Команда CHKDSK предназначена для проверки и устранения логических ошибок на жестком диске. Ниже мы рассмотрим особенности её работы и другие функции утилиты.
Содержание
- Проверка жесткого диска в работающей Windows
- Проверка диска из командной строки
- Команды для работы с CHKDSK в командной строке
- Восстановление информации с проблемного жесткого диска
Команда CHKDSK является встроенной утилитой, основная функция которой заключается в проверке и исправлении ошибок жесткого диска. Помимо этого, при помощи CHKDSK можно быстро находить и исправлять поврежденные сектора, а также ошибки в файловой системе накопителя.
Таким образом, CHKDSK – важная утилита, позволяющая продлить строк службы жесткого диска, а также увеличить скорость его работы, поэтому абсолютно каждый пользователь ОС Windows должен уметь пользоваться и проверять свои носители встроенными средствами. Ниже будет представлено несколько способов проверки дисков из работающей ОС и командной строки.
Проверка жесткого диска в работающей Windows
Для проверки логических разделов жесткого диска при помощи CHKDSK в работающей Windows необходимо:
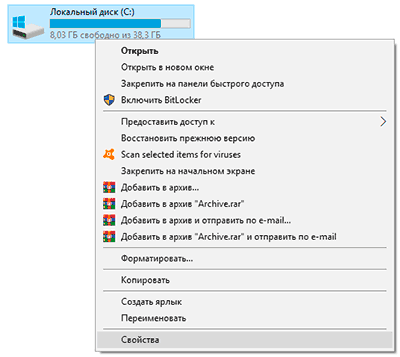
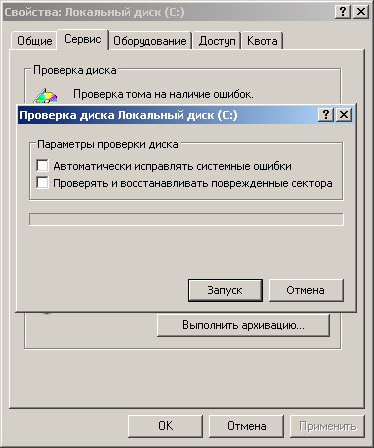
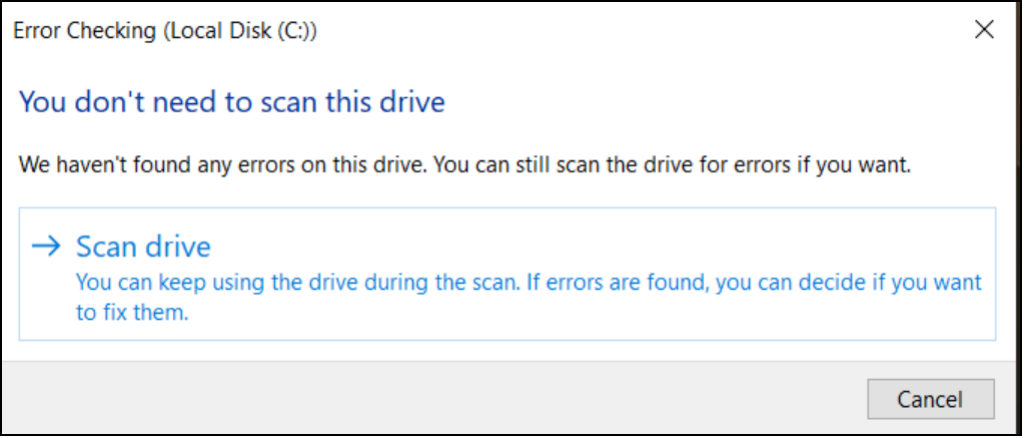
Шаг 1. Открыть каталог «Этот компьютер», нажать правой кнопкой мыши по необходимому логическому разделу и выбрать пункт «Свойства».
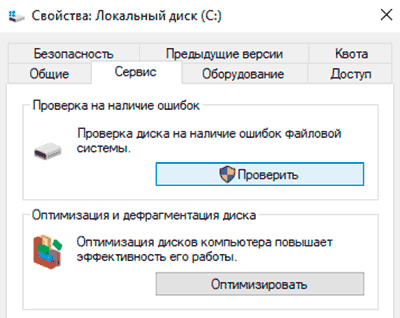
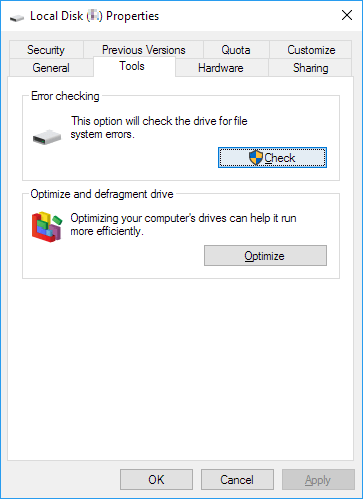
Шаг 2. В открывшемся окне перейти во вкладку «Сервис» и выбрать пункт «Проверить».
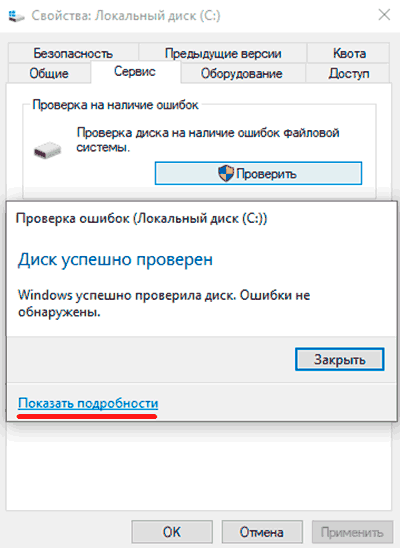
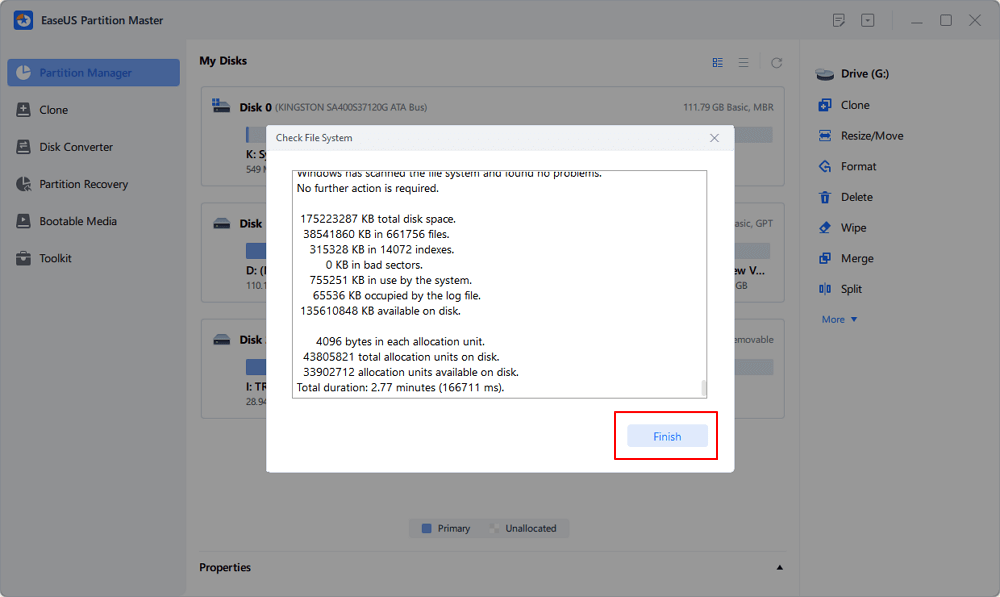
Шаг 3. Подтверждаем проверку диска и после ее завершения нажимаем по кнопке «Показать подробности».
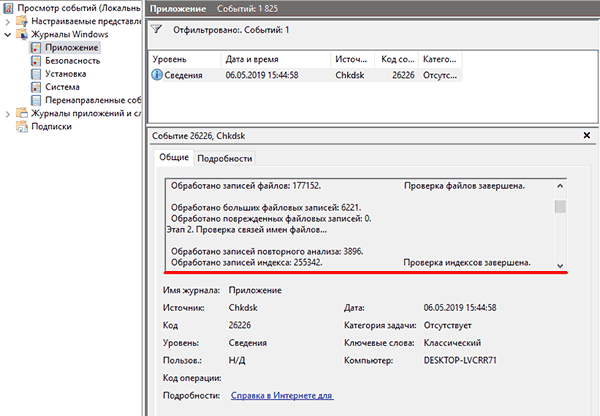
Шаг 4. Вся информация и результаты проверки диска будут доступны в графе «Сведения».
Проверка диска из командной строки
В некоторых ситуациях пользователю может понадобиться запуск утилиты CHKDSK из командной строки. Такая возможность позволит проверить и восстановить диск в том случае, если система не запускается и графический интерфейс Windows остается недоступным.
Чтобы запустить командную строку из среды восстановления ОС, необходимо:
Шаг 1. Воспользоваться установочным диском или загрузочной флешкой Windows и после окна выбора языка нажать по пункту «Восстановление системы». Перейдя в среду восстановления, следует нажать по пункту «Поиск и устранение неисправностей».
Шаг 2. На следующем окне следует выбрать пункт «Дополнительные параметры», после чего можно обнаружить кнопку «Командная строка».
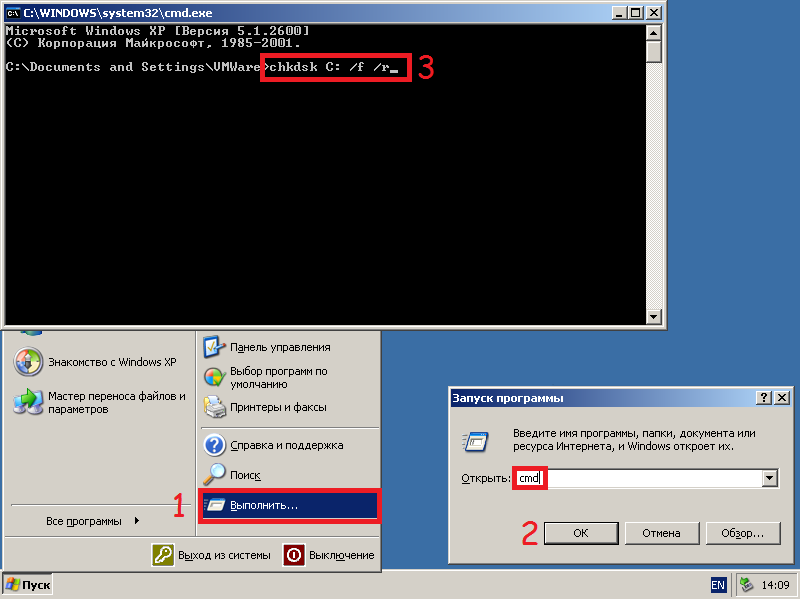
Также всегда остается возможность запустить утилиту проверки дисков через командную строку из работающей системы. Важно! Для использования полного потенциала CHKDSK следует производить запуск командной строки только с правами администратора. В ином случае утилита CHKDSK проведет проверку без устранения выявленных неполадок.
Запустить командную строку или Windows PowerShell от имени администратора можно, нажав правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск» и выбрав пункт «Командная строка(администратор)».
Команды для работы с CHKDSK в командной строке
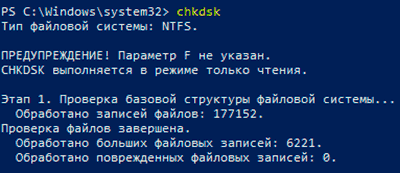
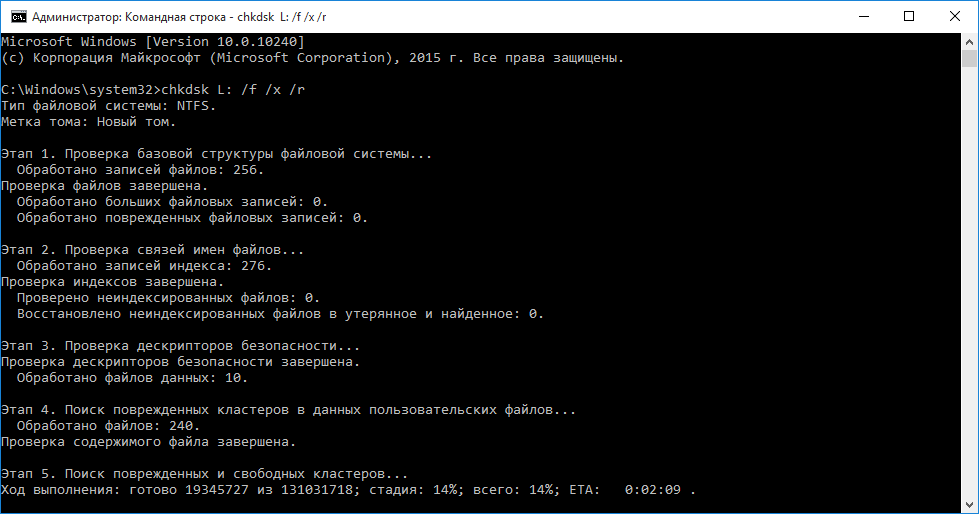
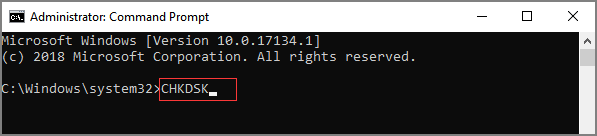
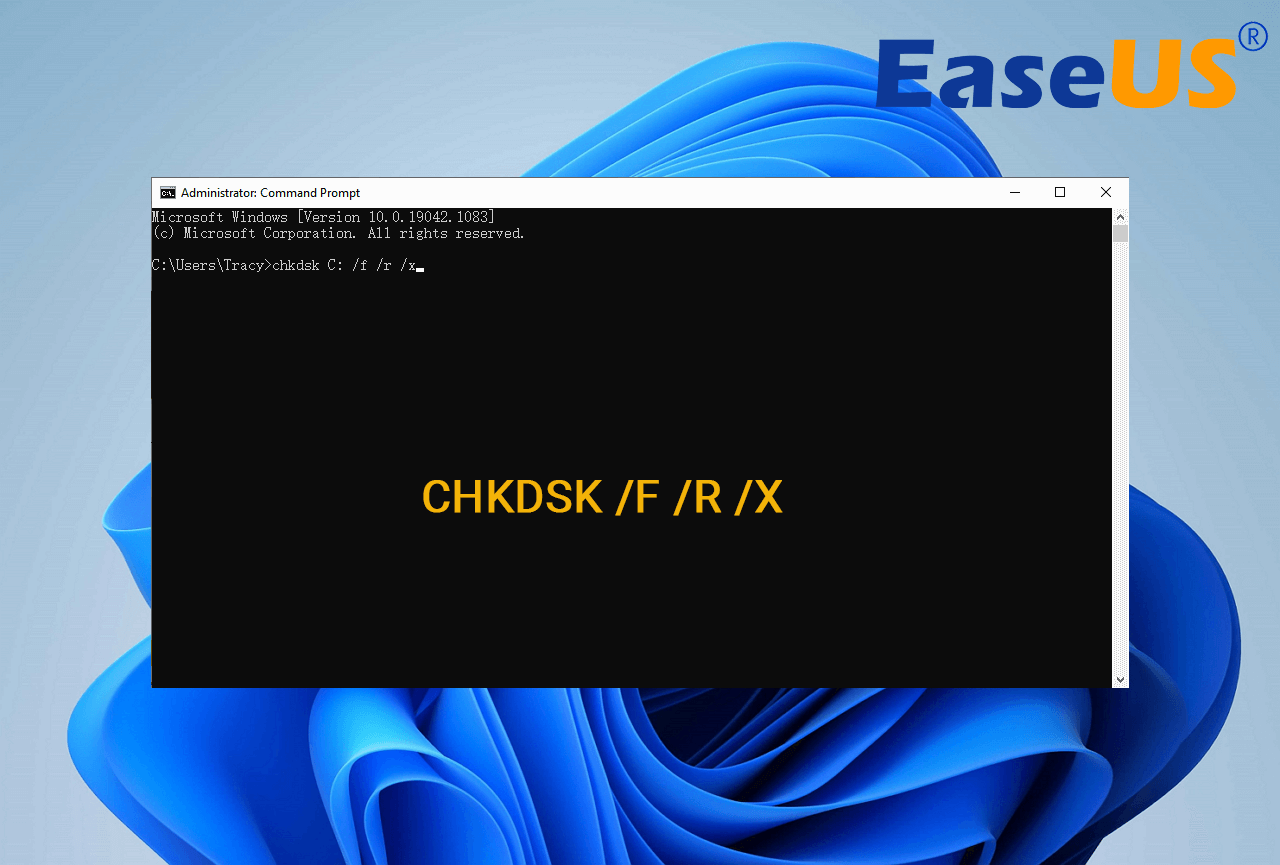
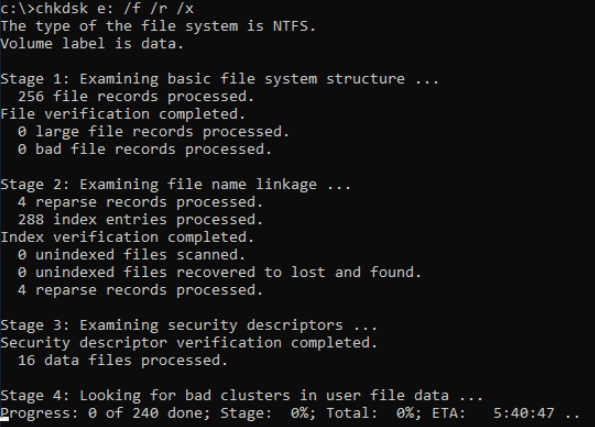
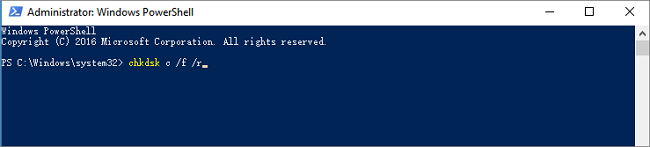
Находясь в командной строке, можно провести быструю проверку жесткого диска (аналогичная проверка была описана в начале) без перезагрузки системы. Для этого достаточно ввести команду «CHKDSK» и подтвердить действие кнопкой Enter.
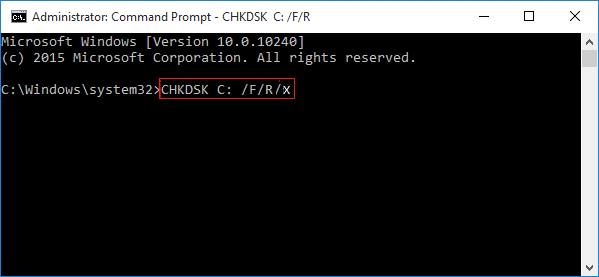
Для проверки диска и исправления логических ошибок на нем необходимо воспользоваться командой «chkdsk C: /F /R», где С – имя необходимого диска.
Для подтверждения проверки диска после перезагрузки необходимо нажать клавишу «Y».
Помимо полного анализа и по возможности исправления поврежденных секторов, утилита может выполнять проверку и решение ошибок только файловой системы. Для этого следует воспользоваться командой «chkdsk C: /F» и подтвердить действие «Y».
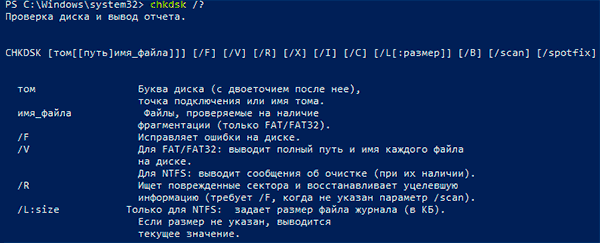
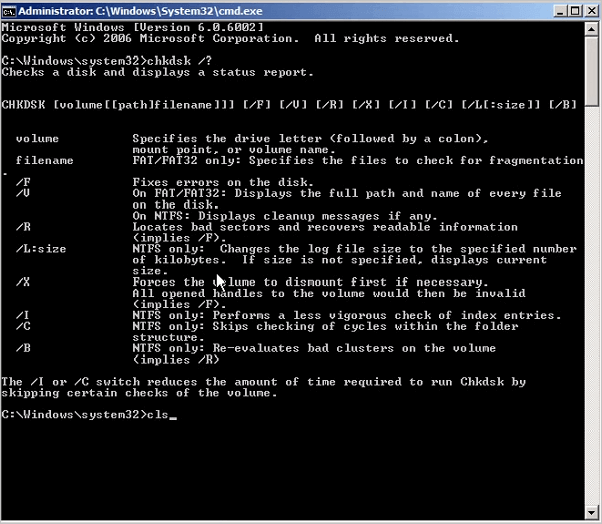
С полным списком и описанием возможностей утилиты можно ознакомится, введя команду «chkdsk /?».
Стоит отметить, что проблемы с диском могут быть вызваны не только программными ошибками, но и физическим износом, механическими повреждениями поверхности и другими факторами, которые невозможно исправить при помощи встроенной утилиты CHKDSK.
Чтобы получить полную картину о состоянии носителя, можно воспользоваться бесплатной программой для проверки дисков Victoria. Узнать о том, как пользоваться, исправлять и проводить диагностику HDD с помощью Victoria Вы сможете в статье: «Используем программу Victoria для тестирования и исправления жесткого диска»
Восстановление информации с проблемного жесткого диска
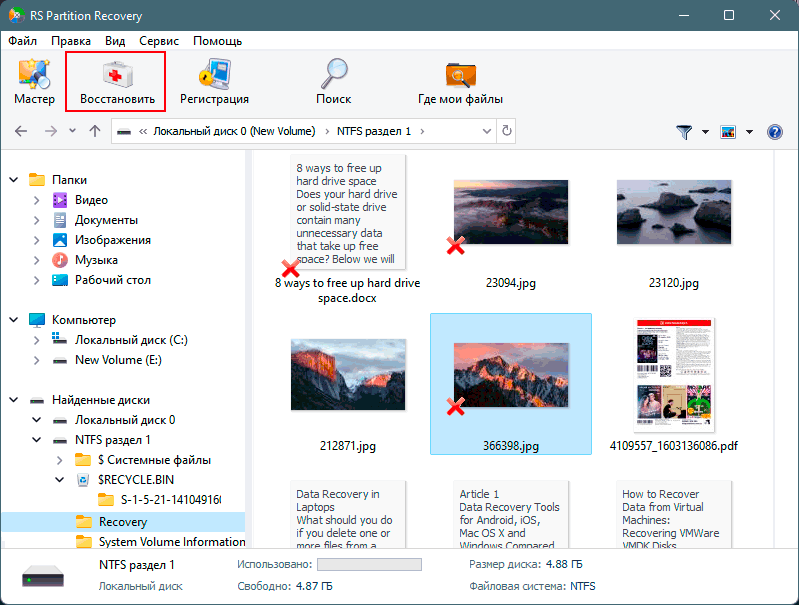
Проблемы с жестким диском – всегда большая угроза для важной информации и документов, хранящихся на компьютере. Чтобы быть готовым к любым обстоятельствам, рекомендуем всегда иметь под рукой специальную программу для эффективного восстановления файлов RS Partition Recovery. Данная утилита поможет восстановить всю утерянную информацию даже в самых сложных случаях.
При помощи RS Partition Recovery можно восстанавливать:
- Случайно удаленные файлы и документы.
- Отформатированные фотографии и медиафайлы.
- Данные, удаленные вирусами.
- Информацию, которая была утеряна при изменении файловой системы и структуры диска.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
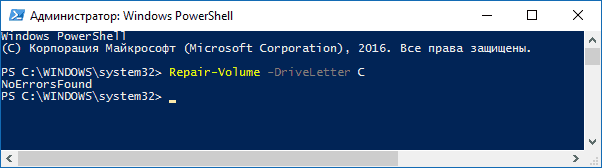
CHKDSK это системная утилита, которая предназначена для работы с дисками. CHKDSK не имеет графического интерфейса. Все команды выполняются в командной строке или Windows PowerShell.
Запустите режим Windows Recovery и выберите «Командная строка». Затем выполните командe: «chkdsk C: /F /R». Если нужно просканировать и исправить ошибки на любом другом диске — замените букву «С» на букву вашего диска.
В таких случаях лучше сразу же использовать RS Partition Recovery. Программа создана как раз для таких ситуаций и успешно восстанавливает данные в 99% случаев.
К сожалению нет. CHKDSK занимается поиском и исправлением логических ошибок на диске, в то время как ошибка RAW – это ошибка файловой системы. В таком случае лучше всего восстановить важные данные при помощи RS Partition Recovery, а затем отформатировать диск.
В поиске Windows впишите «Windows Event Viewer» и в открывшейся программе перейдите в Windows Logs -> Application. Затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Найти». Введите «chkdsk» и нажмите «Enter». В открывшихся результатах поиска найдите последнее событие с Event ID 1001 и источником Wininit. Затем откройте вкладку «General». Там вы найдете подробный лог сканирования накопителя.
Chkdsk — проверка диска на ошибки
Служебная программа Check Disk (Chkdsk.exe) применяется для проверки диска на ошибки и поврежденные сектора. Эта утилита командной строки Windows проверяет целостность как базовых, так и динамических дисков. Она применяется для проверки и исправления ошибок, обнаруженных на томах NTFS и более старых форматов как FAT, FAT32.
Check Disk способен найти и исправить много видов ошибок. Утилита прежде всего ищет несогласованность в файловой системе и связанных с ней метаданных. Один из способов, при помощи которого Check Disk находит ошибки это сравнение битовой карты тома с дисковыми секторами, назначенными файлам.
У многих пользователей возникает вопрос — Как запустить CHKDSK? Для этого нужно:
- Запускаем командную строку с правами администратора — Пуск — Выполнить — Cmd;
- В командной строке вводим команду CHKDSK /? и ознакамливаемся с ее параметрами.
Параметры команды CHKDSK
CHKDSK [том[[путь]имя_файла]] [/F] [/V] [/R] [/X] [/I] [/C] [/L[:размер]] [/B], где
- Том — Определяет точку подключения, имя тома или букву проверяемого диска с двоеточием.
- имя_файла — Файлы, проверяемые на наличие фрагментации (только FAT/FAT32).
- /F — Исправление ошибок на диске.
- /V — Для FAT/FAT32: вывод полного пути и имени каждого файла на диске. Для NTFS: вывод сообщений об очистке (при их наличии).
- /R — Поиск поврежденных секторов и восстановление уцелевшего содержимого (требует /F).
- /L:размер — Только для NTFS: задание размера файла журнала (в КБ). Если размер не указан, выводится текущее значение размера.
- /X — Предварительное отключение тома (при необходимости). Все открытые дескрипторы для этого тома будут недействительны (требует /F)
- /I — Только для NTFS: менее строгая проверка элементов индекса.
- /C — Только для NTFS: пропуск проверки циклов внутри структуры папок.
- /B — Только для NTFS: повторная оценка поврежденных кластеров на диске (требует /R)
- Параметры /I или /C сокращают время выполнения Chkdsk за счет пропуска некоторых проверок тома.
Пример анализа диска без исправления ошибок Chkdsk
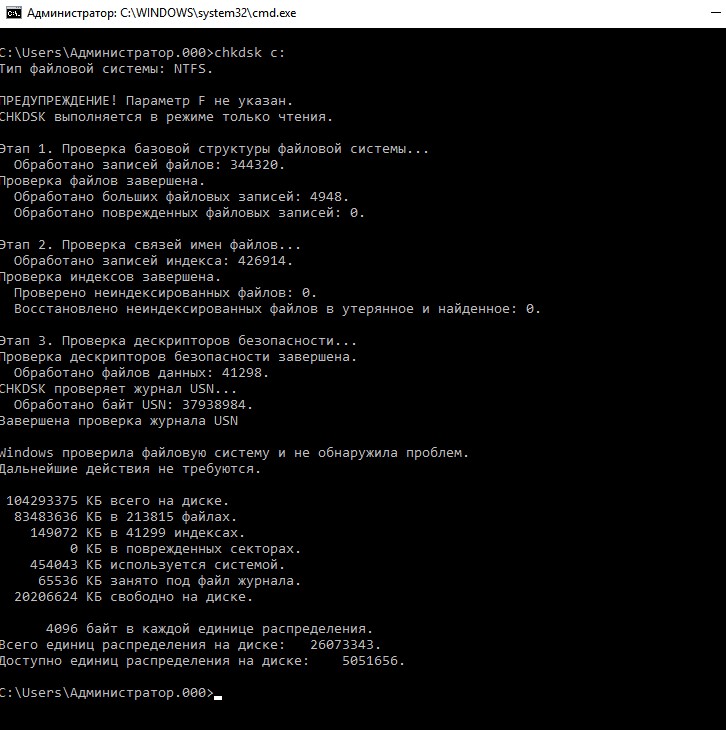
Вы можете проверить целостность диска, введя имя команды и букву диска с двоеточием. Например, для проверки целостности диска С, введите:
- chkdsk с:
Если в результате проверки индексов будут найдены потерянные файлы, Check Disk восстановит их такими, как они есть. Обычно восстановленные файлы хранятся с расширением .chk в корневом каталоге соответствующего диска. В завершение Check Disk выводит отчет, где сообщает, было ли свободное пространство ошибочно отмечено как используемое, и если да, рекомендует исправить ошибку, запустив Check Disk с ключом / F.
Пример исправления ошибок диска с помощью Chkdsk
Анализируя диск, вы его проверяете, но в действительности ничего не исправляете. Для проверки диска и устранения любых обнаруженных проблем нужно указывать ключ /f, после чего Check Disk будет искать и исправлять ошибки:
- chkdsk /f С:
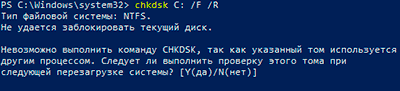
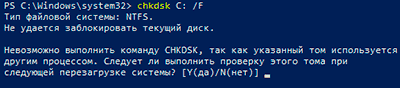
Check Disk не может восстанавливать тома, которые находятся в использовании. Если том используется, Check Disk запрашивает, хотите ли вы, чтобы том был проверен при следующей загрузке компьютера. Ключ /R задает поиск плохих секторов диска и восстановление читаемой информации, а ключ /X — принудительное отключение NTFS-тома в случае необходимости.
Check Disk может выводить более подробную информацию о ходе проверки при помощи ключа /V. Для томов NTFS можно ограничить проверку индексов, задав ключ /I, и пропустить проверку циклов внутри структур папок, указав ключ /С.
| title | description | ms.topic | ms.assetid | author | ms.author | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
chkdsk |
Reference article for the chkdsk command, which checks the file system and file system metadata of a volume for logical and physical errors. |
reference |
62912a3c-d2cc-4ef6-9679-43709a286035 |
jasongerend |
alalve |
11/22/2022 |
Checks the file system and file system metadata of a volume for logical and physical errors. If used without parameters, chkdsk displays only the status of the volume and does not fix any errors. If used with the /f, /r, /x, or /b parameters, it fixes errors on the volume.
[!IMPORTANT]
Membership in the local Administrators group, or equivalent, is the minimum required to run chkdsk. To open a command prompt window as an administrator, right-click Command prompt in the Start menu, and then click Run as administrator.
[!IMPORTANT]
Interrupting chkdsk is not recommended. However, canceling or interrupting chkdsk should not leave the volume any more corrupt than it was before chkdsk was run. Running chkdsk again checks and should repair any remaining corruption on the volume.
[!NOTE]
Chkdsk can be used only for local disks. The command cannot be used with a local drive letter that has been redirected over the network.
Syntax
chkdsk [<volume>[[<path>]<filename>]] [/f] [/v] [/r] [/x] [/i] [/c] [/l[:<size>]] [/b]
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
<volume> |
Specifies the drive letter (followed by a colon), mount point, or volume name. |
[ [<path>]<filename> |
Use with file allocation table (FAT) and FAT32 only. Specifies the location and name of a file or set of files that you want chkdsk to check for fragmentation. You can use the ? and * wildcard characters to specify multiple files. |
| /f | Fixes errors on the disk. The disk must be locked. If chkdsk cannot lock the drive, a message appears that asks you if you want to check the drive the next time you restart the computer. |
| /v | Displays the name of each file in every directory as the disk is checked. |
| /r | Locates bad sectors and recovers readable information. The disk must be locked. /r includes the functionality of /f, with the additional analysis of physical disk errors. |
| /x | Forces the volume to dismount first, if necessary. All open handles to the drive are invalidated. /x also includes the functionality of /f. |
| /i | Use with NTFS only. Performs a less vigorous check of index entries, which reduces the amount of time required to run chkdsk. |
| /c | Use with NTFS only. Does not check cycles within the folder structure, which reduces the amount of time required to run chkdsk. |
/l[:<size>] |
Use with NTFS only. Changes the log file size to the size you type. If you omit the size parameter, /l displays the current size. |
| /b | Use with NTFS only. Clears the list of bad clusters on the volume and rescans all allocated and free clusters for errors. /b includes the functionality of /r. Use this parameter after imaging a volume to a new hard disk drive. |
| /scan | Use with NTFS only. Runs an online scan on the volume. |
| /forceofflinefix | Use with NTFS only (must be used with /scan). Bypass all online repair; all defects found are queued for offline repair (for example, chkdsk /spotfix). |
| /perf | Use with NTFS only (must be used with /scan). Uses more system resources to complete a scan as fast as possible. This may have a negative performance impact on other tasks running on the system. |
| /spotfix | Use with NTFS only. Runs spot fixing on the volume. |
| /sdcleanup | Use with NTFS only. Garbage collect unneeded security descriptor data (implies /f). |
| /offlinescanandfix | Runs an offline scan and fix on the volume. |
| /freeorphanedchains | Use with FAT/FAT32/exFAT only. Frees any orphaned cluster chains instead of recovering their contents. |
| /markclean | Use with FAT/FAT32/exFAT only. Marks the volume clean if no corruption was detected, even if /f was not specified. |
| /? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
Remarks
-
The /i or /c switch reduces the amount of time required to run chkdsk by skipping certain volume checks.
-
If you want chkdsk to correct disk errors, you can’t have open files on the drive. If files are open, the following error message appears:
Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restarts? (Y/N) -
If you choose to check the drive the next time you restart the computer, chkdsk checks the drive and corrects errors automatically when you restart the computer. If the drive partition is a boot partition, chkdsk automatically restarts the computer after it checks the drive.
-
You can also use the
chkntfs /ccommand to schedule the volume to be checked the next time the computer is restarted. Use thefsutil dirty setcommand to set the volume’s dirty bit (indicating corruption), so that Windows runs chkdsk when the computer is restarted. -
You should use chkdsk occasionally on FAT and NTFS file systems to check for disk errors. Chkdsk examines disk space and disk use and provides a status report specific to each file system. The status report shows errors found in the file system. If you run chkdsk without the /f parameter on an active partition, it might report spurious errors because it cannot lock the drive.
-
Chkdsk corrects logical disk errors only if you specify the /f parameter. Chkdsk must be able to lock the drive to correct errors.
Because repairs on FAT file systems usually change a disk’s file allocation table and sometimes cause a loss of data, chkdsk might display a confirmation message similar to the following:
10 lost allocation units found in 3 chains. Convert lost chains to files?-
If you press Y, Windows saves each lost chain in the root directory as a file with a name in the format File
<nnnn>.chk. When chkdsk finishes, you can check these files to see if they contain any data you need. -
If you press N, Windows fixes the disk, but it does not save the contents of the lost allocation units.
-
-
If you don’t use the /f parameter, chkdsk displays a message that the file needs to be fixed, but it does not fix any errors.
-
If you use
chkdsk /f*on a very large disk or a disk with a very large number of files (for example, millions of files),chkdsk /fmight take a long time to complete. -
Use the /r parameter to find physical disk errors in the file system and attempt to recover data from any affected disk sectors.
-
If you specify the /f parameter, chkdsk displays an error message if there are open files on the disk. If you do not specify the /f parameter and open files exist, chkdsk might report lost allocation units on the disk. This could happen if open files have not yet been recorded in the file allocation table. If chkdsk reports the loss of a large number of allocation units, consider repairing the disk.
-
Because the Shadow Copies for Shared Folders source volume cannot be locked while Shadow Copies for Shared Folders is enabled, running chkdsk against the source volume might report false errors or cause chkdsk to unexpectedly quit. You can, however, check shadow copies for errors by running chkdsk in Read-only mode (without parameters) to check the Shadow Copies for Shared Folders storage volume.
-
The chkdsk command, with different parameters, is available from the Recovery Console.
-
On servers that are infrequently restarted, you may want to use the chkntfs or the
fsutil dirty querycommands to determine whether the volume’s dirty bit is already set before running chkdsk.
Understanding exit codes
The following table lists the exit codes that chkdsk reports after it has finished.
| Exit code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No errors were found. |
| 1 | Errors were found and fixed. |
| 2 | Performed disk cleanup (such as garbage collection) or did not perform cleanup because /f was not specified. |
| 3 | Could not check the disk, errors could not be fixed, or errors were not fixed because /f was not specified. |
Examples
To check the disk in drive D and have Windows fix errors, type:
If it encounters errors, chkdsk pauses and displays messages. Chkdsk finishes by displaying a report that lists the status of the disk. You cannot open any files on the specified drive until chkdsk finishes.
To check all files on a FAT disk in the current directory for noncontiguous blocks, type:
Chkdsk displays a status report, and then lists the files that match the file specifications that have noncontiguous blocks.
Viewing chkdsk logs
There are two methods that can be used to retrieve chkdsk log file(s) in Windows. View the methods described below:
Event Viewer
To view logs with Event Viewer, navigate to the following:
-
Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Event Viewer.
Alternatively, press Win + R keys to bring up the run dialog box, type eventvwr.msc, and select OK.
-
Expand Windows Logs > right-click on Application > select Filter Current Log.
-
Within the Filter Current Log window, navigate to Event sources drop-down menu, select Chkdsk and Wininit.
-
Click OK to finish filtering for these two sources.
PowerShell
There are two source types when retrieving logs in PowerShell, chkdsk and wininit. Run one of the two commands in PowerShell to view the most current chkdsk log:
get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname="Application"} | ?{$_.providername -match "chkdsk"} | fl timecreated, message
get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname="Application"} | ?{$_.providername -match "wininit"} | fl timecreated, message
To export the log to a specific location, the following can be added to the end of the command | out-file "$env:userprofilelocationfilename.txt". Example:
get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname="Application"} | ?{$_.providername -match "chkdsk"} | fl timecreated, message | out-file "C:UsersAdministratorDesktopChkdsk_Log.txt"
get-winevent -FilterHashTable @{logname="Application"} | ?{$_.providername -match "wininit"} | fl timecreated, message | out-file "C:UsersAdministratorDesktopWininit_Log.txt"
Related links
- Command-Line Syntax Key

Параметры команды CHKDSK
CHKDSK [том[[путь]имя_файла]] [/F] [/V] [/R] [/X] [/I] [/C] [/L[:размер]] [/B], где
- Том — Определяет точку подключения, имя тома или букву проверяемого диска с двоеточием.
- имя_файла — Файлы, проверяемые на наличие фрагментации (только FAT/FAT32).
- /F — Исправление ошибок на диске.
- /V — Для FAT/FAT32: вывод полного пути и имени каждого файла на диске. Для NTFS: вывод сообщений об очистке (при их наличии).
- /R — Поиск поврежденных секторов и восстановление уцелевшего содержимого (требует /F).
- /L:размер — Только для NTFS: задание размера файла журнала (в КБ). Если размер не указан, выводится текущее значение размера.
- /X — Предварительное отключение тома (при необходимости). Все открытые дескрипторы для этого тома будут недействительны (требует /F)
- /I — Только для NTFS: менее строгая проверка элементов индекса.
- /C — Только для NTFS: пропуск проверки циклов внутри структуры папок.
- /B — Только для NTFS: повторная оценка поврежденных кластеров на диске (требует /R)
- Параметры /I или /C сокращают время выполнения Chkdsk за счет пропуска некоторых проверок тома.
Пример анализа диска без исправления ошибок Chkdsk
Вы можете проверить целостность диска, введя имя команды и букву диска с двоеточием. Например, для проверки целостности диска С, введите:
- chkdsk с:
Если в результате проверки индексов будут найдены потерянные файлы, Check Disk восстановит их такими, как они есть. Обычно восстановленные файлы хранятся с расширением .chk в корневом каталоге соответствующего диска. В завершение Check Disk выводит отчет, где сообщает, было ли свободное пространство ошибочно отмечено как используемое, и если да, рекомендует исправить ошибку, запустив Check Disk с ключом / F.
Пример исправления ошибок диска с помощью Chkdsk
Анализируя диск, вы его проверяете, но в действительности ничего не исправляете. Для проверки диска и устранения любых обнаруженных проблем нужно указывать ключ /f, после чего Check Disk будет искать и исправлять ошибки:
- chkdsk /f С:
Check Disk не может восстанавливать тома, которые находятся в использовании. Если том используется, Check Disk запрашивает, хотите ли вы, чтобы том был проверен при следующей загрузке компьютера. Ключ /R задает поиск плохих секторов диска и восстановление читаемой информации, а ключ /X — принудительное отключение NTFS-тома в случае необходимости.
Check Disk может выводить более подробную информацию о ходе проверки при помощи ключа /V. Для томов NTFS можно ограничить проверку индексов, задав ключ /I, и пропустить проверку циклов внутри структур папок, указав ключ /С.