A classpath is a list of locations to load classes from.
These ‘locations’ can either be directories, or jar files.
For directories, the JVM will follow an expected pattern for loading a class. If I have the directory C:/myproject/classes in my classpath, and I attempt to load a class com.mycompany.Foo, it will look under the classes directory for a directory called com, then under that a directory called mycompany, and finally it will look for a file called Foo.class in that directory.
In the second instance, for jar files, it will search the jar file for that class. A jar file is in reality just a zipped collection of directories like the above. If you unzip a jar file, you’ll get a bunch of directories and class files following the pattern above.
So the JVM traverses a classpath from start to finish looking for the definition of the class when it attempts to load the class definition. For example, in the classpath :
C:/myproject/classes;C:/myproject/lib/stuff.jar;C:/myproject/lib/otherstuff.jar
The JVM will attempt to look in the directory classes first, then in stuff.jar and finally in otherstuff.jar.
When you get a ClassNotFoundException, it means the JVM has traversed the entire classpath and not found the class you’ve attempted to reference. The solution, as so often in the Java world, is to check your classpath.
You define a classpath on the command line by saying java -cp and then your classpath. In an IDE such as Eclipse, you’ll have a menu option to specify your classpath.
ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception and occurs when the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) tries to load a particular class and the specified class cannot be found in the classpath.
In older days, there are no editors like Eclipse are available. Even in Notepad, people have done java coding and by using the “javac” command to compile the java files, and they will create a ‘.class’ file. Sometimes accidentally the generated class files might be lost or set in different locations and hence there are a lot of chances of “ClassNotFoundException” occurs. After the existence of editors like Eclipse, Netbeans, etc., IDE creates a “ClassPath” file kind of entries.
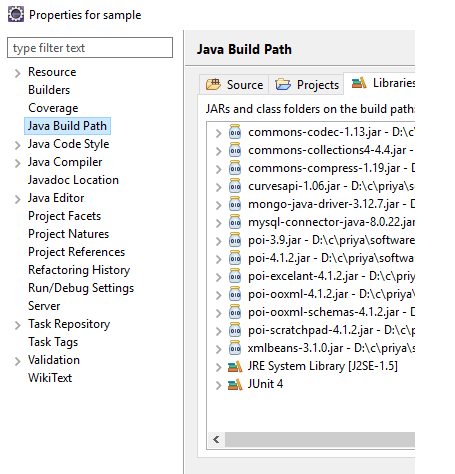
From the above image, we can see that many jar files are present. They are absolutely necessary if the java code wants to interact with MySQL, MongoDB, etc., kind of databases, and also few functionalities need these jar files to be present in the build path. If they are not added, first editors show the errors themselves and provide the option of corrections too.
Implementation: Sample program of connecting to MySQL database and get the contents
Example
Java
import java.sql.*;
public class MySQLConnectivityCheck {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(
"---------------------------------------------");
Connection con = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"root", "");
try {
}
catch (SQLException s) {
System.out.println(
"SQL statement is not executed!");
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
res = null;
con = null;
}
}
}
Output:
Case 1: In the above code, we are using com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver and in that case if we are not having mysql-connector-java-8.0.22.jar, then we will be getting ClassNotFoundException.
Case 2: So, keep the jar in the build path as shown below.
Note: Similarly for any database connectivity, we need to have the respective jars for connecting to that database. The list of database driver jars required by java to overcome ClassNotFoundException is given below in a tabular format
| Database | Command Line |
|---|---|
| MySQL | mysql-connector-java-8.0.22.jar |
| MongoDB | mongo-java-driver-3.12.7.jar |
| SQL Server | sqljdbc4.jar |
| MYSQL | sqljdbc.jar |
| Oracle | oracle.jdbc.driver.oracledriver |
Note:
- When we are developing Web based applications, the jars must be present in ‘WEB-INF/lib directory’.
- In Maven projects, jar dependency should be present in pom.xml
- Sample snippet of pom.xml for spring boot
Example 1 With Spring boot
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
Example 2 Without spring boot
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb-driver</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3</version>
</dependency>
Example 3 Gradle based dependencies (MongoDB)
XML
dependencies {
compile 'org.mongodb:mongodb-driver:3.2.2'
}
Similarly, other DB drivers can be specified in this way. It depends upon the project nature, the dependencies has to be fixed. For ordinary class level projects, all the classes i.e parent class, child class, etc should be available in the classpath. If there are errors, then also .class file will not be created which leads to ClassNotFoundException, and hence in order to get the whole code working, one should correct the errors first by fixing the dependencies. IDE is much helpful to overcome such sort scenarios such as when the program throws ClassNotFoundException, it will provide suggestions to users about the necessity of inclusion of jar files(which contains necessary functionalities like connecting to database.
Last Updated :
30 Sep, 2021
Like Article
Save Article
The java.lang.ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception in Java that occurs when the JVM tries to load a particular class but does not find it in the classpath.
Since the ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception, it must be explicitly handled in methods which can throw this exception — either by using a try-catch block or by throwing it using the throws clause.
Install the Java SDK to identify and fix exceptions
What Causes ClassNotFoundException in Java
Common causes of the java.lang.ClassNotFoundException are using the following methods to load a class:
Class.forName()ClassLoader.findSystemClass()ClassLoader.loadClass()
In all the above cases, the class attempted to be loaded is not found on the classpath, leading to the ClassNotFoundException in Java.
ClassNotFoundException in Java Example
A very common example of ClassNotFoundException is when a JDBC driver is attempted to be loaded using Class.forName() and the driver’s JAR file is not present in the classpath:
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionExample {
private static final String DRIVER_CLASS = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Loading MySQL JDBC driver");
Class.forName(DRIVER_CLASS);
}
}
Since the MySQL JDBC driver JAR file is not present in the classpath, running the above code leads to a java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:
Loading MySQL JDBC driver
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:602)
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:178)
at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:522)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:340)
at ClassNotFoundExceptionExample.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionExample.java:6)To fix the Java exception, the mysql-connector JAR should be included in the application classpath.
How to Resolve ClassNotFoundException in Java
The following steps should be followed to resolve a ClassNotFoundException in Java:
- Find out which JAR file contains the problematic Java class. For example, in the case of com.mysql.jdbc.driver, the JAR file that contains it is mysql-connector-java.jar.
- Check whether this JAR is present in the application classpath. If not, the JAR should be added to the classpath in Java and the application should be recompiled.
- If that JAR is already present in the classpath, make sure the classpath is not overridden (e.g. by a start-up script). After finding out the exact Java classpath used by the application, the JAR file should be added to it.
To fix the Java exception, the mysql-connector JAR should be included in the application classpath.
Track, Analyze and Manage Java Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates Java error monitoring and triaging, making fixing errors easier than ever. Try it today.
From the above image, we can see that many jar files are present. They are absolutely necessary if the java code wants to interact with MySQL, MongoDB, etc., kind of databases, and also few functionalities need these jar files to be present in the build path. If they are not added, first editors show the errors themselves and provide the option of corrections too.
Implementation: Sample program of connecting to MySQL database and get the contents
Example
Java
import java.sql.*;
public class MySQLConnectivityCheck {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(
"---------------------------------------------");
Connection con = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"root", "");
try {
}
catch (SQLException s) {
System.out.println(
"SQL statement is not executed!");
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
res = null;
con = null;
}
}
}
Output:
Case 1: In the above code, we are using com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver and in that case if we are not having mysql-connector-java-8.0.22.jar, then we will be getting ClassNotFoundException.
Case 2: So, keep the jar in the build path as shown below.
Note: Similarly for any database connectivity, we need to have the respective jars for connecting to that database. The list of database driver jars required by java to overcome ClassNotFoundException is given below in a tabular format
| Database | Command Line |
|---|---|
| MySQL | mysql-connector-java-8.0.22.jar |
| MongoDB | mongo-java-driver-3.12.7.jar |
| SQL Server | sqljdbc4.jar |
| MYSQL | sqljdbc.jar |
| Oracle | oracle.jdbc.driver.oracledriver |
Note:
- When we are developing Web based applications, the jars must be present in ‘WEB-INF/lib directory’.
- In Maven projects, jar dependency should be present in pom.xml
- Sample snippet of pom.xml for spring boot
Example 1 With Spring boot
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
Example 2 Without spring boot
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb-driver</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3</version>
</dependency>
Example 3 Gradle based dependencies (MongoDB)
XML
dependencies {
compile 'org.mongodb:mongodb-driver:3.2.2'
}
Similarly, other DB drivers can be specified in this way. It depends upon the project nature, the dependencies has to be fixed. For ordinary class level projects, all the classes i.e parent class, child class, etc should be available in the classpath. If there are errors, then also .class file will not be created which leads to ClassNotFoundException, and hence in order to get the whole code working, one should correct the errors first by fixing the dependencies. IDE is much helpful to overcome such sort scenarios such as when the program throws ClassNotFoundException, it will provide suggestions to users about the necessity of inclusion of jar files(which contains necessary functionalities like connecting to database.
Last Updated :
30 Sep, 2021
Like Article
Save Article
The java.lang.ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception in Java that occurs when the JVM tries to load a particular class but does not find it in the classpath.
Since the ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception, it must be explicitly handled in methods which can throw this exception — either by using a try-catch block or by throwing it using the throws clause.
Install the Java SDK to identify and fix exceptions
What Causes ClassNotFoundException in Java
Common causes of the java.lang.ClassNotFoundException are using the following methods to load a class:
Class.forName()ClassLoader.findSystemClass()ClassLoader.loadClass()
In all the above cases, the class attempted to be loaded is not found on the classpath, leading to the ClassNotFoundException in Java.
ClassNotFoundException in Java Example
A very common example of ClassNotFoundException is when a JDBC driver is attempted to be loaded using Class.forName() and the driver’s JAR file is not present in the classpath:
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionExample {
private static final String DRIVER_CLASS = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Loading MySQL JDBC driver");
Class.forName(DRIVER_CLASS);
}
}
Since the MySQL JDBC driver JAR file is not present in the classpath, running the above code leads to a java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:
Loading MySQL JDBC driver
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:602)
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:178)
at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:522)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:340)
at ClassNotFoundExceptionExample.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionExample.java:6)To fix the Java exception, the mysql-connector JAR should be included in the application classpath.
How to Resolve ClassNotFoundException in Java
The following steps should be followed to resolve a ClassNotFoundException in Java:
- Find out which JAR file contains the problematic Java class. For example, in the case of com.mysql.jdbc.driver, the JAR file that contains it is mysql-connector-java.jar.
- Check whether this JAR is present in the application classpath. If not, the JAR should be added to the classpath in Java and the application should be recompiled.
- If that JAR is already present in the classpath, make sure the classpath is not overridden (e.g. by a start-up script). After finding out the exact Java classpath used by the application, the JAR file should be added to it.
To fix the Java exception, the mysql-connector JAR should be included in the application classpath.
Track, Analyze and Manage Java Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates Java error monitoring and triaging, making fixing errors easier than ever. Try it today.
Introduction to Java ClassNotFoundException
As it goes by the name, ClassNotFoundException occurs in Java when a specific class is tried to load by a Java Virtual Machine(JVM). The requested class is not found in the path of the class specified by you, meaning that the path of the class specified by you is broken, which problem is really common in the world of Java. Hence, ClassNotFoundException is also common in Java. This problem is very confusing for those who are beginners in Java, and ClassNotFoundException must be catch or thrown to the caller ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception.
The syntax ofClassNotFoundException in Java is as follows:
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:Class_name at locationWorking of ClassNotFoundException in Java
- When a class loader is not able to find the class in the path of the class specified while the application is trying to load the class, that is when the ClassNotFoundExceptionoccurs in Java.
- Making use of Class.forName and ClassLoader.loadClass for loading the class while passing string name of the class as the parameter which is not found in the path of the class that is specified is one of the common causes for java.lang.ClassNotFoundException in Java.
- ClassNotFoundException in Java must be catch or thrown to the caller because it is a checked exception.
- The class is indirectly loading using the Classloader. As a result, ClassNotFoundException in Java occurs at runtime. There is no way that a Java compiler can know if a class is present in the path of the class specified or not at runtime.
- Trying to load the JDBC drivers using Class.forName and not adding the jar file in the path of the class is one of the common examples of ClassNotFoundExceptionin Java.
- Consider the below program to demonstrate ClassNotFoundException in Java:
//a class called program is defined
public class Program
{
//main method is called
public static void main(String args[])
{
//class not found exception is defined using try and catch block
try
{
// the forname method in class class looks for the mentioned class
Class.forName("The Class do not Exist");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
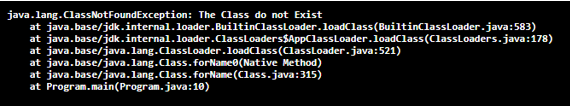
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, a class called Program is defined. Then the main method is called. Then class not found exception is defined using try and catch block. There is noThe class does not exist.java class which the class loader is trying to find andtheforname method in class looks for the mentioned class, which it fails to find; hence the ClassNotFoundException is thrown. The output of the program is as shown in the snapshot above.
Constructors
There are several constructors for ClassNotFoundException in Java. They are:
- ClassNotFoundException(): A new ClassNotFoundException is constructed which includes the current trace of the stack.
- ClassNotFoundException(String): A new ClassNotFoundException is constructed, which includes the current trace of the stack and the message in detail, specified.
- ClassNotFoundException(IntPtr, JniHandleOwnership): During the creation of JNI objects, while managing their representations, this constructor is used, and the runtime calls it.
- ClassNotFoundException(String, Throwable): A new ClassNotFoundException is constructed, which includes the current trace of the stack along with the message in detail that is specified and the exception that occurs when trying to load the class.
Examples of Java ClassNotFoundException
Here are the following examples mention below:
Example #1
Java program to demonstrate ClassNotFoundException:
Code:
//a class called exceptiondemo is defined
public class Exceptiondemo
{
//a string variable is defined
private static final String DRIVE_CLASS = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//main method is called including the exception
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("MySQL JDBC driver loading attempt");
//the forname method in class class looks for the mentioned class
Class.forName(DRIVE_CLASS);
}
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, a class called Exception demo is defined. Then the main method is called. Then a string variable is defined to which the JDBC driver path is assigned. Then the main method is called, which throws the exception. The class loader is trying to find the JDBC driver path of the class specified and the forname method in class looks for the mentioned class, which it fails to find; hence the ClassNotFoundException is thrown. The output of the program is as shown in the snapshot above.
Example #2
Java program to demonstrate ClassNotFoundException(String)
Code:
//a class called check is defined
public class Check
{
//main method is called
public static void main(String args[])
{
//class not found exception is defined using try catch block
try
{
//the forname method in class class looks for the mentioned class
Class.forName("Demonstrating class not found exception");
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException e)
{
//the string specified along with the class not found exception is displayed.
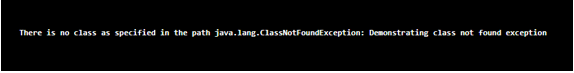
System.out.println("There is no class as specified in the path " + e);
}
}
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, a class called check is defined. Then the main method is called. Then the main method is called. Then class not found exception is defined by using try and catch block. Then the forename method in class looks for the mentioned class, which it fails to find; hence the ClassNotFoundException is thrown and the string specified as a detailed message along with the class not found exception is displayed. The output of the program is as shown in the snapshot above.
How to Avoid ClassNotFoundException?
Steps to avoid ClassNotFoundException:
- The file of the class causing the problem on which the jar file is present must be found out.
- We should check if the path of the class or classpath consists of that jar. If the jar is not present in the classpath or path of the class, the class must be added in the class or classpath path.
- If the class is present in the class or classpath path, then the chances are that there is an overriding of classpath or path of the class or the path specified in the jar file or the script used for starting up is being used by the application. To solve this problem, we need to find the exact path of the class that is being used by the application.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we understand the concept of Class Not Found Exception in Java through definition, the syntax of Class Not Found Exception in Java, working of Class Not Found Exception in Java, and their constructors through examples and their outputs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java ClassNotFoundException. Here we discuss the working of ClassNotFoundException in Java along with programming examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Finally in Java
- Java min()
- copy() in Java
- EJB in Java
In this tutorial, we will discuss the java.lang.classnotfoundexception – ClassNotFoundException. This exception is thrown when an application tries to load a class through its string name, but no definition for the specified class name could be found. A class can be loaded using one of the following methods:
- The
forNamemethod that resides inside theClassclass. - The
findSystemClassmethod that resides inside theClassLoaderclass. - The
loadClassmethod that resides inside theClassLoaderclass.
You can also check this tutorial in the following video:


This exception java.lang.classnotfoundexception extends the ReflectiveOperationException, which is defined as the common superclass of exceptions thrown by reflective operations in core reflection. Finally, after the Java 1.4 release, the ClassNotFoundException has been retrofitted to conform to the general purpose exception-chaining mechanism. The raising exception may be accessed via the Throwable.getCause() method.
The java.lang.ClassNotFoundException is thrown when the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) tries to load a particular class and the specified class cannot be found in the classpath. The Java ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception and thus, must be declared in a method or constructor’s throws clause.
The following example tries to load a class using the forName method. However, the specified class name cannot be found and thus, a ClassNotFoundException is thrown.ClassNotFoundExceptionDemo.java
/**
* @author Santosh Balgar Sachchidananda
* This class tries to load MySQL driver. For the demo of ClassNotFoundexception
* I haven't added the jar file in classpath. Add the mysql-connector jar in classpath
* to fix this exception
*/
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionDemo {
private static final String DRIVER_CLASS = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
System.out.println("Trying to load MySQL JDBC driver");
Class.forName(DRIVER_CLASS);
}
}
A sample execution is shown below:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:581) at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:178) at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:521) at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method) at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:315) at com.jcg.ClassNotFoundExceptionDemo.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionDemo.java:14)
To fix the exception download the mysql-connector jar from Oracle website and include in your class path.
Above scenario is the most common scenario when CLassNotFoundException is raised. However, it can become bit ugly or messy sometimes in a complex web deployment environments. Suppose your application is deployed as an EAR and it contains multiple jar and WAR files, it can sometimes raise this exception because of class visibility issues. Jar files and class files under EAR’s lib folder are visible to classes in WAR file, however jars and classes under war file’s lib folder can’t be seen by other modules or jars. It becomes even messier when different modules involved refer to different versions of same jar file. You need to be careful when such inter-dependencies exist.
2. How to deal with the java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
- Verify that the name of the requested class is correct and that the appropriate
.jarfile exists in your classpath. If not, you must explicitly add it to your application’s classpath. - In case the specified
.jarfile exists in your classpath then, your application’s classpath is getting overridden and you must find the exact classpath used by your application. - In case the exception is caused by a third party class, you must identify the class that throws the exception and then, add the missing
.jarfiles in your classpath.
Below is the simple example to illustrate ClassNotFoundException and a way to fix it.
MainClass is dependent on DependentClass for the successful execution, if everything is there as expected then you will see below output,
Hello from main class Loading dependent class Hello From Dependent Class Dependent class loaded successfully
For the demo purpose, I have removed DependentClass.class from the output directory. Now if you try to run the MainClass you get below output,
Hello from main class Loading dependent class Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: com/jcg/DependentClass at com.jcg.MainClass.main(MainClass.java:7) Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.jcg.DependentClass at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:581) at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:178) at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:521) ... 1 more
To fix this we need to make DependentClass.class available. This can be done by rebuilding the project in our case. Otherwise you need to verify the classes and libraries in your class path and fix the same.
Below is the code for our example,DependentClass.java
public class DependentClass {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello From Dependent Class");
}
}
MainClass.java
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello from main class");
System.out.println("Loading dependent class");
DependentClass dClass = new DependentClass();
dClass.sayHello();
System.out.println("Dependent class loaded successfully");
}
}
3. ClassNotFoundException vs NoClassDefFoundError vs UnSupportedClassVersionError
ClassNotFoundException is generally thrown when you try to load a class using Class.forname or loadClass and findSytemClass methods in ClassLoader methods, the class you are trying to load is not present in the Classpath. Another scenario when it can happen is the class you are trying to load is not a valid class.
NoClassDefFoundError is an error and it occurs when a class is present at compile-time and the same is missing at the run time. This is a fatal error and happens when you try to instantiate class or when you try to call a static method.
UnSupportedClassVersionEorror this error happens when the class is compiled with a higher JDK version than the one used for execution. When you encounter this error, verify the installed Java version and the Java path set in the JAVA_HOME environment variable.
4. More articles
- java.lang.StackOverflowError – How to solve StackOverflowError
- Unreachable Statement Java Error – How to resolve it
- java.lang.NullPointerException Example – How to handle Java Null Pointer Exception (with video)
- Try Catch Java Example
- Java Constructor Example (with video)
- Online Java Compiler – What options are there
- What is null in Java
5. Download the source code
For the demo program, I have used IntelliJ Idea IDE and Java 11 version.
Last updated on Jul. 23rd, 2021

Sotirios-Efstathios (Stathis) Maneas is a PhD student at the Department of Computer Science at the University of Toronto. His main interests include distributed systems, storage systems, file systems, and operating systems.