when am trying to open mysql in windows cmd by typing mysql. the following error is occuring.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ODBC@localhost (using password: NO)
And then by looking similar queries i somehow got a temporary solution by using
C:> mysql -u root -p and then typing the password, mysql is working. But when i close and open, the same problem is recurring.
One more thing is that i have created a user ‘admin’. but when am trying to open mysql using the command C:> mysql --user=admin --password=root, the following error is occuring:
C:Usersabhay kumar>mysql --user=admin --password=root
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'admin'@'localhost' (using password:NO)
Any help will great
asked May 30, 2014 at 9:00
1
for some reason, the ODBC user is the default username under windows even if you didn’t create that user at setup time. simply typing
mysql
without specifying a username will attempt to connect with the non-existent ODBC username, and give:
Error 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
Instead, try specifying a username that you know, for example:
mysql -u root -p
where -u root specified the username root and -p will make the command prompt for a password.
If you have installed using Chocolatey on Windows :-
The default username would be root and the password will be blank
answered Mar 18, 2015 at 1:42
NishNish
1,4801 gold badge9 silver badges8 bronze badges
4
You need to create an user «ODBC» for MySql with no password. Do that in PHPMyAdmin. That will solve your problem.
But remember, if it’s only your local development environment, no problem. It’ll create a serious security hole in your production environment.
answered May 29, 2015 at 6:47
ImtiazImtiaz
2,4442 gold badges25 silver badges32 bronze badges
2
I tried this and it worked:
C:cd MySQL installed pathMySQL -uyourusername -pyourpassword
James
4,6335 gold badges36 silver badges48 bronze badges
answered Jun 6, 2015 at 13:58
C:Usersabhay kumar>mysql --user=admin --password=root..
This command is working for root user..you can access mysql tool from any where using command prompt..
C:Userslelaprasad>mysql --user=root --password=root
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 4
Server version: 5.5.47 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
Tunaki
132k46 gold badges331 silver badges418 bronze badges
answered Apr 12, 2016 at 11:39
I know it’s been three years since this was asked, but I just figured out this problem for myself. I was using into outfile and getting the error. When I commented out this part of the query, it worked.
The FILE privilege is separate from all the others and must be granted to the user running the script.
GRANT FILE ON *.* TO 'asdfsdf'@'localhost';
answered Jun 23, 2017 at 20:18
1
Just create a file my.ini file in installation dir and have the below config as part of this file to solve this permanently.
[mysql]
user=root
password=root
answered Aug 22, 2018 at 14:32
varravarra
1648 bronze badges
1
Try this command:
mysql -uroot -p
then it will ask for password
enter root as the password.
answered Mar 28, 2022 at 19:55
If you are using dj-database-url check the schema in your DATABASES
https://github.com/kennethreitz/dj-database-url
MySQL is
'default': dj_database_url.config(default='mysql://USER:PASSWORD@localhost:PORT/NAME')
It solves the same error even without the PORT
You set the password with:
mysql -u user -p
answered Aug 31, 2017 at 21:21
Rider Rider
396 bronze badges
Try using following command it work.
mysql --user=root --password=root_password
answered Apr 12, 2019 at 5:52
Why you can’t just use mysqlsh?
PS C:UsersarturDesktop> mysqlsh --user root
MySQL Shell 8.0.17
Copyright (c) 2016, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates.
Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Type 'help' or '?' for help; 'quit' to exit.
Creating a session to 'root@localhost'
Fetching schema names for autocompletion... Press ^C to stop.
Your MySQL connection id is 13 (X protocol)
Server version: 8.0.17 MySQL Community Server - GPL
No default schema selected; type use <schema> to set one.
MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl JS >
mate00
2,6875 gold badges25 silver badges34 bronze badges
answered Aug 13, 2019 at 11:50
1
I have found the answer for this:
enter mysql -u user -p
this will leads to Enter Password .
Then enter the password which you have given…
below is the example:
*****C:Usersadmin>mysql -u root -p
**Enter password: **********************
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 26
Server version: 8.0.31 MySQL Community Server — GPL
This is worked for me
answered Nov 22, 2022 at 7:00
- open command line (run as admin)
- go into Mysql server bin folder
- run command:
mysqldump -u root -p mydbscheme > mydbscheme_dump.sql - give your password here against root.
It will work perfect !!
Stephen Rauch♦
47.5k31 gold badges106 silver badges135 bronze badges
answered Aug 2, 2017 at 5:36
You can create user with no password in phpmyadmin and it solves the problem!
Lebbar Abdelhadi,
answered May 11, 2020 at 13:33
It seems like You haven’t set the Mysql server path, Set Environment Variable For MySql Server. Then restart the command prompt and enter mysql -u root-p then it asks for a password enter it.
Thank you.
Happy learning!
Dharman♦
30.4k22 gold badges84 silver badges132 bronze badges
answered Sep 13, 2020 at 4:37
pavankumarpavankumar
3175 silver badges12 bronze badges
You can connect to SQL from a python Jupiter notebook using this syntax:
import mysql.connector as conn
conn.connect(host = 'localhost', user = 'root', passwd = 'xxx')
xxx = your password for MySQL
user = your MySQL user name, which might be different from root. Check your MySQL userid, and change it accordingly.
SherylHohman
16.3k17 gold badges86 silver badges93 bronze badges
answered Jan 11, 2022 at 12:51
Let me what worked for me —
Step 1 — In cmd, give a command
set path=%PATH%;set path=%PATH%;C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin
[Note — make sure you are replacing ‘C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL
Server’ with your ‘MySQL server path’ above]
Step 2 — type,
mysql -u user -p
👆🏽 This will ask for password and you are good to go but sometimes
it does not work…Then try this 👇🏽
Alternative of Step 2 —
--user=root --password=1234
👆🏽Must replace your username and password with above
Step 3 — Check out by
mysql --version
I hope this may help…🤞🏽👍🏽
answered Nov 2, 2022 at 9:02
To overcome the above error, you can simply create the ODBC named user:
CREATE USER ODBC@localhost;
And then grant it all the privileges:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ODBC@localhost;
This will solve the error. If you want to persist this user, you can, but I would suggest that you delete it once your work has been done:
DROP USER ODBC@localhost;
answered May 27 at 6:01
i entered in Mysql Workbench and i changed the password. It seem the password was expired. it works!
answered Oct 9, 2018 at 8:27
samivicsamivic
1,18813 silver badges13 bronze badges
So, all of you missed to say these:
at first install, connect with mysql.exe -u root -p and at password press enter, and you are logged in, create new user or alter root user with new password. create database, etc !!!
answered Feb 27 at 15:37
I encountered this problem today. I tried mysql -u root -p, but it doesn’t work.
I restarted the mysql service by two commands:
net stop mysql and net start mysql
then tried the command mysql. It worked.
techspider
3,36013 gold badges37 silver badges61 bronze badges
answered Jun 13, 2016 at 14:27
This guide provides an in-depth analysis of the common database error: «Access Denied for User ‘odbc’@’localhost'» and offers step-by-step solutions to fix this issue. It also includes an FAQ section to address some common questions related to this error.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Causes of the Error
- Step-by-Step Solutions
- FAQs
- Related Links
Introduction
The «Access Denied for User ‘odbc’@’localhost'» error is a common database connection issue that developers may encounter while working with MySQL, PostgreSQL, or other SQL-based databases. This error generally occurs when an application or script is trying to establish a connection to the database server using the ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) driver but fails due to incorrect authentication or insufficient privileges.
Causes of the Error
There are several reasons that can cause the «Access Denied for User ‘odbc’@’localhost'» error. Some of the most common causes include:
- Incorrect username or password
- Insufficient privileges for the user
- The host is not allowed to connect to the database server
- The user account is locked or expired
- ODBC driver misconfiguration
Step-by-Step Solutions
To fix the «Access Denied for User ‘odbc’@’localhost'» error, you can follow the steps outlined below:
Step 1: Verify the Username and Password
Ensure that the username and password used to connect to the database server are correct. Check your application configuration files or connection strings for any typos or incorrect credentials.
Step 2: Grant Appropriate Privileges
Make sure that the user account has the necessary privileges to connect to the database and perform the required operations. You can grant the appropriate privileges using the following SQL command:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.* TO 'odbc'@'localhost';
Replace database_name with the name of the database that the user needs access to.
Step 3: Allow Host to Connect
If the error persists, verify that the host is allowed to connect to the database server. You can add a new host or modify an existing one using the following SQL command:
CREATE USER 'odbc'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.* TO 'odbc'@'localhost';
Replace your_password with the desired password and database_name with the name of the database that the user needs access to.
Step 4: Unlock or Renew User Account
If the user account is locked or expired, unlock or renew the account using the following SQL commands:
ALTER USER 'odbc'@'localhost' ACCOUNT UNLOCK;
or
ALTER USER 'odbc'@'localhost' PASSWORD EXPIRE NEVER;
Step 5: Check ODBC Driver Configuration
Ensure that the ODBC driver is properly configured on your system. Verify the configuration settings in your ODBC Data Source Administrator (Windows) or /etc/odbc.ini file (Linux).
FAQs
1. What is ODBC?
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) is a standard API that allows applications to access and manipulate data stored in database management systems, regardless of the database type and operating system.
2. What are the common ODBC drivers for SQL databases?
Some common ODBC drivers for SQL databases include:
- MySQL Connector/ODBC
- PostgreSQL ODBC driver (psqlODBC)
- Microsoft SQL Server ODBC driver
- Oracle ODBC driver
3. How can I view the list of MySQL users and their privileges?
You can view the list of MySQL users and their privileges by executing the following SQL command:
SELECT User, Host, Grant_priv, Super_priv FROM mysql.user;
4. How do I create a new MySQL user with specific privileges?
To create a new MySQL user with specific privileges, execute the following SQL commands:
CREATE USER 'new_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_password';
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE ON database_name.* TO 'new_user'@'localhost';
Replace new_user with the desired username, your_password with the desired password, and database_name with the name of the database that the user needs access to.
5. How do I change the password for a MySQL user?
To change the password for a MySQL user, execute the following SQL command:
ALTER USER 'user_name'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';
Replace user_name with the username and new_password with the desired new password.
- MySQL Connector/ODBC Developer Guide
- PostgreSQL ODBC driver (psqlODBC) Documentation
- Oracle ODBC driver Documentation
Дата: 25.11.2013
Автор: Василий Лукьянчиков , vl (at) sqlinfo (dot) ru
Статистика форума SQLinfo показывает, что одной из наиболее популярных проблем является ошибка mysql №1045 (ошибка доступа).
Текст ошибки содержит имя пользователя, которому отказано в доступе, компьютер, с которого производилось подключение, а также ключевое слово YES или NO, которые показывают использовался ли при этом пароль или была попытка выполнить подключение с пустым паролем.
Типичные примеры:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) — сервер MySQL
— сообщает, что была неудачная попытка подключения с локальной машины пользователя с именем root и
— не пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем root при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем ODBC при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
Причина возникновения ошибки 1045
Как ни банально, но единственная причина это неправильная комбинация пользователя и пароля. Обратите внимание, речь идет о комбинации пользователь и пароль, а не имя пользователя и пароль. Это очень важный момент, так как в MySQL пользователь характеризуется двумя параметрами: именем и хостом, с которого он может обращаться. Синтаксически записывается как ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’.
Таким образом, причина возникновения MySQL error 1045 — неправильная комбинация трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля.
В качестве имени хоста могут выступать ip адреса, доменные имена, ключевые слова (например, localhost для обозначения локальной машины) и групповые символы (например, % для обозначения любого компьютера кроме локального). Подробный синтаксис смотрите в документации
Замечание: Важно понимать, что в базе не существует просто пользователя с заданным именем (например, root), а существует или пользователь с именем root, имеющий право подключаться с заданного хоста (например, root@localhost) или даже несколько разных пользователей с именем root (root@127.0.0.1, root@webew.ru, root@’мой домашний ip’ и т.д.) каждый со своим паролем и правами.
Примеры.
1) Если вы не указали в явном виде имя хоста
GRANT ALL ON publications.* TO ‘ODBC’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘newpass’;
то у вас будет создан пользователь ‘ODBC’@’%’ и при попытке подключения с локальной машины вы получите ошибку:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
так как пользователя ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ у вас не существует.
2) Другой первопричиной ошибки mysql 1045 может быть неправильное использование кавычек.
CREATE USER ‘new_user@localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘mypass’; — будет создан пользователь ‘new_user@localhost’@’%’
Правильно имя пользователя и хоста нужно заключать в кавычки отдельно, т.е. ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’
3) Неочевидный вариант. IP адрес 127.0.0.1 в имени хоста соответствует ключевому слову localhost. С одной стороны, root@localhost и ‘root’@’127.0.0.1’ это синонимы, с другой, можно создать двух пользователей с разными паролями. И при подключении будет выбран тот, который распологается в таблице привелегий (mysql.user) раньше.
4) Аккаунт с пустым именем пользователя трактуется сервером MySQL как анонимный, т.е. позволяет подключаться пользователю с произвольным именем или без указания имени.
Например, вы создали пользователя »@localhost с пустым паролем, чтобы каждый мог подключиться к базе. Однако, если при подключении вы укажите пароль отличный от пустого, то получите ошибку 1045. Как говорилось ранее, нужно совпадение трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля, а пароль в данном случае не совпадает с тем, что в базе.
Что делать?
Во-первых, нужно убедиться, что вы используете правильные имя пользователя и пароль. Для этого нужно подключиться к MySQL с правами администратора (если ошибка 1045 не дает такой возможности, то нужно перезапустить сервер MySQL в режиме —skip-grant-tables), посмотреть содержимое таблицы user служебной базы mysql, в которой хранится информация о пользователях, и при необходимости отредактировать её.
Пример.
SELECT user,host,password FROM mysql.user;
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
| user | host | password |
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
| root | house-f26710394 | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
| aa | localhost | *196BDEDE2AE4F84CA44C47D54D78478C7E2BD7B7 |
| test | localhost | |
| new_user | % | |
| | % | *D7D6F58029EDE62070BA204436DE23AC54D8BD8A |
| new@localhost | % | *ADD102DFD6933E93BCAD95E311360EC45494AA6E |
| root | localhost | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
Если изначально была ошибка:
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
значит вы указывали при подключении неверный пароль, так как пользователь root@localhost существует. Сам пароль храниться в зашифрованном виде и его нельзя узнать, можно лишь задать новый
SET PASSWORD FOR root@localhost=PASSWORD(‘новый пароль’);
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
в данном случае в таблице привилегий отсутствует пользователь ‘ODBC’@’localhost’. Его нужно создать, используя команды GRANT, CREATE USER и SET PASSWORD.
Экзотический пример. Устанавливаете новый пароль для root@localhost в режиме —skip-grant-tables, однако после перезагрузки сервера по прежнему возникает ошибка при подключении через консольный клиент:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
Оказалось, что было установлено два сервера MySQL, настроенных на один порт.
phpmyadmin
При открытии в браузере phpmyadmin получаете сообщение:
Error
MySQL said:
#1045 — Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
Connection for controluser as defined in your configuration failed.
phpMyAdmin tried to connect to the MySQL server, and the server rejected the connection. You should check the host, username and password in your configuration and make sure that they correspond to the information given by the administrator of the MySQL server.
Ни логина, ни пароля вы не вводили, да и пхпадмин их нигде требовал, сразу выдавая сообщение об ошибке. Причина в том, что данные для авторизации берутся из конфигурационного файла config.inc.php Необходимо заменить в нем строчки
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘root’; // MySQL user
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = »; // MySQL password (only needed
на
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘ЛОГИН’;
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = ‘ПАРОЛЬ’
Установка новой версии
Устанавливаете новую версию MySQL, но в конце при завершении конфигурации выпадает ошибка:
ERROR Nr. 1045
Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO)
Это происходит потому, что ранее у вас стоял MySQL, который вы удалили без сноса самих баз. Если вы не помните старый пароль и вам нужны эти данные, то выполните установку новой версии без смены пароля, а потом смените пароль вручную через режим —skip-grant-tables.
P.S. Статья написана по материалам форума SQLinfo, т.е. в ней описаны не все потенциально возможные случаи возникновения ошибки mysql №1045, а только те, что обсуждались на форуме. Если ваш случай не рассмотрен в статье, то задавайте вопрос на форуме SQLinfo
Вам ответят, а статья будет расширена.
Дата публикации: 25.11.2013
© Все права на данную статью принадлежат порталу SQLInfo.ru. Перепечатка в интернет-изданиях разрешается только с указанием автора и прямой ссылки на оригинальную статью. Перепечатка в бумажных изданиях допускается только с разрешения редакции.
I’ve a user account setup asteriskpbx@localhost. From this account I’m trying to execute the following command:
echo "select 1" | isql -v asterisk-connector
However, I get this error :
[S1000][unixODBC][MySQL][ODBC 5.1 Driver]Access denied for user 'administrator'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
Why does it show Access denied for user ‘administrator’@’localhost’ when I’m running this command from asteriskpbx@localhost ?
Note: I’ve database permissions setup for asteriskpbx user account, which I don’t want to compromise on.
asked May 6, 2013 at 15:30
6
As seen from the error, in your /etc/odbc.ini in asterisk-connector you have
UID = administrator # where asteriskpbx should be
This is the only reason why isql would try to connect as administrator that I can think of.
If this connects (delete -h [host-ip] if you ran it on localhost):
mysql -h [host-ip] — u asteriskpbx —password=[asteriskpbx-password]
Than after change of odbc.ini you shouldn’t have any problems
Hope it helps.
Mirko
answered May 24, 2013 at 7:52
1
I’ve just made changes in /etc/odbc.ini.
For MySQL Driver Connect:
Changed: UserName to UID and it works.
Below is the configuration details:
[MYSQL]
Description = MySQL connection
Driver = MySQL
Database = <Database Name>
Server = <Host Name>
UID = <Your-DB Username>
Password = <Your-password>
Port = 3306
Jawa
3,60913 gold badges31 silver badges36 bronze badges
answered Aug 12, 2015 at 7:37
I was able to create a database, Grant permissions and flush privileges to activate the new permissions in a batch file:
Start of MySQLrun.bat
@echo off
:: I had to use the root user because the user I created didn't have any authority
set user=root
::set user=MyUser
:: When I first installed MySQL I set a password
set password=MyPassword
set host=localhost
CD C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 5.5bin
:: Create a database file
:: The log will be in C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 5.5bin
mysql -h %host% -u %user% -p%password% < c:DnloadMySQLCommands.sql --tee=Run.log --comments --debug-info --verbose
cmd
End of MySQLrun.bat
The bat file runs the commands in the MySQLCommands.sql file:
Start of MySQLCommands.sql
drop database if exists MyDatabaseFileName;
CREATE DATABASE MyDatabaseFileName;
# An example of how to GRANT ALL privileges to a user
#grant all ON mydatabasefilename.* TO 'Myuser'@localhost identified by 'MyPassword';
# GRANT INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, SELECT ON databasename.* TO ‘username’@'localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’;
# To activate the new permissions, issue the following command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
# How to log in to a specific database on a MySQL server:
show grants for 'MyUser'@'localhost'
End of MySQLCommands.sql
Please Note: All usernames, Database names and passwords are case sensitive.
There are many ways to create a database. This is just one of them.
Дата: 25.11.2013
Автор: Василий Лукьянчиков , vl (at) sqlinfo (dot) ru
Статистика форума SQLinfo показывает, что одной из наиболее популярных проблем является ошибка mysql №1045 (ошибка доступа).
Текст ошибки содержит имя пользователя, которому отказано в доступе, компьютер, с которого производилось подключение, а также ключевое слово YES или NO, которые показывают использовался ли при этом пароль или была попытка выполнить подключение с пустым паролем.
Типичные примеры:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) — сервер MySQL
— сообщает, что была неудачная попытка подключения с локальной машины пользователя с именем root и
— не пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем root при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем ODBC при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
Как ни банально, но единственная причина это неправильная комбинация пользователя и пароля. Обратите внимание, речь идет о комбинации пользователь и пароль, а не имя пользователя и пароль. Это очень важный момент, так как в MySQL пользователь характеризуется двумя параметрами: именем и хостом, с которого он может обращаться. Синтаксически записывается как ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’.
Таким образом, причина возникновения MySQL error 1045 — неправильная комбинация трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля.
В качестве имени хоста могут выступать ip адреса, доменные имена, ключевые слова (например, localhost для обозначения локальной машины) и групповые символы (например, % для обозначения любого компьютера кроме локального). Подробный синтаксис смотрите в документации
Замечание: Важно понимать, что в базе не существует просто пользователя с заданным именем (например, root), а существует или пользователь с именем root, имеющий право подключаться с заданного хоста (например, root@localhost) или даже несколько разных пользователей с именем root (root@127.0.0.1, root@webew.ru, root@’мой домашний ip’ и т.д.) каждый со своим паролем и правами.
Примеры.
1) Если вы не указали в явном виде имя хоста
GRANT ALL ON publications.* TO ‘ODBC’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘newpass’;
то у вас будет создан пользователь ‘ODBC’@’%’ и при попытке подключения с локальной машины вы получите ошибку:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
так как пользователя ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ у вас не существует.
2) Другой первопричиной ошибки mysql 1045 может быть неправильное использование кавычек.
CREATE USER ‘new_user@localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘mypass’; — будет создан пользователь ‘new_user@localhost’@’%’
Правильно имя пользователя и хоста нужно заключать в кавычки отдельно, т.е. ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’
3) Неочевидный вариант. IP адрес 127.0.0.1 в имени хоста соответствует ключевому слову localhost. С одной стороны, root@localhost и ‘root’@’127.0.0.1’ это синонимы, с другой, можно создать двух пользователей с разными паролями. И при подключении будет выбран тот, который распологается в таблице привелегий (mysql.user) раньше.
4) Аккаунт с пустым именем пользователя трактуется сервером MySQL как анонимный, т.е. позволяет подключаться пользователю с произвольным именем или без указания имени.
Например, вы создали пользователя »@localhost с пустым паролем, чтобы каждый мог подключиться к базе. Однако, если при подключении вы укажите пароль отличный от пустого, то получите ошибку 1045. Как говорилось ранее, нужно совпадение трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля, а пароль в данном случае не совпадает с тем, что в базе.
Что делать?
Во-первых, нужно убедиться, что вы используете правильные имя пользователя и пароль. Для этого нужно подключиться к MySQL с правами администратора (если ошибка 1045 не дает такой возможности, то нужно перезапустить сервер MySQL в режиме —skip-grant-tables), посмотреть содержимое таблицы user служебной базы mysql, в которой хранится информация о пользователях, и при необходимости отредактировать её.
Пример.
SELECT user,host,password FROM mysql.user;
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
| user | host | password |
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
| root | house-f26710394 | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
| aa | localhost | *196BDEDE2AE4F84CA44C47D54D78478C7E2BD7B7 |
| test | localhost | |
| new_user | % | |
| | % | *D7D6F58029EDE62070BA204436DE23AC54D8BD8A |
| new@localhost | % | *ADD102DFD6933E93BCAD95E311360EC45494AA6E |
| root | localhost | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
Если изначально была ошибка:
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
значит вы указывали при подключении неверный пароль, так как пользователь root@localhost существует. Сам пароль храниться в зашифрованном виде и его нельзя узнать, можно лишь задать новый
SET PASSWORD FOR root@localhost=PASSWORD(‘новый пароль’);
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
в данном случае в таблице привилегий отсутствует пользователь ‘ODBC’@’localhost’. Его нужно создать, используя команды GRANT, CREATE USER и SET PASSWORD.
Экзотический пример. Устанавливаете новый пароль для root@localhost в режиме —skip-grant-tables, однако после перезагрузки сервера по прежнему возникает ошибка при подключении через консольный клиент:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
Оказалось, что было установлено два сервера MySQL, настроенных на один порт.
phpmyadmin
При открытии в браузере phpmyadmin получаете сообщение:
Error
MySQL said:
#1045 — Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
Connection for controluser as defined in your configuration failed.
phpMyAdmin tried to connect to the MySQL server, and the server rejected the connection. You should check the host, username and password in your configuration and make sure that they correspond to the information given by the administrator of the MySQL server.
Ни логина, ни пароля вы не вводили, да и пхпадмин их нигде требовал, сразу выдавая сообщение об ошибке. Причина в том, что данные для авторизации берутся из конфигурационного файла config.inc.php Необходимо заменить в нем строчки
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘root’; // MySQL user
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = »; // MySQL password (only needed
на
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘ЛОГИН’;
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = ‘ПАРОЛЬ’
Установка новой версии
Устанавливаете новую версию MySQL, но в конце при завершении конфигурации выпадает ошибка:
ERROR Nr. 1045
Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO)
Это происходит потому, что ранее у вас стоял MySQL, который вы удалили без сноса самих баз. Если вы не помните старый пароль и вам нужны эти данные, то выполните установку новой версии без смены пароля, а потом смените пароль вручную через режим —skip-grant-tables.
P.S. Статья написана по материалам форума SQLinfo, т.е. в ней описаны не все потенциально возможные случаи возникновения ошибки mysql №1045, а только те, что обсуждались на форуме. Если ваш случай не рассмотрен в статье, то задавайте вопрос на форуме SQLinfo
Вам ответят, а статья будет расширена.
Дата публикации: 25.11.2013
© Все права на данную статью принадлежат порталу SQLInfo.ru. Перепечатка в интернет-изданиях разрешается только с указанием автора и прямой ссылки на оригинальную статью. Перепечатка в бумажных изданиях допускается только с разрешения редакции.
Автор: Василий Лукьянчиков , vl (at) sqlinfo (dot) ru
Статистика форума SQLinfo показывает, что одной из наиболее популярных проблем является ошибка mysql №1045 (ошибка доступа).
Текст ошибки содержит имя пользователя, которому отказано в доступе, компьютер, с которого производилось подключение, а также ключевое слово YES или NO, которые показывают использовался ли при этом пароль или была попытка выполнить подключение с пустым паролем.
Типичные примеры:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) — сервер MySQL
— сообщает, что была неудачная попытка подключения с локальной машины пользователя с именем root и
— не пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем root при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем ODBC при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
Причина возникновения ошибки 1045
Как ни банально, но единственная причина это неправильная комбинация пользователя и пароля. Обратите внимание, речь идет о комбинации пользователь и пароль, а не имя пользователя и пароль. Это очень важный момент, так как в MySQL пользователь характеризуется двумя параметрами: именем и хостом, с которого он может обращаться. Синтаксически записывается как ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’.
Таким образом, причина возникновения MySQL error 1045 — неправильная комбинация трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля.
В качестве имени хоста могут выступать ip адреса, доменные имена, ключевые слова (например, localhost для обозначения локальной машины) и групповые символы (например, % для обозначения любого компьютера кроме локального). Подробный синтаксис смотрите в документации
Замечание: Важно понимать, что в базе не существует просто пользователя с заданным именем (например, root), а существует или пользователь с именем root, имеющий право подключаться с заданного хоста (например, root@localhost) или даже несколько разных пользователей с именем root (root@127.0.0.1, root@webew.ru, root@’мой домашний ip’ и т.д.) каждый со своим паролем и правами.
Примеры.
1) Если вы не указали в явном виде имя хоста
ПРЕДОСТАВЛЯЙТЕ ВСЕ НА ПУБЛИКАЦИЯХ . * ДЛЯ ‘ODBC’ ИДЕНТИФИЦИРОВАНО ‘Newpass’ ;
то у вас будет создан пользователь ‘ODBC’@’%’ и при попытке подключения с локальной машины вы получите ошибку:
ОШИБКА 1045 ( 28000 ) : доступ запрещен для пользователя ‘ODBC’ @ ‘localhost’ ( с использованием пароля: ДА )
так как пользователя ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ у вас не существует.
2) Другой первопричиной ошибки mysql 1045 может быть неправильное использование кавычек.
CREATE USER ‘new_user@localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘mypass’; — будет создан пользователь ‘new_user@localhost’@’%’
Правильно имя пользователя и хоста нужно заключать в кавычки отдельно, т.е. ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’
3) Неочевидный вариант. IP адрес 127.0.0.1 в имени хоста соответствует ключевому слову localhost. С одной стороны, root@localhost и ‘root’@’127.0.0.1’ это синонимы, с другой, можно создать двух пользователей с разными паролями. И при подключении будет выбран тот, который распологается в таблице привелегий (mysql.user) раньше.
4) Аккаунт с пустым именем пользователя трактуется сервером MySQL как анонимный, т.е. позволяет подключаться пользователю с произвольным именем или без указания имени. Например, вы создали пользователя »@localhost с пустым паролем, чтобы каждый мог подключиться к базе. Однако, если при подключении вы укажите пароль отличный от пустого, то получите ошибку 1045. Как говорилось ранее, нужно совпадение трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля, а пароль в данном случае не совпадает с тем, что в базе.
Что делать?
Во-первых, нужно убедиться, что вы используете правильные имя пользователя и пароль. Для этого нужно подключиться к MySQL с правами администратора (если ошибка 1045 не дает такой возможности, то нужно перезапустить сервер MySQL в режиме —skip-grant-tables), посмотреть содержимое таблицы user служебной базы mysql, в которой хранится информация о пользователях, и при необходимости отредактировать её.
Пример.
ВЫБЕРИТЕ пользователя, хост, пароль ОТ mysql.user; + ————
—- + —————— + ————— —————————- + | пользователь | хозяин | пароль | + ————— + —————— + ————— —————————- + | корень | дом-f26710394 | * 81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B | | аа | местный хост | * 196BDEDE2AE4F84CA44C47D54D78478C7E2BD7B7 | | тест | местный хост | | | new_user | % | | | | % | * D7D6F58029EDE62070BA204436DE23AC54D8BD8A |
| новый @ localhost | % | * ADD102DFD6933E93BCAD95E311360EC45494AA6E |
| корень | местный хост | * 81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
+ ————— + —————— + ————— —————————- +
Если изначально была ошибка:
-
ОШИБКА 1045 ( 28000 ) : доступ запрещен для пользователя ‘root’ @ ‘localhost’ ( с использованием пароля: ДА )
значит вы указывали при подключении неверный пароль, так как пользователь root@localhost существует. Сам пароль храниться в зашифрованном виде и его нельзя узнать, можно лишь задать новый
SET PASSWORD FOR root@localhost=PASSWORD(‘новый пароль’);
-
ОШИБКА 1045 ( 28000 ) : доступ запрещен для пользователя ‘ODBC’ @ ‘localhost’ ( с использованием пароля: ДА )
в данном случае в таблице привилегий отсутствует пользователь ‘ODBC’@’localhost’. Его нужно создать, используя команды GRANT, CREATE USER и SET PASSWORD.
Экзотический пример. Устанавливаете новый пароль для root@localhost в режиме —skip-grant-tables, однако после перезагрузки сервера по прежнему возникает ошибка при подключении через консольный клиент:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) Оказалось, что было установлено два сервера MySQL, настроенных на один порт.
PHPMyAdmin
При открытии в браузере phpmyadmin получаете сообщение:
Ошибка
MySQL говорит: # 1045 — Доступ запрещен для пользователя ‘root’ @ ‘localhost’ (с использованием пароля: НЕТ). Соединение для controluser, как определено в вашей конфигурации, не удалось. phpMyAdmin попытался подключиться к серверу MySQL , и сервер отклонил соединение. Вы должны проверить хост, имя пользователя и пароль в вашей конфигурации и убедиться, что они соответствуют информации, предоставленной администратором сервера MySQL .
Ни логина, ни пароля вы не вводили, да и пхпадмин их нигде требовал, сразу выдавая сообщение об ошибке. Причина в том, что данные для авторизации берутся из конфигурационного файла config.inc.php Необходимо заменить в нем строчки
$ cfg [ ‘Servers’ ] [ $ i ] [ ‘user’ ] = ‘root’ ; // MySQL user $ cfg [ ‘Servers’ ] [ $ i ] [ ‘password’ ] = » ; // Пароль MySQL (нужен только
на
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘ЛОГИН’;
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = ‘ПАРОЛЬ’
Установка новой версии
Устанавливаете новую версию MySQL, но в конце при завершении конфигурации выпадает ошибка:
ОШИБКА Nr. 1045 Доступ запрещен для пользователя ‘root’ @ ‘localhost’ ( используется пароль: НЕТ )
Это происходит потому, что ранее у вас стоял MySQL, который вы удалили без сноса самих баз. Если вы не помните старый пароль и вам нужны эти данные, то выполните установку новой версии без смены пароля, а потом смените пароль вручную через режим —skip-grant-tables.
P.S. Статья написана по материалам форума SQLinfo, т.е. в ней описаны не все потенциально возможные случаи возникновения ошибки mysql №1045, а только те, что обсуждались на форуме. Если ваш случай не рассмотрен в статье, то задавайте вопрос на форуме SQLinfo
Вам ответят, а статья будет расширена.
I just installed a fresh copy of Ubuntu 10.04.2 LTS on a new machine. I logged into MySQL as root:
david@server1:~$ mysql -u root -p123
I created a new user called repl. I left host blank, so the new user can may have access from any location.
mysql> CREATE USER 'repl' IDENTIFIED BY '123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
I checked the user table to verify the new user repl was properly created.
mysql> select host, user, password from mysql.user;
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| host | user | password |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| localhost | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| server1 | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| 127.0.0.1 | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| ::1 | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| localhost | | |
| server1 | | |
| localhost | debian-sys-maint | *27F00A6BAAE5070BCEF92DF91805028725C30188 |
| % | repl | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
I then exit, try to login as user repl, but access is denied.
david@server1:~$ mysql -u repl -p123
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'repl'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
david@server1:~$ mysql -urepl -p123
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'repl'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
david@server1:~$
Why is access denied?
asked Mar 28, 2013 at 19:44
1
The reason you could not login as repl@'%' has to do with MySQL’s user authentication protocol. It does not cover patterns of users as one would believe.
Look at how you tried to logged in
mysql -u repl -p123
Since you did not specify an IP address, mysql assumes host is localhost and tries to connect via the socket file. This is why the error message says Access denied for user 'repl'@'localhost' (using password: YES).
One would think repl@'%' would allow repl@localhost. According to how MySQL perform user authentication, that will simply never happen. Would doing this help ?
mysql -u repl -p123 -h127.0.0.1
Believe it or not, mysql would attempt repl@localhost again. Why? The mysql client sees 127.0.0.1 and tries the socket file again.
Try it like this:
mysql -u repl -p123 -h127.0.0.1 --protocol=tcp
This would force the mysql client to user the TCP/IP protocol explicitly. It would then have no choice but to user repl@'%'.
answered Mar 28, 2013 at 20:40
RolandoMySQLDBARolandoMySQLDBA
177k32 gold badges307 silver badges505 bronze badges
0
You should issue for localhost specific to it.
GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'repl'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123';
And try connecting.
answered Mar 29, 2013 at 5:40
MannojMannoj
1,4992 gold badges14 silver badges34 bronze badges
The problem is these two accounts, added by default.
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.5/en/default-privileges.html
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| host | user | password |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| localhost | | |
| server1 | | |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
A blank user name is a wildcard, so no matter what account you use, it matches this user if MySQL thinks you’re connecting from localhost or your local server name (server1 in this case)… since they have no password, any password you try is wrong. User authentication only tries the first match, so the user you created never gets noticed when your host is localhost (or your server name).
Delete these two from the mysql.user table and then FLUSH PRIVILEGES;.
Or, the mysql_secure_installation script can do this for you, although I tend to prefer doing things manually.
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.5/en/mysql-secure-installation.html
answered Mar 30, 2013 at 2:02
Michael — sqlbotMichael — sqlbot
22.2k2 gold badges46 silver badges75 bronze badges
Database may not be configured yet just issue a no-arg call:
mysql <enter>
Server version: xxx
Copyright (c) xxx
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
Mysql [(none)]>
If Mysql must be set a root password, you can use
mysql_secure_installation
answered Apr 18, 2020 at 7:45
Make sure that all fields in the connector are set up with the correct details
host = «localhost»,
user = «CorrectUser»,
passwd = «coRrectPasswd»,
database = «CorreCTDB»
Check for upper and lowercase errors as well — 1045 is not a Syntax error, but has to do with incorrect details in the connector
answered Dec 13, 2019 at 22:59
This could be an issue with corruption of your mysql database. Tables inside mysql database like user table can get corrupt and may cause issued.
Please do a check on those
myisamchk /var/lib/mysql/mysql/ *.MYI
Usually while checking or fixing myisam tables we would like to take mysql down first. If this problem is still not solve please try this out aswell.
If they are corrupt then you can fix them using
myisamchk —silent —force —fast /path/table-name.MYI
Thanks,
Masood
answered Mar 31, 2013 at 17:25
Are you looking for a solution to fix the MySQL ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘user’@’localhost’ (using password: YES) error message?
If you’re an experienced MySQL database manager, you may have come across some vague and confusing problems, like MySQL Error 1045 (28000) messages. Fortunately, while resolving this error can be confusing at first due to its many potential causes, its solutions tend to be relatively simple. Once you determine the reason behind the database error you’re seeing, you should be able to fix it fairly quickly.
In this post, we’ll cover the various possible causes of the MySQL Error 1045 (28000). Then we’ll share solutions for each common situation, to help you get your database and your site back up and running.
Why the MySQL Error 1045 (28000) Error Occurs
The MySQL Error 1045 (28000) is an authentication error. «MySQL ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘user’@’localhost’ (using password: YES)» typically indicates that MySQL cannot log you in using the username and password you’ve specified.
This usually occurs when you provide an incorrect username/password combination when making the database connection. However, there are many other different situations that can lead to this type of behaviour.
- Connecting to the wrong host or port
- Provided user does not exist
- User does exist but client host have insufficient permission to connect, or be IP banned
- Wrong password provided
- Bash converts special characters in the password to a different encoding
Wrong host or port
If you don’t specify the host to connect (with the -h flag), MySQL client will try to automatically connect to the localhost instance. You may be trying to connect to another host/port instance. In this case, simply add -h flag followed by the hostname you’re trying to connect to.
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
Also, double check if you are trying to connect to the right port. MySQL, by default, listen on port 3306, but different setups use different ports for security purposes. Providing -P flag and a port number in the command is a great way to remind you of this detail.
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
[[email protected]]# mysql -u root -psekret -h <IP_or_hostname> -P 3306
Provided user does not exist
MySQL stores user data in a table called user in a database named mysql (by default). The following query will return 1 if a user with the specified username exists, 0 otherwise.
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
mysql> SELECT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM mysql.user WHERE user = 'username') Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
If the user does not exist, you can create a new user:
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
mysql> CREATE USER 'username'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Client host have insufficient permission
By default, the MySQL server listens for connections only from localhost, which means it can be accessed only by applications running on the same host.
Remote root access is disabled by default. If you want to enable that, run this SQL command locally:
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
And then find the following line and comment it out in your my.cnf file, which usually lives on /etc/mysql/my.cnf on Unix/OSX systems. In some cases the location for the file is /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf).
Alternatively, you can check to see which host user/host MySQL allows connections with the following query:
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
mysql> SELECT Host, User FROM mysql.user WHERE User='user01'; +-------------+-------------+ | Host | User | +-------------+-------------+ | 192.168.0.1 | user01 | +-------------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Wrong password provided
This is by far the most common reason for MySQL ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘user’@’localhost’ (using password: YES).
MySQL lists user accounts in the user table of the mysql database. Each MySQL account can be assigned a password, although the user table does not store the cleartext version of the password, but a hash value computed from it.
You cannot read user passwords in plain text from MySQL as the password hash is used for authentication, but if you can get into MySQL command line interface (with root privileges), you can compare what you remember with the hashed value with “PASSWORD” function with the command below.
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
mysql> SELECT Host, User, authentication_string, PASSWORD('forgotten') FROM mysql.user WHERE User='nonexistant'; +-------------+-------------+-------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------+ | Host | User | authentication_string | PASSWORD('forgotten') | +-------------+-------------+-------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------+ | 192.168.0.1 | nonexistant | *AF9E01EA8519CE58E3739F4034EFD3D6B4CA6324 | *70F9DD10B4688C7F12E8ED6C26C6ABBD9D9C7A41 | | % | nonexistant | *AF9E01EA8519CE58E3739F4034EFD3D6B4CA6324 | *70F9DD10B4688C7F12E8ED6C26C6ABBD9D9C7A41 | +-------------+-------------+-------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
From the output, we can clearly see that the hashed value for ‘forgotten’ does not match the authentication_string column, which means ‘forgotten’ is the wrong password.
Executing the following query will overwrite the current password with a new one :
Code language: PHP (php)
mysql> set password for 'nonexistant'@'%' = 'helloworld'; Empty set (0.00 sec)
Special characters in the password
If you’re using Bash as your main shell, you should know that not all characters are treated equal in Bash. Some characters are evaluated by Bash to have a non-literal meaning. Instead, these characters carry out a special instruction, or have an alternate meaning; they are called «special characters», or «meta-characters».
In this case, your password contains some of the those special characters which might be mistakenly converted to another form by Bash. To prevent this from happening, wrap your password in single quotes in the command:
Code language: PHP (php)
[[email protected]]# mysql -u user01 -p'hello$!*&^%$#@!' mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure ... mysql>
Regain access to the database
If you’re locked out and need to bypass the authentication mechanisms to regain access to the database, here are simple steps to do so. Please note that we’re using MariaDB to demonstrate the steps.
- Stop the instance by running
sudo systemctl stop mariadb - Use
mysqld_safeto start mysqld server by running the command:mysqld_ safe –user=mysql –skip-grant-tables –skip-networking - Now you can open up a new terminal and access the MySQL server instance with
rootprivileges by runningmysql -u root -h localhost. - Please do note that since we’re running
grant-skip-tables, any GRANT/CREATE/SET PASSWORD statements won’t work straight away. In order to fix this, run FLUSH PRIVILEGES;. - Run
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = '[email protected]!'to change the password forrootuser. - Alternatively, you can modify
mysql.userstable with a query which modifies the password for User and Host like UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD(‘newpwd’) WHERE User=’root’ and Host=’localhost’; - Stop the
mysqld_safeinstance and restart MySQL again fromsystemctl. - You should be able to login with
rootfrom the localhost with the new password and do any other necessary corrective operations with root user.
MySQL users often face an issue called Error 1045 (28000) access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: yes). This usually occurs when you enter an incorrect password or password for your database. Fixing these credentials can resolve this error in no time.
In this article, we will look at the ways to resolve this error.
How to fix “Error 1045 (28000) access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: yes)”?
The error looks something like this —
mysql -uroot -proot
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
It arises when you perform a fresh installation of MySQL and try to login with a password. The default password of MySQL is blank () (i.e. empty string).
So, you can login to the MySQL server using the same password.
Example
>mysql -uroot -pEnter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 9
Server version: 10.4.11-MariaDB mariadb.org binary distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;’ or ‘h’ for help. Type ‘c’ to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]>The best practice is to change the password after the new installation.
Set root user password
You must set the root user password after performing the new installation. Here is the code to set it –
Login as user root with blank password
>mysql -u root
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'abc';Now the new password for root user is abc.
How to fix the Error 1045 (28000)?
Let us look at the ways to fix this problem –
-
Enter the correct credentials
The primary method to fix this error is to enter the correct username and password using the following command –
mysql –u username –p -
Ensure the user is correct
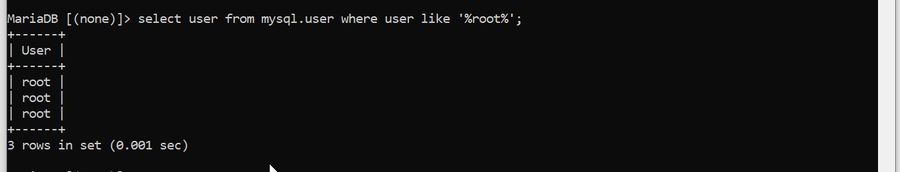
Sometimes, the user you might be trying to access does not exist on the MySQL server. You can check if the user exists using the following code-
MariaDB [(none)]> select user from mysql.user where user like '%root%';
+------+
| User |
+------+
| root |
| root |
| root |
+------+
3 rows in set (0.001 sec) If the user does not exist, create it with the desired username.
-
Enter the correct host name
You might be trying to access the server from a host that is different from the defined host name. You will encounter Error 1045 in this case. You can use this code to view details of the user –
To fix this, you can update the host name for the user using the code below –
mysql> mysql -u root -pabc -h <IP> -P 3306You might encounter the error in due to the following scenarios –
Entered wrong password
>mysql -uroot -pssssss
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
Host doesn’t not have permission to connect databaseThis is a very common error that occurs while connecting to a remote database. While connecting to such a database we need to give access to the HOST IP ADDRESS to connect to it.
This is the IP Address of the source system which connects to the database server.
If access is not given, then run the given command –
CREATE USER ‘dbuser1’@'< Host IP >’ IDENTIFIED VIA mysql_native_password USING ‘***’;GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ‘dbuser1’@'< Host IP >’ REQUIRE NONE WITH GRANT OPTION MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_UPDATES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS 0;
Conclusion
Apart from all this, make sure the host contains the correct IP address and host name, to avoid the Error 1045 (28000) access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: yes).
grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
Sort date (newest date)
You may see something like this;
[root@SERVER ~]# grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
2016-01-16T18:07:29.688164Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: O,k5.marHfFu
2016-01-22T13:14:17.974391Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: b5nvIu!jh6ql
2016-01-22T15:35:48.496812Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: (B*=T!uWJ7ws
2016-01-22T15:52:21.088610Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: %tJXK7sytMJV
2016-01-22T16:24:41.384205Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: lslQDvgwr3/S
2016-01-22T22:11:24.772275Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: S4u+J,Rce_0t
[root@SERVER ~]# mysql_secure_installation
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
Enter password for user root:
The existing password for the user account root has expired. Please set a new password.
New password:
Re-enter new password:
If you see it says
... Failed! Error: Your password does not satisfy the current policy requirements
That means your password needs to have a character such as ! . # - etc...
mix characters well, upper case, lower case, ! . , # etc...
New password:
Re-enter new password:
The 'validate_password' plugin is installed on the server.
The subsequent steps will run with the existing configuration
of the plugin.
Using existing password for root.
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Change the password for root ? ((Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user,
allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have
a user account created for them. This is intended only for
testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother.
You should remove them before moving into a production
environment.
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
Success.
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
Success.
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
and should be removed before moving into a production
environment.
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
- Dropping test database...
Success.
- Removing privileges on test database...
Success.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
made so far will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
Success.
All done!
[root@SERVER ~]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.
Your MySQL connection id is 11
Server version: 5.7.10 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Watch the last 10 minutes of this video, it teaches you how you do it.