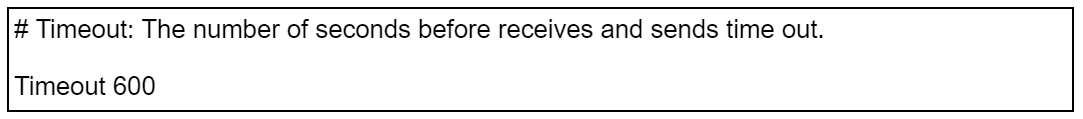На чтение 3 мин. Просмотров 1.4k. Опубликовано 25.06.2019
Содержание
- Методы исправления ошибки тайм-аута запроса 408
- Как исправить ошибку времени ожидания запроса 408
- Ошибки, как 408 Время ожидания запроса
Методы исправления ошибки тайм-аута запроса 408
Ошибка 408 Request Timeout – это код состояния HTTP, который означает, что запрос, отправленный вами на сервер веб-сайта (например, запрос на загрузку веб-страницы), занял больше времени, чем сервер веб-сайта был готов ждать. Другими словами, ваше соединение с сайтом “истекло”.
Сообщения об ошибках 408 Request Timeout часто настраиваются каждым веб-сайтом, особенно очень большими, поэтому имейте в виду, что эта ошибка может проявляться в большем количестве случаев, чем перечисленные ниже:
408: время ожидания запроса
Ошибка HTTP 408 - время ожидания запроса
Ошибка 408 Request Timeout отображается в окне интернет-браузера, как и веб-страницы.
Как исправить ошибку времени ожидания запроса 408
-
Повторите попытку веб-страницы, нажав кнопку «Обновить/перезагрузить» или еще раз попробовав URL из адресной строки. Во многих случаях медленное соединение вызывает задержку, которая вызывает ошибку 408 Request Timeout, и это часто является только временным. Попытка повторить страницу часто будет успешной.
- Примечание . Если в процессе оформления заказа у интернет-продавца появляется сообщение об ошибке 408 «Время ожидания запроса», имейте в виду, что повторные попытки оформления заказа могут привести к созданию нескольких заказов – и нескольких сборов! У большинства продавцов есть автоматическая защита от подобных действий, но об этом еще нужно помнить.
-
Возможно, у вас возникла проблема с подключением к Интернету, которая вызывает длительные задержки при доступе к страницам. Чтобы исключить это, посетите другой веб-сайт, например, Google или Yahoo.
- Если страницы загружаются так быстро, как вы привыкли их видеть, проблема, вызывающая ошибку 408 Request Timeout, вероятно, связана с веб-сайтом.
- Однако, если все веб-сайты работают медленно, возможно, у вас проблемы с интернет-соединением. Запустите тест скорости Интернета, чтобы проверить текущую пропускную способность, или обратитесь к поставщику услуг Интернета за технической поддержкой.
-
Вернуться позже. Ошибка 408 Request Timeout является распространенным сообщением об ошибке на очень популярных веб-сайтах, когда огромное увеличение трафика посетителями (это вы!) Перегружает серверы.
- По мере того, как все больше и больше посетителей покидают сайт, шансы на успешную загрузку страницы для вас возрастают.
-
Если ничего не помогает, вы можете попытаться связаться с веб-мастером или другим контактом сайта и сообщить им об ошибке 408 Request Timeout.
- С веб-мастером большинства веб-сайтов можно связаться по электронной почте по адресу: веб-мастер @ website.com , заменив website.com фактическим именем сайта.
Ошибки, как 408 Время ожидания запроса
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и поэтому в некоторой степени связаны с ошибкой тайм-аута запроса 408: неверный запрос 400, несанкционированный 401, запрещенный 403 и не найденный 404.
Также существует несколько кодов HTTP-статуса на стороне сервера , например, часто встречающаяся внутренняя ошибка сервера (500 Internal Server Error). Просмотрите их все в нашем списке ошибок кода состояния HTTP.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost. The status code is deprecated.[4]
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[5]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[6]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[7][8]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[9]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[10]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[11]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[12] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[11]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[14] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[15] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[16] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[17] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[18]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[19]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[20]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[21]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[22]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[23] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[24][25][26] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[27][28]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[9]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[9]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[9]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[29]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[29]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[29]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[30] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[31]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[32]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[9]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfil it.[33]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[29]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[34]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[35] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[36]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[37]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[38]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[38]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[39]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[40]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[41]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[42]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[43]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[44]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[45] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[46]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[47] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[48][49]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[50] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[51]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[52]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[53]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[54]
AWS Elastic Load Balancer
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[55]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[55]
- 464
- Incompatible protocol versions between Client and Origin server.[55]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[55]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[56][57]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[58]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ Fielding, Roy T. «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «102 Processing — HTTP MDN». 102 status code is deprecated
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved May 17, 2023.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry at the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- MDN status code reference at mozilla.org
Чтобы на веб-странице появился контент, браузер должен получить от сервера, на котором расположен сайт, необходимые данные. Когда на устройстве пользователя, на веб-сервере или на другом промежуточном узле (например, прокси) возникают неполадки, вместо содержимого сайта в браузере появляется страница с ошибкой. Для устранения сбоя, необходимо знать, на чьей стороне он произошел и по какой причине. Понять, что является источником проблемы, помогает цифровой код ошибки. Если он имеет формат 5xx, значит, сбой происходит на стороне сервера. Разбираем в статье ошибку 504 на сайте и способы ее устранения.
Что значит ошибка 504 и когда она появляется
Ошибка 504 Gateway Time Out — это ошибка, возникающая при загрузке сайта, если запрос пользователя передавался на сервер, хранящий данные веб-ресурса, через промежуточный сервер, действующий как шлюз или прокси, и в процессе обработки данного запроса один из серверов не получил ответ от другого в течение максимально допустимого времени ожидания. Обмен данными происходит по HTTP, и если возникает «тайм-аут шлюза», браузер показывает на веб-странице код 504, указывающий на соответствующее состояние протокола.
На выполнение некоторых операций на сервере выделяется определенное количество времени. Например, обработка http-запроса на Nginx по умолчанию должна быть завершена за 30 секунд. Лимит времени устанавливается для того, чтобы при избыточной нагрузке сервер мог прервать процесс, который не может выполнить, и перейти к следующей задаче. Средняя продолжительность загрузки сайта составляет всего 1–3 секунды, однако иногда она может увеличиваться, например, если сервер выполняет ресурсоемкие скрипты. Когда на это требуется больше максимально допустимого времени, соединение с клиентом (браузером) разрывается и возникает один из вариантов сообщения «HTTP Error 504 — Gateway Timeout». К повышенной нагрузке на сервер могут привести внутренние сбои на сайте, проблемы с безопасностью, настройки браузера и так далее.
Если говорить простыми словами, то ошибка 504 означает, что сервер, на котором расположен сайт, не успевает вовремя обработать запрос и ответить пользователю.
Как исправить ошибку 504 владельцу сайта
Чтобы исправить ошибку 504, необходимо установить и устранить причину ее возникновения. Некоторые способы решения проблемы требуют вмешательства администратора сайта.
Долго обрабатывается скрипт
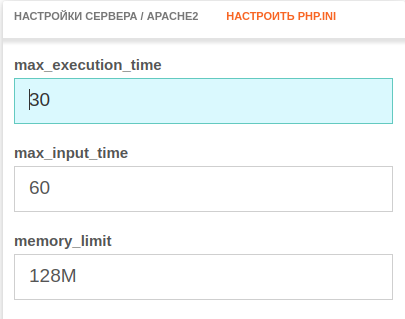
Если скрипт тяжелый, сервер может не успеть полностью его обработать до появления ошибки. Лучшим решением проблемы будет облегчение скрипта или его замена. Когда это невозможно, увеличивают период ожидания сервера. Лимит времени, за которое скрипт должен быть отработан, устанавливается через директиву «max_execution_time» в файле «php.ini». По умолчанию он составляет 30 секунд. Чтобы он стал больше, необходимо открыть файл и подставить в строку «max_execution_time = 30» новую допустимую продолжительность операции. Кроме того, поменять настройки можно в Nginx и Apache.
Нестандартные параметры времени ожидания сервера могут понадобиться, если вы используете Nginx в качестве прокси-сервера для Apache. Изменение времени выполнения скрипта на веб-сервере производится в файле «nginx.conf». Порядок действий:
- Подключение к серверу по Secure Shell (протоколу для удаленного управления операционной системой).
- Ввод команды «sudo nano/etc/nginx/nginx.conf» для запуска файла.
-
Редактирование блока server: увеличение времени до наступления тайм-аута с 300 секунд до 600:
- Перезагрузка веб-сервера командой «service nginx reload».
Коррекцию файлов «php.ini» и «nginx.conf» лучше проводить совместно. В обоих документах необходимо указать одинаковое время обработки запроса.
При использовании Apache время обработки запроса редактируется через «httpd.conf». Что необходимо сделать:
- Открыть файл.
-
Ввести строку:
- Сохранить корректировки и заново запустить сервер.
Проблемы с CDN
CDN ― это несколько связанных серверов, предназначенных для того, чтобы ускорить передачу данных сайта его пользователям. CDN сохраняют контент, часто запрашиваемый аудиторией, на кеш-сервере. При повторном запросе этих данных сервер достает их из временной памяти. Таким образом, снижается нагрузка на сервер, являющийся источником контента, и сокращается время обработки запросов пользователей.
Иногда ошибка 504 может возникать при использовании CDN. Если после отключения от системы работоспособность сайта восстановится, сообщите о проблеме разработчикам сервиса.
Выросла нагрузка на один из серверов
К повышенной нагрузке на сервер может привести резкий рост трафика. Наплыв пользователей может быть связан как с намеренными действиями владельца веб-ресурса — с запуском рекламной кампании, так и со случайными событиями — временным увеличением спроса на сезонный товар, продающийся в интернет-магазине. Поскольку количество операций, которое сервер может выполнять одновременно, ограничено его вычислительной мощностью, при избыточной нагрузке хостинг-компьютер перестает отвечать на запросы пользователей. Чтобы он снова мог отдавать данные браузеру, достаточно арендовать компьютер с более мощным железом, например, с виртуального хостинга перейти на VPS. Если планируется проведение маркетинговых мероприятий, лучше заранее арендовать дополнительные вычислительные ресурсы (оперативную память, место на жестком диске и т. д.).
В компании «Интернет Хостинг Центр» клиенты могут арендовать VPS сервер в России с бесплатной защитой от DDoS на всех тарифах. Выделенный IP и техподдержка входят в стоимость.
Проверка службы DNS
Сообщение «Error 504 — Gateway Timeout» может появиться, если DNS-служба не справилась с преобразованием доменного имени в IP-адрес. Причиной ошибки становится перенос веб-ресурса с локального ПК на веб-сервер и автоматически пропадет, после того как новые DNS-данные распространяются по всему Интернету. Процесс занимает около двух суток.
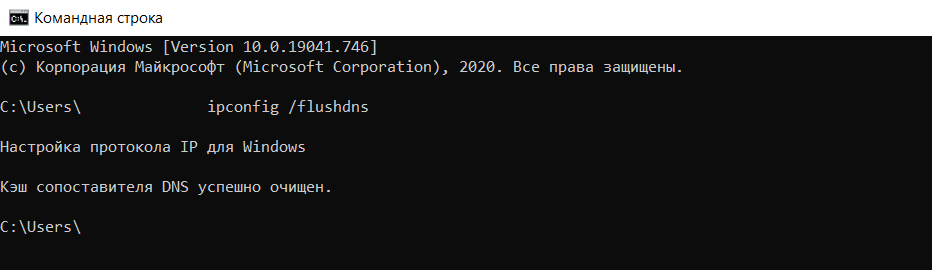
Проблемы с DNS могут возникнуть на компьютере пользователя. Для их устранения на ПК вызывается командная строка операционной системы, где вводится специальная команда для очистки DNS-кэша, в Windows — это «ipconfig /flushdns».
Спам, вирусы и DDoS-атаки
Перегрузка сервера может быть вызвана не только возросшим интересом пользователей к вашим товарам и услугам, но и менее позитивными причинами — спамом, вирусами и DDoS-атаками. Для защиты веб-ресурса от вредоносных программ и действий хакеров, необходимо предпринять несколько профилактических мер:
- проверить наличие антивируса в административной панели хостинга;
- включить защиту от DDoS;
- подключить анти-спам плагины в CMS сайта;
- проверить лог-файлы на наличие часто повторяющихся IP-адресов;
- установить SSL/TLS;
- защитить формы обратной связи с помощью капчи;
- предотвратить публикацию комментариев со ссылками на вредоносное ПО, подключив модерирование контента и так далее.
Проблемы с плагинами в CMS
Функции на сайте, созданном с помощью CMS, реализуются благодаря плагинам. Не все они работают достаточно быстро, некоторые из них обрабатываются медленно, что приводит к тайм-ауту шлюза. Чтобы проверить, не является ли установленный плагин причиной сбоя, его необходимо отключить, а затем запустить сайт без него. Если веб-ресурс загрузится, значит, нужно выбрать другой функциональный модуль.
Как решить проблему, если вы — пользователь
Неполадки могут возникнуть на стороне пользователя: в его DNS-службе, браузере, программном обеспечении, роутере или модеме. Убедитесь, что настройки ваших устройств, выставлены правильно:
- обновите страницу, заново указав URL в адресной строке и нажав кнопку ввода (Enter);
- откройте сайт в другом браузере, если в нем сбой не повторится, обновите браузер с ошибкой до последней версии;
- запустите веб-ресурс на другом устройстве, чтобы проверить, не связаны ли проблемы с программным обеспечением вашего компьютера;
- очистите файлы кэша и cookies, чтобы избавиться от ошибок, накопленных браузером за длительное время использования;
- перезагрузите роутер, чтобы устранить конфликт между обновленным ПО провайдера и вашим устройством;
- очистите кэш DNS через командную строку ОС.
Заключение
Мы разобрали самые популярные причины возникновения ошибки 504 и привели способы решения каждой из них. Надеемся, что наша статья поможет Вам справиться с любой проблемой, способной привести к тайм-ауту шлюза.
Иногда при посещении отдельных страниц сайта мы сталкиваемся с тем, что на экране вместо желаемого контента появляется сообщение об ошибке с цифровым кодом. Для «непосвященного» пользователя это просто набор цифр, но на самом деле в этих цифрах заложена определенная информация. Все они группируются по видам причин возникновения сбоя.
Сообщения, кодирующиеся в формате 5хх, говорят о проблеме на стороне сервера, например, когда невозможно выполнить запрос из-за нарушения связи между несколькими серверами. Ошибка 504 Gateway Time Out не является распространенной, но это не значит, что на нее не стоит обращать внимания, особенно владельцу сайта. Рассмотрим некоторые причины возникновения данной ошибки и способы ее устранения как на стороне обычного посетителя, так и администратором веб-ресурса.
Ошибка 504 Gateway Time Out – это код состояния HTTP, который появляется, когда в течение заданного периода времени один сервер не получает своевременный ответ от другого сервера, который действует как шлюз или прокси.
Описания ошибки могут иметь различную форму:
- 504 Gateway Timeout nginx
- Gateway Timeout Error
- HTTP Error 504
- 504 Gateway Time-out – The server didn’t respond in time
- HTTP Error 504 – Gateway Timeout
Наличие дополнительного словесного описания помогает конкретизировать причину возникновения сбоя.
Производительный хостинг в подарок при заказе лицензии 1С-Битрикс
Выбирайте надежную CMS с регулярными обновлениями системы и профессиональной поддержкой. А мы подарим вам год хостинга – специально для сайтов на 1С-Битрикс.
Заказать
Что делать посетителю сайта при возникновении ошибки 504
Итак, вы столкнулись с появлением на экране сообщения «error 504». Не спешите уходить с сайта, ведь возникновение сбоя может говорить о неправильной работе вашего браузера или даже наличии более серьезных проблем на уровне пользовательского софта. Попробуйте произвести довольно простые действия, чтобы убедиться, что с вашим программным обеспечением и настройками все в порядке.
- Перезагрузите проблемную страницу или текущий браузер. Если проблема устранилась и не повторяется вновь, особенно при посещении других сайтов, о ней можно просто забыть. При регулярном возникновении однотипных ошибок во время посещения разных ресурсов стоит покопаться в настройках собственного ПО поглубже.
- Зайдите на тот же самый сайт, где возникла ошибка сервера 504, используя альтернативный браузер. В случае, когда страница во время тестирования открылась корректно, обновите браузер, в котором случился сбой, до последней версии.
- Проверьте, как открываются страницы этого же сайта с другого компьютера или смартфона. Это позволит вам понять, не связано ли появление ошибки 504 с ПО конкретного устройства.
- При регулярном появлении HTTP ошибок, в т.ч. с кодом 504, очистите кэш браузера, удалите файлы cookies. Со временем в любом браузере накапливается много «мусора». Произведя очистку, вы поможете программе работать более корректно и даже быстрее.
- Произведите сброс настроек роутера или модема, отключив оборудование на некоторое время от сети. Данная операция вряд ли приведет к устранению ошибки 504, но может улучшить качество интернет-соединения. Провайдеры регулярно вносят изменения в настройки собственного софта, обновляют его. Иногда это приводит к конфликту в корректном взаимодействии пользовательского оборудования и серверов оператора. Перезагрузка устройства по питанию в большинстве случаев решает такие проблемы.
- Очистите кэш DNS. Данная операция кажется сложной для обычного пользователя, но на деле выполнить ее достаточно легко. Способ очистки зависит от вашей операционной системы, найдите соответствующий мануал в интернете.
- Для опытных пользователей подойдет рекомендация временно переключить DNS-сервер на Google Public DNS, что как минимум поможет определить, возник ли ошибочный код состояния HTTP по причине DNS проблемы.
Если после проведения всех вышеозначенных рекомендаций любая ошибка, в т.ч. 504 Gateway Time Out, продолжает возникать регулярно, обратитесь в техподдержку проблемного интернет-ресурса.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Решение проблем с появлением ошибки сервера 504 администратором веб-ресурса
Некорректная работа сайта чаще всего просто раздражает посетителя и приводит к тому, что пользователь находит альтернативный ресурс. Для владельца сайта такие сбои могут носить более глобальные последствия. Поэтому очень важно своевременно обнаруживать баги и максимально быстро устранять их. Для раннего мониторинга стоит использовать все возможные инструменты:
- проводить регулярную симуляцию пользовательского поведения на сайте;
- настроить автоматизированный мониторинг работоспособности ресурса как встроенными инструментами администрирования, так и с использованием специальных скриптов;
- обеспечить качественную работу службы технической поддержки сайта, своевременную обработку всех поступающих сообщений, особенно связанных с информацией о появлении разного рода ошибок на стороне пользователя.
Соблюдение последнего правила не только позволит практически без дополнительных затрат отслеживать все возможные проблемы, которые возникают при посещении сайта. Своевременная обработка пользовательских запросов, быстрый ответ, выдача рекомендаций и публичное обсуждение повышают лояльность и создают дополнительный PR-эффект.
Почти все ошибки с кодом 5хх, возникающие из-за невозможности обработки определенного количества запросов, поступающих на сервер, решаются методом апгрейда железа (использованием высокопроизводительного хостинга) либо оптимизацией работы программного обеспечения. Второй способ зависит от вида движка, на котором создан конкретный сайт. При использовании условно-бесплатных программ (WordPress, OpeneCart и других) все проблемы придется решать на уровне администрирования, с привлечением конкретного веб-программиста, разработавшего данный сайт. Если баги возникают на платных платформах (1С-Битрикс, UMI.CMS, NetCat CMS), напишите об ошибке 504 Gateway Time Out в техподдержку разработчика. Отправить сообщение о проблеме следует и разработчикам платных скриптов, если они установлены на вашем сайте, и вы считаете, что сбои возникают по причине их некорректного исполнения.
Вот некоторые причины, приводящие к возникновению ошибки 504 Gateway Time Out
- Резкий скачок нагрузки на сайт вследствие поступления большого количества внешних запросов, вызванного DDoS-атаками или действиями вирусного ПО, пиковым посещением сайта, например, в момент проведения различных акций в интернет-магазине, или единовременной загрузкой на сайт большого объема контента (импорт информации из CSV- или XML-файлов).
- Некорректная работа скриптов, плагинов и дополнений, конфликтующих как между собой, так и внутри.
- Превышение лимита доступных ресурсов при использовании виртуального хостинга.
Еще одна возможная причина возникновения ошибки 504 – исполняемый скрипт не укладывается в отведенный лимит времени. Это бывает, когда скрипт обращается к другим сайтам либо просто выполняет тяжелую операцию, например, строит поисковый индекс.
Рекомендации по устранению ошибки 504 Gateway Time Out методами администрирования сайта
Ошибка 504 Gateway Time Out может быть вызвана недавними изменениями или обновлениями на сайте. Если после отката к состоянию, предшествующему изменениям, баг исчез, следует найти конкретное действие, повлекшее возникновение ошибки. Для этого необходимо проверить журнал ошибок соответствующей CMS. Пользователи WordPress могут включить журналирование ошибок в файле wp-config.php добавлением следующих строк:
define( 'wp_debug', true );
define( 'wp_debug_log', true );
define( 'wp_debug_display', false )
Все возникающие варианты ошибок будут записаны в файле wp-contents/debug.log.
Для проверки работоспособности плагинов и расширений попробуйте отключить те, которые вызывают подозрение как источники возникновения ошибки 504. В первую очередь это касается устаревших скриптов, но причиной могут оказаться и обновления. Если проблема исчезла, далее следует найти некорректный плагин или дополнение и устранить или исправить его. Один из способов улучшения работы исполняемого скрипта – увеличить значение параметра PHP max_execution_time или облегчить скрипт.
При использовании CDN для более быстрого получения контента, в частности CloudFlare, который работает как CDN и как сервис предотвращения негативных последствий от DDoS, вы можете столкнуться с двумя типами ошибок 504. В случае возникновения проблемы на стороне CloudFlare лучшим решением будет связаться с поддержкой CloudFlare или отключить его. Второй вариант – когда сбой возникает на стороне хостинг-провайдера. В этой ситуации также необходимо обратиться в службу поддержки хостера.
Часто ошибку 504 можно видеть на серверах, где используется VPS-хостинг и установлен Nginx в качестве фронтенда и Apache в качестве бэкенда. Для устранения проблемы в Apache можно увеличить значение timeout по умолчанию в файле httpd.conf:
# Timeout: The number of seconds before receives and sends time out. Timeout 600
Также увеличить лимит в max_execution_time в php.ini:
После внесения изменений следует перезапустить Apache. Ошибка 504 Gateway Time Out должна исчезнуть.
Аналогичным образом проблема с появлением ошибки HTTP 504 решается пользователями Nginx. Попробуйте увеличить такие параметры в файле /etc/nginx/conf.d/timeout.conf:
proxy_connect_timeout 600; proxy_send_timeout 600; proxy_read_timeout 600; send_timeout 600;
Также рекомендуется увеличить max_execution_time в php.ini:
Далее перезапустите Nginx и откройте сайт.
Более простым решением устранения данной проблемы является использование панели управления сервером.
Данный способ позволяет администрировать настройки веб-сервера без использования консоли, один раз настроить их под ваш проект и больше не подключаться к серверу без острой необходимости.
Например, в бесплатной панели управления Vesta Control Panel достаточно внести изменения в раздел «Сервер» и навсегда забыть о возможности возникновения ошибок на сайте.
Аналогичным способом проблема устраняется и при использовании альтернативных панелей управления хостингом – Ajenti, CentOS Web Panel, ISPmanager и других.
Если вы считаете, что появление 504 Gateway Timeout вызвано превышением лимита использования ресурсов серверного железа, оптимальным решением будет аренда выделенного сервера или VPS. Когда ваш сайт уже размещен на виртуальном хостинге, но ни одна из рекомендаций не привела к исправлению error 504, обратитесь к хостинг-провайдеру. В этом случае подробно опишите причины, которые, как вы полагаете, привели к появлению сбоя.
Заключение
В данной статье мы рассмотрели основные причины возникновения ошибки HTTP 504 Gateway Timeout и популярные способы устранения неполадки. Уверен, некоторые администраторы веб-ресурсов сталкивались с подобными проблемами, выходящими за рамки приведенных примеров и рекомендаций.
Буду благодарен, если вы поделитесь своим опытом в комментариях.
Код ошибки в формате 5хх говорит о том, что на стороне сервера есть проблема: сервер не может обработать запрос от клиента. Клиентом в данном случае выступает браузер.
Ошибка 504 Gateway Time Out возникает, когда в заданный промежуток времени сервер не получает ответ от другого сервера, при этом другой сервер выполняет роль прокси или шлюза.
Ошибка 504 что значит
Какие ещё бывают варианты отображения ошибки:
- HTTP Error 504,
- Gateway Timeout Error,
- HTTP Error 504 – Gateway Timeout,
- 504 Gateway Timeout nginx,
- 504 Gateway Time-out – The server didn’t respond in time,
- Ошибка 504 Время ответа сервера истекло,
- Время ожидания шлюза (504),
- Ошибка тайм-аута шлюза,
- HTTP 504,
- 504 Ошибка.
В этой статье мы расскажем, как устранить код ошибки 504.
Как исправить ошибку 504 посетителю сайта
Итак, вы перешли на сайт, но вместо веб-страницы видите сообщение с кодом 504.
Что такое тайм аут шлюза
Проблема может быть как со стороны сайта, так и со стороны устройства, например настроек браузера.
Чтобы убедиться в том, что настройки браузера в порядке:
1) Обновите страницу. Но обновите не клавишей F5, а выделите содержимое адресной строки и нажмите Enter. Если после этих действий ошибка 504 не возникает ни на текущем, ни на любом другом сайте – её можно проигнорировать.
2) Зайдите на тот же ресурс через другой браузер. Если в этом случае сайт открылся корректно, перейдите к следующему пункту.
3) Очистите кэш браузера и удалите файлы cookie. После этого браузер будет работать быстрее.
Воспользуйтесь инструкцией Как очистить кэш браузера.
4) Перезагрузите роутер или модем. Отключите устройство от сети примерно на 10 минут.
5) Очистите кэш DNS. Для этого воспользуйтесь инструкцией ниже.
Как очистить кэш DNS
В зависимости от вашей операционной системы очистите кэш по одной из инструкций.
1) Откройте командную строку. Для этого введите в поисковую строку «Командная строка» и выберите появившееся приложение:
2) Введите команду:
3) Дождитесь сообщения об очистке кэша:
1) Откройте терминал клавишами Ctrl+Alt+T.
2) Введите команду:
Для Ubuntu:
sudo service network-manager restartДля других дистрибутивов:
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart1) Войдите в терминал. Для этого нажмите клавиши Command + Space. Введите Терминал и нажмите на найденное приложение.
2) Введите команду:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponderГотово, вы очистили кэш DNS.
6) Обратитесь в техподдержку вашего интернет-провайдера. Возможно, это проблема сети, за которую отвечает провайдер.
Если эти действия не принесли результата – обратитесь в техническую поддержку сайта.
Если вы владелец сайта
Как исправить ошибку 504 на виртуальном хостинге
1 способ
Эта ошибка может возникнуть в случае, если для Nginx был превышен лимит на время ответа сайта. По умолчанию это 30 секунд, при этом среднее время загрузки сайта не должно превышать 1-3 секунды.
Если скрипты вашего сайта должны исполняться дольше 30 секунд, вы можете миновать Nginx и обратиться к сайту по другим портам. Если ваша панель управления хостингом:
- ISPManager – используйте порт 8081
- cPanel или Plesk – используйте порт 8080.
2 способ
Если этот вариант вам не подходит, рекомендуем перенести ваш сайт на Облачный сервер, на котором доступна гибкая настройка сервера, в том числе и лимитов. Для этого закажите услугу «Облачные серверы» и перенесите сайт по инструкции Как перенести сайты между услугами REG.RU.
3 способ
Также вы можете изменить директиву max_execution_time в файле php.ini. Она указывает на время, за которое должен отрабатываться скрипт. Для этого:
- 1.
-
2.
Укажите нужное значение в строке:
Где 30 – время выполнения скрипта в секундах.
4 способ
Если вы используете CDN, проблема может быть связана с ней.
Что такое CDN
CDN – это сетевая инфраструктура, которая распределена географически. Она обеспечивает быструю загрузку контента пользователям веб-сервисов и сайтов. Серверы, которые входят в состав CDN, географически расположены так, чтобы сделать время ответа сайта или сервиса минимальным для пользователей.
Пользователь ищет ресурс и тем самым посылает запрос. Запрос идентифицируется и направляется на PoP – на ближайший к пользователю кэширующий сервер в этой инфраструктуре. Возможны два варианта:
- Если в кэше PoP есть данные об этом запросе, он отвечает браузеру, а тот отображает контент.
- Если в кэше этого сервера нет данных, запрос переадресовывается к ориджину – центральному серверу, на котором хранятся все данные. Когда ориджин отвечает на запрос, PoP кэширует его и передаёт ответ браузеру. После этого контент отображается в браузере.
Ошибку 504 может вернуть кэширующий сервер, если превышено время ожидания от центрального сервера.
Если ошибку исправить не удалось, обратитесь в техническую поддержку.
Как исправить ошибку 504 на VPS
1 способ
Эта ошибка может возникнуть в случае, если для Nginx был превышен лимит на время ответа сайта. По умолчанию это 30 секунд, при этом среднее время загрузки сайта не должно превышать 1-3 секунды.
Чтобы избавиться от этой ошибки, попробуйте повысить время ожидания веб-сервера Nginx.
2 способ
Также ошибка 504 может возникать, когда Nginx используется как прокси-сервер для Apache. В этом случае нужно настроить параметры времени ожидания при проксировании. Максимальное время исполнения скрипта в настройках веб-сервера — 300 секунд.
Изменить параметры ожидания можно в конфигурационном файле nginx.conf. Для этого:
-
1.
Подключитесь к серверу по SSH.
-
2.
Откройте конфигурационный файл с помощью команды:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf -
3.
Добавьте строки в блоке server:
#server { #... proxy_connect_timeout 600; proxy_send_timeout 600; proxy_read_timeout 600; send_timeout 600; #... #}Где 600 — время в секундах.
-
4.
Перезапустите Nginx с помощью команды:
Если решить проблему не удалось, обратитесь в техническую поддержку или на тематические форумы по Nginx.