I’m getting this error :
Exception in Tkinter callback
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:Python34libtkinter__init__.py", line 1538, in __call__
return self.func(*args)
File "C:/Users/Marc/Documents/Programmation/Python/Llamachat/Llamachat/Llamachat.py", line 32, in download
with open(place_to_save, 'wb') as file:
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/goodbye.txt'
When running this :
def download():
# get selected line index
index = films_list.curselection()[0]
# get the line's text
selected_text = films_list.get(index)
directory = filedialog.askdirectory(parent=root,
title="Choose where to save your movie")
place_to_save = directory + '/' + selected_text
print(directory, selected_text, place_to_save)
with open(place_to_save, 'wb') as file:
connect.retrbinary('RETR ' + selected_text, file.write)
tk.messagebox.showwarning('File downloaded',
'Your movie has been successfully downloaded!'
'nAnd saved where you asked us to save it!!')
Can someone tell me what I am doing wrong?
Specs :
Python 3.4.4 x86
Windows 10 x64
Gulzar
22.5k23 gold badges106 silver badges189 bronze badges
asked Apr 5, 2016 at 18:54
10
This happens if you are trying to open a file, but your path is a folder.
This can happen easily by mistake.
To defend against that, use:
import os
path = r"my/path/to/file.txt"
assert os.path.isfile(path)
with open(path, "r") as f:
pass
The assertion will fail if the path is actually of a folder.
answered Jun 7, 2020 at 11:14
GulzarGulzar
22.5k23 gold badges106 silver badges189 bronze badges
1
There are basically three main methods of achieving administrator execution privileges on Windows.
- Running as admin from
cmd.exe - Creating a shortcut to execute the file with elevated privileges
- Changing the permissions on the
pythonexecutable (Not recommended)
A) Running cmd.exe as and admin
Since in Windows there is no sudo command you have to run the terminal (cmd.exe) as an administrator to achieve to level of permissions equivalent to sudo. You can do this two ways:
-
Manually
- Find
cmd.exeinC:Windowssystem32 - Right-click on it
- Select
Run as Administrator - It will then open the command prompt in the directory
C:Windowssystem32 - Travel to your project directory
- Run your program
- Find
-
Via key shortcuts
- Press the windows key (between
altandctrlusually) +X. - A small pop-up list containing various administrator tasks will appear.
- Select
Command Prompt (Admin) - Travel to your project directory
- Run your program
- Press the windows key (between
By doing that you are running as Admin so this problem should not persist
B) Creating shortcut with elevated privileges
- Create a shortcut for
python.exe - Righ-click the shortcut and select
Properties - Change the shortcut target into something like
"C:path_topython.exe" C:path_toyour_script.py" - Click «advanced» in the property panel of the shortcut, and click the option «run as administrator»
Answer contributed by delphifirst in this question
C) Changing the permissions on the python executable (Not recommended)
This is a possibility but I highly discourage you from doing so.
It just involves finding the python executable and setting it to run as administrator every time. Can and probably will cause problems with things like file creation (they will be admin only) or possibly modules that require NOT being an admin to run.
Gulzar
22.5k23 gold badges106 silver badges189 bronze badges
answered Apr 7, 2016 at 7:29
MixoneMixone
1,3181 gold badge13 silver badges24 bronze badges
5
Make sure the file you are trying to write is closed first.
answered Feb 7, 2019 at 3:39
Chrono HaxChrono Hax
5094 silver badges3 bronze badges
0
Change the permissions of the directory you want to save to so that all users have read and write permissions.
Alexander
2,4571 gold badge14 silver badges17 bronze badges
answered Apr 7, 2016 at 7:41
0
You can run CMD as Administrator and change the permission of the directory using cacls.exe. For example:
cacls.exe c: /t /e /g everyone:F # means everyone can totally control the C: disc
answered Mar 10, 2020 at 3:41
OutroOutro
916 bronze badges
0
In my case the problem was that I hid the file (The file had hidden atribute):
How to deal with the problem in python:
Edit: highlight the unsafe methods, thank you d33tah
# Use the method nr 1, nr 2 is vulnerable
# 1
# and just to let you know there is also this way
# so you don't need to import os
import subprocess
subprocess.check_call(["attrib", "-H", _path])
# Below one is unsafe meaning that if you don't control the filePath variable
# there is a possibility to make it so that a malicious code would be executed
import os
# This is how to hide the file
os.system(f"attrib +h {filePath}")
file_ = open(filePath, "wb")
>>> PermissionError <<<
# and this is how to show it again making the file writable again:
os.system(f"attrib -h {filePath}")
file_ = open(filePath, "wb")
# This works
answered Jul 22, 2020 at 21:19
1
I had a similar problem. I thought it might be with the system. But, using shutil.copytree() from the shutil module solved the problem for me!
answered Dec 17, 2019 at 21:02
The problem could be in the path of the file you want to open. Try and print the path and see if it is fine
I had a similar problem
def scrap(soup,filenm):
htm=(soup.prettify().replace("https://","")).replace("http://","")
if ".php" in filenm or ".aspx" in filenm or ".jsp" in filenm:
filenm=filenm.split("?")[0]
filenm=("{}.html").format(filenm)
print("Converted a file into html that was not compatible")
if ".aspx" in htm:
htm=htm.replace(".aspx",".aspx.html")
print("[process]...conversion fron aspx")
if ".jsp" in htm:
htm=htm.replace(".jsp",".jsp.html")
print("[process]..conversion from jsp")
if ".php" in htm:
htm=htm.replace(".php",".php.html")
print("[process]..conversion from php")
output=open("data/"+filenm,"w",encoding="utf-8")
output.write(htm)
output.close()
print("{} bits of data written".format(len(htm)))
but after adding this code:
nofilenametxt=filenm.split('/')
nofilenametxt=nofilenametxt[len(nofilenametxt)-1]
if (len(nofilenametxt)==0):
filenm=("{}index.html").format(filenm)
It Worked perfectly
Gulzar
22.5k23 gold badges106 silver badges189 bronze badges
answered Feb 26, 2019 at 11:41
oyamooyamo
411 silver badge3 bronze badges
in my case. i just make the .idlerc directory hidden.
so, all i had do is to that directory and make recent-files.lst unhidden after that, the problem was solved
henriquehbr
1,0444 gold badges19 silver badges41 bronze badges
answered Dec 14, 2019 at 10:37
0
I got this error as I was running a program to write to a file I had opened. After I closed the file and reran the program, the program ran without errors and worked as expected.
answered Sep 6, 2021 at 5:07
1
I faced a similar problem. I am using Anaconda on windows and I resolved it as follows:
1) search for «Anaconda prompt» from the start menu
2) Right click and select «Run as administrator»
3) The follow the installation steps…
This takes care of the permission issues
answered Sep 6, 2018 at 14:38
0
Here is how I encountered the error:
import os
path = input("Input file path: ")
name, ext = os.path.basename(path).rsplit('.', 1)
dire = os.path.dirname(path)
with open(f"{dire}\{name} temp.{ext}", 'wb') as file:
pass
It works great if the user inputs a file path with more than one element, like
C:\Users\Name\Desktop\Folder
But I thought that it would work with an input like
file.txt
as long as file.txt is in the same directory of the python file. But nope, it gave me that error, and I realized that the correct input should’ve been
.\file.txt
answered Dec 18, 2020 at 21:40
Ann ZenAnn Zen
26.7k7 gold badges36 silver badges57 bronze badges
2
As @gulzar said, I had the problem to write a file 'abc.txt' in my python script which was located in Z:projecttest.py:
with open('abc.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write("TEST123")
Every time I ran a script in fact it wanted to create a file in my C drive instead Z!
So I only specified full path with filename in:
with open('Z:\project\abc.txt', 'w') as file: ...
and it worked fine. I didn’t have to add any permission nor change anything in windows.
answered Apr 21, 2021 at 9:54
NooneNoone
1511 silver badge6 bronze badges
That’s a tricky one, because the error message lures you away from where the problem is.
When you see "__init__.py" of an imported module at the root of an permission error, you have a naming conflict. I bed a bottle of Rum, that there is "from tkinter import *" at the top of the file. Inside of TKinter, there is the name of a variable, a class or a function which is already in use anywhere else in the script.
Other symptoms would be:
- The error is prompted immediately after the script is run.
- The script might have worked well in previous Python versions.
- User Mixon’s long epos about administrator execution privileges has no impact at all. There would be no access errors to the files mentioned in the code from the console or other pieces of software.
Solution:
Change the import line to «import tkinter» and add the namespace to tkinter methods in the code.
answered Aug 8, 2021 at 2:30
HelenHelen
861 silver badge5 bronze badges
Two easy steps to follow:
- Close the document which is used in your script if it’s open in your PC
- Run Spyder from the Windows menu as «Run as administrator»
Error resolved.
answered Feb 11 at 7:33
In my case, I had the file (to be read or accessed through python code) opened and unsaved.
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'path_to_the_open_file'
I had to save and close the file to read/access, especially using pandas read (pd.read_excel, pd.read_csv etc.) or the command with open():
answered Mar 15 at 12:00
Bhanu ChanderBhanu Chander
3701 gold badge5 silver badges16 bronze badges
The most common reason for this could be, permission to the folder/file for that particular user.
Grant write permissions to the directory where you want to write files. You can do this by changing the ownership or permissions of the directory using the chmod or chown commands.
Example:
# Change ownership of the directory to the current user
sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /path/to/directory
# Grant write permissions to the directory
sudo chmod -R 777 /path/to/directory
answered May 25 at 15:37
This error actually also comes when using keras.preprocessing.image so for example:
img = keras.preprocessing.image.load_img(folder_path, target_size=image_size)
will throw the permission error. Strangely enough though, the problem is solved if you first import the library: from keras.preprocessing import image and only then use it. Like so:
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(180,180))
Gulzar
22.5k23 gold badges106 silver badges189 bronze badges
answered Dec 11, 2020 at 15:03
BendemannBendemann
70511 silver badges30 bronze badges
2
Python responds with PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied message when you try to open a file with the following exceptions:
This article will help you to resolve the issues above and fix the PermissionError message.
You specify a path to a directory instead of a file
When you call the open() function, Python will try to open a file so that you can edit that file.
The following code shows how to open the output.txt file using Python:
with open('text_files/output.txt', 'w') as file_obj:
file_obj.write('Python is awesome')
While opening a file works fine, the open() function can’t open a directory.
When you forget to specify the file name as the first argument of the open() function, Python responds with a PermissionError.
The code below:
with open('text_files', 'w') as file_obj:
Gives the following output:
Because text_files is a name of a folder, the open() function can’t process it. You need to specify a path to one file that you want to open.
You can write a relative or absolute path as the open() function argument.
An absolute path is a complete path to the file location starting from the root directory and ending at the file name.
Here’s an example of an absolute path for my output.txt file below:
abs_path = "/Users/nsebhastian/Desktop/DEV/python/text_files/output.txt"
When specifying a Windows path, you need to add the r prefix to your string to create a raw string.
This is because the Windows path system uses the backslash symbol to separate directories, and Python treats a backslash as an escape character:
# Define a Windows OS path
abs_path = r"DesktopDEVpythontext_filesoutput.txt"
Once you fixed the path to the file, the PermissionError message should be resolved.
The file is already opened elsewhere (in MS Word or Excel, .etc)
Microsoft Office programs like Word and Excel usually locked a file as long as it was opened by the program.
When the file you want to open in Python is opened by these programs, you will get the permission error as well.
See the screenshot below for an example:
To resolve this error, you need to close the file you opened using Word or Excel.
Python should be able to open the file when it’s not locked by Microsoft Office programs.
You don’t have the required permissions to open the file
Finally, you will see the permission denied error when you are trying to open a file created by root or administrator-level users.
For example, suppose you create a file named get.txt using the sudo command:
The get.txt file will be created using the root user, and a non-root user won’t be able to open or edit that file.
To resolve this issue, you need to run the Python script using the root-level user privilege as well.
On Mac or Linux systems, you can use the sudo command. For example:
On Windows, you need to run the command prompt or terminal as administrator.
Open the Start menu and search for “command”, then select the Run as administrator menu as shown below:
Run the Python script using the command prompt, and you should be able to open and write to the file.
Conclusion
To conclude, the error “PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied” in Python can be caused by several issues, such as: opening a directory instead of a file, opening a file that is already open in another program, or opening a file for which you do not have the required permissions.
To fix this error, you need to check the following steps:
- Make sure that you are specifying the path to a file instead of a directory
- Close the file if it is open in another program
- Run your Python script with the necessary permissions.
By following these steps, you can fix the “PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied” error and successfully open and edit a file in Python.
Table of Contents
Hide
- What is PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error?
- How to Fix PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error?
- Case 1: Insufficient privileges on the file or for Python
- Case 2: Providing the file path
- Case 3: Ensure file is Closed
- Conclusion
If we provide a folder path instead of a file path while reading file or if Python does not have the required permission to perform file operations(open, read, write), you will encounter PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error
In this article, we will look at what PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error means and how to resolve this error with examples.
We get this error mainly while performing file operations such as read, write, rename files etc.
There are three main reasons behind the permission denied error.
- Insufficient privileges on the file or for Python
- Passing a folder instead of file
- File is already open by other process
How to Fix PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error?
Let us try to reproduce the “errno 13 permission denied” with the above scenarios and see how to fix them with examples.
Case 1: Insufficient privileges on the file or for Python
Let’s say you have a local CSV file, and it has sensitive information which needs to be protected. You can modify the file permission and ensure that it will be readable only by you.
Now let’s create a Python program to read the file and print its content.
# Program to read the entire file (absolute path) using read() function
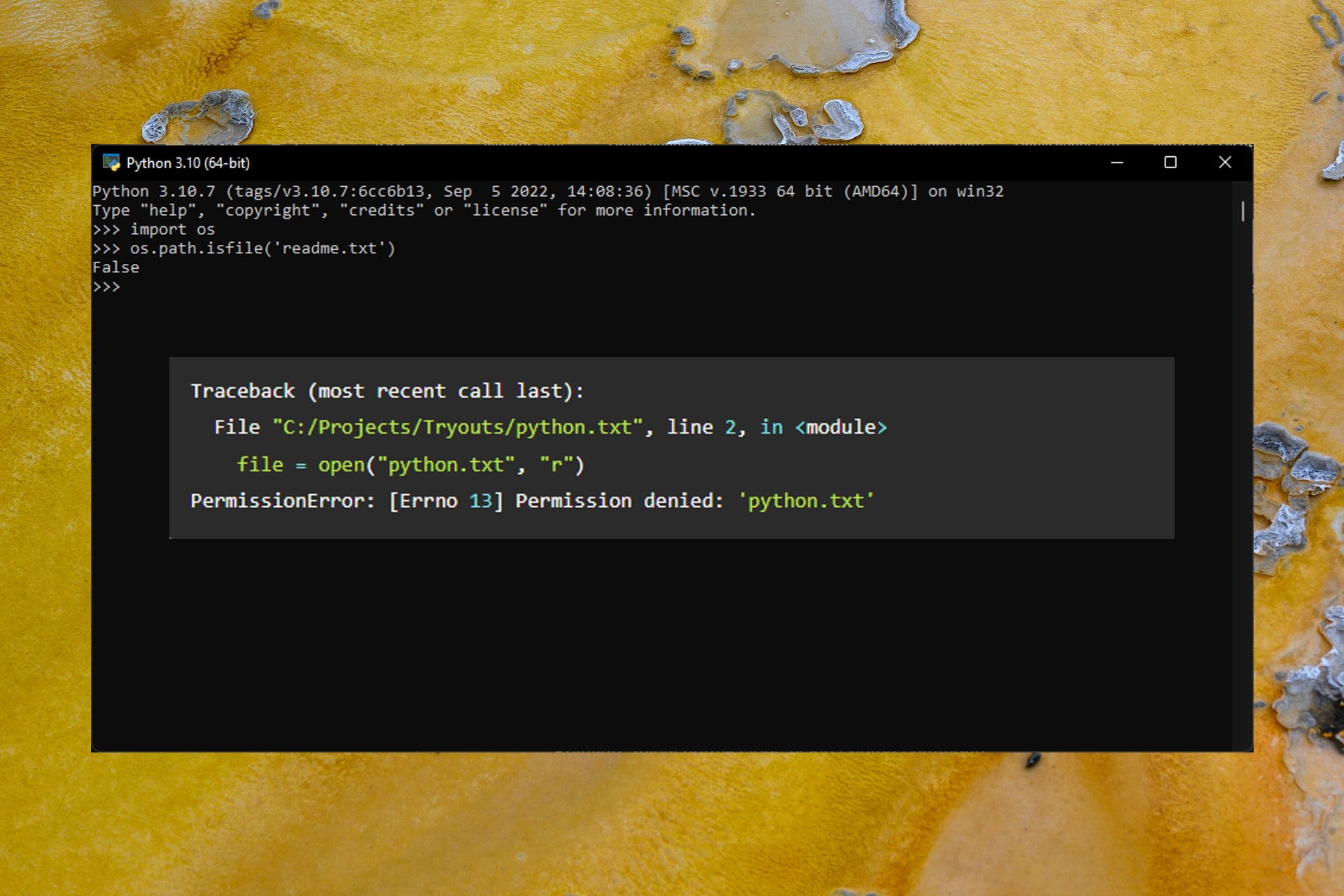
file = open("python.txt", "r")
content = file.read()
print(content)
file.close()Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:/Projects/Tryouts/python.txt", line 2, in <module>
file = open("python.txt", "r")
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'python.txt'When we run the code, we have got PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error because the root user creates the file. We are not executing the script in an elevated mode(admin/root).
In windows, we can fix this error by opening the command prompt in administrator mode and executing the Python script to fix the error. The same fix even applies if you are getting “permissionerror winerror 5 access is denied” error
In the case of Linux the issue we can use the sudo command to run the script as a root user.
Alternatively, you can also check the file permission by running the following command.
ls -la
# output
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root srinivas 46 Jan 29 03:42 python.txtIn the above example, the root user owns the file, and we don’t run Python as a root user, so Python cannot read the file.
We can fix the issue by changing the permission either to a particular user or everyone. Let’s make the file readable and executable by everyone by executing the following command.
chmod 755 python.txt
We can also give permission to specific users instead of making it readable to everyone. We can do this by running the following command.
chown srinivas:admin python.txt
When we run our code back after setting the right permissions, you will get the following output.
Dear User,
Welcome to Python Tutorial
Have a great learning !!!
CheersCase 2: Providing the file path
In the below example, we have given a folder path instead of a valid file path, and the Python interpreter will raise errno 13 permission denied error.
# Program to read the entire file (absolute path) using read() function
file = open("C:\Projects\Python\Docs", "r")
content = file.read()
print(content)
file.close()Output
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "c:PersonalIJSCodeprogram.py", line 2, in <module>
file = open("C:\Projects\Python\Docs", "r")
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'C:\Projects\Python\Docs'We can fix the error by providing the valid file path, and in case we accept the file path dynamically, we can change our code to ensure if the given file path is a valid file and then process it.
# Program to read the entire file (absolute path) using read() function
file = open("C:\Projects\Python\Docspython.txt", "r")
content = file.read()
print(content)
file.close()Output
Dear User,
Welcome to Python Tutorial
Have a great learning !!!
CheersCase 3: Ensure file is Closed
While performing file operations in Python, we forget to close the file, and it remains in open mode.
Next time, when we access the file, we will get permission denied error as it’s already in use by the other process, and we did not close the file.
We can fix this error by ensuring by closing a file after performing an i/o operation on the file. You can read the following articles to find out how to read files in Python and how to write files in Python.
Conclusion
In Python, If we provide a folder path instead of a file path while reading a file or if the Python does not have the required permission to perform file operations(open, read, write), you will encounter PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error.
We can solve this error by Providing the right permissions to the file using chown or chmod commands and also ensuring Python is running in the elevated mode permission.
Srinivas Ramakrishna is a Solution Architect and has 14+ Years of Experience in the Software Industry. He has published many articles on Medium, Hackernoon, dev.to and solved many problems in StackOverflow. He has core expertise in various technologies such as Microsoft .NET Core, Python, Node.JS, JavaScript, Cloud (Azure), RDBMS (MSSQL), React, Powershell, etc.
Try these solutions to fix PermissionError [Errno 13] Permission denied
by Megan Moore
Megan is a Windows enthusiast and an avid writer. With an interest and fascination in all things tech, she enjoys staying up to date on exciting new developments… read more
Updated on February 9, 2023
Reviewed by
Vlad Turiceanu
Srinivas Ramakrishna is a Solution Architect and has 14+ Years of Experience in the Software Industry. He has published many articles on Medium, Hackernoon, dev.to and solved many problems in StackOverflow. He has core expertise in various technologies such as Microsoft .NET Core, Python, Node.JS, JavaScript, Cloud (Azure), RDBMS (MSSQL), React, Powershell, etc.
Try these solutions to fix PermissionError [Errno 13] Permission denied
by Megan Moore
Megan is a Windows enthusiast and an avid writer. With an interest and fascination in all things tech, she enjoys staying up to date on exciting new developments… read more
Updated on February 9, 2023
Reviewed by
Vlad Turiceanu
Passionate about technology, Windows, and everything that has a power button, he spent most of his time developing new skills and learning more about the tech world. Coming… read more
- If Python cannot locate a file or does not have the necessary permissions to open it, then the PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error may occur.
- Release 3.7 introduced Python into the Microsoft Store which can cause permission denied errors.
- The latest version of Python is 3.10.7 and is available for macOS, Linux/UNIX, and Windows 8 or newer.
XINSTALL BY CLICKING THE DOWNLOAD FILE
This tool repairs common computer errors by replacing the problematic system files with the initial working versions. It also keeps you away from system errors, BSoDs, and repairs damages made by malware and viruses. Fix PC issues and remove viruses damage now in 3 easy steps:
- Download and Install Fortect on your PC
- Launch the tool and Start scanning to find broken files that are causing the problems
- Right-click on Start Repair to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Fortect has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
Python is a program designed for building websites, software, and more using a high-level programming language. However, users have recently reported receiving a permission denied error in Windows 11. Here’s how to fix PermissionError [Errno 13] Permission denied error in Python.
Because Python uses a general-purpose language, it can be used to build a variety of different types of programs rather than focusing on a specific variable.
For those wanting to learn more about developing and coding, Python is one of the easiest programming languages to learn, making it perfect for beginners.
Why do I get the permission denied error in Python?
Users encounter PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied error if providing Python with a file path that does not have permission to open or edit the file. By default, some files do not allow certain permissions. This error may also occur if providing a folder rather than a file.
If the file is already being operated by another process, then you may encounter the permission denied error in Python. If you’re receiving the Python runtime error, we offer solutions for that as well.
How do I fix the Python permission denied error in Windows 11?
1. Check file path
One of the main causes of PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied is because Python is trying to open a folder as a file. Double-check the location of where you want to open the file and ensure there isn’t a folder that exists with the same name.
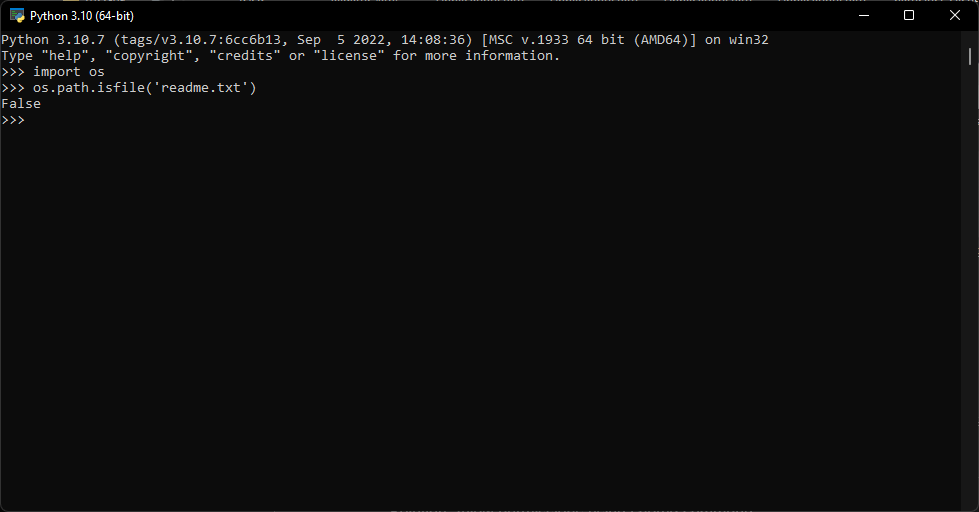
Run the os.path.isfile(filename) command replacing filename with your file to check if it exists. If the response is false, then the file does not exist or Python cannot locate it.
2. Allow permissions using chomd
If the file does not have read and write permissions enabled for everyone, then you may encounter the permission denied error in Python. Try entering the chomd 755 filename command and replace filename with the name of your file.
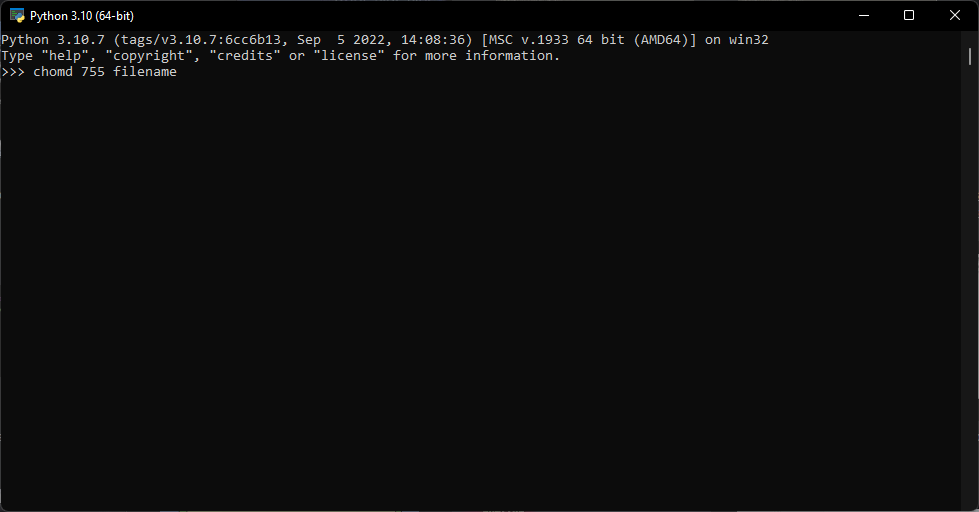
This command gives everyone permission to read, write, and execute the file, including the owner. Users can also apply this command to entire directories. Running the ls -al command will provide a list of files and directories and their permissions.
3. Adjust file permissions
- Navigate to the location of your file in file explorer.
- Right-click on the file and select Properties.
- Click the Security tab then select your name under Group or user names.
- Select Edit and go through and check permissions.
- Click Apply then OK.
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to missing or corrupted system files and repositories of your Windows.
Be sure to use a dedicated tool, such as Fortect, which will scan and replace your broken files with their fresh versions from its repository.
Adjusting the permissions of the file that you’re trying to open will allow Python to read, write, and execute the file.
- Fix: the new Outlook could not successfully launch error
- OBS Stuttering When Recording? 3 Ways to Quickly Fix it
- Apoint.exe: What is it & How to Fix its Errors
- NTVDM.exe: What is it & How to Fix its Errors
- Windows 11’s Clipboard needs shelf support, users say
4. Turn off execution aliases
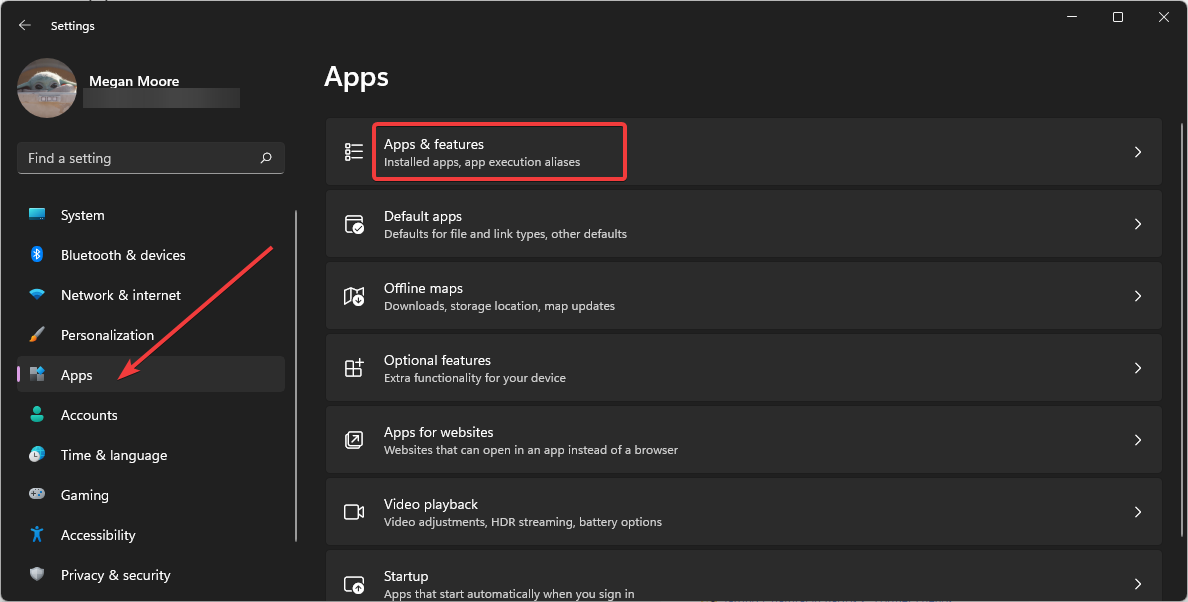
- Click on Start and open Settings (or press Windows + I).
- Open Apps then select Apps & features.
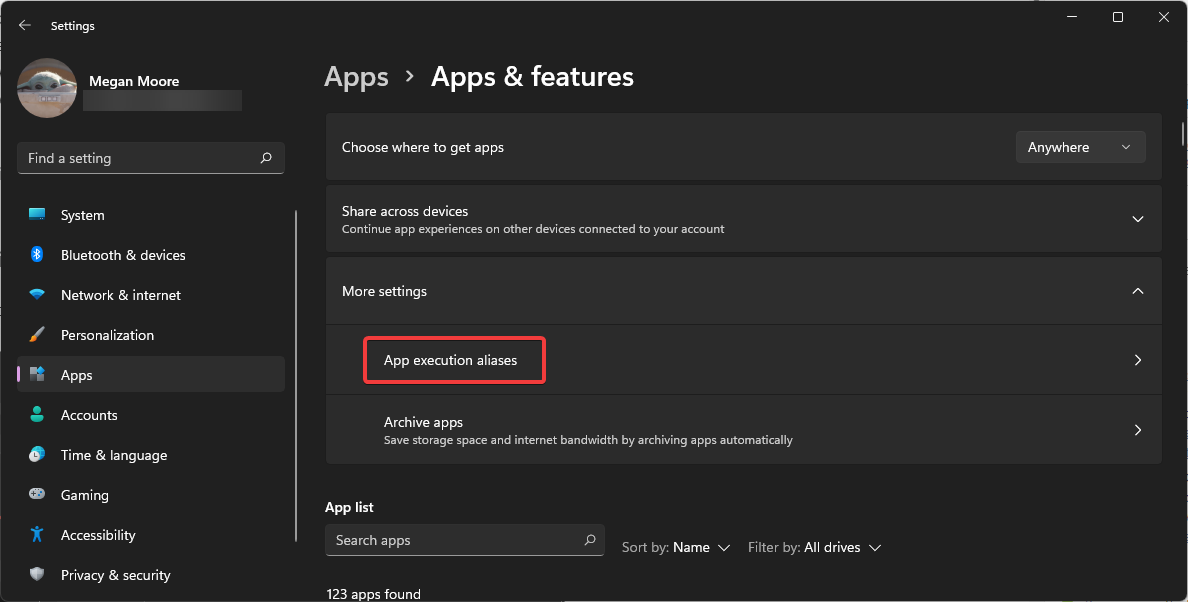
- Open the drop-down menu next to More settings.
- Click App execution aliases.
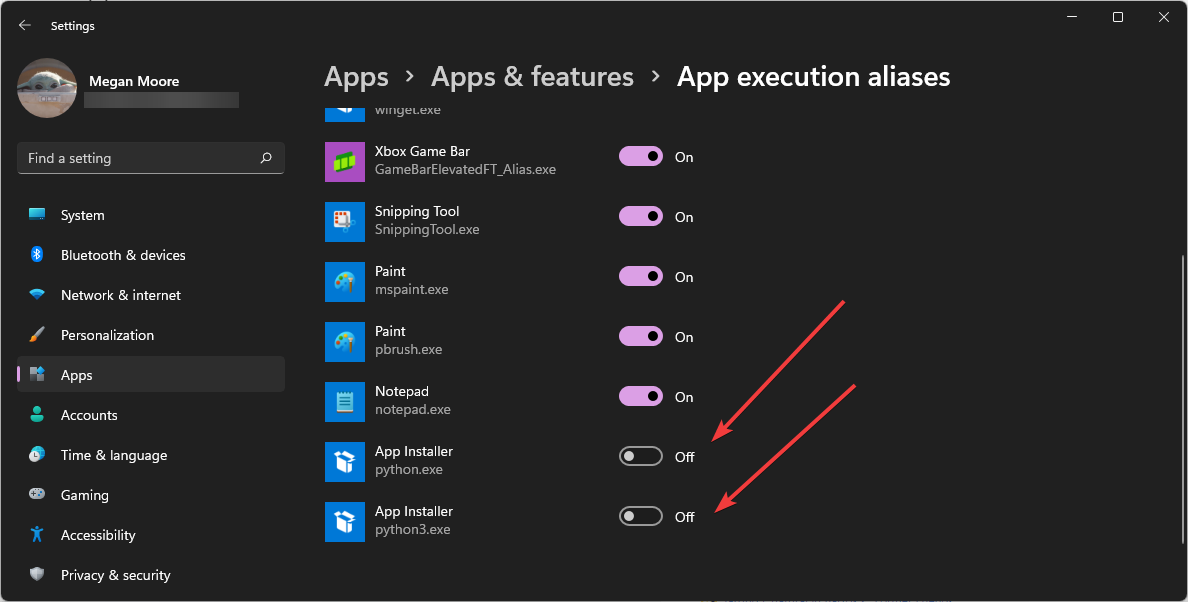
- Locate the two App Installers for python.exe and python3.exe and toggle both to Off.
Python was added to the Microsoft Store for version 3.7 which introduced permission denied errors because it created two installers: python.exe and python3.exe. Disabling the Microsoft Store versions of Python should fix the permissions denied error.
5. Update Windows and drivers
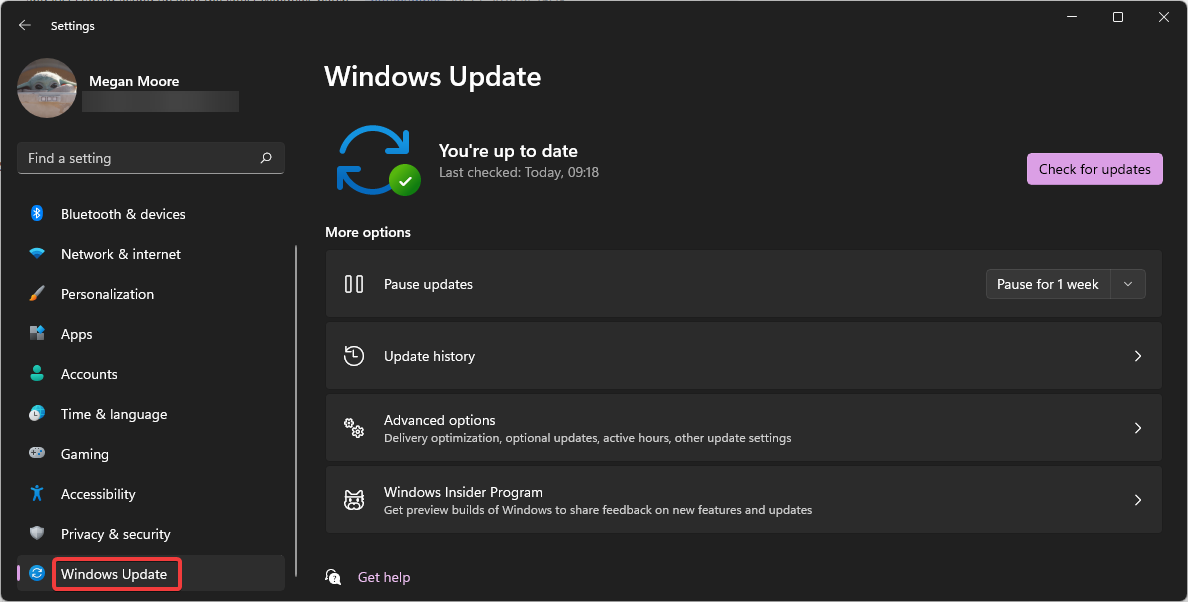
- Click on Start and open Settings (or press Windows + I).
- Scroll down and select Windows Update.
- Perform any available updates.
- Select Advanced options.
- Under Additional options, click on Optional updates.
- Run any driver updates.
If you’re suddenly encountering the Python permission denied error and none of the above solutions worked, then check for any Windows 11 updates and perform any available driver updates.
If this method didn’t work either, we recommend you use specialized driver update software, DriverFix.
DriverFix is a fast and automated solution for finding all outdated drivers and updating them to their latest versions. The installation process it’s fast and safe so no additional issues will occur.

DriverFix
Fast and simple tool to maintain all drivers updated.
What is the latest version of Python?
As of the release of this article, the latest version of Python is 3.10.7 which is available for Windows 8 and newer and is not compatible with older versions including Windows 7. Python supports Windows, macOS, Linux/UNIX, and more.
However, If users want to use older versions of Python, they can access releases 2.7 and newer or they can download a specific version of a release.
If you want a quick way to open PY files on Windows 10 and 11, we offer a guide for that as well.
Hopefully, one of the above solutions helped you fix the Python permission denied error in Windows 11. Let us know in the comments which step worked for you or if you have any suggestions for a different solution.
Still experiencing issues?
SPONSORED
If the above suggestions have not solved your problem, your computer may experience more severe Windows troubles. We suggest choosing an all-in-one solution like Fortect to fix problems efficiently. After installation, just click the View&Fix button and then press Start Repair.
Table of Contents
Hide
-
What is permission denied error?
- How these permissions are defined?
-
Reasons of permissionerror ERRNO 13 in Python
- Using folder path instead of file path while opening a file
- Trying to write to a file which is a folder
- Trying to write to a file which is already opened in an application
- File permission not allowing python to access it
- File is hidden with hidden attribute
-
Conclusion
- Related Posts
Permission denied means you are not allowed to access a file. But why this happens? This is because a file has 3 access properties – read, write, and execute. And 3 sets of users – owner, group, and others. In this article we will look at different solutions to resolve PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied.
What is permission denied error?
Suppose you have a file in your computer but you can’t open it. Strangely another user can open the same file. This is because you don’t have permission to read the content of that file.
Permission denied on files to protect them. For example, you have stored username & password for your database in a file so you never want it to be accessible to anyone except the database application and you. That’s why you will restrict it from other applications, software, processes, users, APIs etc.
In a system, root user can access everything. So, we seldom use the root account otherwise there is no meaning of security. A software running with root privilege can access your password file which you wanted to be secure. That’s why sudo should be used with caution.
How these permissions are defined?
There are 3 types of permissions – read, write and execute. With read permission a software, process, application, user etc. can read a file. Similarly, with write permission they can write to the file. Execute is used to run it.
Now the question is, how to apply these permissions to different software, users etc.? Well there are 3 types of users – owner, group, and others. So, you can assign 3 sets of permissions, like this –
| User | Description | Permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Owner | An account of system who we want to separately assign permissions | r – read w – write x – execute |
| Group | A set of multiple accounts, software, processes who can share the same permissions | r – read w – write x – execute |
| Others | All the other entities of system | r – read w – write x – execute |
Let’s get back to our password file example. Now you are into others user category because you are not the owner of the file and probably not the part of group. People use to give least permissions to the others because these are the access levels for everyone.
The password file won’t have any permission in others category. And trying to access that will result in permission error: permission denied.
Reasons of permissionerror ERRNO 13 in Python
Primarily these are the reasons of permissionerror: errno13 permission denied in Python –
- Using folder path instead of file path while opening a file.
- Trying to write to a file which is a folder.
- Trying to write to a file which is already opened in an application.
- File permission not allowing python to access it.
- File is hidden with hidden attribute.
Let’s understand each of these reasons one by one and check their solutions.
Using folder path instead of file path while opening a file
To open a file for reading or writing, you need to provide the absolute or relative path to the file in open function. Sometimes we create path of parent folder instead of file and that will lead to the permission error 13. Check out this code –
file = open("C:\users\akash\Python\Documents", "r")
file.close()
The output will be –
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "jdoodle.py", line 2, in <module>
file = open("C:\users\akash\Python\Documents", "r")
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'C:\users\akash\Python\Documents'
The reason for the error in above code is that we have used C:usersakashPythonDocuments as path which is a directory. Instead we needed to use C:usersakashPythonDocuments\myFile.csv.
Trying to write to a file which is a folder
This is a common case. Suppose you want to write to a file using Python but a folder with same name exists at that location then Python will get confused and try to write to a folder. This is not a right behavior because folders are not files and you can’t write anything on them. They are used for holding files only.
Trying to write to a file which is a folder will lead to permission error errno 13. Check this code –
# Directory Structure
# 📂/
# |_ 📂Users
# |_ 📁myFile
file = open("/Users/myFile", "w")
file.write("hello")
file.close()
The output will be –
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "jdoodle.py", line 2, in <module>
file = open("/Users/myFile", "r")
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/Users/myFile'
In the above example we showed the directory structure and tried to write to myFile. But myFile is already a name of directory in the path. Generally, if a file doesn’t exist and we try to write to it then Python creates the file for us. But in this case there is already a directory with the provided name and Python will pick it. This will lead to permission error.
The solution to this problem is to either delete the conflicting directory or use a different file name.
Trying to write to a file which is already opened in an application
If a file is already opened in an application then a lock is added to it so that no other application an make changes to it. It depends on the applications whether they want to lock those files or not.
If you try to write to those files or more, replace, delete them then you will get permission denied error.
This is very common in PyInstaller if you open a command prompt or file explorer inside the dist folder, then try to rebuild your program. PyInstaller wants to replace the contents of dist but it’s already open in your prompt/explorer.
The solution to this problem is to close all the instances of applications where the file is opened.
File permission not allowing python to access it
In the above section we talked about file permissions. Python will be in others category if it is not set as user or in a group. If the file has restrictive permissions for others then Python won’t be able to access it.
Suppose the permission to the file is –
Owner – read, write, execute
Group – read, write
Others – none
Then only owner and group will be able to read and write to the file. Others will not be able to access it. Check out this image –
In this image the file owner is www, group is www, owner permissions are read+write, group permission is read only, while others have no permissions.
The solution to this problem is to either provide appropriate permission to the file for others, or add Python as owner or to the group.
Another solution is to run Python with root privilege.
File is hidden with hidden attribute
If your file is hidden then python will raise permission error. You can use subprocess.check_call() function to hide/unhide files. Check this code –
import subprocess myPath = "/Users/myFile.txt" subprocess.check_call(["attrib", "-H", myPath]) file_ = open(myPath, "w")
In the above code -H attribute is used to unhide the file. You an use +H to hide it again.
Conclusion
In this article we saw a number of reasons for Python to throw PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied and discussed about their solutions with code examples. Follow the steps provided in article and you will be able to resolve this issue.
Errno 13 permission denied is an error message when Python cannot read your file due to an error in your code or a conflict in the file system of your operating system. This article will show you other causes of this error message as well, and we’ll teach you how to fix them all.
Everything that you’ll learn will let you understand how Python handles files and how it responds if it encounters a problem in the process. Now, switch on your computer, and let’s solve the “permission denied” error in Python.
Contents
- Why Is Python Denied a Permission? All Possible Causes
- – You’re Reading a Folder Like a File
- – Python Is Not Permitted To Read the File
- – The File Is Opened in Another Program
- – There Is Forward Slash Before the Folder Name
- – You’re Using “Python 3.7” From Microsoft Store
- How To Solve the “Permission Denied Error” in Python? Simplified
- – Confirm That You’re Opening a File Using “OS.path.isfile()”
- – Grant Python Permissions To Read the File
- – Close the Application That’s Using the File
- – Remove the Forward Slash Before Your Folder
- – Toggle off Application Execution Aliases in Windows
- Conclusion
Why Is Python Denied a Permission? All Possible Causes
Python was denied permission because of the following:
- You’re reading a folder like a file
- Python is not permitted to read the file
- The file is opened in another program
- There is a forward slash before the folder name
- You’re using “Python 3.7” from Microsoft Store
– You’re Reading a Folder Like a File
The first cause of the “permission denied” error is when Python tries to open a folder name like a file using Python’s in-built “open()” function. By default, this function will open files in a directory, and it will return a file object. But it’s not designed to open a folder, and if you tell it to open a folder, that’s when the permission error occurs.
For example, the following code aims to open a file in a directory, but there is no reference to the file.
# results in a permission error.
file = open(“C:\Users\HP\Desktop\PIE\PIE_CLE_01”)
# Read the file.
file_content = file.read()
# Print the file.
print(file_content)
# Close the file handle.
file.close()
– Python Is Not Permitted To Read the File
When Python is not permitted to read a file, it will also report a “permission denied” error. This happens because, on operating systems like Windows and Linux, you can configure file access for a user account.
So, if your user account does not have access to a file, any Python installation for your account cannot open the file. This means any attempt to open the file using the “open()” function in Python will result in a permission error.
– The File Is Opened in Another Program
In the Windows operating system, if a file is opened in an application, you can’t read it using Python. For example, if you’re working with “File_A.csv” in Microsoft Excel, Windows will not allow Python to open “File_A.csv” using its “open()” function.
This prevents conflicts where one application can make changes, and another can delete those changes at the same time. That’s because, when you open a file using the “open()”, you can change the file content.
– There Is Forward Slash Before the Folder Name
In Unix, if there is a forward slash before the folder name in your file-uploading code, you’ll run into the permission error. That’s because the forward slash before a folder’s name in Unix is a sign that the folder should be in the “root directory”.
This directory contains the core and sensitive files and directories of your Unix system, for example, “/bin/” and “/usr/”. However, ordinary processes like your file-uploading code don’t have permission to modify this “root directory”.
– You’re Using “Python 3.7” From Microsoft Store
If you’re using “Python 3.7” from Microsoft Store, you can encounter the “permission denied” error while working with Python. That’s because this Python has two executables, “python.exe” and “python3.exe” and this can create a conflict when working with files.
How To Solve the “Permission Denied Error” in Python? Simplified
You can solve the “permission denied error” in Python using the following:
- Confirm that you’re opening a file using “os.path.isfile()”
- Grant Python permissions to read the file
- Close the application that’s using the file
- Remove the forward slash before your folder
- Toggle off application execution aliases in Windows
– Confirm That You’re Opening a File Using “OS.path.isfile()”
Before your code opens a file, you should confirm that the “file” is a file using “os.path.isfile()”. The “isfile()” function accepts a “file path”, and it will return Boolean “true” if the path belongs to a file and “false” otherwise.
Now, the following is the updated code that was reading a folder name instead of a file. This time, we use “os.path.isfile()” to check the file path, and if it’s a file, you can read and print the file content.
# Assign a file path
file_path = “C:\Users\HP\Desktop\PIE\PIE_CLE_01”
# Check the file
is_file = os.path.isfile(file_path)
# If it’s a file, open and print the file
# content.
if (is_file):
file = open(file_path)
# Read the file
file_content = file.read()
# Print the file
print(file_content)
# Close the file handle
file.close()
else:
print(“Not a file.”)
– Grant Python Permissions To Read the File
If you have “File_A.txt” that’s not accessible to your user account and your Python file (“File_B.py”), you can change the file permissions of “File_A.txt” or update the “file permissions” of the Python file, “File_B.py”.
On Windows, you can use the following steps to update the privilege of your Python file:
- Open Windows explorer and navigate to the location of the Python file.
- Right-click on it and select “Properties” to open a dialog window
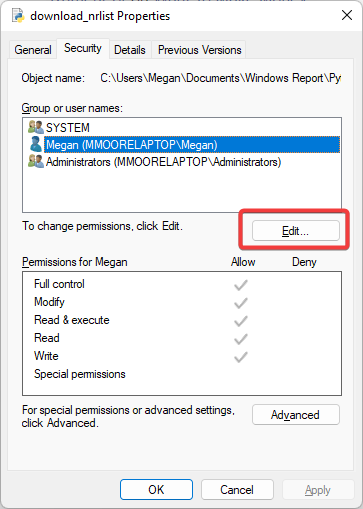
- Select the “Security” tab and choose your account username under “Group or user names”.
- Click on “Edit” and set the permissions that are required. This will be “Full Control”, “Modify”, “Read & execute”, “Read” and “Write”.
- Save your changes using the “Apply” button and click on “OK” to confirm.
On Linux, you can change the file permission using the “chmod 755 your_file_name.extension” or “chown account_username:admin your_file_name.extension”.
The “chmod 755” command will give you read/write/execute privilege on “your_file_name.extension” and the latter is a valid file on your computer. While the “chown” command is short for “change ownership” and here, the command will assign you administrator rights on the file.
You can use command on your Linux terminal, and then you can read the file using Python and the “open()” function.
– Close the Application That’s Using the File
When another application has opened a file that you’ll like to read in Python, you should close the application. On Windows, you do the following:
- Locate the application’s icon on the Taskbar.
- Right-click on it and select “Close”.
However, if the application failed to close using the steps above, you can use the command prompt:
- Click on the “Start” menu and search for “cmd”.
- Right-click the command prompt and select “Run as administrator”.
- Type “tasklist” on the command line and hit “enter” on your keyboard.
- Locate the application from the command output and take note of its PID number.
- Type the following and replace 1234 with the application’s PID: taskkill /f /PID 1234
- Press enter on your keyboard to close the application.
- Return to your Python code, and it should have access to the file.
– Remove the Forward Slash Before Your Folder
While working on Unix, you should remove the forward slash from your folder name to prevent the permission error. So, in your code, if you have something like “path = ‘/folderX/folderY’” change it to “path = ‘folder1/folder2′”.
From the latter, we removed the forward-slash (“/”) before “folder1”, and this defaults it to the current working directory. This is safe, and Unix will not stop your code from uploading to “folder1”.
– Toggle off Application Execution Aliases in Windows
You can toggle off application execution aliases in Windows if you’re getting the permission “denied error” from the Python that’s installed from Microsoft Store. To do this, use the following steps:
- Click on the “Start” menu and select “Settings”.
- Locate “Apps” in the left sidebar and choose “Apps & features”.
- Open “More settings” and click on “App execution aliases”.
- Locate the application installers for “python3.exe” and “python.exe” and toggle them off.
- Switch back to your Python code, and it should read your file.
Conclusion
This article explains why Python shows the “errno 13 permission denied” error and how you can fix it. The following are what you should remember about this error:
- An attempt to read a folder name like a file will result in the permission denied error.
- You will get a permission error if your user account is not permitted to read a file.
- If an application like Microsoft Excel has the file opened, an attempt to read the file in Python will result in a permission error.
- You can solve the “permission denied” error by checking the validity of the file using “os.path.isfile()” or “chmod 755 your_file_name.extension”.
At this stage, you know how to solve and prevent the “Python permission” error. Teach your fellow Python developers your newly found knowledge by sharing our article.
- Author
- Recent Posts
Your Go-To Resource for Learn & Build: CSS,JavaScript,HTML,PHP,C++ and MYSQL. Meet The Team

Your Go-To Resource for Learn & Build: CSS,JavaScript,HTML,PHP,C++ and MYSQL. Meet The Team
The python error “PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied” can be fixed in various ways after knowing the root cause. This error mainly occurs through the open method which is used to open and read file. For example, if the path passed into the open() method as an argument is not a file, python will throw an error. Also, if you passed in a folder path instead of a file path. The solution to this approach is to apply how programmers think and check first if the path is a file with the os.path.isfile() method before you open.
import os
path = r"/path/to/filename.txt"
// check if the path is a file to avoid error
assert os.path.isfile(path)
with open(path, "r") as f:
passThe above code will help us to know if the path called in the open method is really a file. If is not, because we’re checking we will be able to perform another operation. That’s how you fix the python error permissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied if the bug is related to the file path.
Another cause of the above error is related to the operating system and python. It could be that there is a restriction on the directory where you want to perform the file operation. If that is the case, then python will not have the required permission to open, read or write to a file and if you try, it will throw the error PermissionError: [errno 13] permission denied.
NB: The PermissionError: [errno 13] permission denied error occurs when you try to access a file from Python without having the required permissions to perform file operation.
import csv
with open("employees.csv", "r") as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
for r in reader:
print(r)If we run the above python application, because we don’t have the necessary permission to read the file, it will throw an error with a stack-trace.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "app.py", line 3, in <module>
with open("employees.csv", "r") as file:
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'employees.csv'To fix this error, open the employees.csv file directory in your terminal and run this ls -la command to check permission.
Ls -laCheck also, fix error – type of expression is ambiguous without more context in swift
If you take a look at the response of the above command. You will see that the file is owned by the root user and no other person can have access to it except him/she alone.
rw-rw-rw- 1 root staff 46 Oct 5 07:01 employees.csvTo get it resolve, you need to change the user of the file so that anyone can access it and by doing that we can use our python application to also perform operations on the same file. So type and hit enter on the command-line whiles in the file directory.
chmod 755 employees.csvThis solves the error and if we run application, it will read the content of the file and print it successfully.
That’s how you fix the permission denied errno 13 bug in python
Tagged permission denied errno 13
Python can only open, read from, and write to files if an interpreter has the necessary permissions. If you try to open, read from, or write to a file over which Python has no permissions, you’ll encounter the PermissionError: [errno 13] permission denied error.
In this guide, we discuss what this error means and why it is raised. We’ll walk through an example so you can learn exactly how to solve this error.

Find Your Bootcamp Match
- Career Karma matches you with top tech bootcamps
- Access exclusive scholarships and prep courses
Select your interest
First name
Last name
Phone number
By continuing you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy, and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email.
PermissionError: [errno 13] permission denied
Computers use file permissions to protect the integrity of files. Some files have restricted access by default. You can change the access permissions of a file at any time.
Let’s say you are working on an important program. You may only want that program to be readable by you. To accomplish this, you could modify the “read” permissions on all the files and folders in your program. This would limit access to your program.
Any file that you try to access from a Python program must be readable by the user or group that is running the file.
If you are running a Python script from a web server process, for instance, you would need to make sure that the user that owns the web server has access to all the files that you reference in your code.
An Example Scenario
We’re going to build a program that reads a list of NFL scores from a file into a program.
We have a file called afc_east.csv which contains the following:
Bills,4,0 Patriots,2,1 Dolphins,1,3 Jets,0,4
Our file is a CSV. We’re going to import the Python csv module into our code so we can work with the file:
Next, let’s open up our file in our Python program. We can do this using the csv.reader() statement:
with open("afc_east.csv", "r") as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
for r in reader:
print(r)
This code will open up the file called afc_east.csv in read mode. Then, the CSV reader will interpret the file. The CSV reader will return a list of values over which we can iterate. We then print each of these values to the console using a for loop and a print() statement so we can see the contents of our file line-by-line.
Let’s run our program to see if it works:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test.py", line 3, in <module>
with open("afc_east.csv", "r") as file:
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: 'afc_east.csv'
Our code returns an error.
The Solution
A PermissionError indicates that Python does not have the right permissions to access a file.
Let’s check the permissions of our file. We can do this using the ls -la command:
We can see that the afc_east.csv file is owned by the root user:
-rw-rw-rw- 1 root staff 46 Oct 5 07:01 afc_east.csv
This is a problem because we don’t run Python as root. This means that Python cannot read our file. To fix this error, we need to change the ownership permissions of our file using the chown command:
chown james:admin afc_east.csv
This command makes the “james” user and the “admin” group the owners of the file.
Alternatively, we could change the permissions of the file using the chmod command:
This command makes our file readable and executable by everyone. The file is only writable by the owner. Let’s try to run our Python script again:
['Bills', '4', '0'] ['Patriots', '2', '1'] ['Dolphins', '1', '3'] ['Jets', '0', '4']
Our code successfully prints out all of the scores from our file.
Conclusion
The PermissionError: [errno 13] permission denied error occurs when you try to access a file from Python without having the necessary permissions.
To fix this error, use the chmod or chown command to change the permissions of the file so that the right user and/or group can access the file. Now you have the skills you need to solve this error like a pro!