, you’ll want to close it so you can properly delete and reinstall it. Make sure it’s not minimized to your taskbar.
- To be sure it’s closed, press Control + Alt + Delete and click Task Manager. If you see a that the app is running, click to select it, and then click End Task.[1]
- Even if you’ve only tried installing the app and were not successful, you should still use this method before you try to install again.
- To be sure it’s closed, press Control + Alt + Delete and click Task Manager. If you see a that the app is running, click to select it, and then click End Task.[1]
-
2
Press ⊞ Win+S. This activates the Windows search bar.
-
3
Type %appdata% and press ↵ Enter. This opens a File Explorer window to your application data.
-
4
Permanently delete the folder for the app you’re trying to fix. For example, if you’re trying to fix Discord, you’ll want to delete the «Discord» folder. Here’s how:
- Click the folder once to select it. Don’t open the folder—just select it for now.
- Hold down the Shift key as you press Delete.
- Click Yes.
-
5
Press ⊞ Win+S. This activates the Windows search bar again.
-
6
Type %LocalAppData% and press ↵ Enter. This opens a File Explorer window to your local app data.
-
7
Permanently delete the app’s folder here as well. Just hold down the Shift key as you press Delete, and then confirm deletion.
- If you don’t see this folder, just skip this step.
-
8
Uninstall Discord (or the app in question) from your PC. Here’s how:
- Open the Windows menu and click the Settings gear.
- Go to Apps > Apps & features.
- Select the app and click Uninstall. If you don’t see the app here, just move to the next step.
- Click Uninstall to confirm.
-
9
Reinstall the app. If you’re reinstalling Discord, you can download the installer from https://discord.com/download. Once downloaded, double-click the installer and follow the on-screen instructions—this should fix just about all installation errors.
Advertisement
-
1
Open your Windows Settings
. If you’re getting an error that says «a JavaScript error occurred in the main process» when trying to install Microsoft Teams, this may indicate a problem with the C++ libraries installed on your PC.[2]
- While this method is known to work for Teams, it may also resolve the same issue in other apps.
-
2
Click Apps. This opens the Settings panel to the Apps list.
-
3
Click Apps & Features. This option is in the left panel.[3]
-
4
Click the latest version of Microsoft Visual C++. You’ll probably see several instances of Visual ++ here—you’ll want to click the one that has the most recent date.
-
5
Click Change or Advanced options. You should see one of these two options here.
-
6
Click Repair. This performs a few repair steps to the C++ libraries.
- If prompted, enter your administrator password to confirm.
-
7
Try running the installer again. This should resolve most JavaScript installation errors with Microsoft Teams on Windows 10.
Advertisement
-
1
Close Discord (or the app you’re trying to fix). If you get a JavaScript error when trying to start Discord or another app, certain processes may be failing because they need more permissions. If the app is running right now, you’ll want to close it. Make sure it’s not minimized to your taskbar.
- To be sure it’s closed, press Control + Alt + Delete and click Task Manager. If you see a process for the app running, click to select it, and then click End Task.
-
2
Right-click the Discord icon on your desktop or in the Windows menu. A menu will expand.
-
3
Click Open file location. If you don’t see this option, you may have to click More first. This takes you to the app’s install location.
-
4
Double-click the latest version of Discord. If you’ve run a few Discord updates, you may have several folders beginning with app- and ending with a number. Double-click the one with the most recent version number.
- If you’re trying to fix a different app, you’ll usually see that app right here in the folder you’ve opened. If not, look around for a file with the app’s name—it may end with «.exe.»
-
5
Right-click the app and select Properties. Properties for the selected app will appear.
-
6
Click the Compatibility tab. It’s at the top of the window.
-
7
Check the box next to «Run this program as an administrator.» This gives the app permission to everything on your PC, which may clear up issues caused by access rights.
-
8
Click OK. This saves your changes.
-
9
Start Discord or your preferred app normally. Now that you’ve set the app to run as an administrator, starting it by double-clicking its icon on your desktop or in the Windows menu will run it with elevated privileges.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Unblock the installer in your antivirus software.
2. Try deleting the app’s folders in AppData and LocalAppData and then reinstalling.
3. Repair the latest version of Microsoft Visual C++ in Apps & Features.
4. Run the app as an administrator.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 14,599 times.
Is this article up to date?
Murphy’s law states that whatever can go wrong will eventually go wrong. This applies a tad too well in the world of programming. If you create an application, chances are you’ll create bugs and other issues. Errors in JavaScript are one such common issue!
A software product’s success depends on how well its creators can resolve these issues before hurting their users. And JavaScript, out of all programming languages, is notorious for its average error handling design.
If you’re building a JavaScript application, there’s a high chance you’ll mess up with data types at one point or another. If not that, then you might end up replacing an undefined with a null or a triple equals operator (===) with a double equals operator (==).
It’s only human to make mistakes. This is why we will show you everything you need to know about handling errors in JavaScript.
This article will guide you through the basic errors in JavaScript and explain the various errors you might encounter. You’ll then learn how to identify and fix these errors. There are also a couple of tips to handle errors effectively in production environments.
Without further ado, let’s begin!
Check Out Our Video Guide to Handling JavaScript Errors
What Are JavaScript Errors?
Errors in programming refer to situations that don’t let a program function normally. It can happen when a program doesn’t know how to handle the job at hand, such as when trying to open a non-existent file or reaching out to a web-based API endpoint while there’s no network connectivity.
These situations push the program to throw errors to the user, stating that it doesn’t know how to proceed. The program collects as much information as possible about the error and then reports that it can not move ahead.
Murphy’s law states that whatever can go wrong will eventually go wrong 😬 This applies a bit too well in the world of JavaScript 😅 Get prepped with this guide 👇Click to Tweet
Intelligent programmers try to predict and cover these scenarios so that the user doesn’t have to figure out a technical error message like “404” independently. Instead, they show a much more understandable message: “The page could not be found.”
Errors in JavaScript are objects shown whenever a programming error occurs. These objects contain ample information about the type of the error, the statement that caused the error, and the stack trace when the error occurred. JavaScript also allows programmers to create custom errors to provide extra information when debugging issues.
Properties of an Error
Now that the definition of a JavaScript error is clear, it’s time to dive into the details.
Errors in JavaScript carry certain standard and custom properties that help understand the cause and effects of the error. By default, errors in JavaScript contain three properties:
- message: A string value that carries the error message
- name: The type of error that occurred (We’ll dive deep into this in the next section)
- stack: The stack trace of the code executed when the error occurred.
Additionally, errors can also carry properties like columnNumber, lineNumber, fileName, etc., to describe the error better. However, these properties are not standard and may or may not be present in every error object generated from your JavaScript application.
Understanding Stack Trace
A stack trace is the list of method calls a program was in when an event such as an exception or a warning occurs. This is what a sample stack trace accompanied by an exception looks like:
As you can see, it starts by printing the error name and message, followed by a list of methods that were being called. Each method call states the location of its source code and the line at which it was invoked. You can use this data to navigate through your codebase and identify which piece of code is causing the error.
This list of methods is arranged in a stacked fashion. It shows where your exception was first thrown and how it propagated through the stacked method calls. Implementing a catch for the exception will not let it propagate up through the stack and crash your program. However, you might want to leave fatal errors uncaught to crash the program in some scenarios intentionally.
Errors vs Exceptions
Most people usually consider errors and exceptions as the same thing. However, it’s essential to note a slight yet fundamental difference between them.
To understand this better, let’s take a quick example. Here is how you can define an error in JavaScript:
const wrongTypeError = TypeError("Wrong type found, expected character")And this is how the wrongTypeError object becomes an exception:
throw wrongTypeErrorHowever, most people tend to use the shorthand form which defines error objects while throwing them:
throw TypeError("Wrong type found, expected character")This is standard practice. However, it’s one of the reasons why developers tend to mix up exceptions and errors. Therefore, knowing the fundamentals is vital even though you use shorthands to get your work done quickly.
Types of Errors in JavaScript
There’s a range of predefined error types in JavaScript. They are automatically chosen and defined by the JavaScript runtime whenever the programmer doesn’t explicitly handle errors in the application.
This section will walk you through some of the most common types of errors in JavaScript and understand when and why they occur.
RangeError
A RangeError is thrown when a variable is set with a value outside its legal values range. It usually occurs when passing a value as an argument to a function, and the given value doesn’t lie in the range of the function’s parameters. It can sometimes get tricky to fix when using poorly documented third-party libraries since you need to know the range of possible values for the arguments to pass in the correct value.
Some of the common scenarios in which RangeError occurs are:
- Trying to create an array of illegal lengths via the Array constructor.
- Passing bad values to numeric methods like
toExponential(),toPrecision(),toFixed(), etc. - Passing illegal values to string functions like
normalize().
ReferenceError
A ReferenceError occurs when something is wrong with a variable’s reference in your code. You might have forgotten to define a value for the variable before using it, or you might be trying to use an inaccessible variable in your code. In any case, going through the stack trace provides ample information to find and fix the variable reference that is at fault.
Some of the common reasons why ReferenceErrors occur are:
- Making a typo in a variable name.
- Trying to access block-scoped variables outside of their scopes.
- Referencing a global variable from an external library (like $ from jQuery) before it’s loaded.
SyntaxError
These errors are one of the simplest to fix since they indicate an error in the syntax of the code. Since JavaScript is a scripting language that is interpreted rather than compiled, these are thrown when the app executes the script that contains the error. In the case of compiled languages, such errors are identified during compilation. Thus, the app binaries are not created until these are fixed.
Some of the common reasons why SyntaxErrors might occur are:
- Missing inverted commas
- Missing closing parentheses
- Improper alignment of curly braces or other characters
It’s a good practice to use a linting tool in your IDE to identify such errors for you before they hit the browser.
TypeError
TypeError is one of the most common errors in JavaScript apps. This error is created when some value doesn’t turn out to be of a particular expected type. Some of the common cases when it occurs are:
- Invoking objects that are not methods.
- Attempting to access properties of null or undefined objects
- Treating a string as a number or vice versa
There are a lot more possibilities where a TypeError can occur. We’ll look at some famous instances later and learn how to fix them.
InternalError
The InternalError type is used when an exception occurs in the JavaScript runtime engine. It may or may not indicate an issue with your code.
More often than not, InternalError occurs in two scenarios only:
- When a patch or an update to the JavaScript runtime carries a bug that throws exceptions (this happens very rarely)
- When your code contains entities that are too large for the JavaScript engine (e.g. too many switch cases, too large array initializers, too much recursion)
The most appropriate approach to solve this error is to identify the cause via the error message and restructure your app logic, if possible, to eliminate the sudden spike of workload on the JavaScript engine.
URIError
URIError occurs when a global URI handling function such as decodeURIComponent is used illegally. It usually indicates that the parameter passed to the method call did not conform to URI standards and thus was not parsed by the method properly.
Diagnosing these errors is usually easy since you only need to examine the arguments for malformation.
EvalError
An EvalError occurs when an error occurs with an eval() function call. The eval() function is used to execute JavaScript code stored in strings. However, since using the eval() function is highly discouraged due to security issues and the current ECMAScript specifications don’t throw the EvalError class anymore, this error type exists simply to maintain backward compatibility with legacy JavaScript code.
If you’re working on an older version of JavaScript, you might encounter this error. In any case, it’s best to investigate the code executed in the eval() function call for any exceptions.
Creating Custom Error Types
While JavaScript offers an adequate list of error type classes to cover for most scenarios, you can always create a new error type if the list doesn’t satisfy your requirements. The foundation of this flexibility lies in the fact that JavaScript allows you to throw anything literally with the throw command.
So, technically, these statements are entirely legal:
throw 8
throw "An error occurred"However, throwing a primitive data type doesn’t provide details about the error, such as its type, name, or the accompanying stack trace. To fix this and standardize the error handling process, the Error class has been provided. It’s also discouraged to use primitive data types while throwing exceptions.
You can extend the Error class to create your custom error class. Here is a basic example of how you can do this:
class ValidationError extends Error {
constructor(message) {
super(message);
this.name = "ValidationError";
}
}And you can use it in the following way:
throw ValidationError("Property not found: name")And you can then identify it using the instanceof keyword:
try {
validateForm() // code that throws a ValidationError
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof ValidationError)
// do something
else
// do something else
}Top 10 Most Common Errors in JavaScript
Now that you understand the common error types and how to create your custom ones, it’s time to look at some of the most common errors you’ll face when writing JavaScript code.
Check Out Our Video Guide to The Most Common JavaScript Errors
1. Uncaught RangeError
This error occurs in Google Chrome under a few various scenarios. First, it can happen if you call a recursive function and it doesn’t terminate. You can check this out yourself in the Chrome Developer Console:
So to solve such an error, make sure to define the border cases of your recursive function correctly. Another reason why this error happens is if you have passed a value that is out of a function’s parameter’s range. Here’s an example:
The error message will usually indicate what is wrong with your code. Once you make the changes, it will be resolved.
2. Uncaught TypeError: Cannot set property
This error occurs when you set a property on an undefined reference. You can reproduce the issue with this code:
var list
list.count = 0Here’s the output that you’ll receive:
To fix this error, initialize the reference with a value before accessing its properties. Here’s how it looks when fixed:
3. Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property
This is one of the most frequently occurring errors in JavaScript. This error occurs when you attempt to read a property or call a function on an undefined object. You can reproduce it very easily by running the following code in a Chrome Developer console:
var func
func.call()Here’s the output:
An undefined object is one of the many possible causes of this error. Another prominent cause of this issue can be an improper initialization of the state while rendering the UI. Here’s a real-world example from a React application:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
const CardsList = () => {
const [state, setState] = useState();
useEffect(() => {
setTimeout(() => setState({ items: ["Card 1", "Card 2"] }), 2000);
}, []);
return (
<>
{state.items.map((item) => (
<li key={item}>{item}</li>
))}
</>
);
};
export default CardsList;The app starts with an empty state container and is provided with some items after a delay of 2 seconds. The delay is put in place to imitate a network call. Even if your network is super fast, you’ll still face a minor delay due to which the component will render at least once. If you try to run this app, you’ll receive the following error:
This is because, at the time of rendering, the state container is undefined; thus, there exists no property items on it. Fixing this error is easy. You just need to provide an initial default value to the state container.
// ...
const [state, setState] = useState({items: []});
// ...Now, after the set delay, your app will show a similar output:
The exact fix in your code might be different, but the essence here is to always initialize your variables properly before using them.
4. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not an object
This error occurs in Safari when you try to access the properties of or call a method on an undefined object. You can run the same code from above to reproduce the error yourself.
The solution to this error is also the same — make sure that you have initialized your variables correctly and they are not undefined when a property or method is accessed.
5. TypeError: null is not an object
This is, again, similar to the previous error. It occurs on Safari, and the only difference between the two errors is that this one is thrown when the object whose property or method is being accessed is null instead of undefined. You can reproduce this by running the following piece of code:
var func = null
func.call()Here’s the output that you’ll receive:
Since null is a value explicitly set to a variable and not assigned automatically by JavaScript. This error can occur only if you’re trying to access a variable you set null by yourself. So, you need to revisit your code and check if the logic that you wrote is correct or not.
6. TypeError: Cannot read property ‘length’
This error occurs in Chrome when you try to read the length of a null or undefined object. The cause of this issue is similar to the previous issues, but it occurs quite frequently while handling lists; hence it deserves a special mention. Here’s how you can reproduce the problem:
However, in the newer versions of Chrome, this error is reported as Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined. This is how it looks now:
The fix, again, is to ensure that the object whose length you’re trying to access exists and is not set to null.
7. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not a function
This error occurs when you try to invoke a method that doesn’t exist in your script, or it does but can not be referenced in the calling context. This error usually occurs in Google Chrome, and you can solve it by checking the line of code throwing the error. If you find a typo, fix it and check if it solves your issue.
If you have used the self-referencing keyword this in your code, this error might arise if this is not appropriately bound to your context. Consider the following code:
function showAlert() {
alert("message here")
}
document.addEventListener("click", () => {
this.showAlert();
})If you execute the above code, it will throw the error we discussed. It happens because the anonymous function passed as the event listener is being executed in the context of the document.
In contrast, the function showAlert is defined in the context of the window.
To solve this, you must pass the proper reference to the function by binding it with the bind() method:
document.addEventListener("click", this.showAlert.bind(this))8. ReferenceError: event is not defined
This error occurs when you try to access a reference not defined in the calling scope. This usually happens when handling events since they often provide you with a reference called event in the callback function. This error can occur if you forget to define the event argument in your function’s parameters or misspell it.
This error might not occur in Internet Explorer or Google Chrome (as IE offers a global event variable and Chrome attaches the event variable automatically to the handler), but it can occur in Firefox. So it’s advisable to keep an eye out for such small mistakes.
9. TypeError: Assignment to constant variable
This is an error that arises out of carelessness. If you try to assign a new value to a constant variable, you’ll be met with such a result:
While it seems easy to fix right now, imagine hundreds of such variable declarations and one of them mistakenly defined as const instead of let! Unlike other scripting languages like PHP, there’s minimal difference between the style of declaring constants and variables in JavaScript. Therefore it’s advisable to check your declarations first of all when you face this error. You could also run into this error if you forget that the said reference is a constant and use it as a variable. This indicates either carelessness or a flaw in your app’s logic. Make sure to check this when trying to fix this issue.
10. (unknown): Script error
A script error occurs when a third-party script sends an error to your browser. This error is followed by (unknown) because the third-party script belongs to a different domain than your app. The browser hides other details to prevent leaking sensitive information from the third-party script.
You can not resolve this error without knowing the complete details. Here’s what you can do to get more information about the error:
- Add the
crossoriginattribute in the script tag. - Set the correct
Access-Control-Allow-Originheader on the server hosting the script. - [Optional] If you don’t have access to the server hosting the script, you can consider using a proxy to relay your request to the server and back to the client with the correct headers.
Once you can access the details of the error, you can then set down to fix the issue, which will probably be with either the third-party library or the network.
How to Identify and Prevent Errors in JavaScript
While the errors discussed above are the most common and frequent in JavaScript, you’ll come across, relying on a few examples can never be enough. It’s vital to understand how to detect and prevent any type of error in a JavaScript application while developing it. Here is how you can handle errors in JavaScript.
Manually Throw and Catch Errors
The most fundamental way of handling errors that have been thrown either manually or by the runtime is to catch them. Like most other languages, JavaScript offers a set of keywords to handle errors. It’s essential to know each of them in-depth before you set down to handle errors in your JavaScript app.
throw
The first and most basic keyword of the set is throw. As evident, the throw keyword is used to throw errors to create exceptions in the JavaScript runtime manually. We have already discussed this earlier in the piece, and here’s the gist of this keyword’s significance:
- You can
throwanything, including numbers, strings, andErrorobjects. - However, it’s not advisable to throw primitive data types such as strings and numbers since they don’t carry debug information about the errors.
- Example:
throw TypeError("Please provide a string")
try
The try keyword is used to indicate that a block of code might throw an exception. Its syntax is:
try {
// error-prone code here
}It’s important to note that a catch block must always follow the try block to handle errors effectively.
catch
The catch keyword is used to create a catch block. This block of code is responsible for handling the errors that the trailing try block catches. Here is its syntax:
catch (exception) {
// code to handle the exception here
}And this is how you implement the try and the catch blocks together:
try {
// business logic code
} catch (exception) {
// error handling code
}Unlike C++ or Java, you can not append multiple catch blocks to a try block in JavaScript. This means that you can not do this:
try {
// business logic code
} catch (exception) {
if (exception instanceof TypeError) {
// do something
}
} catch (exception) {
if (exception instanceof RangeError) {
// do something
}
}Instead, you can use an if...else statement or a switch case statement inside the single catch block to handle all possible error cases. It would look like this:
try {
// business logic code
} catch (exception) {
if (exception instanceof TypeError) {
// do something
} else if (exception instanceof RangeError) {
// do something else
}
}finally
The finally keyword is used to define a code block that is run after an error has been handled. This block is executed after the try and the catch blocks.
Also, the finally block will be executed regardless of the result of the other two blocks. This means that even if the catch block cannot handle the error entirely or an error is thrown in the catch block, the interpreter will execute the code in the finally block before the program crashes.
To be considered valid, the try block in JavaScript needs to be followed by either a catch or a finally block. Without any of those, the interpreter will raise a SyntaxError. Therefore, make sure to follow your try blocks with at least either of them when handling errors.
Handle Errors Globally With the onerror() Method
The onerror() method is available to all HTML elements for handling any errors that may occur with them. For instance, if an img tag cannot find the image whose URL is specified, it fires its onerror method to allow the user to handle the error.
Typically, you would provide another image URL in the onerror call for the img tag to fall back to. This is how you can do that via JavaScript:
const image = document.querySelector("img")
image.onerror = (event) => {
console.log("Error occurred: " + event)
}However, you can use this feature to create a global error handling mechanism for your app. Here’s how you can do it:
window.onerror = (event) => {
console.log("Error occurred: " + event)
}With this event handler, you can get rid of the multiple try...catch blocks lying around in your code and centralize your app’s error handling similar to event handling. You can attach multiple error handlers to the window to maintain the Single Responsibility Principle from the SOLID design principles. The interpreter will cycle through all handlers until it reaches the appropriate one.
Pass Errors via Callbacks
While simple and linear functions allow error handling to remain simple, callbacks can complicate the affair.
Consider the following piece of code:
const calculateCube = (number, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const cube = number * number * number
callback(cube)
}, 1000)
}
const callback = result => console.log(result)
calculateCube(4, callback)The above function demonstrates an asynchronous condition in which a function takes some time to process operations and returns the result later with the help of a callback.
If you try to enter a string instead of 4 in the function call, you’ll get NaN as a result.
This needs to be handled properly. Here’s how:
const calculateCube = (number, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof number !== "number")
throw new Error("Numeric argument is expected")
const cube = number * number * number
callback(cube)
}, 1000)
}
const callback = result => console.log(result)
try {
calculateCube(4, callback)
} catch (e) { console.log(e) }This should solve the problem ideally. However, if you try passing a string to the function call, you’ll receive this:
Even though you have implemented a try-catch block while calling the function, it still says the error is uncaught. The error is thrown after the catch block has been executed due to the timeout delay.
This can occur quickly in network calls, where unexpected delays creep in. You need to cover such cases while developing your app.
Here’s how you can handle errors properly in callbacks:
const calculateCube = (number, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof number !== "number") {
callback(new TypeError("Numeric argument is expected"))
return
}
const cube = number * number * number
callback(null, cube)
}, 2000)
}
const callback = (error, result) => {
if (error !== null) {
console.log(error)
return
}
console.log(result)
}
try {
calculateCube('hey', callback)
} catch (e) {
console.log(e)
}Now, the output at the console will be:
This indicates that the error has been appropriately handled.
Handle Errors in Promises
Most people tend to prefer promises for handling asynchronous activities. Promises have another advantage — a rejected promise doesn’t terminate your script. However, you still need to implement a catch block to handle errors in promises. To understand this better, let’s rewrite the calculateCube() function using Promises:
const delay = ms => new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, ms));
const calculateCube = async (number) => {
if (typeof number !== "number")
throw Error("Numeric argument is expected")
await delay(5000)
const cube = number * number * number
return cube
}
try {
calculateCube(4).then(r => console.log(r))
} catch (e) { console.log(e) }The timeout from the previous code has been isolated into the delay function for understanding. If you try to enter a string instead of 4, the output that you get will be similar to this:
Again, this is due to the Promise throwing the error after everything else has completed execution. The solution to this issue is simple. Simply add a catch() call to the promise chain like this:
calculateCube("hey")
.then(r => console.log(r))
.catch(e => console.log(e))Now the output will be:
You can observe how easy it is to handle errors with promises. Additionally, you can chain a finally() block and the promise call to add code that will run after error handling has been completed.
Alternatively, you can also handle errors in promises using the traditional try-catch-finally technique. Here’s how your promise call would look like in that case:
try {
let result = await calculateCube("hey")
console.log(result)
} catch (e) {
console.log(e)
} finally {
console.log('Finally executed")
}However, this works inside an asynchronous function only. Therefore the most preferred way to handle errors in promises is to chain catch and finally to the promise call.
throw/catch vs onerror() vs Callbacks vs Promises: Which is the Best?
With four methods at your disposal, you must know how to choose the most appropriate in any given use case. Here’s how you can decide for yourselves:
throw/catch
You will be using this method most of the time. Make sure to implement conditions for all possible errors inside your catch block, and remember to include a finally block if you need to run some memory clean-up routines after the try block.
However, too many try/catch blocks can make your code difficult to maintain. If you find yourself in such a situation, you might want to handle errors via the global handler or the promise method.
When deciding between asynchronous try/catch blocks and promise’s catch(), it’s advisable to go with the async try/catch blocks since they will make your code linear and easy to debug.
onerror()
It’s best to use the onerror() method when you know that your app has to handle many errors, and they can be well-scattered throughout the codebase. The onerror method enables you to handle errors as if they were just another event handled by your application. You can define multiple error handlers and attach them to your app’s window on the initial rendering.
However, you must also remember that the onerror() method can be unnecessarily challenging to set up in smaller projects with a lesser scope of error. If you’re sure that your app will not throw too many errors, the traditional throw/catch method will work best for you.
Callbacks and Promises
Error handling in callbacks and promises differs due to their code design and structure. However, if you choose between these two before you have written your code, it would be best to go with promises.
This is because promises have an inbuilt construct for chaining a catch() and a finally() block to handle errors easily. This method is easier and cleaner than defining additional arguments/reusing existing arguments to handle errors.
Keep Track of Changes With Git Repositories
Many errors often arise due to manual mistakes in the codebase. While developing or debugging your code, you might end up making unnecessary changes that may cause new errors to appear in your codebase. Automated testing is a great way to keep your code in check after every change. However, it can only tell you if something’s wrong. If you don’t take frequent backups of your code, you’ll end up wasting time trying to fix a function or a script that was working just fine before.
This is where git plays its role. With a proper commit strategy, you can use your git history as a backup system to view your code as it evolved through the development. You can easily browse through your older commits and find out the version of the function working fine before but throwing errors after an unrelated change.
You can then restore the old code or compare the two versions to determine what went wrong. Modern web development tools like GitHub Desktop or GitKraken help you to visualize these changes side by side and figure out the mistakes quickly.
A habit that can help you make fewer errors is running code reviews whenever you make a significant change to your code. If you’re working in a team, you can create a pull request and have a team member review it thoroughly. This will help you use a second pair of eyes to spot out any errors that might have slipped by you.
Best Practices for Handling Errors in JavaScript
The above-mentioned methods are adequate to help you design a robust error handling approach for your next JavaScript application. However, it would be best to keep a few things in mind while implementing them to get the best out of your error-proofing. Here are some tips to help you.
1. Use Custom Errors When Handling Operational Exceptions
We introduced custom errors early in this guide to give you an idea of how to customize the error handling to your application’s unique case. It’s advisable to use custom errors wherever possible instead of the generic Error class as it provides more contextual information to the calling environment about the error.
On top of that, custom errors allow you to moderate how an error is displayed to the calling environment. This means that you can choose to hide specific details or display additional information about the error as and when you wish.
You can go so far as to format the error contents according to your needs. This gives you better control over how the error is interpreted and handled.
2. Do Not Swallow Any Exceptions
Even the most senior developers often make a rookie mistake — consuming exceptions levels deep down in their code.
You might come across situations where you have a piece of code that is optional to run. If it works, great; if it doesn’t, you don’t need to do anything about it.
In these cases, it’s often tempting to put this code in a try block and attach an empty catch block to it. However, by doing this, you’ll leave that piece of code open to causing any kind of error and getting away with it. This can become dangerous if you have a large codebase and many instances of such poor error management constructs.
The best way to handle exceptions is to determine a level on which all of them will be dealt and raise them until there. This level can be a controller (in an MVC architecture app) or a middleware (in a traditional server-oriented app).
This way, you’ll get to know where you can find all the errors occurring in your app and choose how to resolve them, even if it means not doing anything about them.
3. Use a Centralized Strategy for Logs and Error Alerts
Logging an error is often an integral part of handling it. Those who fail to develop a centralized strategy for logging errors may miss out on valuable information about their app’s usage.
An app’s event logs can help you figure out crucial data about errors and help to debug them quickly. If you have proper alerting mechanisms set up in your app, you can know when an error occurs in your app before it reaches a large section of your user base.
It’s advisable to use a pre-built logger or create one to suit your needs. You can configure this logger to handle errors based on their levels (warning, debug, info, etc.), and some loggers even go so far as to send logs to remote logging servers immediately. This way, you can watch how your application’s logic performs with active users.
4. Notify Users About Errors Appropriately
Another good point to keep in mind while defining your error handling strategy is to keep the user in mind.
All errors that interfere with the normal functioning of your app must present a visible alert to the user to notify them that something went wrong so the user can try to work out a solution. If you know a quick fix for the error, such as retrying an operation or logging out and logging back in, make sure to mention it in the alert to help fix the user experience in real-time.
In the case of errors that don’t cause any interference with the everyday user experience, you can consider suppressing the alert and logging the error to a remote server for resolving later.
5. Implement a Middleware (Node.js)
The Node.js environment supports middlewares to add functionalities to server applications. You can use this feature to create an error-handling middleware for your server.
The most significant benefit of using middleware is that all of your errors are handled centrally in one place. You can choose to enable/disable this setup for testing purposes easily.
Here’s how you can create a basic middleware:
const logError = err => {
console.log("ERROR: " + String(err))
}
const errorLoggerMiddleware = (err, req, res, next) => {
logError(err)
next(err)
}
const returnErrorMiddleware = (err, req, res, next) => {
res.status(err.statusCode || 500)
.send(err.message)
}
module.exports = {
logError,
errorLoggerMiddleware,
returnErrorMiddleware
}You can then use this middleware in your app like this:
const { errorLoggerMiddleware, returnErrorMiddleware } = require('./errorMiddleware')
app.use(errorLoggerMiddleware)
app.use(returnErrorMiddleware)You can now define custom logic inside the middleware to handle errors appropriately. You don’t need to worry about implementing individual error handling constructs throughout your codebase anymore.
6. Restart Your App To Handle Programmer Errors (Node.js)
When Node.js apps encounter programmer errors, they might not necessarily throw an exception and try to close the app. Such errors can include issues arising from programmer mistakes, like high CPU consumption, memory bloating, or memory leaks. The best way to handle these is to gracefully restart the app by crashing it via the Node.js cluster mode or a unique tool like PM2. This can ensure that the app doesn’t crash upon user action, presenting a terrible user experience.
7. Catch All Uncaught Exceptions (Node.js)
You can never be sure that you have covered every possible error that can occur in your app. Therefore, it’s essential to implement a fallback strategy to catch all uncaught exceptions from your app.
Here’s how you can do that:
process.on('uncaughtException', error => {
console.log("ERROR: " + String(error))
// other handling mechanisms
})You can also identify if the error that occurred is a standard exception or a custom operational error. Based on the result, you can exit the process and restart it to avoid unexpected behavior.
8. Catch All Unhandled Promise Rejections (Node.js)
Similar to how you can never cover for all possible exceptions, there’s a high chance that you might miss out on handling all possible promise rejections. However, unlike exceptions, promise rejections don’t throw errors.
So, an important promise that was rejected might slip by as a warning and leave your app open to the possibility of running into unexpected behavior. Therefore, it’s crucial to implement a fallback mechanism for handling promise rejection.
Here’s how you can do that:
const promiseRejectionCallback = error => {
console.log("PROMISE REJECTED: " + String(error))
}
process.on('unhandledRejection', callback)If you create an application, there are chances that you’ll create bugs and other issues in it as well. 😅 Learn how to handle them with help from this guide ⬇️Click to Tweet
Summary
Like any other programming language, errors are quite frequent and natural in JavaScript. In some cases, you might even need to throw errors intentionally to indicate the correct response to your users. Hence, understanding their anatomy and types is very crucial.
Moreover, you need to be equipped with the right tools and techniques to identify and prevent errors from taking down your application.
In most cases, a solid strategy to handle errors with careful execution is enough for all types of JavaScript applications.
Are there any other JavaScript errors that you still haven’t been able to resolve? Any techniques for handling JS errors constructively? Let us know in the comments below!
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275+ PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Murphy’s law states that whatever can go wrong will eventually go wrong. This applies a tad too well in the world of programming. If you create an application, chances are you’ll create bugs and other issues. Errors in JavaScript are one such common issue!
A software product’s success depends on how well its creators can resolve these issues before hurting their users. And JavaScript, out of all programming languages, is notorious for its average error handling design.
If you’re building a JavaScript application, there’s a high chance you’ll mess up with data types at one point or another. If not that, then you might end up replacing an undefined with a null or a triple equals operator (===) with a double equals operator (==).
It’s only human to make mistakes. This is why we will show you everything you need to know about handling errors in JavaScript.
This article will guide you through the basic errors in JavaScript and explain the various errors you might encounter. You’ll then learn how to identify and fix these errors. There are also a couple of tips to handle errors effectively in production environments.
Without further ado, let’s begin!
Check Out Our Video Guide to Handling JavaScript Errors
What Are JavaScript Errors?
Errors in programming refer to situations that don’t let a program function normally. It can happen when a program doesn’t know how to handle the job at hand, such as when trying to open a non-existent file or reaching out to a web-based API endpoint while there’s no network connectivity.
These situations push the program to throw errors to the user, stating that it doesn’t know how to proceed. The program collects as much information as possible about the error and then reports that it can not move ahead.
Murphy’s law states that whatever can go wrong will eventually go wrong 😬 This applies a bit too well in the world of JavaScript 😅 Get prepped with this guide 👇Click to Tweet
Intelligent programmers try to predict and cover these scenarios so that the user doesn’t have to figure out a technical error message like “404” independently. Instead, they show a much more understandable message: “The page could not be found.”
Errors in JavaScript are objects shown whenever a programming error occurs. These objects contain ample information about the type of the error, the statement that caused the error, and the stack trace when the error occurred. JavaScript also allows programmers to create custom errors to provide extra information when debugging issues.
Properties of an Error
Now that the definition of a JavaScript error is clear, it’s time to dive into the details.
Errors in JavaScript carry certain standard and custom properties that help understand the cause and effects of the error. By default, errors in JavaScript contain three properties:
- message: A string value that carries the error message
- name: The type of error that occurred (We’ll dive deep into this in the next section)
- stack: The stack trace of the code executed when the error occurred.
Additionally, errors can also carry properties like columnNumber, lineNumber, fileName, etc., to describe the error better. However, these properties are not standard and may or may not be present in every error object generated from your JavaScript application.
Understanding Stack Trace
A stack trace is the list of method calls a program was in when an event such as an exception or a warning occurs. This is what a sample stack trace accompanied by an exception looks like:
As you can see, it starts by printing the error name and message, followed by a list of methods that were being called. Each method call states the location of its source code and the line at which it was invoked. You can use this data to navigate through your codebase and identify which piece of code is causing the error.
This list of methods is arranged in a stacked fashion. It shows where your exception was first thrown and how it propagated through the stacked method calls. Implementing a catch for the exception will not let it propagate up through the stack and crash your program. However, you might want to leave fatal errors uncaught to crash the program in some scenarios intentionally.
Errors vs Exceptions
Most people usually consider errors and exceptions as the same thing. However, it’s essential to note a slight yet fundamental difference between them.
To understand this better, let’s take a quick example. Here is how you can define an error in JavaScript:
const wrongTypeError = TypeError("Wrong type found, expected character")And this is how the wrongTypeError object becomes an exception:
throw wrongTypeErrorHowever, most people tend to use the shorthand form which defines error objects while throwing them:
throw TypeError("Wrong type found, expected character")This is standard practice. However, it’s one of the reasons why developers tend to mix up exceptions and errors. Therefore, knowing the fundamentals is vital even though you use shorthands to get your work done quickly.
Types of Errors in JavaScript
There’s a range of predefined error types in JavaScript. They are automatically chosen and defined by the JavaScript runtime whenever the programmer doesn’t explicitly handle errors in the application.
This section will walk you through some of the most common types of errors in JavaScript and understand when and why they occur.
RangeError
A RangeError is thrown when a variable is set with a value outside its legal values range. It usually occurs when passing a value as an argument to a function, and the given value doesn’t lie in the range of the function’s parameters. It can sometimes get tricky to fix when using poorly documented third-party libraries since you need to know the range of possible values for the arguments to pass in the correct value.
Some of the common scenarios in which RangeError occurs are:
- Trying to create an array of illegal lengths via the Array constructor.
- Passing bad values to numeric methods like
toExponential(),toPrecision(),toFixed(), etc. - Passing illegal values to string functions like
normalize().
ReferenceError
A ReferenceError occurs when something is wrong with a variable’s reference in your code. You might have forgotten to define a value for the variable before using it, or you might be trying to use an inaccessible variable in your code. In any case, going through the stack trace provides ample information to find and fix the variable reference that is at fault.
Some of the common reasons why ReferenceErrors occur are:
- Making a typo in a variable name.
- Trying to access block-scoped variables outside of their scopes.
- Referencing a global variable from an external library (like $ from jQuery) before it’s loaded.
SyntaxError
These errors are one of the simplest to fix since they indicate an error in the syntax of the code. Since JavaScript is a scripting language that is interpreted rather than compiled, these are thrown when the app executes the script that contains the error. In the case of compiled languages, such errors are identified during compilation. Thus, the app binaries are not created until these are fixed.
Some of the common reasons why SyntaxErrors might occur are:
- Missing inverted commas
- Missing closing parentheses
- Improper alignment of curly braces or other characters
It’s a good practice to use a linting tool in your IDE to identify such errors for you before they hit the browser.
TypeError
TypeError is one of the most common errors in JavaScript apps. This error is created when some value doesn’t turn out to be of a particular expected type. Some of the common cases when it occurs are:
- Invoking objects that are not methods.
- Attempting to access properties of null or undefined objects
- Treating a string as a number or vice versa
There are a lot more possibilities where a TypeError can occur. We’ll look at some famous instances later and learn how to fix them.
InternalError
The InternalError type is used when an exception occurs in the JavaScript runtime engine. It may or may not indicate an issue with your code.
More often than not, InternalError occurs in two scenarios only:
- When a patch or an update to the JavaScript runtime carries a bug that throws exceptions (this happens very rarely)
- When your code contains entities that are too large for the JavaScript engine (e.g. too many switch cases, too large array initializers, too much recursion)
The most appropriate approach to solve this error is to identify the cause via the error message and restructure your app logic, if possible, to eliminate the sudden spike of workload on the JavaScript engine.
URIError
URIError occurs when a global URI handling function such as decodeURIComponent is used illegally. It usually indicates that the parameter passed to the method call did not conform to URI standards and thus was not parsed by the method properly.
Diagnosing these errors is usually easy since you only need to examine the arguments for malformation.
EvalError
An EvalError occurs when an error occurs with an eval() function call. The eval() function is used to execute JavaScript code stored in strings. However, since using the eval() function is highly discouraged due to security issues and the current ECMAScript specifications don’t throw the EvalError class anymore, this error type exists simply to maintain backward compatibility with legacy JavaScript code.
If you’re working on an older version of JavaScript, you might encounter this error. In any case, it’s best to investigate the code executed in the eval() function call for any exceptions.
Creating Custom Error Types
While JavaScript offers an adequate list of error type classes to cover for most scenarios, you can always create a new error type if the list doesn’t satisfy your requirements. The foundation of this flexibility lies in the fact that JavaScript allows you to throw anything literally with the throw command.
So, technically, these statements are entirely legal:
throw 8
throw "An error occurred"However, throwing a primitive data type doesn’t provide details about the error, such as its type, name, or the accompanying stack trace. To fix this and standardize the error handling process, the Error class has been provided. It’s also discouraged to use primitive data types while throwing exceptions.
You can extend the Error class to create your custom error class. Here is a basic example of how you can do this:
class ValidationError extends Error {
constructor(message) {
super(message);
this.name = "ValidationError";
}
}And you can use it in the following way:
throw ValidationError("Property not found: name")And you can then identify it using the instanceof keyword:
try {
validateForm() // code that throws a ValidationError
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof ValidationError)
// do something
else
// do something else
}Top 10 Most Common Errors in JavaScript
Now that you understand the common error types and how to create your custom ones, it’s time to look at some of the most common errors you’ll face when writing JavaScript code.
Check Out Our Video Guide to The Most Common JavaScript Errors
1. Uncaught RangeError
This error occurs in Google Chrome under a few various scenarios. First, it can happen if you call a recursive function and it doesn’t terminate. You can check this out yourself in the Chrome Developer Console:
So to solve such an error, make sure to define the border cases of your recursive function correctly. Another reason why this error happens is if you have passed a value that is out of a function’s parameter’s range. Here’s an example:
The error message will usually indicate what is wrong with your code. Once you make the changes, it will be resolved.
2. Uncaught TypeError: Cannot set property
This error occurs when you set a property on an undefined reference. You can reproduce the issue with this code:
var list
list.count = 0Here’s the output that you’ll receive:
To fix this error, initialize the reference with a value before accessing its properties. Here’s how it looks when fixed:
3. Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property
This is one of the most frequently occurring errors in JavaScript. This error occurs when you attempt to read a property or call a function on an undefined object. You can reproduce it very easily by running the following code in a Chrome Developer console:
var func
func.call()Here’s the output:
An undefined object is one of the many possible causes of this error. Another prominent cause of this issue can be an improper initialization of the state while rendering the UI. Here’s a real-world example from a React application:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
const CardsList = () => {
const [state, setState] = useState();
useEffect(() => {
setTimeout(() => setState({ items: ["Card 1", "Card 2"] }), 2000);
}, []);
return (
<>
{state.items.map((item) => (
<li key={item}>{item}</li>
))}
</>
);
};
export default CardsList;The app starts with an empty state container and is provided with some items after a delay of 2 seconds. The delay is put in place to imitate a network call. Even if your network is super fast, you’ll still face a minor delay due to which the component will render at least once. If you try to run this app, you’ll receive the following error:
This is because, at the time of rendering, the state container is undefined; thus, there exists no property items on it. Fixing this error is easy. You just need to provide an initial default value to the state container.
// ...
const [state, setState] = useState({items: []});
// ...Now, after the set delay, your app will show a similar output:
The exact fix in your code might be different, but the essence here is to always initialize your variables properly before using them.
4. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not an object
This error occurs in Safari when you try to access the properties of or call a method on an undefined object. You can run the same code from above to reproduce the error yourself.
The solution to this error is also the same — make sure that you have initialized your variables correctly and they are not undefined when a property or method is accessed.
5. TypeError: null is not an object
This is, again, similar to the previous error. It occurs on Safari, and the only difference between the two errors is that this one is thrown when the object whose property or method is being accessed is null instead of undefined. You can reproduce this by running the following piece of code:
var func = null
func.call()Here’s the output that you’ll receive:
Since null is a value explicitly set to a variable and not assigned automatically by JavaScript. This error can occur only if you’re trying to access a variable you set null by yourself. So, you need to revisit your code and check if the logic that you wrote is correct or not.
6. TypeError: Cannot read property ‘length’
This error occurs in Chrome when you try to read the length of a null or undefined object. The cause of this issue is similar to the previous issues, but it occurs quite frequently while handling lists; hence it deserves a special mention. Here’s how you can reproduce the problem:
However, in the newer versions of Chrome, this error is reported as Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined. This is how it looks now:
The fix, again, is to ensure that the object whose length you’re trying to access exists and is not set to null.
7. TypeError: ‘undefined’ is not a function
This error occurs when you try to invoke a method that doesn’t exist in your script, or it does but can not be referenced in the calling context. This error usually occurs in Google Chrome, and you can solve it by checking the line of code throwing the error. If you find a typo, fix it and check if it solves your issue.
If you have used the self-referencing keyword this in your code, this error might arise if this is not appropriately bound to your context. Consider the following code:
function showAlert() {
alert("message here")
}
document.addEventListener("click", () => {
this.showAlert();
})If you execute the above code, it will throw the error we discussed. It happens because the anonymous function passed as the event listener is being executed in the context of the document.
In contrast, the function showAlert is defined in the context of the window.
To solve this, you must pass the proper reference to the function by binding it with the bind() method:
document.addEventListener("click", this.showAlert.bind(this))8. ReferenceError: event is not defined
This error occurs when you try to access a reference not defined in the calling scope. This usually happens when handling events since they often provide you with a reference called event in the callback function. This error can occur if you forget to define the event argument in your function’s parameters or misspell it.
This error might not occur in Internet Explorer or Google Chrome (as IE offers a global event variable and Chrome attaches the event variable automatically to the handler), but it can occur in Firefox. So it’s advisable to keep an eye out for such small mistakes.
9. TypeError: Assignment to constant variable
This is an error that arises out of carelessness. If you try to assign a new value to a constant variable, you’ll be met with such a result:
While it seems easy to fix right now, imagine hundreds of such variable declarations and one of them mistakenly defined as const instead of let! Unlike other scripting languages like PHP, there’s minimal difference between the style of declaring constants and variables in JavaScript. Therefore it’s advisable to check your declarations first of all when you face this error. You could also run into this error if you forget that the said reference is a constant and use it as a variable. This indicates either carelessness or a flaw in your app’s logic. Make sure to check this when trying to fix this issue.
10. (unknown): Script error
A script error occurs when a third-party script sends an error to your browser. This error is followed by (unknown) because the third-party script belongs to a different domain than your app. The browser hides other details to prevent leaking sensitive information from the third-party script.
You can not resolve this error without knowing the complete details. Here’s what you can do to get more information about the error:
- Add the
crossoriginattribute in the script tag. - Set the correct
Access-Control-Allow-Originheader on the server hosting the script. - [Optional] If you don’t have access to the server hosting the script, you can consider using a proxy to relay your request to the server and back to the client with the correct headers.
Once you can access the details of the error, you can then set down to fix the issue, which will probably be with either the third-party library or the network.
How to Identify and Prevent Errors in JavaScript
While the errors discussed above are the most common and frequent in JavaScript, you’ll come across, relying on a few examples can never be enough. It’s vital to understand how to detect and prevent any type of error in a JavaScript application while developing it. Here is how you can handle errors in JavaScript.
Manually Throw and Catch Errors
The most fundamental way of handling errors that have been thrown either manually or by the runtime is to catch them. Like most other languages, JavaScript offers a set of keywords to handle errors. It’s essential to know each of them in-depth before you set down to handle errors in your JavaScript app.
throw
The first and most basic keyword of the set is throw. As evident, the throw keyword is used to throw errors to create exceptions in the JavaScript runtime manually. We have already discussed this earlier in the piece, and here’s the gist of this keyword’s significance:
- You can
throwanything, including numbers, strings, andErrorobjects. - However, it’s not advisable to throw primitive data types such as strings and numbers since they don’t carry debug information about the errors.
- Example:
throw TypeError("Please provide a string")
try
The try keyword is used to indicate that a block of code might throw an exception. Its syntax is:
try {
// error-prone code here
}It’s important to note that a catch block must always follow the try block to handle errors effectively.
catch
The catch keyword is used to create a catch block. This block of code is responsible for handling the errors that the trailing try block catches. Here is its syntax:
catch (exception) {
// code to handle the exception here
}And this is how you implement the try and the catch blocks together:
try {
// business logic code
} catch (exception) {
// error handling code
}Unlike C++ or Java, you can not append multiple catch blocks to a try block in JavaScript. This means that you can not do this:
try {
// business logic code
} catch (exception) {
if (exception instanceof TypeError) {
// do something
}
} catch (exception) {
if (exception instanceof RangeError) {
// do something
}
}Instead, you can use an if...else statement or a switch case statement inside the single catch block to handle all possible error cases. It would look like this:
try {
// business logic code
} catch (exception) {
if (exception instanceof TypeError) {
// do something
} else if (exception instanceof RangeError) {
// do something else
}
}finally
The finally keyword is used to define a code block that is run after an error has been handled. This block is executed after the try and the catch blocks.
Also, the finally block will be executed regardless of the result of the other two blocks. This means that even if the catch block cannot handle the error entirely or an error is thrown in the catch block, the interpreter will execute the code in the finally block before the program crashes.
To be considered valid, the try block in JavaScript needs to be followed by either a catch or a finally block. Without any of those, the interpreter will raise a SyntaxError. Therefore, make sure to follow your try blocks with at least either of them when handling errors.
Handle Errors Globally With the onerror() Method
The onerror() method is available to all HTML elements for handling any errors that may occur with them. For instance, if an img tag cannot find the image whose URL is specified, it fires its onerror method to allow the user to handle the error.
Typically, you would provide another image URL in the onerror call for the img tag to fall back to. This is how you can do that via JavaScript:
const image = document.querySelector("img")
image.onerror = (event) => {
console.log("Error occurred: " + event)
}However, you can use this feature to create a global error handling mechanism for your app. Here’s how you can do it:
window.onerror = (event) => {
console.log("Error occurred: " + event)
}With this event handler, you can get rid of the multiple try...catch blocks lying around in your code and centralize your app’s error handling similar to event handling. You can attach multiple error handlers to the window to maintain the Single Responsibility Principle from the SOLID design principles. The interpreter will cycle through all handlers until it reaches the appropriate one.
Pass Errors via Callbacks
While simple and linear functions allow error handling to remain simple, callbacks can complicate the affair.
Consider the following piece of code:
const calculateCube = (number, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const cube = number * number * number
callback(cube)
}, 1000)
}
const callback = result => console.log(result)
calculateCube(4, callback)The above function demonstrates an asynchronous condition in which a function takes some time to process operations and returns the result later with the help of a callback.
If you try to enter a string instead of 4 in the function call, you’ll get NaN as a result.
This needs to be handled properly. Here’s how:
const calculateCube = (number, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof number !== "number")
throw new Error("Numeric argument is expected")
const cube = number * number * number
callback(cube)
}, 1000)
}
const callback = result => console.log(result)
try {
calculateCube(4, callback)
} catch (e) { console.log(e) }This should solve the problem ideally. However, if you try passing a string to the function call, you’ll receive this:
Even though you have implemented a try-catch block while calling the function, it still says the error is uncaught. The error is thrown after the catch block has been executed due to the timeout delay.
This can occur quickly in network calls, where unexpected delays creep in. You need to cover such cases while developing your app.
Here’s how you can handle errors properly in callbacks:
const calculateCube = (number, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof number !== "number") {
callback(new TypeError("Numeric argument is expected"))
return
}
const cube = number * number * number
callback(null, cube)
}, 2000)
}
const callback = (error, result) => {
if (error !== null) {
console.log(error)
return
}
console.log(result)
}
try {
calculateCube('hey', callback)
} catch (e) {
console.log(e)
}Now, the output at the console will be:
This indicates that the error has been appropriately handled.
Handle Errors in Promises
Most people tend to prefer promises for handling asynchronous activities. Promises have another advantage — a rejected promise doesn’t terminate your script. However, you still need to implement a catch block to handle errors in promises. To understand this better, let’s rewrite the calculateCube() function using Promises:
const delay = ms => new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, ms));
const calculateCube = async (number) => {
if (typeof number !== "number")
throw Error("Numeric argument is expected")
await delay(5000)
const cube = number * number * number
return cube
}
try {
calculateCube(4).then(r => console.log(r))
} catch (e) { console.log(e) }The timeout from the previous code has been isolated into the delay function for understanding. If you try to enter a string instead of 4, the output that you get will be similar to this:
Again, this is due to the Promise throwing the error after everything else has completed execution. The solution to this issue is simple. Simply add a catch() call to the promise chain like this:
calculateCube("hey")
.then(r => console.log(r))
.catch(e => console.log(e))Now the output will be:
You can observe how easy it is to handle errors with promises. Additionally, you can chain a finally() block and the promise call to add code that will run after error handling has been completed.
Alternatively, you can also handle errors in promises using the traditional try-catch-finally technique. Here’s how your promise call would look like in that case:
try {
let result = await calculateCube("hey")
console.log(result)
} catch (e) {
console.log(e)
} finally {
console.log('Finally executed")
}However, this works inside an asynchronous function only. Therefore the most preferred way to handle errors in promises is to chain catch and finally to the promise call.
throw/catch vs onerror() vs Callbacks vs Promises: Which is the Best?
With four methods at your disposal, you must know how to choose the most appropriate in any given use case. Here’s how you can decide for yourselves:
throw/catch
You will be using this method most of the time. Make sure to implement conditions for all possible errors inside your catch block, and remember to include a finally block if you need to run some memory clean-up routines after the try block.
However, too many try/catch blocks can make your code difficult to maintain. If you find yourself in such a situation, you might want to handle errors via the global handler or the promise method.
When deciding between asynchronous try/catch blocks and promise’s catch(), it’s advisable to go with the async try/catch blocks since they will make your code linear and easy to debug.
onerror()
It’s best to use the onerror() method when you know that your app has to handle many errors, and they can be well-scattered throughout the codebase. The onerror method enables you to handle errors as if they were just another event handled by your application. You can define multiple error handlers and attach them to your app’s window on the initial rendering.
However, you must also remember that the onerror() method can be unnecessarily challenging to set up in smaller projects with a lesser scope of error. If you’re sure that your app will not throw too many errors, the traditional throw/catch method will work best for you.
Callbacks and Promises
Error handling in callbacks and promises differs due to their code design and structure. However, if you choose between these two before you have written your code, it would be best to go with promises.
This is because promises have an inbuilt construct for chaining a catch() and a finally() block to handle errors easily. This method is easier and cleaner than defining additional arguments/reusing existing arguments to handle errors.
Keep Track of Changes With Git Repositories
Many errors often arise due to manual mistakes in the codebase. While developing or debugging your code, you might end up making unnecessary changes that may cause new errors to appear in your codebase. Automated testing is a great way to keep your code in check after every change. However, it can only tell you if something’s wrong. If you don’t take frequent backups of your code, you’ll end up wasting time trying to fix a function or a script that was working just fine before.
This is where git plays its role. With a proper commit strategy, you can use your git history as a backup system to view your code as it evolved through the development. You can easily browse through your older commits and find out the version of the function working fine before but throwing errors after an unrelated change.
You can then restore the old code or compare the two versions to determine what went wrong. Modern web development tools like GitHub Desktop or GitKraken help you to visualize these changes side by side and figure out the mistakes quickly.
A habit that can help you make fewer errors is running code reviews whenever you make a significant change to your code. If you’re working in a team, you can create a pull request and have a team member review it thoroughly. This will help you use a second pair of eyes to spot out any errors that might have slipped by you.
Best Practices for Handling Errors in JavaScript
The above-mentioned methods are adequate to help you design a robust error handling approach for your next JavaScript application. However, it would be best to keep a few things in mind while implementing them to get the best out of your error-proofing. Here are some tips to help you.
1. Use Custom Errors When Handling Operational Exceptions
We introduced custom errors early in this guide to give you an idea of how to customize the error handling to your application’s unique case. It’s advisable to use custom errors wherever possible instead of the generic Error class as it provides more contextual information to the calling environment about the error.
On top of that, custom errors allow you to moderate how an error is displayed to the calling environment. This means that you can choose to hide specific details or display additional information about the error as and when you wish.
You can go so far as to format the error contents according to your needs. This gives you better control over how the error is interpreted and handled.
2. Do Not Swallow Any Exceptions
Even the most senior developers often make a rookie mistake — consuming exceptions levels deep down in their code.
You might come across situations where you have a piece of code that is optional to run. If it works, great; if it doesn’t, you don’t need to do anything about it.
In these cases, it’s often tempting to put this code in a try block and attach an empty catch block to it. However, by doing this, you’ll leave that piece of code open to causing any kind of error and getting away with it. This can become dangerous if you have a large codebase and many instances of such poor error management constructs.
The best way to handle exceptions is to determine a level on which all of them will be dealt and raise them until there. This level can be a controller (in an MVC architecture app) or a middleware (in a traditional server-oriented app).
This way, you’ll get to know where you can find all the errors occurring in your app and choose how to resolve them, even if it means not doing anything about them.
3. Use a Centralized Strategy for Logs and Error Alerts
Logging an error is often an integral part of handling it. Those who fail to develop a centralized strategy for logging errors may miss out on valuable information about their app’s usage.
An app’s event logs can help you figure out crucial data about errors and help to debug them quickly. If you have proper alerting mechanisms set up in your app, you can know when an error occurs in your app before it reaches a large section of your user base.
It’s advisable to use a pre-built logger or create one to suit your needs. You can configure this logger to handle errors based on their levels (warning, debug, info, etc.), and some loggers even go so far as to send logs to remote logging servers immediately. This way, you can watch how your application’s logic performs with active users.
4. Notify Users About Errors Appropriately
Another good point to keep in mind while defining your error handling strategy is to keep the user in mind.
All errors that interfere with the normal functioning of your app must present a visible alert to the user to notify them that something went wrong so the user can try to work out a solution. If you know a quick fix for the error, such as retrying an operation or logging out and logging back in, make sure to mention it in the alert to help fix the user experience in real-time.
In the case of errors that don’t cause any interference with the everyday user experience, you can consider suppressing the alert and logging the error to a remote server for resolving later.
5. Implement a Middleware (Node.js)
The Node.js environment supports middlewares to add functionalities to server applications. You can use this feature to create an error-handling middleware for your server.
The most significant benefit of using middleware is that all of your errors are handled centrally in one place. You can choose to enable/disable this setup for testing purposes easily.
Here’s how you can create a basic middleware:
const logError = err => {
console.log("ERROR: " + String(err))
}
const errorLoggerMiddleware = (err, req, res, next) => {
logError(err)
next(err)
}
const returnErrorMiddleware = (err, req, res, next) => {
res.status(err.statusCode || 500)
.send(err.message)
}
module.exports = {
logError,
errorLoggerMiddleware,
returnErrorMiddleware
}You can then use this middleware in your app like this:
const { errorLoggerMiddleware, returnErrorMiddleware } = require('./errorMiddleware')
app.use(errorLoggerMiddleware)
app.use(returnErrorMiddleware)You can now define custom logic inside the middleware to handle errors appropriately. You don’t need to worry about implementing individual error handling constructs throughout your codebase anymore.
6. Restart Your App To Handle Programmer Errors (Node.js)
When Node.js apps encounter programmer errors, they might not necessarily throw an exception and try to close the app. Such errors can include issues arising from programmer mistakes, like high CPU consumption, memory bloating, or memory leaks. The best way to handle these is to gracefully restart the app by crashing it via the Node.js cluster mode or a unique tool like PM2. This can ensure that the app doesn’t crash upon user action, presenting a terrible user experience.
7. Catch All Uncaught Exceptions (Node.js)
You can never be sure that you have covered every possible error that can occur in your app. Therefore, it’s essential to implement a fallback strategy to catch all uncaught exceptions from your app.
Here’s how you can do that:
process.on('uncaughtException', error => {
console.log("ERROR: " + String(error))
// other handling mechanisms
})You can also identify if the error that occurred is a standard exception or a custom operational error. Based on the result, you can exit the process and restart it to avoid unexpected behavior.
8. Catch All Unhandled Promise Rejections (Node.js)
Similar to how you can never cover for all possible exceptions, there’s a high chance that you might miss out on handling all possible promise rejections. However, unlike exceptions, promise rejections don’t throw errors.
So, an important promise that was rejected might slip by as a warning and leave your app open to the possibility of running into unexpected behavior. Therefore, it’s crucial to implement a fallback mechanism for handling promise rejection.
Here’s how you can do that:
const promiseRejectionCallback = error => {
console.log("PROMISE REJECTED: " + String(error))
}
process.on('unhandledRejection', callback)If you create an application, there are chances that you’ll create bugs and other issues in it as well. 😅 Learn how to handle them with help from this guide ⬇️Click to Tweet
Summary
Like any other programming language, errors are quite frequent and natural in JavaScript. In some cases, you might even need to throw errors intentionally to indicate the correct response to your users. Hence, understanding their anatomy and types is very crucial.
Moreover, you need to be equipped with the right tools and techniques to identify and prevent errors from taking down your application.
In most cases, a solid strategy to handle errors with careful execution is enough for all types of JavaScript applications.
Are there any other JavaScript errors that you still haven’t been able to resolve? Any techniques for handling JS errors constructively? Let us know in the comments below!
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275+ PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.