The reason for the error is that you’re trying, as the error message says, to access a portion of the list that is currently out of range.
For instance, assume you’re creating a list of 10 people, and you try to specify who the 11th person on that list is going to be. On your paper-pad, it might be easy to just make room for another person, but runtime objects, like the list in python, isn’t that forgiving.
Your list starts out empty because of this:
a = []
then you add 2 elements to it, with this code:
a.append(3)
a.append(7)
this makes the size of the list just big enough to hold 2 elements, the two you added, which has an index of 0 and 1 (python lists are 0-based).
In your code, further down, you then specify the contents of element j which starts at 2, and your code blows up immediately because you’re trying to say «for a list of 2 elements, please store the following value as the 3rd element».
Again, lists like the one in Python usually aren’t that forgiving.
Instead, you’re going to have to do one of two things:
- In some cases, you want to store into an existing element, or add a new element, depending on whether the index you specify is available or not
- In other cases, you always want to add a new element
In your case, you want to do nbr. 2, which means you want to rewrite this line of code:
a[j]=a[j-2]+(j+2)*(j+3)/2
to this:
a.append(a[j-2]+(j+2)*(j+3)/2)
This will append a new element to the end of the list, which is OK, instead of trying to assign a new value to element N+1, where N is the current length of the list, which isn’t OK.
In python, lists are mutable as the elements of a list can be modified. But if you try to modify a value whose index is greater than or equal to the length of the list then you will encounter an Indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Example
If ‘fruits’ is a list, fruits=[‘Apple’,’ Banana’,’ Guava’]and you try to modify fruits[5] then you will get an index error since the length of fruits list=3 which is less than index asked to modify for which is 5.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Type is", type(fruits))
fruits[5] = 'Mango'
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "/example.py", line 3, in <module> fruits[5]='Mango' IndexError: list assignment index out of range
So, as you can see in the above example, we get an error when we try to modify an index that is not present in the list of fruits.
Python Indexerror: list assignment index out of range Solution
Method 1: Using insert() function
The insert(index, element) function takes two arguments, index and element, and adds a new element at the specified index.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the list of fruits on index 1.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.insert(1, "Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava'] Modified list: ['Apple', 'Mango', 'Banana', 'Guava']
It is necessary to specify the index in the insert(index, element) function, otherwise, you will an error that the insert(index, element) function needed two arguments.
Method 2: Using append()
The append(element) function takes one argument element and adds a new element at the end of the list.
Let’s see how you can add Mango to the end of the list using the append(element) function.
Python3
fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava']
print("Original list:", fruits)
fruits.append("Mango")
print("Modified list:", fruits)
Output:
Original list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava'] Modified list: ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Guava', 'Mango']
Last Updated :
04 Jan, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
Ситуация: у нас есть проект, в котором мы математически моделируем игру в рулетку. Мы хотим обработать отдельно нечётные числа, которые есть на рулетке, — для этого нам нужно выбросить из списка все чётные. Проверка простая: если число делится на 2 без остатка — оно чётное и его можно удалить. Для этого пишем такой код:
# в рулетке — 36 чисел, не считая зеро
numbers = [n for n in range(36)]
# перебираем все числа по очереди
for i in range(len(numbers)):
# если текущее число делится на 2 без остатка
if numbers[i] % 2 == 0:
# то убираем его из списка
del numbers[i]Но при запуске компьютер выдаёт ошибку:
❌ IndexError: list index out of range
Почему так произошло, ведь мы всё сделали правильно?
Что это значит: компьютер на старте цикла получает и запоминает одну длину списка с числами, а во время выполнения эта длина меняется. Компьютер, держа в памяти старую длину, пытается обратиться по номерам к тем элементам, которых уже нет в списке.
Когда встречается: когда программа одновременно использует список как основу для цикла и тут же в цикле добавляет или удаляет элементы списка.
В нашем примере случилось вот что:
- Мы объявили список из чисел от 1 до 36.
- Организовали цикл, который зависит от длины списка и на первом шаге получает его размер.
- Внутри цикла проверяем на чётность, и если чётное — удаляем число из списка.
- Фактический размер списка меняется, а цикл держит в голове старый размер, который больше.
- Когда мы по старой длине списка обращаемся к очередному элементу, то выясняется, что список закончился и обращаться уже не к чему.
- Компьютер останавливается и выводит ошибку.
Что делать с ошибкой IndexError: list index out of range
Основное правило такое: не нужно в цикле изменять элементы списка, если список используется для организации этого же цикла.
Если нужно обработать список, то результаты можно складывать в новую переменную, например так:
# в рулетке — 36 чисел, не считая зеро
numbers = [n for n in range(36)]
# новый список для нечётных чисел
new_numbers = []
# перебираем все числа по очереди
for i in range(len(numbers)):
# если текущее число не делится на 2 без остатка
if numbers[i] % 2 != 0:
# то добавляем его в новый список
new_numbers.append(numbers[i])Вёрстка:
Кирилл Климентьев
An IndexError is nothing to worry about. It’s an error that is raised when you try to access an index that is outside of the size of a list. How do you solve this issue? Where can it be raised?
In this article, we’re going to answer those questions. We will discuss what IndexErrors are and how you can solve the “list assignment index out of range” error. We’ll walk through an example to help you see exactly what causes this error.

Find Your Bootcamp Match
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps
- Access exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Select your interest
First name
Last name
Phone number
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
Without further ado, let’s begin!
The Problem: indexerror: list assignment index out of range
When you receive an error message, the first thing you should do is read it. An error message can tell you a lot about the nature of an error.
Our error message is: indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
IndexError tells us that there is a problem with how we are accessing an index. An index is a value inside an iterable object, such as a list or a string.
The message “list assignment index out of range” tells us that we are trying to assign an item to an index that does not exist.
In order to use indexing on a list, you need to initialize the list. If you try to assign an item into a list at an index position that does not exist, this error will be raised.
An Example Scenario
The list assignment error is commonly raised in for and while loops.
We’re going to write a program that adds all the cakes containing the word “Strawberry” into a new array. Let’s start by declaring two variables:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = []
The first variable stores our list of cakes. The second variable is an empty list that will store all of the strawberry cakes. Next, we’re going to write a loop that checks if each value in “cakes” contains the word “Strawberry”.
for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry[c] = cakes[c] print(strawberry)
If a value contains “Strawberry”, it should be added to our new array. Otherwise, nothing will happen. Once our for loop has executed, the “strawberry” array should be printed to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "main.py", line 6, in <module> strawberry[c] = cakes[c] IndexError: list assignment index out of range
As we expected, an error has been raised. Now we get to solve it!
The Solution
Our error message tells us the line of code at which our program fails:
The problem with this code is that we are trying to assign a value inside our “strawberry” list to a position that does not exist.
When we create our strawberry array, it has no values. This means that it has no index numbers. The following values do not exist:
strawberry[0] strawberry[1] …
We are trying to assign values to these positions in our for loop. Because these positions contain no values, an error is returned.
We can solve this problem in two ways.
Solution with append()
First, we can add an item to the “strawberry” array using append():
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
The append() method adds an item to an array and creates an index position for that item. Let’s run our code: [‘Strawberry Tart’, ‘Strawberry Cheesecake’].
Our code works!
Solution with Initializing an Array
Alternatively, we can initialize our array with some values when we declare it. This will create the index positions at which we can store values inside our “strawberry” array.
To initialize an array, you can use this code:
This will create an array with 10 empty values. Our code now looks like this:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] * 10 for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
Let’s try to run our code:
['Strawberry Tart', 'Strawberry Cheesecake']
Our code successfully returns an array with all the strawberry cakes.
This method is best to use when you know exactly how many values you’re going to store in an array.
«Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!»
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Our above code is somewhat inefficient because we have initialized “strawberry” with 10 empty values. There are only a total of three cakes in our “cakes” array that could possibly contain “Strawberry”. In most cases, using the append() method is both more elegant and more efficient.
Conclusion
IndexErrors are raised when you try to use an item at an index value that does not exist. The “indexerror: list assignment index out of range” is raised when you try to assign an item to an index position that does not exist.
To solve this error, you can use append() to add an item to a list. You can also initialize a list before you start inserting values to avoid this error.
Now you’re ready to start solving the list assignment error like a professional Python developer!
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
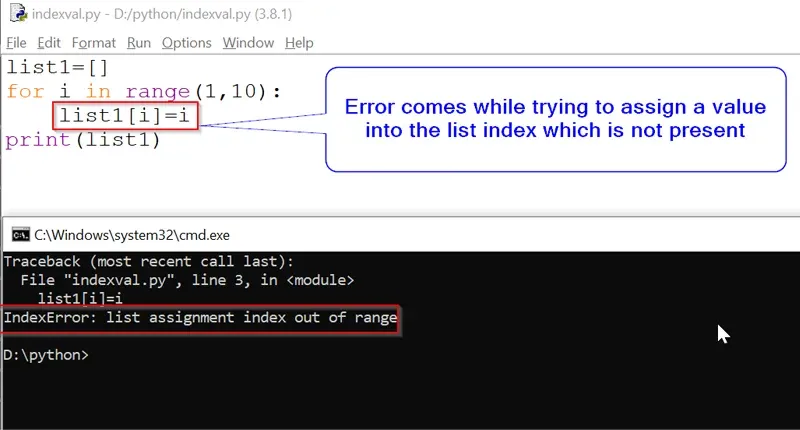
List elements can be modified and assigned new value by accessing the index of that element. But if you try to assign a value to a list index that is out of the list’s range, there will be an error. You will encounter an IndexError list assignment index out of range. Suppose the list has 4 elements and you are trying to assign a value into the 6th position, this error will be raised.
Example:
list1=[]
for i in range(1,10):
list1[i]=i
print(list1)Output:
IndexError: list assignment index out of rangeIn the above example we have initialized a “list1“ which is an empty list and we are trying to assign a value at list1[1] which is not present, this is the reason python compiler is throwing “IndexError: list assignment index out of range”.
Find Your Bootcamp Match
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps
- Access exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Select your interest
First name
Last name
Phone number
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
Without further ado, let’s begin!
The Problem: indexerror: list assignment index out of range
When you receive an error message, the first thing you should do is read it. An error message can tell you a lot about the nature of an error.
Our error message is: indexerror: list assignment index out of range.
IndexError tells us that there is a problem with how we are accessing an index. An index is a value inside an iterable object, such as a list or a string.
The message “list assignment index out of range” tells us that we are trying to assign an item to an index that does not exist.
In order to use indexing on a list, you need to initialize the list. If you try to assign an item into a list at an index position that does not exist, this error will be raised.
An Example Scenario
The list assignment error is commonly raised in for and while loops.
We’re going to write a program that adds all the cakes containing the word “Strawberry” into a new array. Let’s start by declaring two variables:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = []
The first variable stores our list of cakes. The second variable is an empty list that will store all of the strawberry cakes. Next, we’re going to write a loop that checks if each value in “cakes” contains the word “Strawberry”.
for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry[c] = cakes[c] print(strawberry)
If a value contains “Strawberry”, it should be added to our new array. Otherwise, nothing will happen. Once our for loop has executed, the “strawberry” array should be printed to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "main.py", line 6, in <module> strawberry[c] = cakes[c] IndexError: list assignment index out of range
As we expected, an error has been raised. Now we get to solve it!
The Solution
Our error message tells us the line of code at which our program fails:
The problem with this code is that we are trying to assign a value inside our “strawberry” list to a position that does not exist.
When we create our strawberry array, it has no values. This means that it has no index numbers. The following values do not exist:
strawberry[0] strawberry[1] …
We are trying to assign values to these positions in our for loop. Because these positions contain no values, an error is returned.
We can solve this problem in two ways.
Solution with append()
First, we can add an item to the “strawberry” array using append():
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
The append() method adds an item to an array and creates an index position for that item. Let’s run our code: [‘Strawberry Tart’, ‘Strawberry Cheesecake’].
Our code works!
Solution with Initializing an Array
Alternatively, we can initialize our array with some values when we declare it. This will create the index positions at which we can store values inside our “strawberry” array.
To initialize an array, you can use this code:
This will create an array with 10 empty values. Our code now looks like this:
cakes = ["Strawberry Tart", "Chocolate Muffin", "Strawberry Cheesecake"] strawberry = [] * 10 for c in range(0, len(cakes)): if "Strawberry" in cakes[c]: strawberry.append(cakes[c]) print(strawberry)
Let’s try to run our code:
['Strawberry Tart', 'Strawberry Cheesecake']
Our code successfully returns an array with all the strawberry cakes.
This method is best to use when you know exactly how many values you’re going to store in an array.
«Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!»
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
Our above code is somewhat inefficient because we have initialized “strawberry” with 10 empty values. There are only a total of three cakes in our “cakes” array that could possibly contain “Strawberry”. In most cases, using the append() method is both more elegant and more efficient.
Conclusion
IndexErrors are raised when you try to use an item at an index value that does not exist. The “indexerror: list assignment index out of range” is raised when you try to assign an item to an index position that does not exist.
To solve this error, you can use append() to add an item to a list. You can also initialize a list before you start inserting values to avoid this error.
Now you’re ready to start solving the list assignment error like a professional Python developer!

